Endocrinology
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Endocrinology
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (15)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (76)
- General Pediatrics (58)
- Genetics and Metabolism (26)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (54)
- Neurology (96)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins?
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-
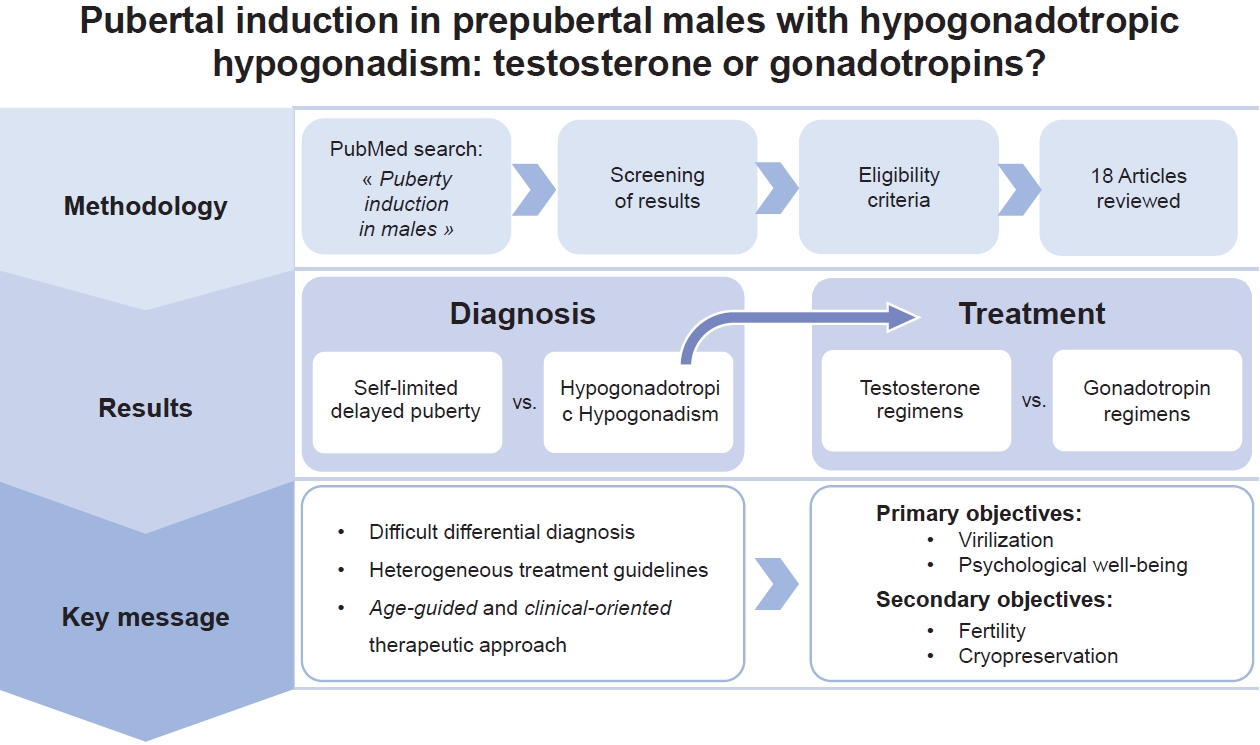
The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Long-term epidemiological insights into rickets: a nationwide population-based retrospective study
- Chun-Hao Chu, Ying-Chuan Chen, Pei-Yao Liu, Chun-Chieh Hu, Yu-Lung Lin, Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Tzu-Ju Hsu, Yu-Tung Hung, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Chien-Ming Lin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):879-891. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: What are the nationwide trends and mortality risk factors of nutritional versus hereditary rickets among children in Asia?
Finding: In 2012–2018, the incidence of rickets steadily increased, whereas mortality rates declined. Mortality is associated with a low household income, anemia, chronic kidney disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and a prolonged hospital stay.
Meaning: Early diagnosis and targeted interventions addressing social and medical vulnerabilities are critical to reducing ricket-related mortality.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Rickets prevalence and treatment outcome: real-world data from Taiwan
- Young Suk Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):868-870. Published online October 23, 2025
-
Rickets should be recognized as a significant public health concern during infancy and childhood. Recent studies from Taiwan have demonstrated a steady increase in the prevalence of nutritional rickets, and a similar trend is likely to emerge in Korea. Therefore, comprehensive clinical evaluation and appropriate biochemical assessment are essential to prevent long-term skeletal and systemic complications. Prompt diagnosis and timely initiation of appropriate treatment are crucial.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Continuous glucose monitoring in Korean pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: current landscape and clinical implications
- Hwa Young Kim, Jaehyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):842-851. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has transformed pediatric type 1 diabetes care by facilitating tighter glycemic control, reducing hypoglycemia, and improving quality of life.
Recent advances in CGM technology and the expansion of insurance coverage in Korea have led to its broader adoption.
Emerging metrics such as time in tight range offer refined tools for individualized glycemic assessment, highlighting CGM’s evolving role in personalized pediatric diabetes management.
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Efficacy of leuprolide acetate versus triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for treatment of central precocious puberty
- Thanaporn Thaneetrakool, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Vichit Supornsilchai, Suttipong Wacharasindhu, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):91-96. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: What are the differences in efficacy between leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Finding: There were no significant intergroup differences in luteinizing hormone suppression or predicted adult height at the end of treatment in girls with CPP.
Meaning: Leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate have comparable efficacy for treating CPP.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Association between pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and birth and neurodevelopmental outcomes: an extensive review
- Ozge Yesildemir, Mensure Nur Celik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):328-346. Published online November 16, 2023
-

· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Applications of genomic research in pediatric endocrine diseases
- Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):520-530. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Recent advances in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of pediatric endocrine disorders and are now used in mainstream medical practice.
· Genome-wide association studies can increase our understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and inform new therapeutic options.
· The identification of founder mutations leads to the efficient localization of the genes underlying Mendelian disorders.
· Next-generation sequencing technologies benefit clinical practice and research of pediatric endocrinology.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-
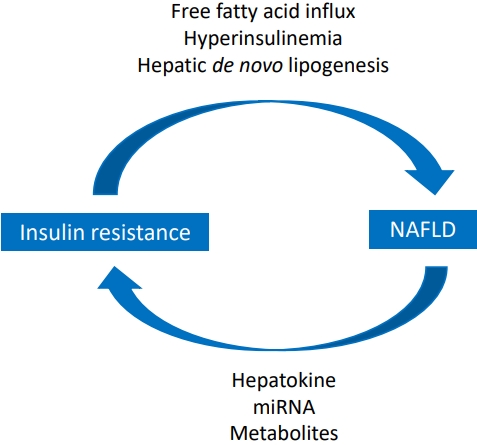
· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Letter to the Editor
- Endocrinology
- Accuracy of predicted adult height using the Greulich-Pyle method and artificial intelligence medical device
- Dongho Cho, Yun Sun Choi, Hayun Oh, Young min Ahn, Ji-Young Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):145-147. Published online January 25, 2023
-
- Clinical Note
- Endocrinology
- Graves’ disease: an uncommon cause of late sequelae following DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms)
- Therdpong Tempark, Amatanun Tangthanapalakul, Tawatchai Deekajorndech, Susheera Chatproedprai, Vichit Supornsilchai, Siriwan Wananukul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):602-604. Published online June 22, 2022
-
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Bisphenol A leaching from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food causes potential health issues
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):450-452. Published online July 25, 2022
-
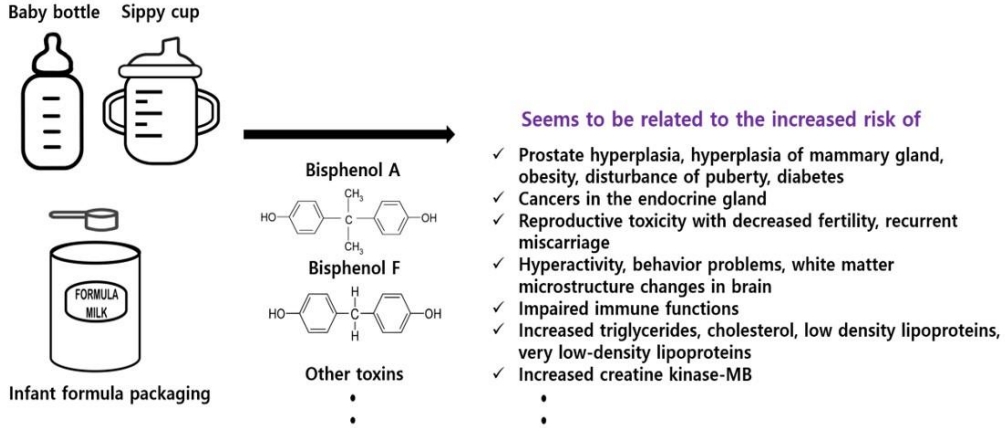
Can bisphenol A (BPA) leach out from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food? BPA and other toxic materials can leach out from baby bottles and increase the risk of various health problems, including endocrine disturbances. Although the use of BPA in baby bottles has been banned, many developing countries still use it, which can cause health issues. Thus, public awareness of this issue is required.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-

Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Low bone mineral density can occur in children after shortterm systemic glucocorticoid treatment
- Moon Bae Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):300-301. Published online April 27, 2022
-

Osteoporosis diagnosed in children with chronic diseases is a major endocrine complication triggered by the disease itself or its treatment. Although age upon starting osteotoxic agents and the their duration of use are vital contributors, spontaneous recovery of bone mass following treatment completion is a privilege of this specific age group. For any patients short-term glucocorticoid therapy, bone health screening is the next step.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric hypertension based on Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines (JSH 2019) with actual school blood pressure screening data in Japan
- Toru Kikuchi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):283-290. Published online November 26, 2021
-

The prevalence of Japanese pediatric hypertension is 0.9% based on proper measurement protocols. Hypertensive children tend to be hypertensive adults. Pediatric essential hypertension is characterized by an absence of symptoms, obesity, a family history of hypertension, and a low birth weight. The most common causes of pediatric secondary hypertension are renal parenchymal and renovascular diseases. Important factors controlling pediatric hypertension include healthy lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children?
- Minsun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):252-253. Published online March 29, 2022
-
· Evidence shows that patients with type 1 diabetes have been severely affected by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in various ways.
· Although there is no reliable evidence that COVID-19 worsens or induces diabetes, it can impair β-cell insulin secretion and glucose control by inducing inflammation and cytokine production.
· A study is needed of the short- and long-term relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 in the Korean pediatric population.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Genetic factors in precocious puberty
- Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):172-181. Published online October 18, 2021
-
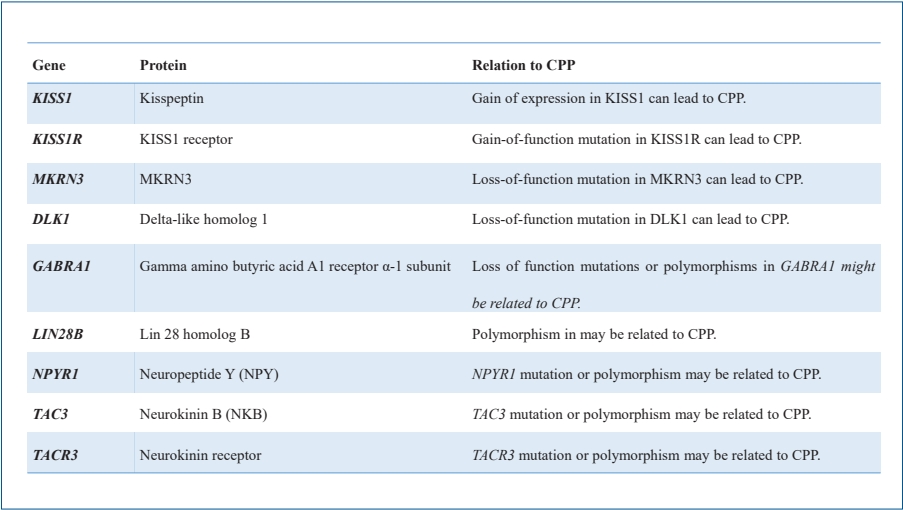
· Mutations in the kisspeptin (KISS1), kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R), makorin ring finger protein 3 (MKRN3), and delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) genes are associated with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP).
· A few genes related to pubertal onset have been implicated in ICPP.
· Epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone posttranslational modifications, and noncoding ribonucleic acids may be related to ICPP
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Clinical and diagnostic importance of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):129-130. Published online January 14, 2022
-
∙ Because childhood lipid concentrations continue into adulthood, early evaluation and treatment are needed, but dyslipidemia awareness is low.
∙ For the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in childhood and adolescence, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in adulthood, lifestyle modifications, appropriate exercise, and drug treatment are required.
∙ A large-scale study of the prevalence and therapeutic effects of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents in Korea is needed.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Association between polycystic ovary syndrome and risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring: a meta-analysis
- Azam Maleki, Saeid Bashirian, Ali Reza Soltanian, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Abdollah Farhadinasab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):85-89. Published online April 15, 2021
-
Question: Have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) increased risk of having an offspring with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
Finding: Six articles (3 cohort and 3 case-control studies; 401,413 total ADHD cases) met the study criteria. Maternal PCOS was associated with an increased risk of ADHD in the offspring based on odds ratio (OR) and relative ratio (RR) (OR, 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27–1.57) and (RR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.35–1.51), respectively.
Meaning: Our study showed that maternal PCOS is a risk factor for ADHD.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Pediatricians must consider familial environment when diagnosing and managing childhood obesity
- Young Suk Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):31-32. Published online April 19, 2021
-
•The prevalence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide, including in the Republic of Korea, creating a major public healthissue.
•Accumulated evidence indicates a strong relationship between parentalandchildobesity.
•A family-based approach is indicated to prevent and manage childhoodandadultobesity.
- Pediatric obesity: life cycle approach of pediatrician and society
- Yong Hee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):29-30. Published online December 28, 2021
-
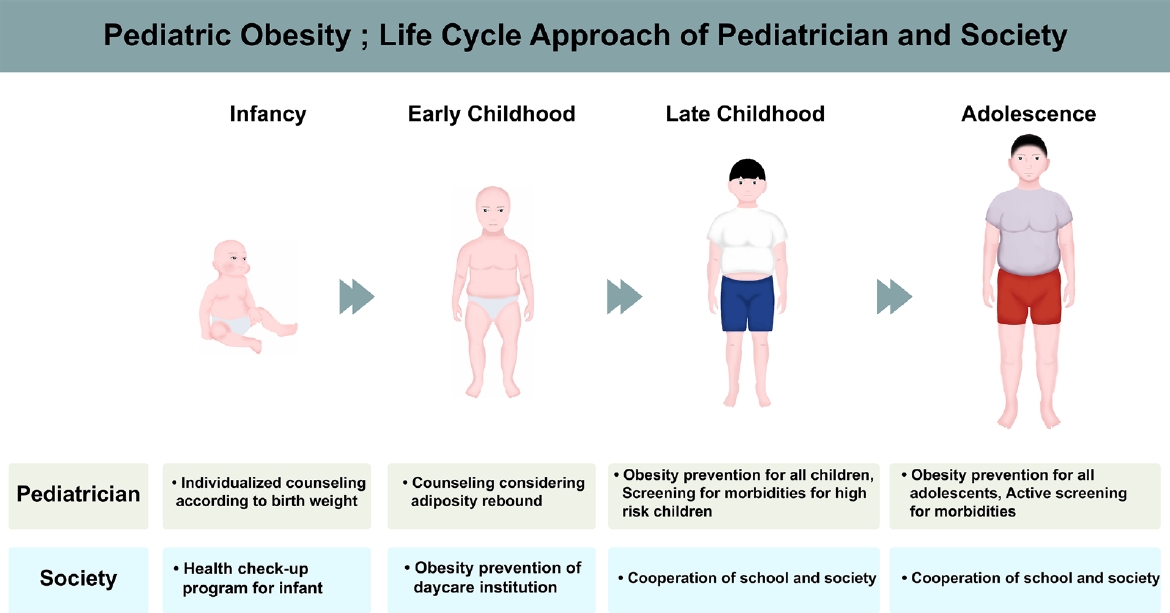
• With the emerging epidemic of pediatric obesity, many endocrine comorbidities classically seen in adulthood are surfacing much earlier in life.
• Appropriate obesity counseling and education should be provided from infancy to adolescence.
• Managing pediatric obesity may require school and society involvement.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
- Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):619-627. Published online August 26, 2021
-
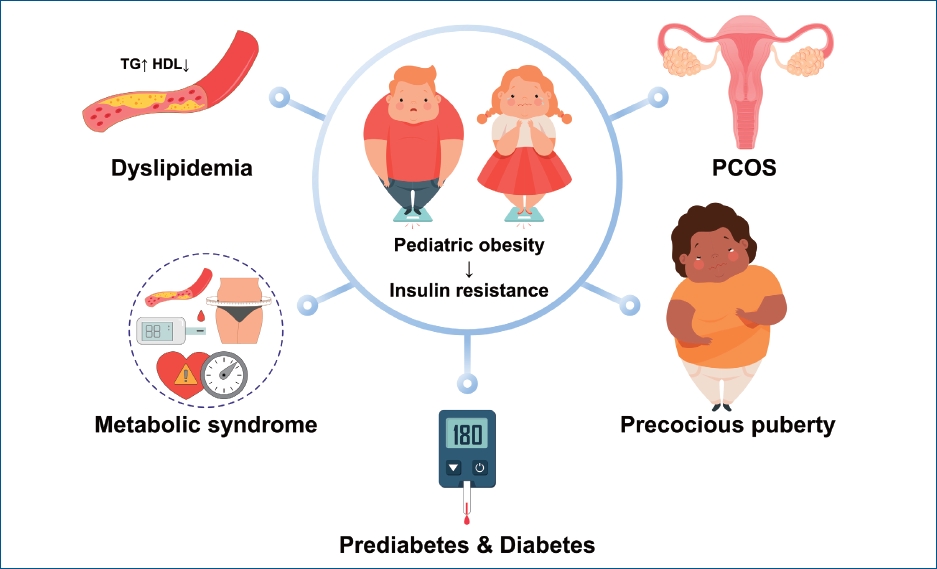
∙ Pediatric obesity can involve endocrine comorbidities such as prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, and central precocious puberty.
∙ Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in youth aged 10–19 years had a prevalence of 25.9% and 0.6% in 2013–2014, respectively.
∙ Dyslipidemia in Korean adolescents aged 10–18 years had a prevalence of 7.64% (total cholesterol ≥200 mg/dL), 6.09% (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL), 8.69% (triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL), and 12.52% (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL) in 2007–2018.
∙ Metabolic syndrome in Korean youth has a prevalence of 1.9%–14.7% in males and 1.7%–12.6% in females with wide variation in definitions.
∙ Appropriate comorbidity screening and management and/or specialist referral are necessary for obese children and adolescents.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











