- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins?
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-
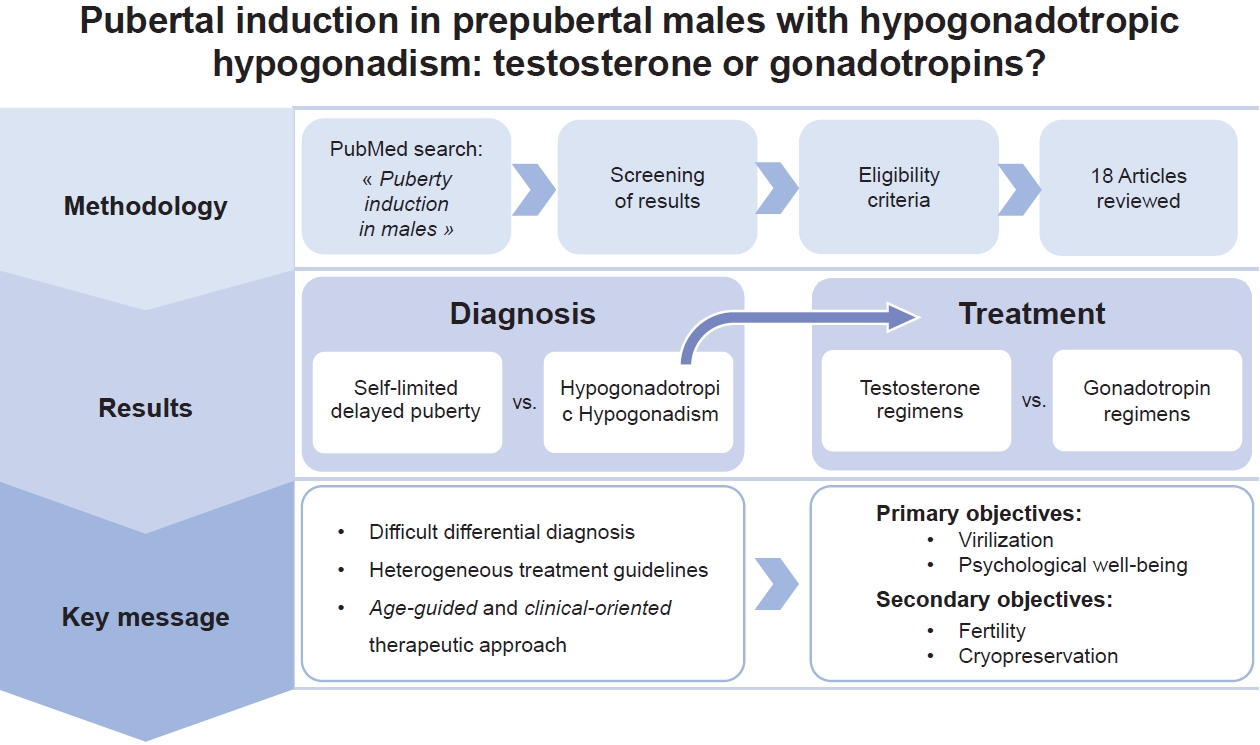
The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Gastroenterology
- Ingestion of foreign bodies and caustic substances in children: a narrative review on clinical evaluation and management update
- Maria Rogalidou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):11-21. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Foreign body and caustic substance ingestion in children aged 1–5 years can feature to severe and, sometimes life-threatening complications. High-risk items include batteries, magnets, and corrosive chemicals. Severity depends on object type, location, and ingestion timing. Prompt diagnosis and early endoscopic intervention are crucial. Individualized management, high clinical suspicion, and parental education are essential to improving outcomes and preventing immediate and long-term complications affecting a child’s quality of life.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Prioritizing maternal sleep: a public health strategy for preventing childhood allergic diseases
- Eunchae Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):22-25. Published online December 18, 2025
-
Sleep disorders affect more than half of pregnancies worldwide and can harm maternal health and offspring outcomes. Prioritizing maternal sleep as a public health strategy may help prevent prenatal and pediatric allergic diseases and reduce their burden. Other maternal health strategies may also reduce the burden of offspring allergic diseases, while adequate maternal sleep is associated with other offspring outcomes, underscoring its importance as a key public health strategy.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota and metabolomic alterations in newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Wan-Hsin Su, Yi-Wei Wang, Chien-Chang Chen, Ming-Wei Lai, Hsun-Chin Chao, Ming-Chou Chiang, Ren-Huei Fu, Pai-Jui Yeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):26-35. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Does maternal gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affect newborn gut microbiota and metabolomic profiles?
Finding: Neonates born to mothers with diet-controlled GDM exhibited reduced gut microbiota α-diversity, altered β-diversity, and metabolic shifts, including changes in fumarate and succinate levels, with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and adipocytokine signaling pathway activation.
Meaning: Maternal GDM affects early microbial colonization and metabolism in newborns and may have long-term health implications.
- Allergy
- Maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and subsequent risk of allergic diseases in Japanese children: the TMM BirThree Cohort Study
- Ami Uematsu, Masatsugu Orui, Mami Ishikuro, Keiko Murakami, Aoi Noda, Genki Shinoda, Taku Obara, Shinichi Kuriyama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):36-45. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Associations have been made between maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and allergic diseases including bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever in their children.
Finding: In the crude model, sleep disorders during pregnancy were associated with all examined allergic diseases in children. After adjustment, significant associations remained for atopic dermatitis and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever.
Meaning: The study highlights associations between maternal sleep and child allergic diseases.
- Rheumatology
- Recurrent immunoglobulin A vasculitis in children and adolescents: prevalence and associated risk factors
- Nootsara Atchariyaphuk, Maynart Sukharomana, Thanaporn Chaiyapak, Sirirat Charuvanij
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):46-55. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: What can predict immunoglobulin A vasculitis (IgAV) recurrence, and when does it occur? How do childhood- and adolescent-onset IgAV compare?
Finding: The IgAV recurrence rate was 35.6%. It usually occurred within 12 months and was associated with corticosteroids treatment.
Meaning: Childhood-onset IgAV more commonly featured gastrointestinal and musculoskeletal manifestations and required hospitalization. Adolescent-onset IgAV more commonly featured renal involvement. Vigilant monitoring for recurrence is necessary, particularly with corticosteroids treatment.
- Critical Care Medicine
- High-dose methylprednisolone and tocilizumab improve survival of patients with high-risk pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy
- Chaonan Fan, Fei Li, Kechun Li, Zheng Li, Yiyang Mao, Lijuan Wang, Gang Liu, Yingchao Liu, Quan Wang, Suyun Qian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):56-64. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Which immunomodulatory strategies can reduce mortality in children with acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE)?
Finding: High-dose methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg/day) significantly improved the survival of high-risk patients, particularly when combined with tocilizumab.
Meaning: These findings support the use of a severity-based immunotherapy approach to optimize the outcomes of pediatric ANE.
- Other
- Comparing ethyl chloride and 10% lignocaine spray for pediatric intravenous cannulation pain relief
- Susmitha Vellanki, Malavika Kulkarni, H.D. Arun Kumar, Deepali Shetty, Nikhil Karthik B, Mathew Tom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):65-72. Published online November 21, 2025
-
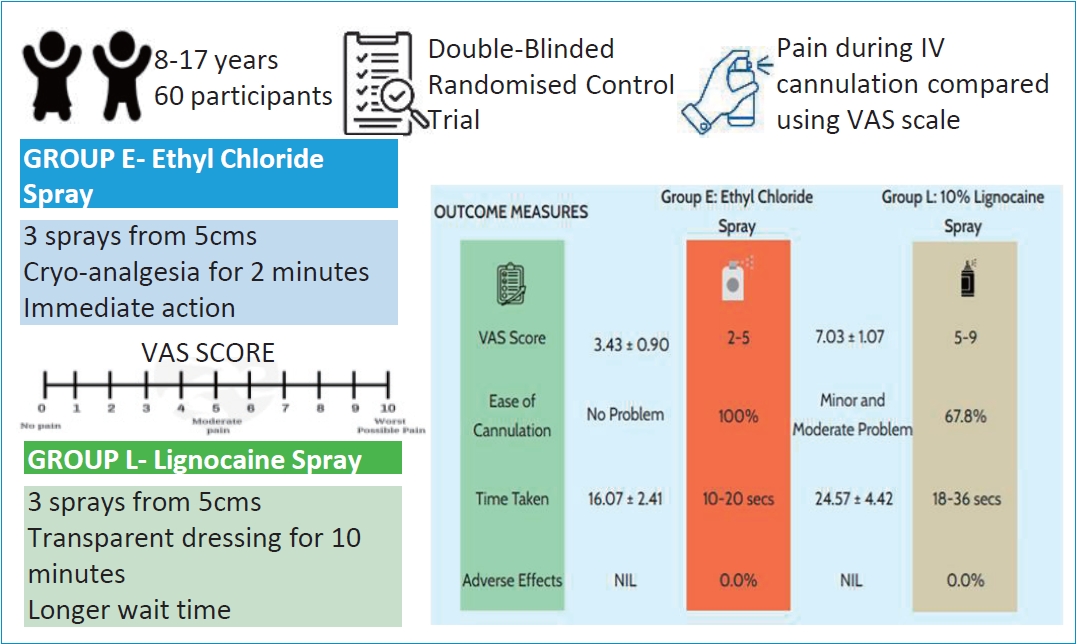
Background: Intravenous cannulation (IVC) is a routine yet distressing procedure in pediatric patients, often provoking significant anxiety and procedural pain. Although eutectic mixtures such as eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream are widely used, their delayed onset limits their applicability in time-sensitive settings. Ethyl chloride vapocoolant spray and 10% lignocaine spray have been proposed as rapid-onset alternatives, yet direct comparative...
- Clinical Note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
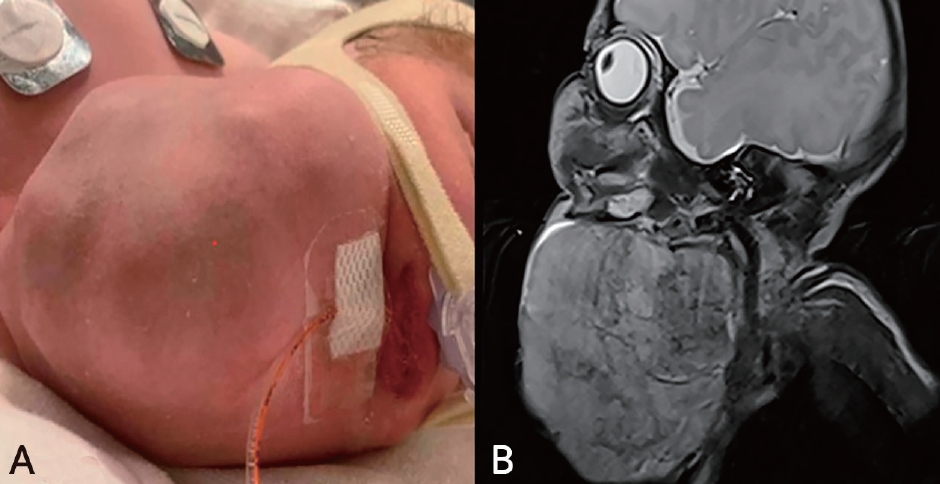
- External tracheal compression and mucosal injury in a neonate with cervical teratoma: a rare airway challenge
- Rhodora Guillen, Arijit Lodha, Prashanth Murthy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):73-75. Published online December 4, 2025
-
- Guideline
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of 15- and 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Korean infants and children
- Ki Wook Yun, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Soo-Han Choi, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):76-83. Published online December 30, 2025
-
Compared to PCV13, PCV15 includes 2 (22F and 33F), and PCV20 includes 7 (8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F) additional serotypes. The vaccination schedule remains the same: primary doses at 2, 4, and 6 months, and a booster at 12–15 months. If PCV13 was administered in the primary series, PCV15 and PCV20 may be used to complete it or as a booster.