Editorial
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Global breastfeeding efforts: a long way to go
- Hye-Jung Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):300-302. Published online November 13, 2024
-

· Despite much effort, breastfeeding practices remain unsatisfactory worldwide.
· Effective breastfeeding-promoting interventions are needed that are appropriate for age, culture, and social environment.
· Interventions can promote breastfeeding, especially in younger populations such as adolescent mothers.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Advancements and challenges in neonatal resuscitation: embracing laryngeal mask airways for improved outcomes
- Jang Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):298-299. Published online November 28, 2024
-
Positive pressure ventilation (PPV) is the most critical intervention provided during delivery room resuscitation. In the new guidelines, this recommendation has been expanded to suggest the use of laryngeal mask airyway (LMA) versus face masks for PPV. Evidence-based information and hands-on training related to this practice will help more healthcare providers become familiar with and appropriately use LMA during delivery room resuscitations.
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Nutrition
- Zinc as a treatment modality for acute infectious diarrhea in children
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):223-224. Published online October 31, 2024
-
· Prevention and management of dehydration is the major goal of treatment in acute infectious diarrhea in children.
· Zinc could be effective as an adjuvant therapy in reducing the duration of acute infectious diarrhea in malnourished children.
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Allergy
- Effect of metabolic syndrome on pulmonary dysfunction in children with asthma
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):136-137. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increased in Korean children during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic owing to reduced physical activity resulting from social distancing.
· Metabolic syndrome impacts pulmonary dysfunction in childhood asthma.
· Further studies are needed to understand the mechanism linking asthma and metabolic syndrome and develop interventions.
- Cardiology
- What we should know about pediatric heart failure: children are not small adults
- Ja-Kyoung Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):62-64. Published online November 6, 2024
-
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) features high morbidity and mortality rates.
· Although adults and children can share a common diagnosis of heart failure, the underlying causes can differ significantly and require distinct therapeutic approaches.
· Treatments designed for adults are often applied to PHF despite the fundamental physiological and developmental differences between them.
· Child-specific data are vital for the development of tailored treatments to meet the unique needs of patients with PHF.
- Allergy
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-

· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Advancements in food allergen immunotherapy: improving quality of life and reducing risks
- Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):672-674. Published online July 31, 2024
-

· Pediatric food allergies considerably impair patient and family quality of life, particularly those with persistent allergies to common food allergens.
· Recent research has focused on developing diverse approaches to food allergen immunotherapy, showing promising outcomes of oral, sublingual, and epicutaneous immuno therapies.
· Critical considerations in immunotherapy candidate selection underscore the need for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers in future studies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Infection
- Preventing bloodstream infections in children after liver transplantation
- Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):599-600. Published online April 18, 2024
-
Liver transplantation (LT) is crucial for children with end-stage liver diseases, yet bloodstream infections (BSI) pose significant risks, despite medical advancements. Immunosuppressants, essential for preventing organ rejection, heighten infection susceptibility. Understanding BSI organisms is vital due to antimicrobial resistance. Pediatric LT recipients have unique risk factors, demanding tailored preventive measures. This systematic review on bacterial BSI emphasizes the urgency of effective prevention strategies, considering the high incidence and distinct organism profile. Further research is vital for optimizing antibiotic management and improving outcomes for this vulnerable population.
- Immunology
- Utility of eosinophil granule proteins in management of pediatric chronic cough
- Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):519-520. Published online April 17, 2024
-

· Pediatric chronic cough often involves eosinophilic inflammation; however, objective measurements are not routinely used in treatment decisions.
· Accurate biomarkers of eosinophil activity, such as eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) and cationic proteins (ECP), should be used. EDN, which overcomes the shortcomings of ECP, recently received approval for use in Korean healthcare settings.
· EDN and ECP can play a role in treatment period and drug selection decisions.
- Neurology
- Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on clinical features of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):456-458. Published online March 25, 2024
-

· The frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) was not significantly influenced by the pandemic.
· The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has further diversified the etiologic enteric viral pathogens of CwG.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Is it possible to provide palliative care to pediatric patients with neurological diseases?
- Young-Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):403-404. Published online February 15, 2024
-
· Patients with neurological diseases often require external mechanical support to maintain mechanical ventilation or supply.
· Little has been done to help the families of affected children make difficult decisions that carry significant physical and psychological consequences.
· The establishment of a department that provides pediatric palliative care for neurological patients should be considered.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Advancing orphan drug development for rare diseases
- Jung Min Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):356-357. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· Rare diseases present unique challenges and unmet needs for which the development of orphan drugs tailored to them offers hope.
· Despite the hurdles posed by limited patient populations, orphan drug designations from regulatory agencies provide incentives, such as extended market exclusivity and tax credits, that ignite transformative advances.
· Scientific progress in genomics, personalized medicine, and analytics empowers precise interventions by decoding genetic anomalies and encouraging effective treatments.
- Neurobehavior
- Importance of pediatrician’s role in preventing positional plagiocephaly
- Hee-Jeong Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):294-295. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Plagiocephaly is characterized by the asymmetrical shape of a baby’s head.
· Since positional plagiocephaly is associated with developmental delay and further musculoskeletal problems, early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents worsening of the condition.
· Pediatricians can educate parents about proper head positioning and encourage supervised tummy time during awake hours.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Exploring the role of laryngeal masks in neonatal resuscitation
- Euiseok Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):247-248. Published online December 28, 2023
-
· Laryngeal masks (LMs) offer stable airway access and skill retention advantages, making them promising alternatives to positive-pressure ventilation in neonatal care.
· The ease of teaching LM insertion techniques to less experienced providers addresses the need for swift intervention and skill retention.
· Careful consideration of the benefits and challenges of LMs is essential in determining their effective integration into enhanced neonatal resuscitation protocols.
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Impacts of maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy on neonatal health and epidemiology
- Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):149-151. Published online December 28, 2023
-

Newborns born to mothers infected with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be closely monitored for respiratory disorders, such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, regardless of their COVID-19 test results. Further research is required of the development of infants born to mothers with COVID-19. The trends in Korea's birth rate and infant mortality rates have not been significantly affected by COVID-19.
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
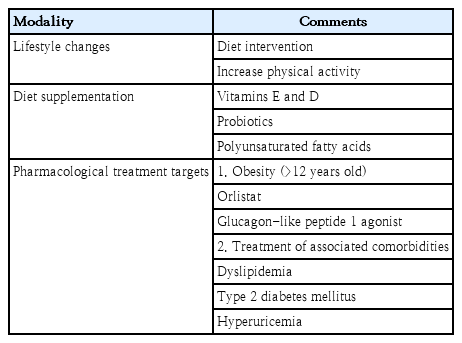
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of kidney complications in children after COVID-19 infection or vaccination
- Jiwon Jung, Joo Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):35-36. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· The proper monitoring for and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill children, are recommended.
· Glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 or its vaccination has been reported, and the overall clinical course is similar to that of non-COVID-19-associated diseases.
· Additional COVID-19 vaccinations are recommended; however, careful and individualized decisions should be made in patients with COVID-19- or vaccination-associated glomerulopathy.
- Infection
- COVID-19 infection and vaccination among children
- Amnuay Kleebayoon, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):531-532. Published online August 30, 2023
-
· Coronavirus disease 2019 (OVID-19) infection and immunization have been linked with kidney problems; however, causality has not been proven.
· Concern about confounders is usually needed.
· Correspondence about a published article on the COVID-19 vaccine
- Gastroenterology
- Noninvasive and simple, but accurate? Meta-analysis of evidence-based point-of-care ultrasound for assessing dehydration in children
- Jin-Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):475-476. Published online July 11, 2023
-
· Point-of-care ultrasound imaging, including measurement of the inferior vena cava/aorta ratio, is powerful for evaluating the hemodynamic status of pediatric patients.
· Owing to the limited feasibility of randomized clinical trials and insufficient data in children, imaging tools require validation.
· Objective validity meta-analyses of imaging studies can affect clinical decision-making and serve as a cornerstone for evidence-based practice in pediatrics.
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders: autoinflammatory and autoimmune disorders
- Young Dae Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):439-440. Published online July 4, 2023
-
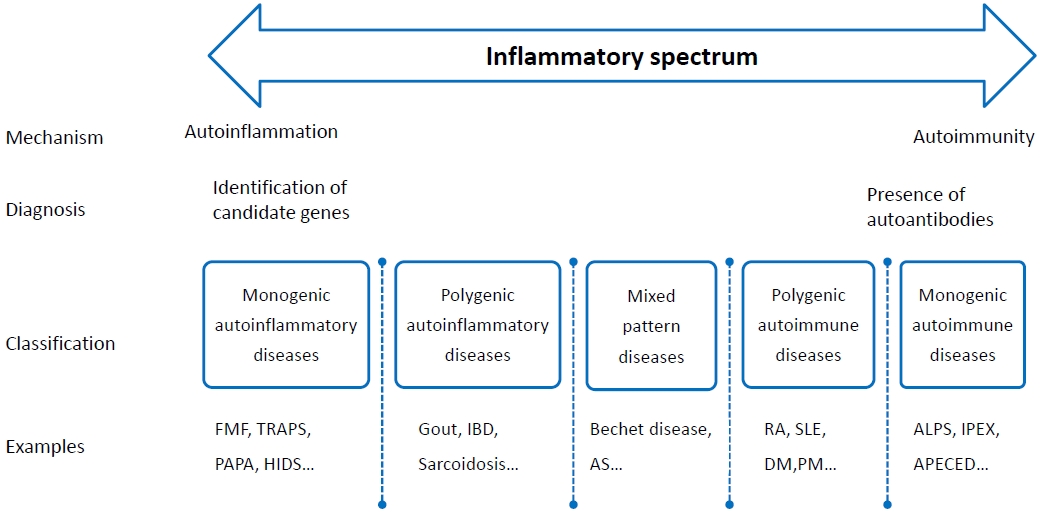
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAIDs) typically have an early onset in life, and may have close relatives may have similar disease.
· SAIDs should be suspected in any patient, especially children, who experience persistent or recurrent inflammatory episodes that fail to fit the pattern of other established diseases.
· Advancements in the understanding of autoinflammation will provide novel diagnostic and therapeutic options for SAIDs patients.
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota’s impact on obesity
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):294-295. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· An imbalance of the gut microbiota with a relative increase in Firmicutes versus Bacteroidetes is associated with the pathogenesis of obesity.
· Dysbiosis is associated with microbial genes associated with short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production and increased colonic SCFA levels. SCFAs have also been shown to regulate appetite and satiety hormones, which can affect food intake and energy balance.
· A dietary high-fat intake is reportedly associated with increased plasma lipopolysaccharide. Altered Toll-like receptor-4 signaling leads to propagating the cascade of further inflammation and promoting insulin resistance.
- Recent advances in epigenetic mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of pediatric gastrointestinal allergic disorders
- Eell Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):250-251. Published online May 19, 2023
-
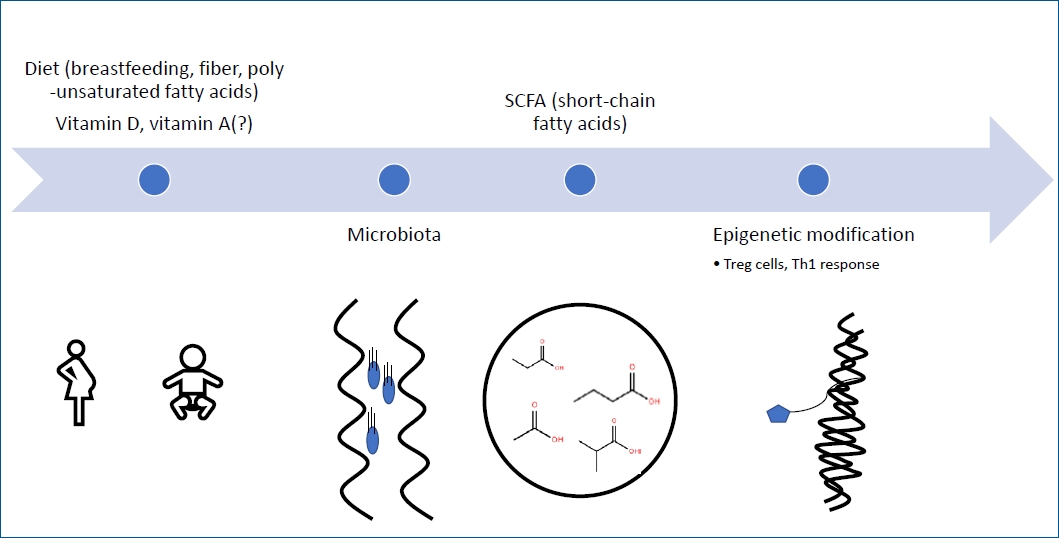
· Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in rapidly increasing food allergy.
· There is still no definitive way to diagnose food allergy.
· Early introduction of peanuts, eggs, and cow’s milk reduces food allergy incidence.
· Administration of probiotics such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium bifidum can partially reduce the occurrence of allergic symptoms.
- Infection
- Impact and role of vitamins as immunonutrition in children during COVID-19 pandemic
- Yoo Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):212-214. Published online April 18, 2023
-
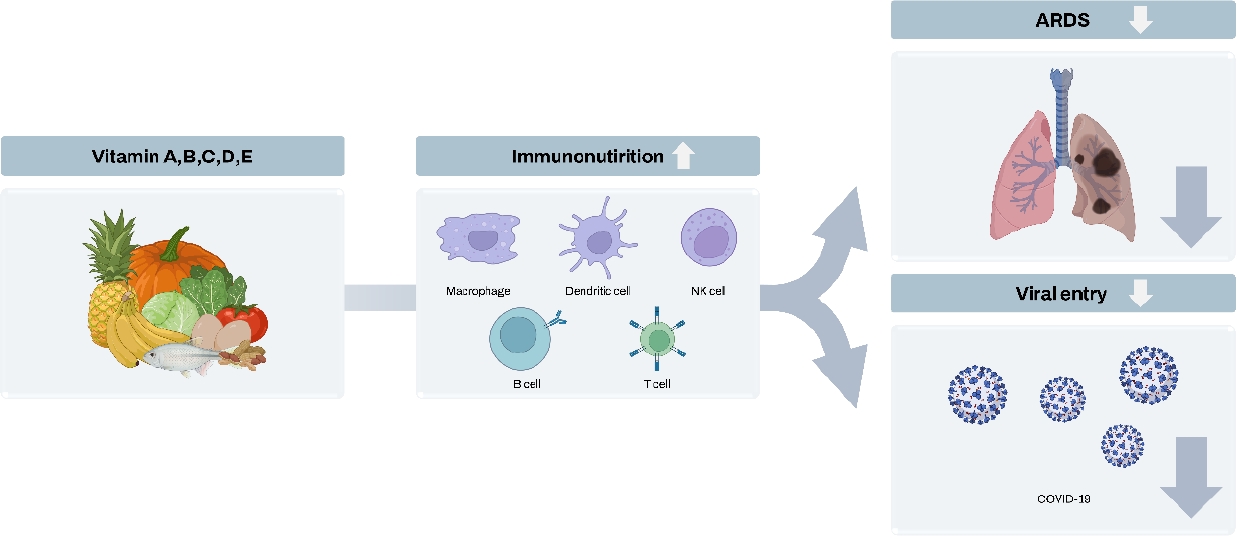
· Vitamins have effector mechanisms in the innate and adaptive immune systems and potential roles in preventing and reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
· Vitamins may be immunonutrients in the treatment of COVID-19 infections and prevention of patient deterioration due to critical illness, thus demonstrating the significance of a nutritious, well-balanced diet.
- Neurology
- Understanding the usefulness of electroencephalography source localization
- Bo Lyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):210-211. Published online April 18, 2023
-
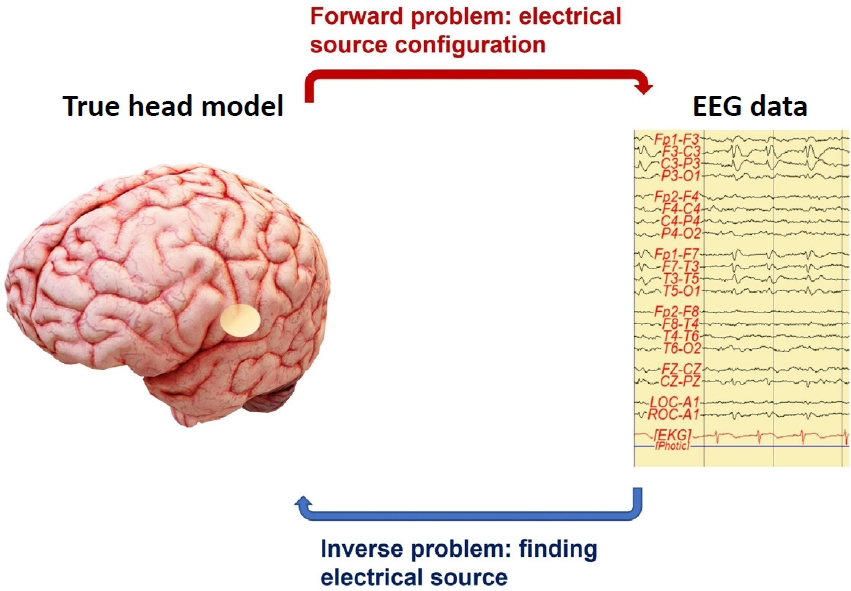
· Electroencephalography (EEG) records brain activity with high temporal resolution.
· EEG source localization, combined with other functional or structural imaging methods, provides information about brain network and connectivity in clinical neuroscience.
· EEG source localization identifies brain location from electrical current sources in several neuropsychiatric diseases such as epilepsy, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and anxiety disorders.
- Other
- Advancing pediatric health: the multifaceted scope of Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics
- Jin Hee Oh, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):171-172. Published online March 29, 2023
-
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics (CEP) is a journal that specializes in pediatric research topics. It covers a wide range of research areas, including basic research, translational research, and research related to improving pediatric health and diseases. CEP also focuses on the coordination of societal structures and processes that orchestrate pediatric health and disease throughout society, and the parallel relationship between regional characteristics and globalization. The journal intends to continue promoting pediatric health through relentless efforts and the discovery of new research areas.
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children?
- Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs.
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











