Allergy
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Allergy
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (60)
- Cardiology (79)
- Critical Care Medicine (10)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (60)
- Gastroenterology (63)
- General Pediatrics (45)
- Genetics and Metabolism (24)
- Hematology (15)
- Immunology (14)
- Infection (72)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (119)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (52)
- Neurology (94)
- Nutrition (28)
- Oncology (16)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (30)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (35)
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Effect of metabolic syndrome on pulmonary dysfunction in children with asthma
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):136-137. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increased in Korean children during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic owing to reduced physical activity resulting from social distancing.
· Metabolic syndrome impacts pulmonary dysfunction in childhood asthma.
· Further studies are needed to understand the mechanism linking asthma and metabolic syndrome and develop interventions.
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-

· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Advancements in food allergen immunotherapy: improving quality of life and reducing risks
- Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):672-674. Published online July 31, 2024
-

· Pediatric food allergies considerably impair patient and family quality of life, particularly those with persistent allergies to common food allergens.
· Recent research has focused on developing diverse approaches to food allergen immunotherapy, showing promising outcomes of oral, sublingual, and epicutaneous immuno therapies.
· Critical considerations in immunotherapy candidate selection underscore the need for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers in future studies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Regional differences in diagnosis and management of cow's milk allergy
- Fabian Hendricx, Emma Robert, Jaime A. Ramirez-Mayans, Karen Rubi Ignorosa Arellano, Erick M. Toro Monjaraz, Yvan Vandenplas
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):601-607. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· Although there is broad consensus on many aspects regarding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cow's milk allergy, the impact of geographical, cultural, and socioeconomic factors remains unestablished.
· Availability and cost of formula for the management of cow's milk allergy have a major impact on the therapeutic choice.
· Region-specific guidelines for the treatment of cow's milk allergy are required.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Comparison and review of international guidelines for treating asthma in children
- Eui Jeong Roh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):447-455. Published online August 20, 2024
-

Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children. Although asthma in children may spontaneously improve, it continues into adulthood in many cases. Therefore, appropriate disease management and medication are essential. Consistent and objective guidelines are needed to manage pediatric asthma and related adverse reactions.
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-

· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Natural course of IgE-mediated food allergy in children
- Kyunguk Jeong, Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):504-511. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Dendritic, regulatory T, and regulatory B cells significantly contribute to the natural course of food allergy.
· Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergies tend to resolve in earlier childhood but recent studies show that 50% of patients still persist into school age.
· The potential factors affecting the natural course of food allergy are age at diagnosis, symptom severity, sensitization status and its change rate, and external factors such as diet and interventions.
· There is a considerable possibility of food allergy outgrow if specific IgE levels are 2–5 kUA/L or less, but other factors such as age and recent symptoms should be considered together.
· With a clear understanding of the natural course of food allergy, pediatricians can provide appropriate assessment and interventions to our patients, and consequently can help patients overcome their food allergy and improve the social safety net.
- Letter to the Editor
- Allergy
- Increased serum eosinophilic cationic protein in children with nonspecific chronic cough
- Young Hwan Kim, Yoon Young Jang, Jieun Jeong, Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):455-457. Published online September 14, 2023
-
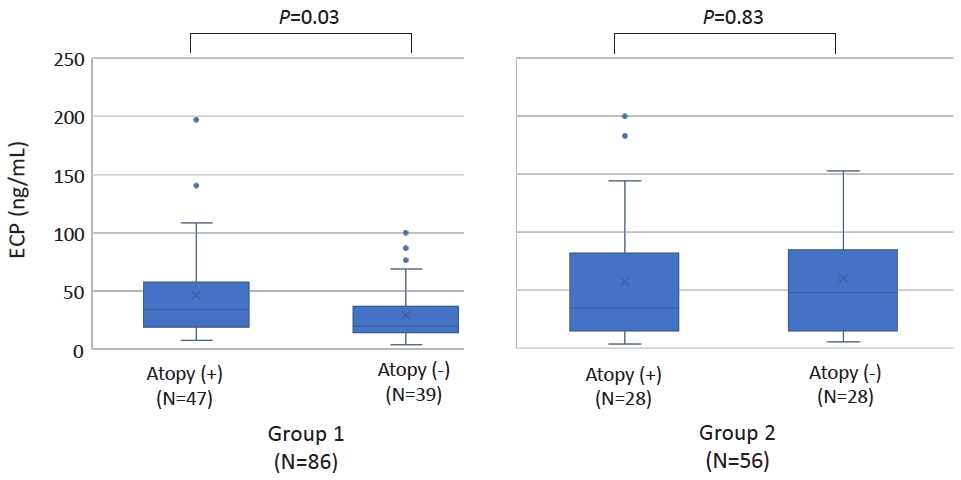
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
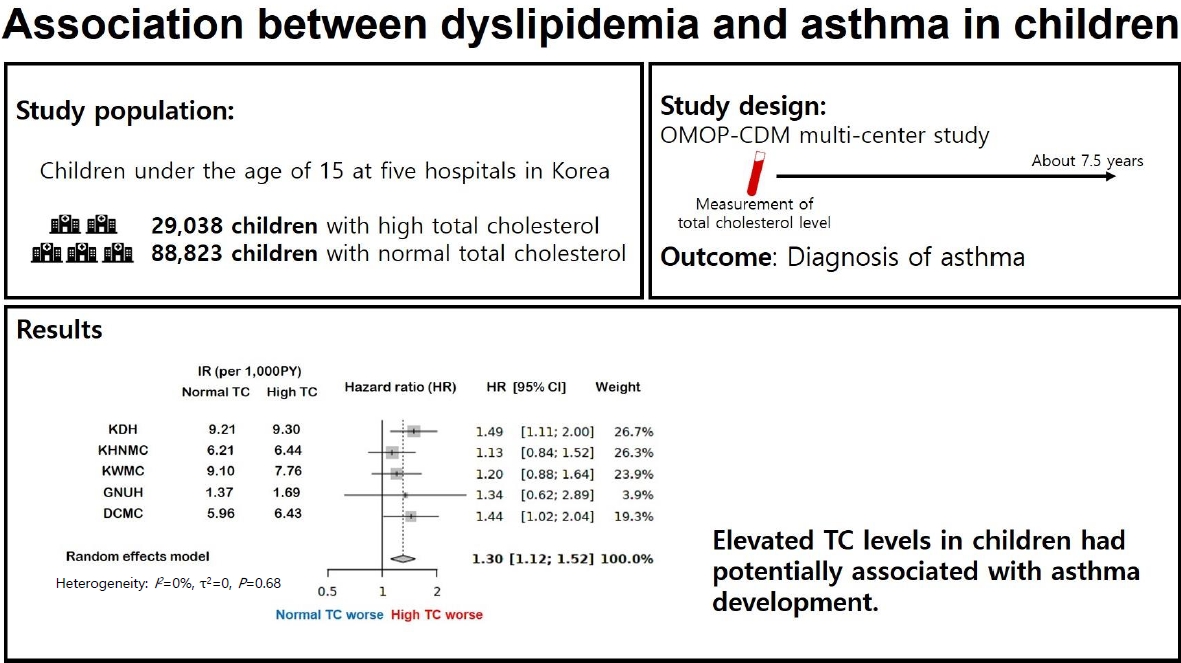
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Recent topics on gastrointestinal allergic disorders
- Yoshiyuki Yamada
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):240-249. Published online January 9, 2023
-
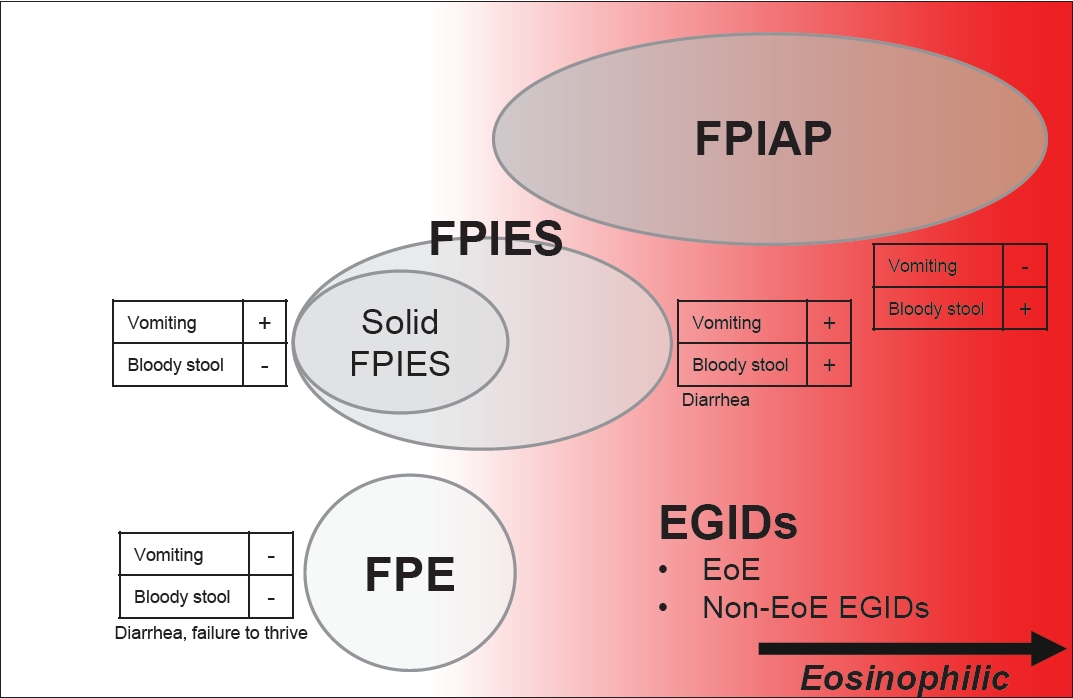
Gastrointestinal (GI) allergies are divided into immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed types. In addition to non-IgE-mediated, overlapping eosinophilic GI disorders (EGIDs) have increased in Japan. EGIDs, a mixed-type allergy category, include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and non-EoE EGIDs. The number of EoE cases has increased in Western countries, followed by Asian countries. Recent GI allergies may also be associated with type 2 inflammation.
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
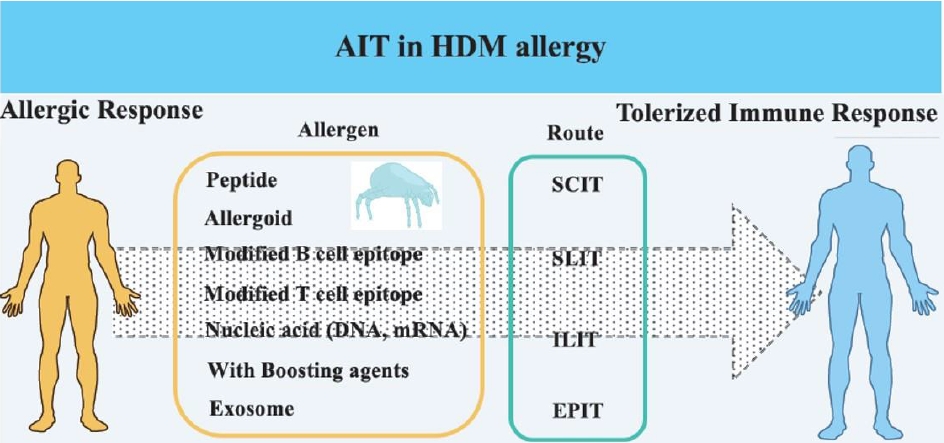
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of allergic diseases in COVID-19 era
- Sungsu Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):587-588. Published online November 29, 2022
-
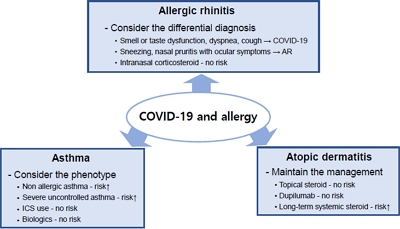
The risk of sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes is not elevated in patients with the type 2 phenotype and well-controlled asthma. Inhaled corticosteroids, intranasal corticosteroids, and topical steroids can be safely used in COVID-19 patients. Biologics can be safely used by patients with allergic diseases without concern about antibody responses.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Diagnosis and management of asthma in infants and preschoolers
- Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):574-584. Published online April 19, 2022
-
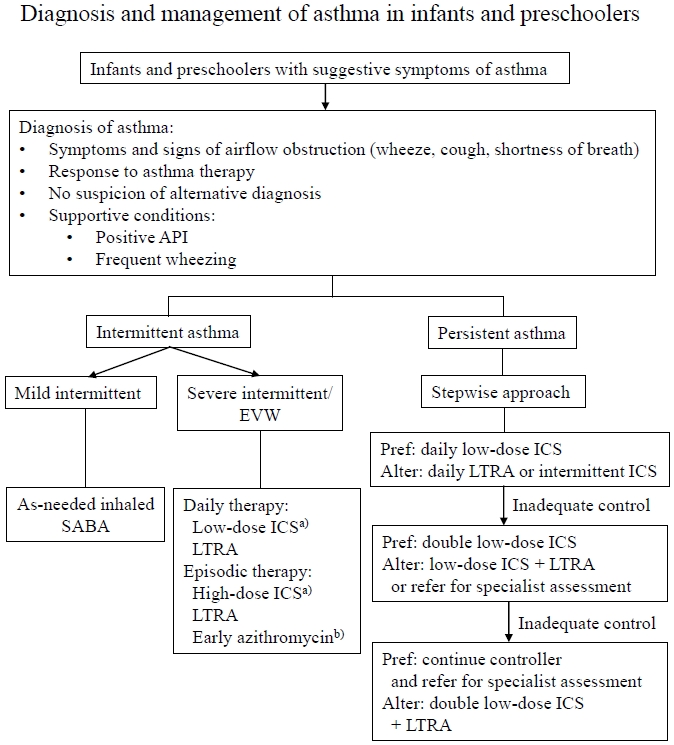
· Asthma in infants and preschoolers involves heterogeneous phenotypes.
· Asthma diagnosis is based on symptom patterns, therapeutic responses, and the presence of risk factors with careful consideration of differential diagnosis.
· Daily inhaled corticosteroid therapy remains the most effective strategy for managing persistent asthma symptoms irrespective of phenotype.
· Future research, including genetic and molecular studies, is needed to develop a clear definition of asthma and personalized therapeutic approaches.
- Management of patients with allergic diseases in the era of COVID-19
- Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):529-535. Published online September 23, 2022
-
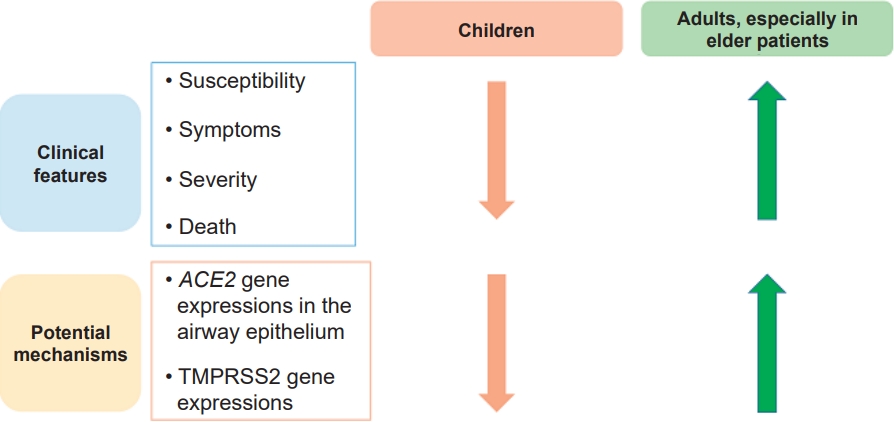
In the early days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, allergic diseases, especially asthma, were considered to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These concerns stemmed from the idea that individuals with allergic diseases are generally more susceptible to respiratory virus infections, which are major causes of exacerbation of allergic diseases. However, epidemiologic data with...
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Dietary restriction misconceptions and food allergy education in children with atopic dermatitis
- You Hoon Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):83-84. Published online January 27, 2022
-
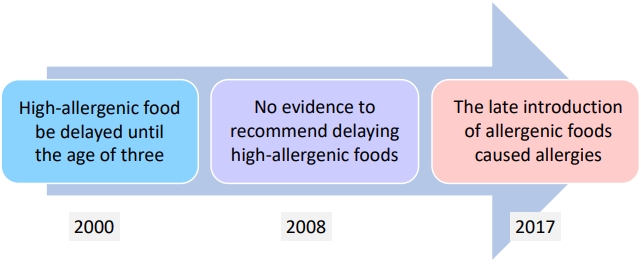
∙ Food intake strategies for preventing food allergies have undergone major changes over the past 20 years.
∙ In children with atopic dermatitis, indiscriminate food restrictions without diagnostic testing leads to nutritional imbalance and poor growth.
∙ When determining food restrictions for pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis, an accurate food allergy diagnosis must be preceded, and continuous parental education about food intake is required.
- Letter to the Editor
- Allergy
- Environmental and dietary factors to be checked for treatment of atopic dermatitis in rural children
- Sanghwa Youm, Eunjoo Lee, Jeongmin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):661-663. Published online October 1, 2021
-
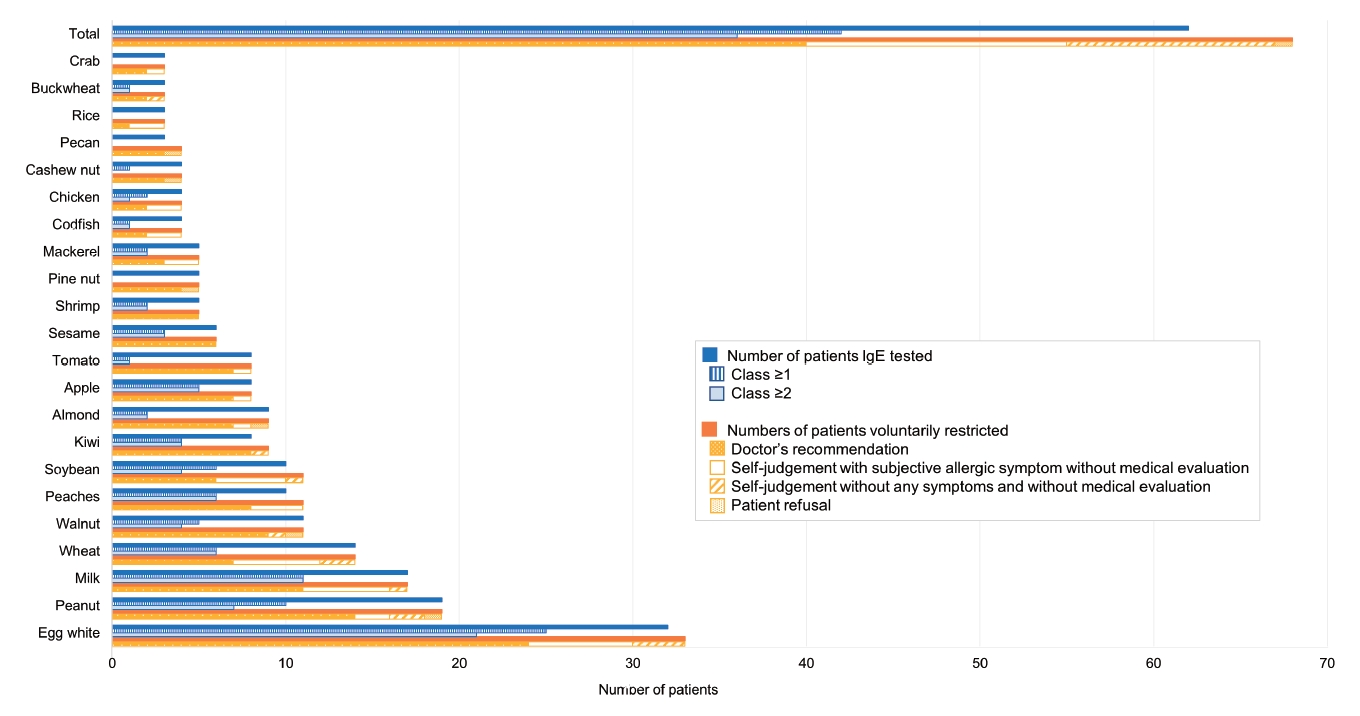
Question: What are the distinctive features of rural children with atopic dermatitis?
Finding: Birch and dog dander were the second most sensitized aeroallergens (32.6%), followed by house dust mites. Doctors and guardians reported food allergy comorbidities differently (19.9% and 43.5%, respectively). Dietary restrictions without medical evaluation were observed in 39.7% of patients.
Meaning: Effects of pollen distribution and indirect animal exposure should be evaluated. Evidence-based dietary restrictions must be implemented.
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Cohort profile: National Investigation of Birth Cohort in Korea study 2008 (NICKs-2008)
- Ju Hee Kim, Jung Eun Lee, So Min Shim, Eun Kyo Ha, Dong Keon Yon, Ok Hyang Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hyun Yong Koh, Kyu Young Chae, Seung Won Lee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):480-488. Published online January 5, 2021
-
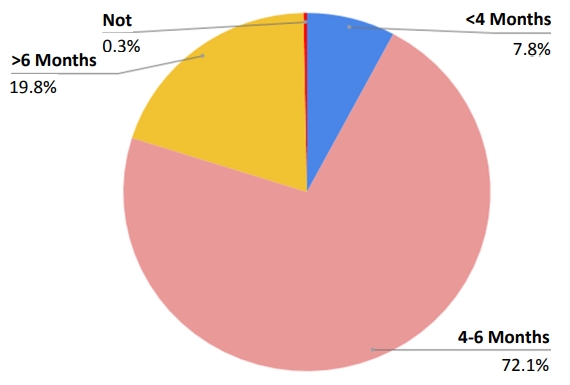
This national cohort study included all Korean children born in 2008 and 2009 observed over a period of more than 10 years. Our findings demonstrate that it is possible to analyze disease onset prior to hospitalization based on information such as lifestyle, eating habits, and risk factors by integrating National Health Insurance System data with national health screening data.
- Influence of age at complementary food introduction on the development of asthma and atopic dermatitis in Korean children aged 1–3 years
- Jihyun Lee, Meeyong Shin, Bora Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):408-414. Published online November 1, 2020
-
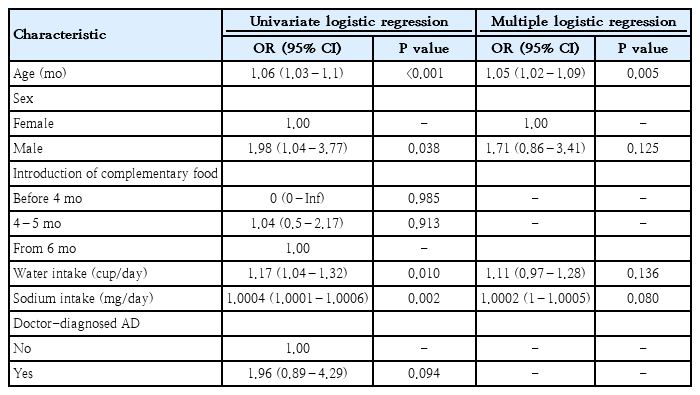
Question: Is age at the time of complementary food introduction associated with asthma and atopic dermatitis (AD) in early childhood?
Finding: We found no significant association between age at the time of complementary food introduction and the incidence of AD and asthma in Koreans aged 1–3 years.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that the influence of individual allergenic foods on the development of AD and asthma should be clarified.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis: role of cofactors
- Meeyong shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):393-399. Published online November 12, 2020
-
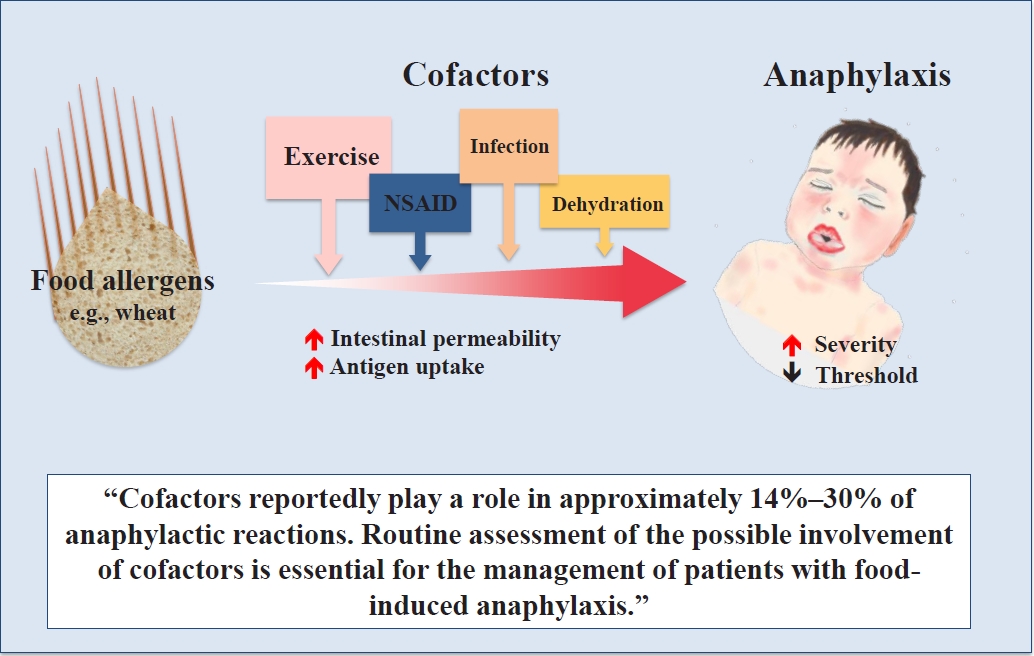
Question: What are the roles of cofactors in food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis?
Finding: Cofactors reportedly play a role in approximately 14%–30% of anaphylactic reactions. Cofactors such as exercise, infection, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, dehydration, and alcohol can increase intestinal permeability and antigen uptake, thereby causing allergic symptoms.
Meaning: Routine assessment of the possible involvement of cofactors is essential for the management of patients with food-induced anaphylaxis.
- Prevalence, comorbidities, diagnosis, and treatment of nonallergic rhinitis: real-world comparison with allergic rhinitis
- Hye Yung Yum, Eun Kyo Ha, Yoon Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):373-383. Published online August 10, 2020
-

Rhinitis is among the most common respiratory diseases in children. Nonallergic rhinitis, which involves nasal symptoms without evidence of systemic allergic inflammation or infection, is a heterogeneous entity with diverse manifestations and intensities. Nonallergic rhinitis accounts for 16%–89% of the chronic rhinitis cases, affecting 1%–50% (median 10%) of the total pediatric population. The clinical course of nonallergic rhinitis is generally...
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Sex-based differences in factors associated with bronchial hyperresponsiveness in adolescents with childhood asthma
- Young Hwan Kim, Yoon Young Jang, Jieun Jeong, Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):229-238. Published online January 14, 2021
-

Question: What factors are associated with bronchial hyperresponsiveness (BHR) in adolescents with childhood asthma?
Finding: Age, mold sensitization, and increased eosinophil count were associated with BHR in boys versus a reduced forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio in girls. Early mold sensitization was a risk factor for persistent BHR in boys only.
Meaning: Sex-specific differences were observed in the factors associated with BHR in adolescents.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Targeting eosinophils: another strategy for asthma treatment
- Hye Mi Jee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):223-224. Published online March 5, 2021
-
Identifying phenotypes and endotypes of asthma patients is challenging, and eosinophilic phenotypes are generally characterized by severe or refractory asthma.
Biologicals targeting eosinophils are promising for the control of severe or refractory asthma symptoms.
To ensure proper treatment, increased understanding of the diverse phenotypes of high Th2 inflammation in pediatric asthma is needed.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Eosinophils and childhood asthma
- Bong Seok Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):60-67. Published online January 6, 2021
-
•In allergic eosinophilic asthma, eosinophils act as important effector cells and antigen-presenting cells, while in nonallergic eosinophilic asthma, type 2 innate lymphoid cells play an important role in eosinophil activation.
•Sputum eosinophil counts can be helpful for evaluating allergic airway inflammation in asthma.
• Anti-interleukin-5 has broadened the scope of asthma treatment.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Insights into pediatric pollen food allergy syndrome
- Jeong Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):483-484. Published online June 1, 2020
-
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











