Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Anxiety disorders presenting as gastrointestinal symptoms in children – a scoping review (15,678 times)
- Anjali Kumar, Pramodh Vallabhaneni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):344-351. Published online January 13, 2025
-

A positive bidirectional relationship between gastrointestinal disorders and anxiety, but with no clear aetiology, was identified. Factors such as somatisation and pain catastrophising resulted in poorer pain-related outcomes in children. Further studies are required to understand this relationship in order to have targeted treatments and ensure better long term outcomes.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management (15,026 times)
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
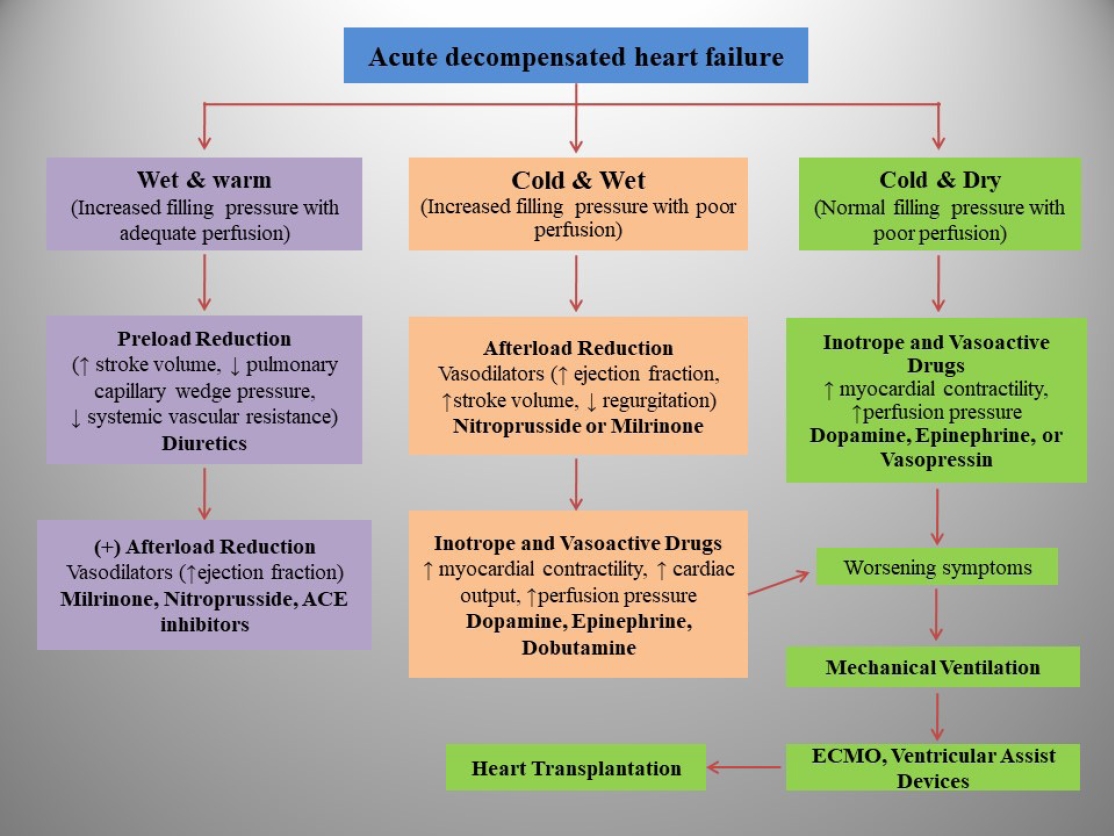
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Hematology
- Iron deficiency in children with a focus on inflammatory conditions (14,630 times)
- Na Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):283-293. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Iron deficiency has important effects on neurodevelopment and the immune system in children.
· Hepcidine plays an important role in iron homeostasis.
· Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic inflammatory disease are important for patients' quality of life and disease course.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis (14,527 times)
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Oncology
- Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for treatment of relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancy in children and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis (14,499 times)
- Ghea Mangkuliguna, Edi Setiawan Tehuteru, Reganedgary Jonlean, Nicholas Adrianto, Stella Kallista
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):712-721. Published online July 4, 2025
-
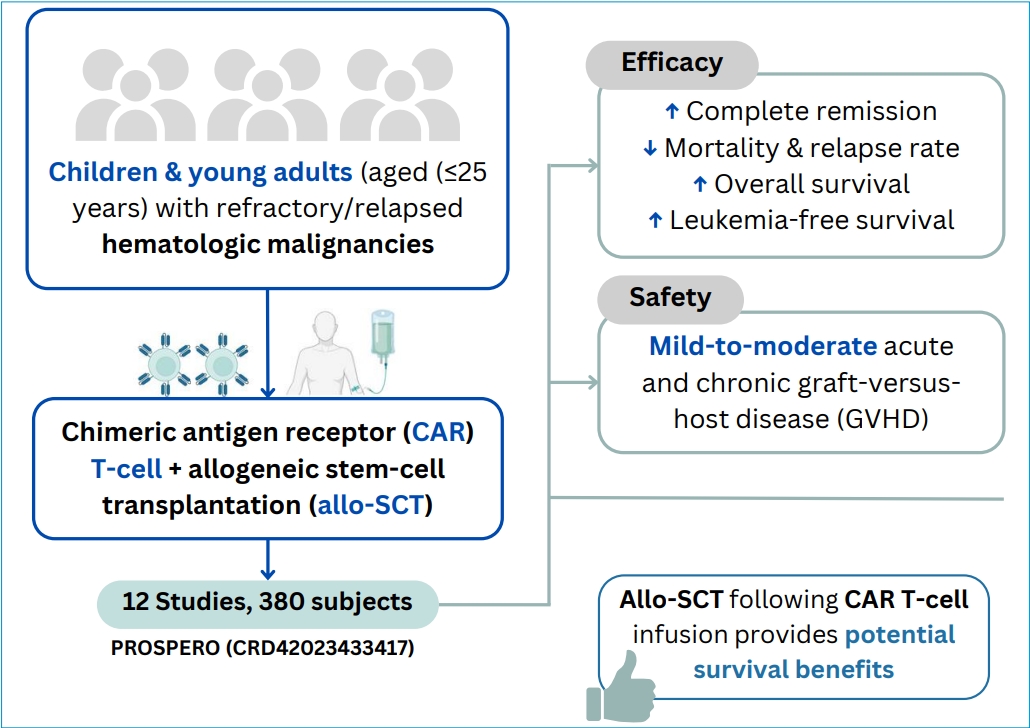
Question: Does consolidative allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy improve outcomes of children and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies?
Finding: The meta-analysis showed reduced relapse rates and favorable survival trends with allo-SCT despite low evidence quality.
Meaning: Consolidative allo-SCT after CAR T-cell therapy may enhance survival; however, further clinical studies are needed.
- Cardiology
- Unsustainable and overworked: unpacking the challenges faced by pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea (14,202 times)
- Soo In Jeong, GI Beom Kim, Sung Hye Kim, Jae Yoon Na, Hong Ju Shin, Sin Weon Yun, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Sang Yun Lee, Chang-Ha Lee, Kwang Ho Choi, Seul Gi Cha, Mi Young Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):732-741. Published online August 6, 2025
-
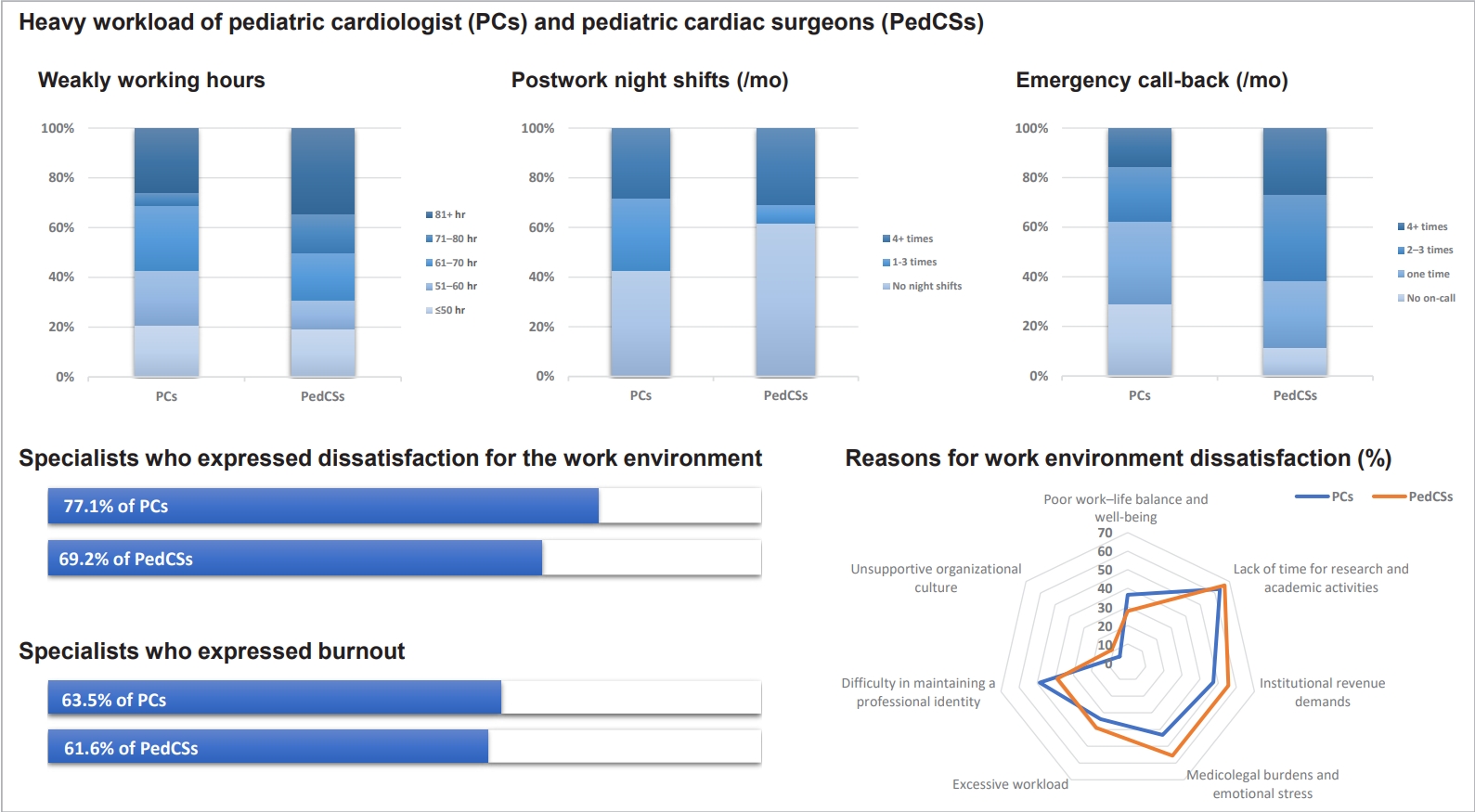
Question: What are the key challenges affecting pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea?
Finding: Excessive workloads, low procedural volumes, and legal risks contribute to high burnout. Regional disparities limit skill maintenance and threaten workforce sustainability.
Meaning: Targeted policies ensuring fair workloads, legal protections, and regional support are essential to stabilizing the pediatric cardiac workforce and maintaining high-quality care.
- Gastroenterology
- Treatment targeting pediatric inflammatory bowel disease-associated anemia: experience from a single tertiary center (14,102 times)
- Ana S.C. Fernandes, Sara Azevedo, Ana Rita Martins, Ana Isabel Lopes
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):722-731. Published online June 10, 2025
-
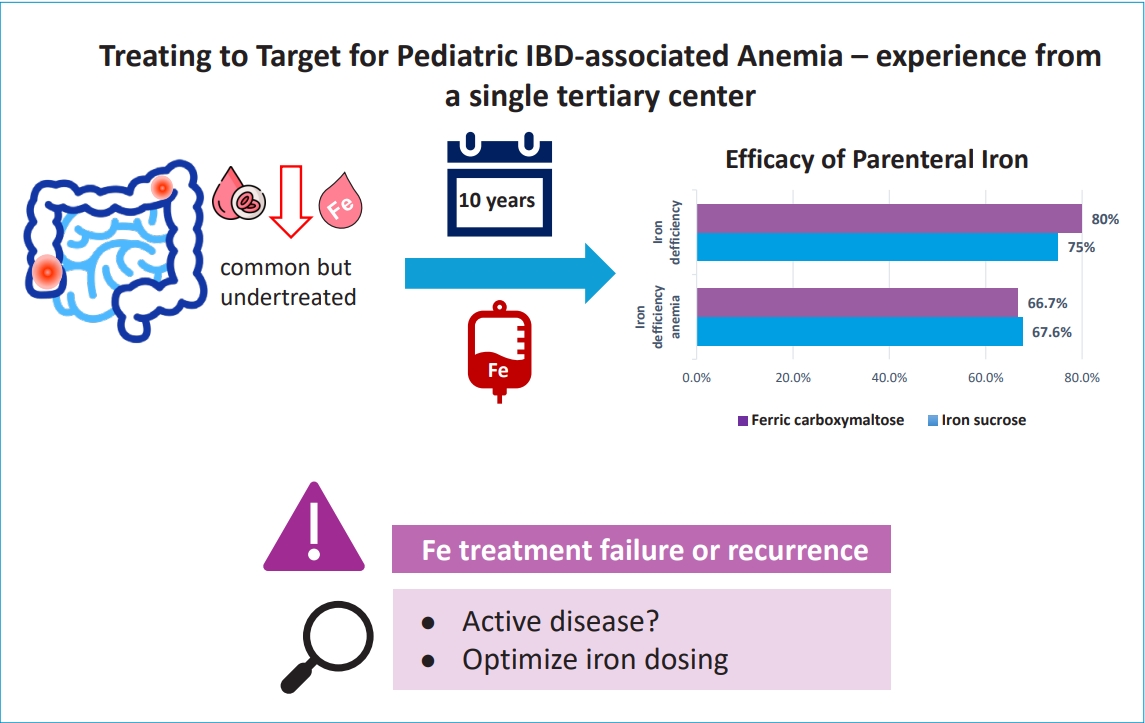
Question: Does treating iron deficiency (ID) using intravenous iron in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) feature long-term safety and efficacy?
Finding: Intravenous iron supplementation was safe and effective. However, the ID recurrence rate was higher than expected.
Meaning: Proactive screening and treatment of ID in pediatric IBD are essential. The Ganzoni formula likely underestimates the iron requirements of pediatric patients. Prospective trials are needed to optimize iron treatment dosing.
- Review Article
- Other
- Cost-effectiveness of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: a systematic review (14,083 times)
- Rezwanul Rana, Syed Afroz Keramat, Moin Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):628-640. Published online April 16, 2025
-
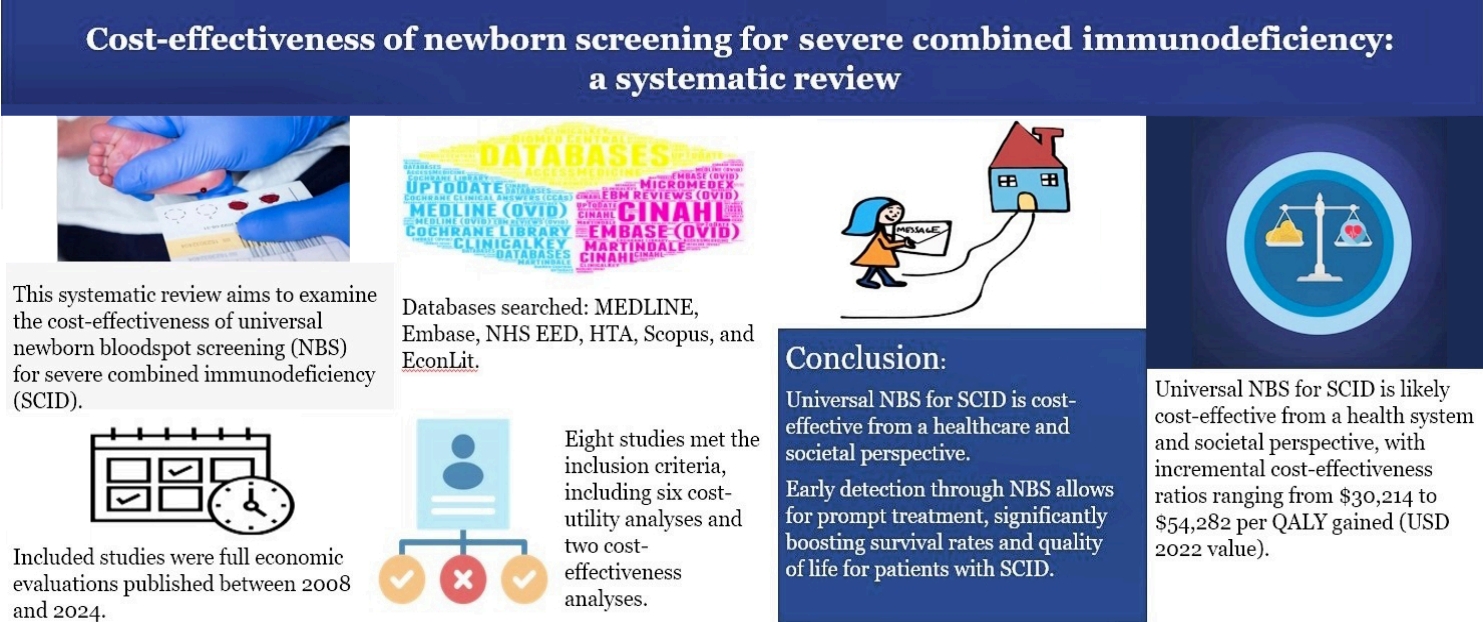
Universal newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) demonstrates robust cost-effectiveness across diverse high-income healthcare systems, both from healthcare and societal standpoints. Early detection yields substantial savings. While uncertainties persist, impacting precise cost-effectiveness, the overall finding is positive. Future research must prioritize enhanced data collection and statistical rigor to refine our understanding of SCID's economic impact within the Australian context.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors (14,010 times)
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Hematology
- Treatment and clinical outcomes of pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia: real-world single-center data from Korea (13,985 times)
- Young Dai Kwon, Eun Sun Jung, Yeon Jung Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):522-529. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Question: Can pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) be effectively managed using first-line steroids?
Finding: In this single-center study, pediatric patients with AIHA achieved normal hemoglobin levels within 16.5 days (range, 9.0–22.0 days) of first-line steroid treatment and maintained effective responses for 2 months.
Meaning: These outcomes highlight the efficacy of steroid treatment in pediatric versus adult AIHA and underscore the need for multicenter trials to establish standardized treatment guidelines.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of total serum bilirubin thresholds for discontinuing phototherapy in jaundiced neonates: a randomized study (13,737 times)
- Ajay Kumar, Nidhi Jain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):539-545. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: What are the outcomes of jaundiced neonates when phototherapy is discontinued at 2 different total serum bilirubin (TSB) thresholds?
Findings: The study involved 80 neonates, comparing a recommended TSB threshold and a lower threshold for phototherapy discontinuation. Results showed a 14.3% reinstitution rate of treatment, with no adverse outcomes.
Meaning: Careful posttreatment monitoring is essential when discontinuing phototherapy, and future research should consider updated guidelines like those from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: bridging potential, clinical practice, and ethical considerations (13,643 times)
- Yoon Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):652-655. Published online August 28, 2025
-
· Artificial intelligence (AI) holds transformative potential for pediatric healthcare, with applications spanning prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up across diverse subspecialties; however, ethical concerns, scarcity of pediatric- specific data, and limited funding remain significant challenges.
· International consensus on pediatric AI guidelines, expanding child-specific datasets, and incorporating explainable AI are essential to ensure safety and trust.
· Multicenter collaboration and increased investment can address these gaps, enabling equitable, reliable, and pediatric- centered AI solutions.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Respiratory severity score-guided postnatal systemic corticosteroid therapy for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants (13,611 times)
- Gyeong Eun Yeom, Ju Sun Heo, Baek Sup Shin, Seh Hyun Kim, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):656-665. Published online July 8, 2025
-
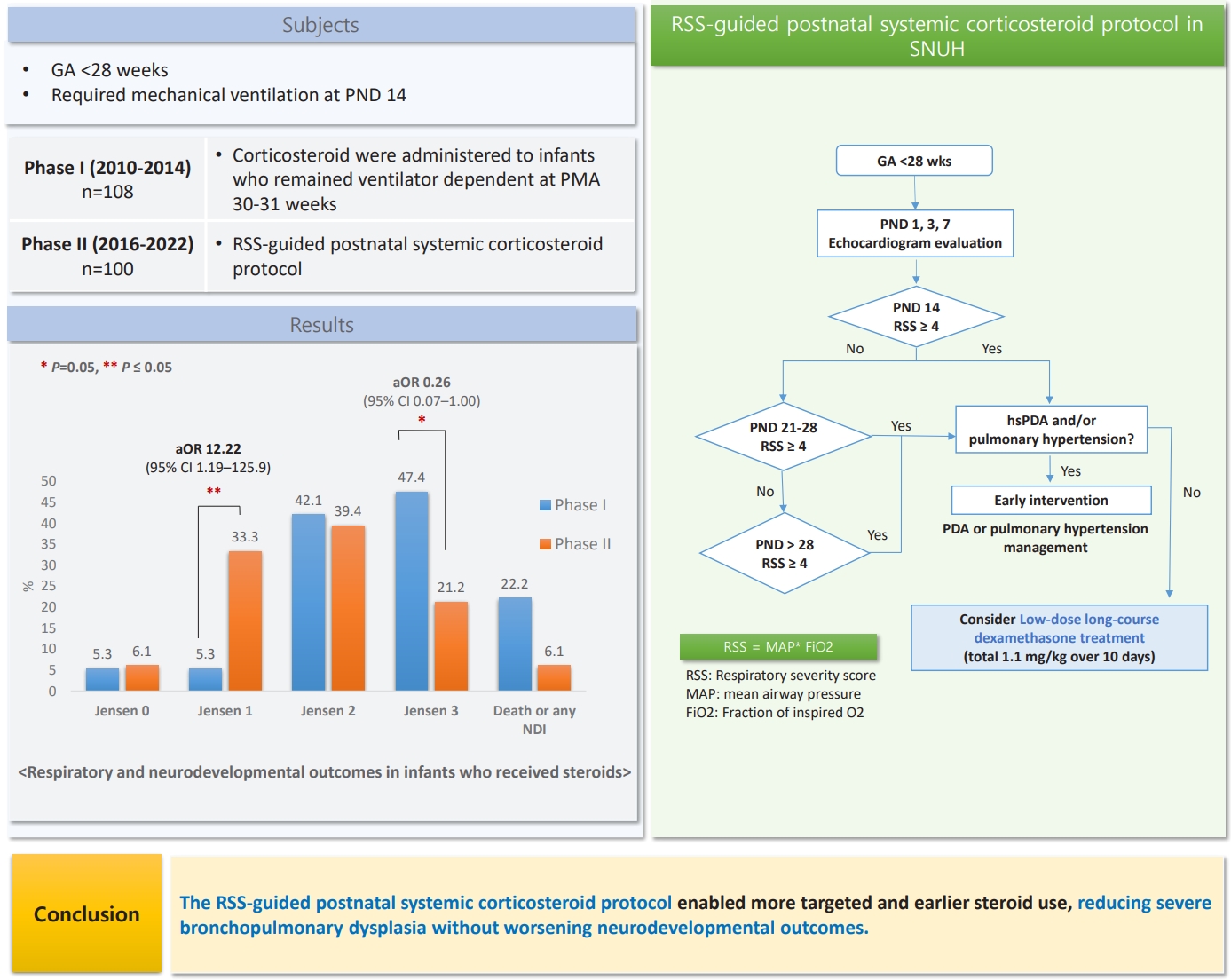
Question: Does a respiratory severity score (RSS)-guided postnatal corticosteroid protocol improve respiratory outcomes of extremely preterm (EP) infants without worsening neurodevelopmental outcomes?
Finding: The protocol enabled targeted and early steroid use, thereby reducing severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia without affecting mortality or causing neurodevelopmental impairments.
Meaning: The RSS-guided protocol may offer a more precise and individualized postnatal corticosteroid therapy for EP infants.
- General Pediatrics
- Lipoprotein(a) prevalence trends in Portuguese children and adolescents: a real-world perspective (13,578 times)
- Isabel Morais Ribeiro, Susete Vieira, Miguel Saraiva, Mónica Tavares, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Mangas Palma, Helena Ferreira Mansilha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1031-1040. Published online November 24, 2025
-

Early lipid screening, including lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), in children/adolescents is key to identifying and managing dyslipidemia and reducing the risk of early-onset cardiovascular disease. This study shows that prevalence of elevated Lp(a) in high-risk Portuguese children is alarming, with over 30% at intermediate/high risk and nearly 1% at very high-risk (>430 nmol/L). Since Lp(a) is mostly genetically determined, one-time early screening in atrisk children is crucial for timely monitoring and prevention.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh (13,335 times)
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Association between pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and birth and neurodevelopmental outcomes: an extensive review (13,054 times)
- Ozge Yesildemir, Mensure Nur Celik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):328-346. Published online November 16, 2023
-

· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development (12,698 times)
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Hematology
- Promising role of voxelotor in managing sickle cell disease in children: a narrative review (12,410 times)
- Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon, Japna Singh, Dalwinder Janjua
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):106-114. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Voxelotor has promising ability to increase hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis markers in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Several preclinical and phase II/III trials have demonstrated its efficacy, dose-dependent responses, and tolerability in children. Ongoing trials are assessing its safety and effectiveness in various populations, including children younger than 12 years. These findings suggest its potential as a disease-modifying drug, warranting further exploration of its role in SCD management.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study (12,182 times)
- Phakwan Laohathai, Rathaporn Sumboonnanonda, Puthita Saengpanit, Chodchanok Vijarnsorn, Chatchawan Srisawat, Kwanjai Chotipanang, Sarawut Junnu, Supawan Kunnangja, Hathaichanok Rukprayoon, Phakkanan Phuangphan, Sompong Liammongkolkul, Arthima Phaokong, Narumon Densupsoontorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):666-672. Published online April 16, 2025
-
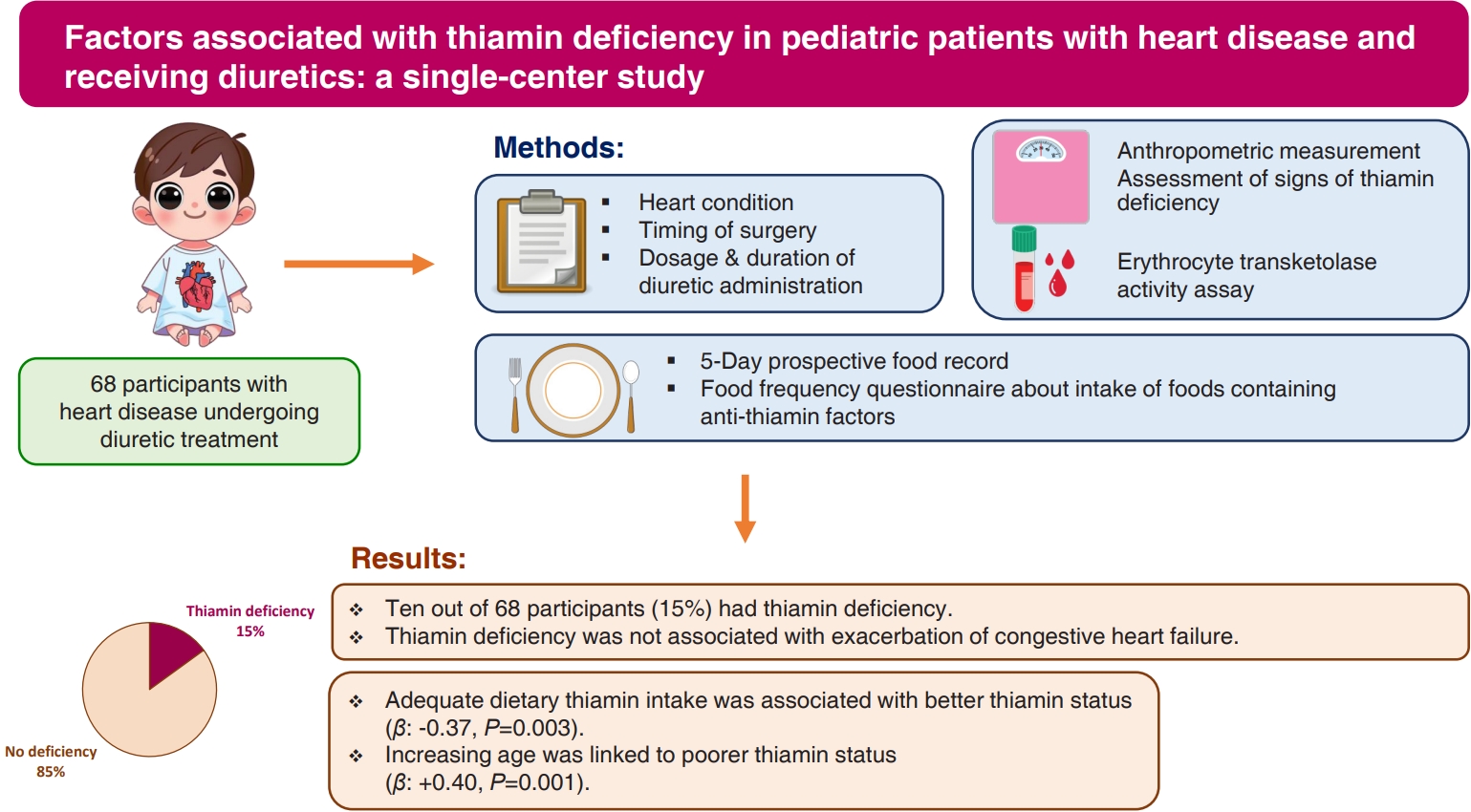
Question: Are pediatric patients with heart disease who are receiving diuretics at risk of thiamin deficiency (TD)?
Finding: Fifteen percent of the patients had TD. TD was associated with inadequate dietary thiamin intake and increasing age.
Meaning: The thiamin pyrophosphate effect should be assessed in those with high risk of TD. Dietary counseling should be emphasized to ensure adequate dietary thiamin intake.
- Guideline
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of 15- and 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Korean infants and children (12,028 times)
- Ki Wook Yun, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Soo-Han Choi, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):76-83. Published online December 30, 2025
-
Compared to PCV13, PCV15 includes 2 (22F and 33F), and PCV20 includes 7 (8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F) additional serotypes. The vaccination schedule remains the same: primary doses at 2, 4, and 6 months, and a booster at 12–15 months. If PCV13 was administered in the primary series, PCV15 and PCV20 may be used to complete it or as a booster.
- Review Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases (12,017 times)
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-

· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in adolescents: transcranial doppler versus autonomic function test results (11,832 times)
- Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):673-679. Published online August 6, 2025
-
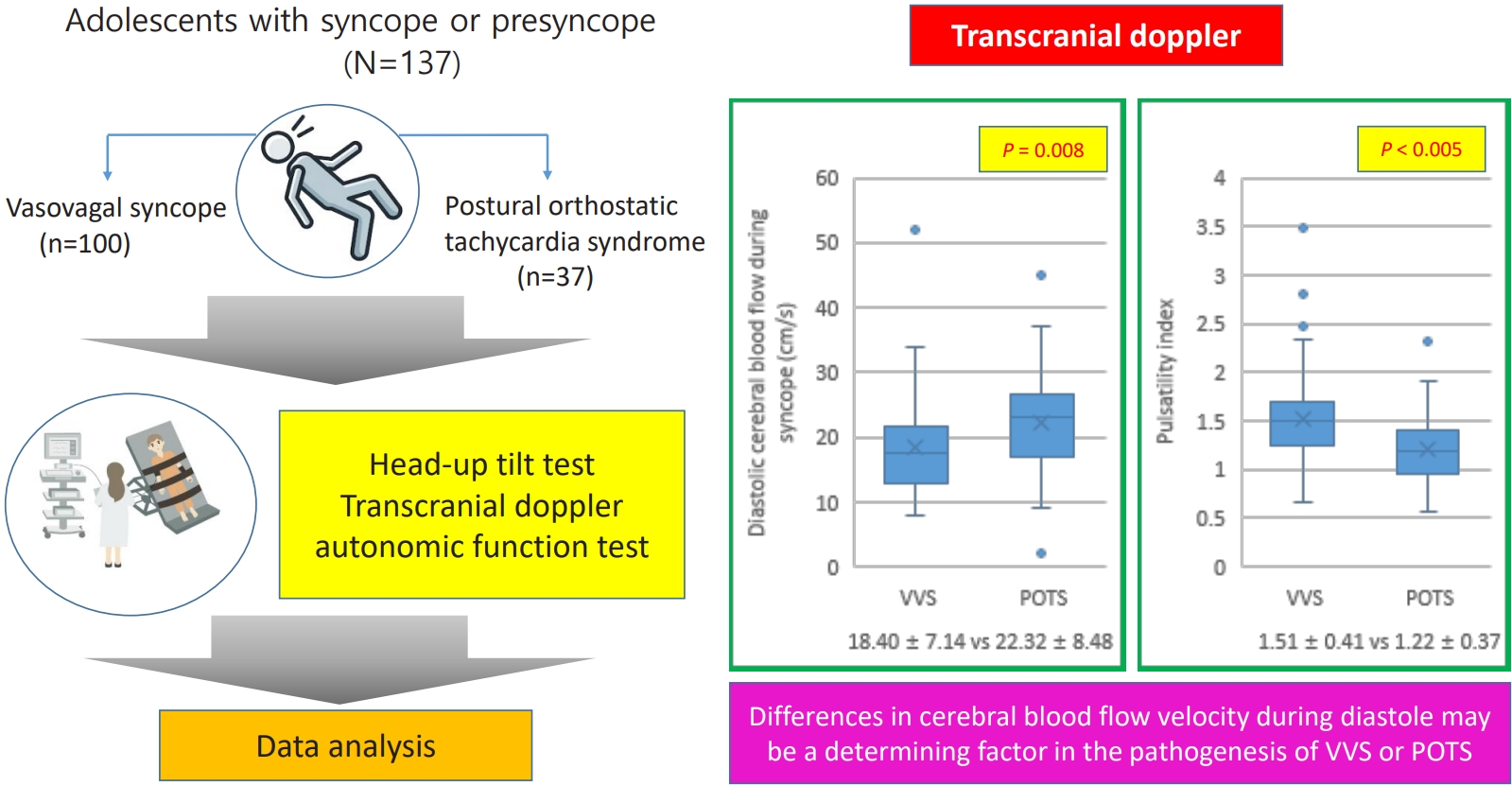
Question: Vasovagal syncope (VVS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) are representative forms of neurally mediated syncope. What influences the occurrence of each?
Finding: Autonomic function test results did not differ, but cerebral blood flow during diastole on transcranial doppler differed between VVS and POTS.
Meaning: Differences in diastolic cerebral blood flow velocity play an important role in VVS and POTS.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial (11,828 times)
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-

Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Recent updates on systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis (11,568 times)
- Jiyoung Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):580-588. Published online November 1, 2024
-
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex disease with multifactorial pathogenesis and variable clinical presentation. Up to one-fifth of patients with AD develop moderate to severe disease that is often refractory to classical therapies and can compromise quality of life. This review summarizes recent clinical evidence on biological agents and small-molecule immunotherapies for the treatment of AD.
- Perspective
- Gastroenterology
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children: a practical update based on Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ISPGHAN) 2024 guidelines (11,482 times)
- Ankit Agrawal, Arghya Samanta
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):546-550. Published online May 12, 2025
-

- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (11,335 times)
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):503-511. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Does the gut microbiota differ between very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: Common respiratory pathogens were notably elevated in the BPD group, whereas anaerobic and butyrate-producing taxa, key components of postbiotics, were dominant in the non-BPD group.
Meaning: In gut-lung communication, the interplay between the intestinal and respiratory systems may implicate pro- and postbiotics in VLBW infants with BPD.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models (11,086 times)
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Editorial
- Other
- Beyond the eye: a multidisciplinary perspective on managing pediatric myopia (10,934 times)
- Eoi Jong Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):566-568. Published online July 18, 2025
-
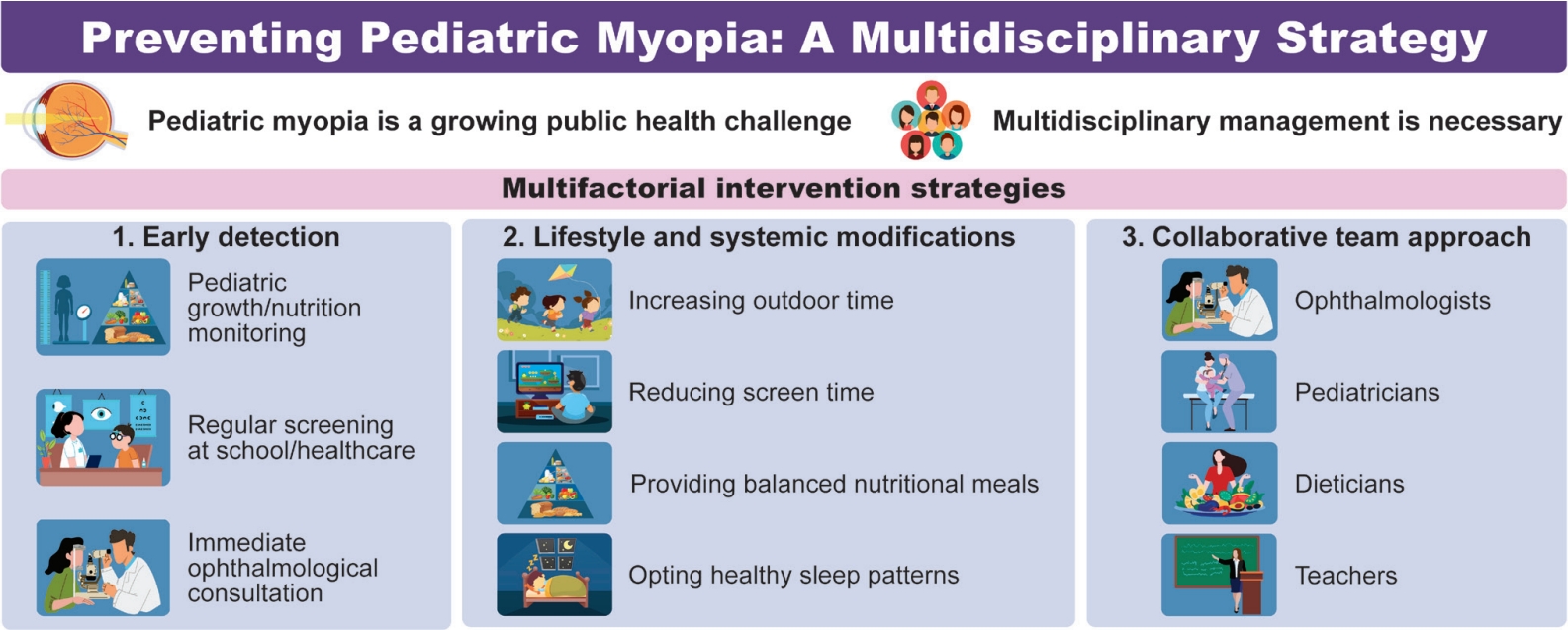
Myopia is a growing global public health concern because of its association with irreversible vision loss such as myopic traction maculopathy, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and glaucoma. The effective prevention of myopia in childhood requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates ophthalmologic care with lifestyle, nutrition, and sleep interventions. Early detection through regular visual screening in schools and primary care settings and timely ophthalmology referrals are critical to preventing high myopia.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases (10,796 times)
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
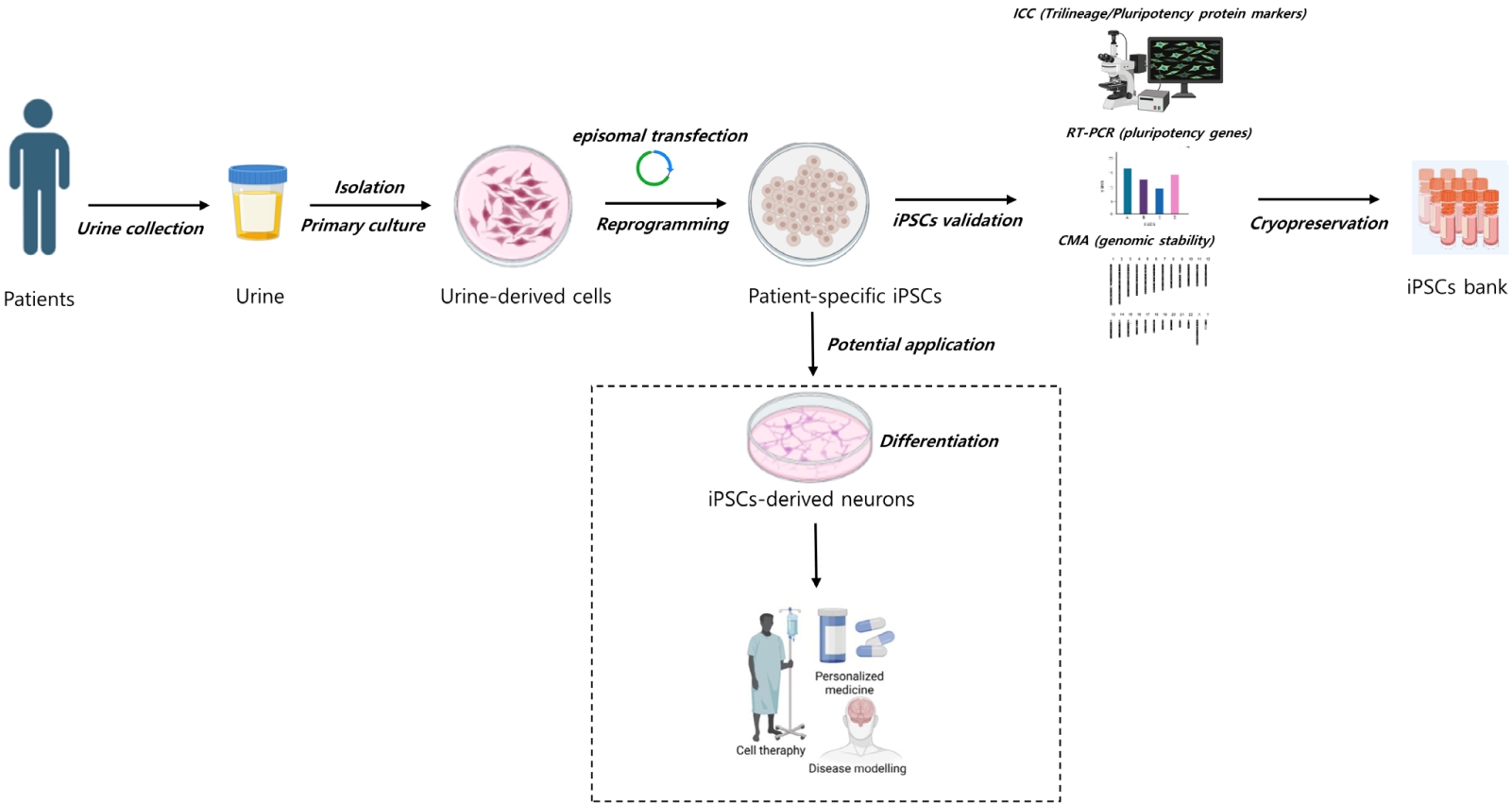
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- Pulmonology
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates (10,770 times)
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-
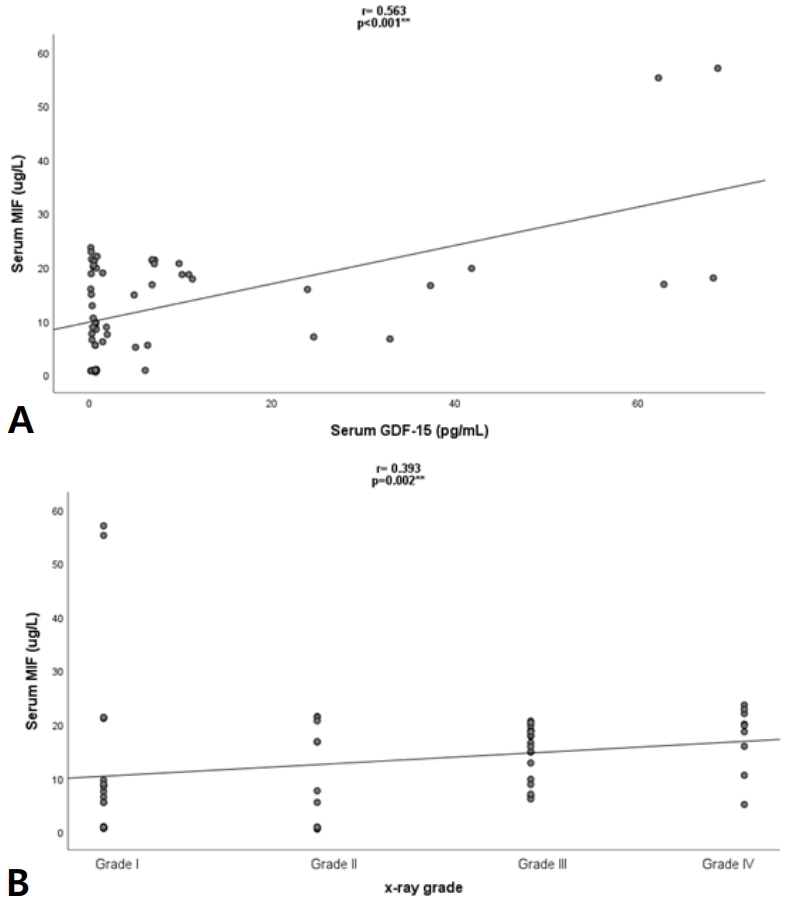
Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











