Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 66(4); 2023 |
|
Abstract
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy, and determines that their action mechanisms are strongly based on immune tolerance. Treatments for HDM allergens have been optimized by modification or/and addition of adjuvants, and clinically evaluated by subcutaneous and sublingual administration. Representative allergens used in AIT are chemically modified allergoids and recombinant allergens, including altered epitopes. The effective mechanisms subsequent to AIT include the suppressive actions of interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-β secreted by regulatory cells, including regulatory T cells and regulatory B cells, and isotype switching from immunoglobulin E to immunoglobulin G4. Further studies of AIT are needed to achieve the milestone in treating allergies.
Graphical abstract
Before the introduction of allergen immunotherapy (AIT), allergic diseases were considered uncontrolled immune diseases. The first clinical trial of AIT was a game-changer, and AIT has now achieved ground-breaking developments to become an essential treatment for asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis in children and adults [1]. However, the precise evaluation of its therapeutic mechanism and efficacy has not been accomplished and continues today.
House dust mite (HDM) is a pivotal component of AIT, and new mite allergen proteins are continuously being identified [2,3]. The novel finding of an allergen is accomplished by a draft HDM genome and designed target receptor, as well as classical allergy proteomics [4-7]. Over the last few decades, modified tools for maximizing the use of allergens as powerful vaccines have been developed by unveiling the effective mechanisms related to AIT [8,9]. Allergen structure and form were altered to minimize or decrease allergic responses such as immunoglobulin E (IgE) production and allergic inflammation, practically made by molecular and chemical biology and efficacy of AIT has been finally evaluated. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have contributed to the development of AIT for the treatment of allergic disease. In addition, clinical studies performed via different injection routes as well as administration of modified allergen or allergen with adjuvant have revealed that immune tolerance may be achieved by unexpected and complex mechanisms, and there is a need to discover a biomarker for predicting the success of AIT [10].
This review focuses on analyzing the currently available AIT using HDM. Based on the results, we predict the possibility and future of AITs as potential agents for the treatment of allergic diseases.
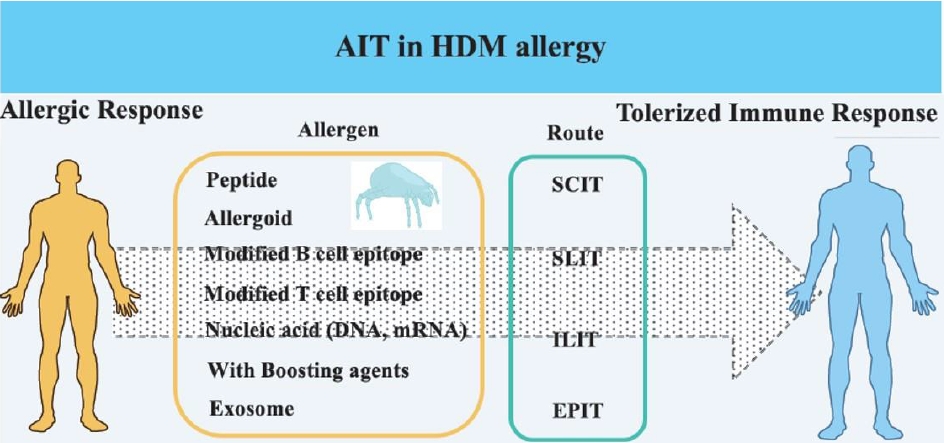
Small fragments of allergens are produced by antigen processing and presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) in antigen-presenting cells. This step activates T cells and results in allergic inflammation [11-13]. Accordingly, a T-cell-based vaccine has been tested and revealed the possibility of being a useful tool for attenuation of allergy, although the outcome was not remarkable. Since it had no effect on the generation of allergen‐specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies, clinical trials of this vaccine may be terminated [14,15]. B-cell epitopes are attractive targets for disturbing the allergen-specific IgE production. Although modified B-cell epitopes of Der p 1, Der p 2, and Der p 23 are recognized by B-cell receptors, they cannot induce IgE production but can induce IgG production via different isotype switching [16,17]. In addition, the in silico prediction of T- and B-cell epitopes of Der f 25 may be useful for AIT [18]. Cutting edge of DNA technology and computational structure analysis boosts the antiallergic effects of this vaccine by mutating, aligning, or combining sequences, resulting in the production of mutant, hybrid allergen, or hypoallergen, respectively [19-21].
Allergoids are allergens that are chemically modified by formaldehyde and glutaraldehyde. Allergoids lack conformational IgE epitopes but contain linear epitopes of T cells, which are important characteristics for the attenuation of allergic responses. Clinical studies recently demonstrated the usefulness of allergoids in actual patients. This effect is related to the genetic and epigenetic reprograming mechanisms [22,23].
High doses and repeated injections of an allergen extract elicit unexpected side effects and mortality as well as anaphylaxis. Hence, instead of the protein, DNA and mRNA of an allergen can be recommended as better tools, similar to the coronavirus 2019 vaccine [24,25]. This strategy has been attempted and updated, alongside the development of gene therapy, for patients with gene mutation or deficiency. Such vaccines induce the Th1 type immune response (similar to the immune reaction of nonallergic subjects) and reduce the IgE production induced by Der p 2 or Der p 5 [26,27]. The mRNAs of several allergens were applied to an asthmatic mouse model, and their effects were analyzed and compared. These papers prove that nucleic acid may be beneficial as an effective vaccine material.
Adjuvants used for AIT contain aluminum hydroxide, calcium phosphate, and microcrystalline tyrosine. These materials strongly elevate the therapeutic effect of allergoid and modified recombinant allergens [28]. Aluminum hydroxide is a well-known classical adjuvant [29]. Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, monophosphoryl lipid A (TLR4 agonist), flagellin A (TLR5 agonist), lipopeptide (TLR2/6 agonist), and cytosine-phosphate-guanosine induce a Th1 response including interferon-γ secretion, which subsequently alleviates the Th2 allergic reaction [30-33]. HDM extract in the liposome protects asthma patients from more severe symptoms and diminishes bronchial provocation due to allergen challenge [34,35]. Liposomes are also used as nucleic acid carriers in DNA or RNA vaccines. The Der p 1 peptide present on virus-like particles efficiently triggers strong IgG responses in human subjects [36]. A recent study reported that virus-like nanoparticles expressing allergens elicited a T helper (Th)1/regulatory T (Treg)-prone response, both in vitro and in an animal model [37]. Liposomes are lipid spheres with the ability to encompass a variety of components, such as therapeutic drugs.
The major AIT using HDM allergen focus on major allergens such as Der p 1, Der p 2, Der f 1, and Der f 2 [38,39]. Der p 5, Der p 7, Der p 10, Der p 21, and Der p 23 are considered as useful components of AIT [40,41]. At the outset, there is a requirement to produce a variety of vaccines for clinical trials using good manufacturing process. This is a pivotal issue that will help to overcome the limited technology available for the development of vaccines required for treating patients afflicted with allergies [42,43]. Moreover, continuous efforts are required to approach newer concepts, in particular, the discovery of a novel tool based on severity of the allergy and personal therapy. Exosomes are small vesicles (10–150 nm) secreted from several types of cells to extracellular environment, and include mRNA, lipids and proteins activating target cell function. Exosomes are arising as promising therapeutic materials in numerous diseases, especially cancer [44,45]. However, exosomes comprise of diverse materials which are as yet unidentified, thereby imparting a disadvantage for its applications. Difficulty in the collection and unknown effective mechanisms of exosomes remain unsolved riddles [46-48]. TLR activators are also used as adjuvants. Der p 38 and Der f 38 has recently been reported as a novel TLR4-binding allergen, which acts as a bidirectional regulator in the transition of predominant eosinophils or/and neutrophils related to asthma severity, and it may be an alternative card in the AIT of HDM allergy [49,50]. A complex combination of current vaccine technologies and an unexpected novel approach will continuously be pursued towards contribution to the development of AIT.
The most popular route of administering AIT is subcutaneous (SC) injection. Although subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) has been a proven mode for a century, it has several strengths and drawbacks [51]. Its main merit is greater efficacy than other immunotherapies. Its limitations include decreased safety, pain due to repeated injection, longer period for inducing tolerance efficacy, and strong side effects such as severe hypersensitivity. SCIT using HDM has shown maximum efficacy (such as reduction of allergic symptoms and airway hyperreaction and medication use) and preventive effects [52]. Crude HDM extract and modified HDM extract are recommended for treating perennial HDM allergic rhinitis [53]. Recently, an efficacy study of a mouse model evaluated components of the HDM allergen, such as Der p 1 and Der p 2, compared to crude HDM extract [54]. The availability of allergen components will probably help in the future development of SCIT.
Sublingual administration is an important and alternative immunotherapy alongside the subcutaneous route. Despite no remarkable efficacy in the treatment for an allergic disease after treatment with HDM extract, sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) with an HDM tablet reduced allergic symptoms [55-59]. The major merit of SLIT is rare onset of moderate or severe systemic side effects. A meta-analysis has shown that SLIT drops or tablets in HDM immunotherapy are less efficacy than SCIT [60]. Determining the immunotherapy route (SCIT or SLIT) requires numerous factors [61]. To ensure an excellent clinical outcome, clinicians must make a clear decision after considering the efficacy and safety of both procedures as well as patients’ allergy severity. Another important factor is the ability to communicate with the patient, making them psychologically comfortable and ready to continue with regular therapy.
Other immunotherapies include oral, intralymphatic immunotherapy (ILIT), and epicutaneous immunotherapy (EPIT). HDM oral immunotherapy in infants with atopy reduces sensitization to allergens; however, no significant preventive effect was noted on HDM sensitization or in symptoms associated with allergy [61].
The ILIT trial was cautiously performed as an alternative method instead of the conventional SCIT and SLIT [62,63]. Allergy symptoms are rapidly alleviated subsequent to ILIT, and its efficacy continues for one year. However, ILIT elicits severe local or systemic hypersensitivity due to the aqueous formulation of allergen extracts used in hypersensitized patients [64]. The safety of cervical ILIT was demonstrated considering that it did not induce moderate to severe adverse side effects [65].
EPIT has been considerably examined in allergic rhinitis. Immunotherapy with microneedles was tested in animal models, and the effective delivery of the HDM extract into the skin was demonstrated [66]. Thus, along with the major methods (SCIT and SLIT), other immunotherapies are steadily being studied for their long-term effects and ability to support better efficacy of immunotherapy.
HDM immunotherapy has been clinically examined to identify more appropriate, efficient, and safe protocols via different injection routes and formulations. HDM proved to be a very useful allergen that imparts protection and prevents allergies (Table 1). There is a steadily growing interest in HDM AIT, and we may need to diversify from familiar methods to create a new concept.
Immune tolerance is a complex and antiallergic mechanism after artificial exposure to a modified allergen [67,68]. First, sensitization to the inhalation or contact of allergen triggers Th2 responses and induces IgE hyperproduction of plasma cells derived from B cells. Basophils and mast cells are finally ready to be activated when a second sensitization occurs. The repetitive and long-term injection of the modified hypoallergen reduces strong allergic responses. The downregulated Th2 cytokines (such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) block the degranulation of basophils and mast cells diminishing the release of histamine and lipid metabolites such as prostaglandin and leukotriene, and decreased tissue injury. Increased levels of IgG4 or IgA prevent the actions of the IgE-mediated allergic cascade accompanied with low IgE levels. The altered isotype switching, i.e., transition of IgE to IgG4, is a pivotal biomarker of AIT outcome (Fig. 1). Novel approaches such as the application of new allergens and exosomes of allergens used in AIT may consolidate the immune tolerance induced by AIT.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are double-edgeds words, depending on their surroundings. During allergen uptake, DCs function as initiators of allergic inflammation, in which they trigger an immune reaction against bacteria. However, some DCs are able to suppress T-cell activation in a specific situation. DCs consist of 4 essential subtypes: conventional DCs (cDC1s and cDC2s), monocyte-derived DCs, and plasmacytoid DCs. Each subtype is responsible for a variety of immune regulation, including cross-presentation of antigen and Th cell activation. Specifically, tolerogenic DCs are differentiated from immature DCs in the absence of an inflammatory environment, and in the presence of interleukin (IL)-10, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, or specific stimulators such as lipopolysaccharide, rapamycin, and dexamethasone [69-71]. de Aragão-França et al. demonstrated that tolerogenic DCs lower airway inflammation due to HDM in a mouse model [72]. Sun et al. [73] reported that tolerogenic DCs activate Treg cells in adoptive cell therapy. In case of peripheral tolerance induced by tolerogenic DCs, they are responsible for secreting IL-10 and TGF-β, and these anti-inflammatory cytokines suppress effector T cells and activate Treg cells to accomplish immune tolerance. Moreover, tolerogenic DCs show low expressions of CD80, CD86, and MHC class II unlike other mature DCs. When tolerogenic DCs present the antigen to T cells, the T cells are not activated because no costimulatory signal occurs after the interaction of CD28 with CD80/86 [74,75]. DCs essentially act as linkers for connecting the antigen with bidirectional immune response, and AIT development will be continually required to increase our understanding the regulation of DCs.
Regulatory cells are derived from T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, and are key inducers of immune tolerance or suppressors of allergic responses [51]. IL-10 or/and TGF-β released by regulatory cells inhibits IgE production and increases IgG4 production [76,77]. Conversion from IgE to IgG4 is an inevitable process in immune tolerance after AIT and suppresses the activation of basophils and mast cells due to IgE by kidnapping the allergen.
Treg cells are differentiated from naive T helper cells (Th0 cells) in the absence of costimulatory signal of DCs and presence of TGF-β. CD4+CD25+ Treg1 cells are representative Treg cells that inhibit the Th2 immune response by producing IL-10 and TGF-β on their own [78,79]. CD4+CD25+ forkhead box P3 (FOXP3)+ Treg1 cells act as crucial regulators to achieve efficient HDM immunotherapy. [80] Boonpiyathad et al. [81] suggested the upregulation of Der p 1-specific FOXP3+ Helios+ and IL‐10+ Treg cells, and the downregulation of immunoglobulin‐like transcript 3 (ILT3)+ Treg cells, are associated with improved allergic symptoms after HDM immunotherapy. Programmed cell death1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 are also involved in the immune tolerance mechanism [82,83]. PD-1 modifies the T cells into anergy, as it binds to a counterpart protein PD-ligand 1 of the antigen-presenting cells.
B cells are generally differentiated into plasma cells and secrete IgE antibody against allergens. A different subset of B cells that prefer the inhibition of an excessive allergic response is named regulatory B 1 (Breg1) cells. They are characterized by CD25+ CD71+CD73lowexpression and produce IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 to decrease the inflammatory response. IL-10 is a considerably more pivotal anti-inflammatory cytokine than TGF-β and IL-35, based on the evidence that IL-10-overexpressing B cells and highly purified IL-10-producing cells show essential effects of allergen tolerance both in vitro and in vivo [84-86]. IL-10-producing Breg1 cells regulate IgG4 generation and induce Treg cell differentiation, which are the main events required to achieve AIT outcomes [87].
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are classified into ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3, depending on transcription factors and secreted cytokines [88-90]. ILC2 produces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 (similar to Th2 cells), and plays a substantial role in the onset and aggravation of allergy due to HDM. Recently, Morita et al. unveiled the existence of IL10-producing regulatory ILCs (ILCregs) originating from ILC2s [90,91].
NK cells are specific lymphocytes in the immune system that act against virus-infected cells and cancer [92]. Distinctive NK cells, revealed by Deniz et al. [93] are responsible for suppressing immune functions by secreting IL-10 and blocking IgE production; these are termed regulatory NK cells. Although NK cells are interesting in the study of allergic diseases, the exact role of regulatory NK cells in AIT remains to be unveiled [92-94].
In line with immune tolerance mechanisms, we can find valuable biomarkers such as increased allergen-specific IgG4, decreased mast cells, eosinophils and ILC2, and increased ILCreg [95]. It has been recently reported that potential gene markers and IL-10 mRNA levels are meaningful biomarkers in HDM AIT study [96,97]. Also, identifying of serum periostin and STAB1 mRNA is invaluable in biomarker development [95]. Biomarkers are highly dependent on AIT tools as well as type of allergies. A single biomarker is insufficient to monitor AIT outcome as a gold standard. According to allergy classification and severity, we must consider the combination of biomarkers and identify novel biomarkers using genomics and proteomics to achieve precise AIT efficacy.
AIT is a promising tool for overcoming allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis and asthma. However, its AIT application is currently considered challenging and requires further development. There exist several obstacles to fully achieving the purpose of AIT. A novel approach and development of AIT may be required to go overcome 3 categories of drawbacks. First, injection routes and products require to ensure better safety and efficacy. In the case of AIT products, modifications of the allergen and combination of HDM allergen components or/and HDM continue along with thorough quality control. Long-term treatment, painful injections, and side effects are uncomfortable for both patients and clinicians. Second, understanding the mechanism of action would prove invaluable in AIT development. Biomarker development is ongoing for the detection and prognosis of AIT efficacy. Component resolved diagnosis is useful for precision diagnosis and personalized medicine. This challenge needs to be conducted in well-coordinated studies, and will pave the way for AIT success.
Fig. 1.
Different allergic mechanisms between naï ve and modified allergens. Onset of allergic response occurs after dendritic cells uptake the allergen, which drives naï ve Th cells (Th0) to be differentiated into Th2 cells. Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 induce both eosinophil activation and IgE production of plasma cells differentiated from B cells. Binding of IgE to FcεR activates basophils and mast cells, which subsequently secrete inflammatory mediators. AIT using modified allergen would trigger immune tolerance rather than allergic inflammation. This is caused by modified allergen causing the inhibition of differentiation of Th0 cells to Th2 cells, and activation of regulatory cells. Finally, these complex cascades inhibit allergic inflammation and enhance immune tolerance to the allergen. EOS, eosinophil; MAST, multiple allergen simultaneous test; BAS, basophil; IL, interleukin; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; Th, T helper; IgE, immunoglobulin E; PL, plasma cell; AIT, allergen immunotherapy; SCIT, subcutaneous immunotherapy; SLIT, sublingual immunotherapy; ILIT, intralymphatic immunotherapy; EPIT, epicutaneous immunotherapy; Treg, regulatory T; Breg, regulatory B; NK, natural killer.

Table 1.
AIT with house dust mite in clinical studies
| Allergen source | Type of vaccination | Injection route | Adjuvant | Clinical phase | Allergy | Major findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDM | Virus-like particles-based and filled with CpG | SC | QbG10 | Phase I/IIa | Asthma, ARC | Reduced symptoms | [70] |
| TLR9 agonist | Increased specific IgG | ||||||
| Transient increase of specific IgE | |||||||
| Reduced skin reactivity to HDM | |||||||
| Der p 1 | Virus-like particles- based and filled with RNA | SC, IM | Phase I | Normal | Increased specific IgG | [71] | |
| Higher IgG concentration in high dose of the vaccine | |||||||
| HDM (DP: Der p 1/Der p 2 ratio, 2:1) | Liposome encapsulated extract | SC | Phase II | Asthma | Reduced symptoms and medication scores | [72] | |
| Increased specific IgG, IgG1, and IgG4 | |||||||
| HDM (DP, DF) | Extract | SC | Phase II | Asthma | Reduced systemic allergic reactions with omalizumab | [73] | |
| HDM | T-cell epitope peptide | ID | Phase II | Asthma, ARC | No serious adverse events | [74] | |
| Reduction of EPSR, LPSR, and CPT | |||||||
| HDM (DP, DF) | Extract (Depigoid) | SC, SL | Aluminum hydroxide | Phase II | Asthma, AR | Improved total symptom score and QoL | [75] |
| Serious adverse effects in 3 adults and one child | |||||||
| HDM (DP, DF) | Extract (Lais) | SL | Phase II | ARC | No case of serious adverse effects or anaphylaxis Improved CPT threshold | [76] | |
| HDM | Carbamylated monomeric allergoids | SL | Phase II | Asthma, AR, ARC | Reduced allergy severity | [77] | |
| Improved CPT threshold | |||||||
| Twenty adverse events related to mild treatment | |||||||
| HDM (DP) | Extract (Alutard SQ 510) | SC | Aluminum hydroxide | Phase II | AR | Increased Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 23-specific IgG | [78] |
| Better clinical efficacy in subjects sensitized to Der p 1 or Der p 2 | |||||||
| HDM (DP) | Extract (Alk-Abello) | SC | Aluminum hydroxide | Phase II | AR | Increased FOXP3+Helios+ and IL-10+ Treg cells | [79] |
| Decreased ILT3+ Treg cells | |||||||
| HDM (DP) | Extract | SC | Pam3CSK4 | Phase II | AR | Improved nasal symptom score | [80] |
| TLR2 ligand | Increased CD137 expression on CD8+ T cells | ||||||
| Decreased nasal nitric oxide |
HDM, house dust mite; CpG, cytosine-phosphate-guanosine; TLR, Toll-like receptor; SC, subcutaneous; ARC, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IM, intramuscular; DP, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; DF, Dermatophagoides farinae; SL, sublingua; AR, allergic rhinitis; ID, intradermal; EPSR, early phase skin responses; LPSR, late phase skin responses; CPT, conjunctival provocation test; QoL, quality of life; FOXP3, forkhead box P3; IL, interleukin; ILT, immunoglobulin-like transcript.
References
1. Pavón-Romero GF, Parra-Vargas MI, Ramírez-Jiménez F, Melgoza-Ruiz E, Serrano-Pérez NH, Teran LM. Allergen immunotherapy: current and future trends. Cells 2022;11:212.



2. Głobińska A, Jansen K, van de Veen W, Akdis M. Modified allergens for immunotherapy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2018;18:9.

3. Jacquet A, Robinson C. Proteolytic, lipidergic and polysaccharide molecular recognition shape innate responses to house dust mite allergens. Allergy 2020;75:33–53.



4. Chua KY, Stewart GA, Thomas WR, Simpson RJ, Dilworth RJ, Plozza TM, et al. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen, Der p 1. Homology with cysteine proteases. J Exp Med 1988;167:175–82.




5. Weghofer M, Grote M, Resch Y, Casset A, Kneidinger M, Kopec J, et al. Identification of Der p 23, a Peritrophin-like protein, as a new major Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen associated with the peritrophic matrix of mite fecal pellets. J Immunol 2013;190:3059–67.



6. Chan TF, Ji KM, Yim AK, Liu XY, Zhou JW, Li RQ, et al. The draft genome, transcriptome, and microbiome of Dermatophagoides farinae reveal a broad spectrum of dust mite allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;135:539–48.


7. Liu XY, Yang KY, Wang MQ, Kwok JS, Zeng X, Yang Z, et al. High-quality assembly of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus genome and transcriptome reveals a wide range of novel allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018;141:2268–71.e8.


8. Kim G, Hong MH, Kashif A, Hong Y, Park BS, Mun JY, et al. Der f 38 Is a novel TLR4-binding allergen related to allergy pathogenesis from Dermatophagoides farinae. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:8440.



9. Mutschlechner S, Deifl S, Bohle B. Genetic allergen modification in the development of novel approaches to specific immunotherapy. Clin Exp Allergy 2009;39:1635–42.


10. Creticos PS. Allergen immunotherapy: vaccine modification. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2016;36:103–24.

11. Huang HJ, Curin M, Banerjee S, Chen KW, Garmatiuk T, Resch‐Marat Y, et al. A hypoallergenic peptide mix containing T cell epitopes of the clinically relevant house dust mite allergens. Allergy 2019;74:2461–78.



12. Curin M, Garmatiuk T, Resch‐Marat Y, Chen KW, Hofer G, Fauland K, et al. Similar localization of conformational IgE epitopes on the house dust mite allergens Der p 5 and Der p 21 despite limited IgE cross‐reactivity. Allergy 2018;73:1653–61.



13. Curin M, Huang HJ, Garmatiuk T, Gutfreund S, Resch-Marat Y, Chen KW, et al. IgE epitopes of the house dust mite allergen Der p 7 are mainly discontinuous and conformational. Front Immunol 2021;12:687294.



14. Dorofeeva Y, Shilovskiy I, Tulaeva I, Focke‐Tejkl M, Flicker S, Kudlay D, et al. Past, present, and future of allergen immunotherapy vaccines. Allergy 2021;76:131–49.



15. Prickett SR, Rolland JM, O’Hehir RE. Immunoregulatory T cell epitope peptides: the new frontier in allergy therapy. Clin Exp Allergy 2015;45:1015–26.




16. Asturias JA, Ibarrola I, Arilla MC, Vidal C, Ferrer A, Gamboa PM, et al. Engineering of major house dust mite allergens Der p 1 and Der p 2 for allergen-specific immunotherapy. Clin Exp Allergy 2009;39:1088–98.


17. Banerjee S, Weber M, Blatt K, Swoboda I, Focke-Tejkl M, Valent P, et al. Conversion of Der p 23, a new major house dust mite allergen, into a hypoallergenic vaccine. J Immunol 2014;192:4867–75.



18. Li X, Yang HW, Chen H, Wu J, Liu Y, Wei JF. In silico prediction of T and B cell epitopes of Der f 25 in Dermatophagoides farinae. Int J Genomics 2014;2014:483905.




19. Tscheppe A, Breiteneder H. Recombinant allergens in structural biology, diagnosis, and immunotherapy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2017;172:187–202.



20. Valenta R, Campana R, Focke-Tejkl M, Niederberger V. Vaccine development for allergen-specific immunotherapy based on recombinant allergens and synthetic allergen peptides: lessons from the past and novel mechanisms of action for the future. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;137:351–7.



21. Takaiwa F. Next-Generation Allergen-specific immunotherapy for Japanese cedar pollinosis using molecular approaches. Immunotargets Ther 2021;10:213–24.




22. Jutel M, Brüggenjürgen B, Richter H, Vogelberg C. Real-world evidence of subcutaneous allergoid immunotherapy in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis and asthma. Allergy 2020;75:2050–8.



23. Benito-Villalvilla C, Pérez-Diego M, Angelina A, Kisand K, Rebane A, Subiza JL, et al. Allergoid-mannan conjugates reprogram monocytes into tolerogenic dendritic cells via epigenetic and metabolic rewiring. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2022;149:212–22.e9.


24. Yang R, Deng Y, Huang B, Huang L, Lin A, Li Y, et al. A core-shell structured COVID-19 mRNA vaccine with favorable biodistribution pattern and promising immunity. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021;6:213.




25. Scheiblhofer S, Thalhamer J, Weiss R. DNA and mRNA vaccination against allergies. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2018;29:679–88.




26. Hsu CH, Chua KY, Tao MH, Lai YL, Wu HD, Huang SK, et al. Immunoprophylaxis of allergen-induced immunoglobulin E synthesis and airway hyperresponsiveness in vivo by genetic immunization. Nat Med 1996;2:540–4.



27. Roesler E, Weiss R, Weinberger EE, Fruehwirth A, Stoecklinger A, Mostböck S, et al. Immunize and disappear-safety-optimized mRNA vaccination with a panel of 29 allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;124:1070–7.e1-11.


28. Klimek L, Fox GC, Thum-Oltmer S. SCIT with a high-dose house dust mite allergoid is well tolerated: safety data from pooled clinical trials and more than 10 years of daily practice analyzed in different subgroups. Allergo J Int 2018;27:131–9.




29. Wüthrich B, Gumowski PL, Fäh J, Hürlimann A, Deluze C, André C, et al. Safety and efficacy of specific immunotherapy with standardized allergenic extracts adsorbed on aluminium hydroxide. J Investing Allergol Clin Immunol 2001;11:149–56.
30. Puggioni F, Durham SR, Francis JN. Monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLR)* promotes allergen-induced immune deviation in favour of Th1 responses. Allergy 2005;60:678–84.


31. Schülke S, Fiedler AH, Junker AC, Flaczyk A, Wolfheimer S, Wangorsch A, et al. Critical role of mammalian target of rapamycin for IL-10 dendritic cell induction by a flagellin A conjugate in preventing allergic sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018;141:1786–98.e11.


32. Fuchs B, Knothe S, Rochlitzer S, Nassimi M, Greweling M, Lauenstein HD, et al. A Toll-like receptor 2/6 agonist reduces allergic airway inflammation in chronic respiratory sensitisation to Timothy grass pollen antigens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2010;152:131–9.



33. Kubo S, Yamada T, Osawa Y, Ito Y, Narita N, Fujieda S. Cytosine–phosphate–guanosine-DNA induces CD274 expression in human B cells and suppresses T helper type 2 cytokine production in pollen antigen-stimulated CD4-positive cells. Clin Exp Immunol 2012;169:1–9.




34. Kündig TM, Senti G, Schnetzler G, Wolf C, Prinz Vavricka BM, Fulurija A, et al. Der p 1 peptide on virus-like particles is safe and highly immunogenic in healthy adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;117:1470–6.


35. Kratzer B, Köhler C, Hofer S, Smole U, Trapin D, Iturri J, et al. Prevention of allergy by virus‐like nanoparticles (VNP) delivering shielded versions of major allergens in a humanized murine allergy model. Allergy 2019;74:246–60.



36. Basomba A, Tabar AI, de Rojas DH, García BE, Alamar R, Olaguíbel JM, et al. Allergen vaccination with a liposome-encapsulated extract of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial in asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;109:943–8.


37. Alvarez MJ, Echechipía S, Garcia B, Tabar AI, Martin S, Rico P, et al. Liposome-entrapped D. pteronyssinus vaccination in mild asthma patients: Effect of 1-year double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on inflammation, bronchial hyper-responsiveness and immediate and late bronchial responses to the allergen. Clin Exp Allergy 2002;32:1574–82.



38. Chen KW, Blatt K, Thomas WR, Swoboda I, Valent P, Valenta R, et al. Hypoallergenic Der p 1/Der p 2 combination vaccines for immunotherapy of house dust mite allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:435–43.e4.



39. Cheng L, Zhou WC. Sublingual immunotherapy of house dust mite respiratory allergy in China. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 2019;47:85–9.


40. González-Pérez R, Poza-Guedes P, Pineda F, Castillo M, Sánchez-Machín I. House dust mite precision allergy molecular diagnosis (PAMD@) in the Th2-prone atopic dermatitis endotype. Life (Basel) 2021;11:1418.



41. Yang L, Yang Y, Xu Q, Zhang W, Jiang Q, Li W, et al. Specific IgE and IgG4 profiles of house dust mite components in allergen-specific immunotherapy. Front Immunol 2022;12:786738.



42. Cox LS, Murphey A, Hankin C. The cost-effectiveness of allergen immunotherapy compared with pharmacotherapy for treatment of allergic rhinitis and asthma. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2020;40:69–85.


43. Rondon C, Sánchez-Borges M, Cupello ER, Fabiano F, Capriles-Hulett A. Aqueous intradermal low-dose house dust mite immunotherapy in tropical settings: a valid cost-effective approach for developing nations? Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 2021;49:31–9.


44. Zhang L, Yu D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2019;1871:455–68.



45. Mashouri L, Yousefi H, Aref AR, Ahadi AM, Molaei F, Alahari SK. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol Cancer 2019;18:75.




46. Maugeri M, Nawaz M, Papadimitriou A, Angerfors A, Camponeschi A, Na M, et al. Linkage between endosomal escape of LNP-mRNA and loading into EVs for transport to other cells. Nat Commun 2019;10:4333.




47. Kojima R, Bojar D, Rizzi G, Hamri GC, El-Baba MD, Saxena P, et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson's disease treatment. Nat Commun 2018;9:1–10.




49. Hong MH, Kashif A, Kim G, Park BS, Lee NR, Yang EJ, et al. Der p 38 is a bidirectional regulator of eosinophils and neutrophils in allergy. J Immunol 2021;207:1735–46.



50. Jeon H, Kim G, Kashif A, Hong MH, Lee JS, Hong Y, et al. Pathogenic mechanism of Der p 38 as a novel allergen homologous to RipA and RipB proteins in atopic dermatitis. Front Immunol 2021;12:646316.



51. Alvaro‐Lozano M, Akdis CA, Akdis M, Alviani C, Angier E, Arasi S, et al. EAACI allergen immunotherapy user’s guide. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2020;31:1–101.




52. Agache I, Lau S, Akdis CA, Smolinska S, Bonini M, Cavkaytar O, et al. EAACI guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: house dust mite-driven allergic asthma. Allergy 2019;74:855–73.



53. Dhami S, Nurmatov U, Arasi S, Khan T, Asaria M, Zaman H, et al. Allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2017;72:1597–631.



54. Hesse L, van Ieperen N, Habraken C, Petersen AH, Korn S, Smilda T, et al. Subcutaneous immunotherapy with purified Der p1 and 2 suppresses type 2 immunity in a murine asthma model. Allergy 2018;73:862–74.



55. Hirsch T, Sähn M, Leupold W. Double-blind placebo-controlled study of sublingual immunotherapy with house dust mite extract (D.pt.) in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 1997;8:21–7.

56. Marcucci F, Sensi L, Frati F, Bernardini R, Novembra E, Barbato A, et al. Effects on inflammation parameters of a double-blind, placebo controlled one-year course of SLIT in children monosensitized to mites. Allergy 2003;58:657–62.


57. de Bot CM, Moed H, Berger MY, Röder E, Hop WC, de Groot H, et al. Sublingual immunotherapy not effective in house dust mite-allergic children in primary care. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012;23:150–8.

58. Nolte H, Bernstein DI, Nelson HS, Kleine-Tebbe J, Sussman GL, Seitzberg D, et al. Efficacy of house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet in North American adolescents and adults in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;138:1631–8.


59. Okubo K, Masuyama K, Imai T, Okamiya K, Stage BS, Seitzberg D, et al. Efficacy and safety of the SQ house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet in Japanese adults and adolescents with house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017;139:1840–8.e10.


60. Kim JY, Jang MJ, Kim DY, Park SW, Han DH. Efficacy of subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy for house dust mite allergy: a network metaanalysis-based comparison. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021;9:4450–8.e6.


61. Zolkipli Z, Roberts G, Cornelius V, Clayton B, Pearson S, Michaelis L, et al. Randomized controlled trial of primary prevention of atopy using house dust mite allergen oral immunotherapy in early childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;136:1541–7.e11.


62. Hylander T, Latif L, Petersson-Westin U, Cardell LO. Intralymphatic allergen-specific immunotherapy: an effective and safe alternative treatment route for pollen-induced allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;131:412–20.


63. Hylander T, Larsson O, Petersson-Westin U, Eriksson M, Kumlien Georén S, Winqvist O, et al. Intralymphatic immunotherapy of pollen-induced rhinoconjunctivitis: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Respir Res 2016;17:10.



64. Lee SP, Choi SJ, Joe E, Lee SM, Lee MW, Shim JW, et al. A pilot study of intralymphatic imunotherapy for house dust mite, cat, and dog allergies. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2017;9:272–7.




65. Wang K, Zheng R, Chen Y, Yu Q, Zhong H, Xiao P, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of cervical intralymphatic immunotherapy for house dust mite allergic rhinitis: a pilot study. Am J Otolaryngol 2019;40:102280.


66. Choi YJ, Kim KA, Jung JH, Choi YS, Baek SK, Kim ST, et al. Epicutaneous allergen administration with microneedles as a novel method of Immunotherapy for house dust mite (HDM) allergic rhinitis. Pharm Res 2021;38:1199–207.



67. Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: multiple suppressor factors at work in immune tolerance to allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;133:621–31.


68. Kucuksezer UC, Ozdemir C, Cevhertas L, Ogulur I, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy and allergen tolerance. Allergol Int 2020;69:549–60.


69. Pulendran B, Tang H, Manicassamy S. Programming dendritic cells to induce T(H)2 and tolerogenic responses. Nat Immunol 2010;11:647–55.



70. Suuring M, Moreau A. Regulatory macrophages and tolerogenic dendritic cells in myeloid regulatory cell-based therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:7970.



71. Castenmiller C, Keumatio-Doungtsop BC, van Ree R, de Jong EC, van Kooyk Y. Tolerogenic immunotherapy: targeting DC surface receptors to induce antigen-specific tolerance. Front Immunol 2021;12:643240.



72. de Aragão-França LS, Aragão-França LS, Rocha VCJ, Rocha VCJ, Cronemberger-Andrade A, da Costa FHB, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells reduce airway inflammation in a model of dust mite triggered allergic inflammation. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2018;10:406–19.




73. Sun W, Wei JW, Li H, Wei FQ, Li J, Wen WP. Adoptive cell therapy of tolerogenic dendritic cells as inducer of regulatory T cells in allergic rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2018;8:1291–9.



74. Wakkach A, Fournier N, Brun V, Breittmayer JP, Cottrez F, Groux H. Characterization of dendritic cells that induce tolerance and T regulatory 1 cell differentiation in vivo. Immunity 2003;18:605–17.


75. Akbari O, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Pulmonary dendritic cells producing IL-10 mediate tolerance induced by respiratory exposure to antigen. Nat Immunol 2001;2:725–31.



76. Jutel M, Van de Veen W, Agache I, Azkur KA, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy and novel ways for vaccine development. Allergol Int 2013;62:425–33.


77. Palomares O, Martín-Fontecha M, Lauener R, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Cavkaytar O, Akdis M, et al. Regulatory T cells and immune regulation of allergic diseases: roles of IL-10 and TGF-β. Genes Immun 2014;15:511–20.



78. Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25- Naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T Cells by TGF-β induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med 2003;198:1875–86.




79. Meiler F, Zumkehr J, Klunker S, Rückert B, Akdis CA, Akdis M. In vivo switch to IL-10-secreting T regulatory cells in high dose allergen exposure. J Exp Med 2008;205:2887–9.




80. Lou W, Wang C, Wang Y, Han D, Zhang L. Responses of CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ and IL-10-secreting type I T regulatory cells to cluster-specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012;23:140–9.


81. Boonpiyathad T, Sokolowska M, Morita H, Rückert B, Kast JI, Wawrzyniak M, et al. Der p 1-specific regulatory T-cell response during house dust mite allergen immunotherapy. Allergy 2019;74:976–85.



82. Palomares O, Akdis M, Martín-Fontecha M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of immune regulation in allergic diseases: the role of regulatory T and B cells. Immunol Rev 2017;278:219–36.



83. Soyer OU, Akdis M, Ring J, Behrendt H, Crameri R, Lauener R, et al. Mechanisms of peripheral tolerance to allergens. Allergy 2013;68:161–70.


84. van de Veen W, Stanic B, Yaman G, Wawrzyniak M, Söllner S, Akdis DG, et al. IgG4 production is confined to human IL-10–producing regulatory B cells that suppress antigen-specific immune responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;131:1204–12.


85. Stanic B, van de Veen W, Wirz OF, Rückert B, Morita H, Söllner S, et al. IL-10-overexpressing B cells regulate innate and adaptive immune responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;135:771–80.e8.


86. Boonpiyathad T, Satitsuksanoa P, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Il-10 producing T and B cells in allergy. Semin Immunol 2019;44:101326.


87. van de Veen W. The role of regulatory B cells in allergen immunotherapy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2017;17:447–52.


88. Boberg E, Johansson K, Malmhäll C, Weidner J, Rådinger M. House dust mite induces bone marrow IL-33-responsive ILC2s and TH Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:3751.



89. Yasuda Y, Nagano T, Kobayashi K, Nishimura Y. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and the house dust mite-induced asthma mouse model. Cells 2020;9:1178.



90. Morita H, Kubo T, Rückert B, Ravindran A, Soyka MB, Rinaldi AO, et al. Induction of human regulatory innate lymphoid cells from group 2 innate lymphoid cells by retinoic acid. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2019;143:2190–201.e9.


91. Tynecka M, Radzikowska U, Eljaszewicz A. IL-10-producing innate lymphoid cells: did we find a missing piece of the puzzle? Allergy 2021;76:3849–51.



92. Amniai L, Ple C, Barrier M, de Nadai P, Marquillies P, Vorng H, et al. Natural killer cells from allergic donors are defective in their response to CCL18 chemokine. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:3879.



93. Deniz G, Erten G, Kücüksezer UC, Kocacik D, Karagiannidis C, Aktas E, et al. Regulatory NK cells suppress antigen-specific T cell responses. J Immunol 2008;180:850–7.



94. Deniz G, van de Veen W, Akdis M. Natural killer cells in patients with allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013;132:527–35.


95. Ogulur I, Pat Y, Ardicli O, Barletta E, Cevhertas L, Fernandez-Santamaria R, et al. Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases. Allergy 2021;76:3659–86.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation