- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Balancing therapeutic benefits and hidden risks of proton pump inhibitors in pediatric practice: a narrative review and update
- Maria Rogalidou, Alexandra Papadopoulou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):186-196. Published online February 25, 2026
-
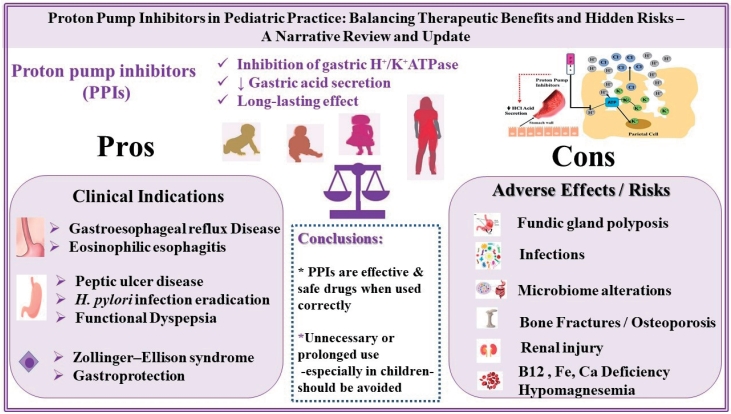
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) effectively treat acid-related disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Long-term use, particularly in children, may lead to microbiome alterations, nutrient deficiencies, infections, renal injury, osteoporosis, fractures, and other gastrointestinal changes. PPI therapy should be guided by clear clinical indications, prescribed at the lowest effective dose for the shortest necessary duration, and regularly reassessed to minimize risks in young children.
- Immunology
- Multiomics approaches in Kawasaki disease: insights into pathogenesis and emerging directions for diagnosis and treatment
- Jong Gyun Ahn, Insoo Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):197-210. Published online February 25, 2026
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile vasculitis and the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. Despite decades of research, the etiology remains unknown and key mechanisms linking systemic inflammation to coronary artery lesions are incompletely defined. High-throughput technologies—including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, epigenomics, and immunomics—have enabled systems-level profiling of KD and highlighted reproducible inflammatory and vascular pathways....
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Early prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia using new classification in high-risk preterm infants
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):211-213. Published online February 25, 2026
-
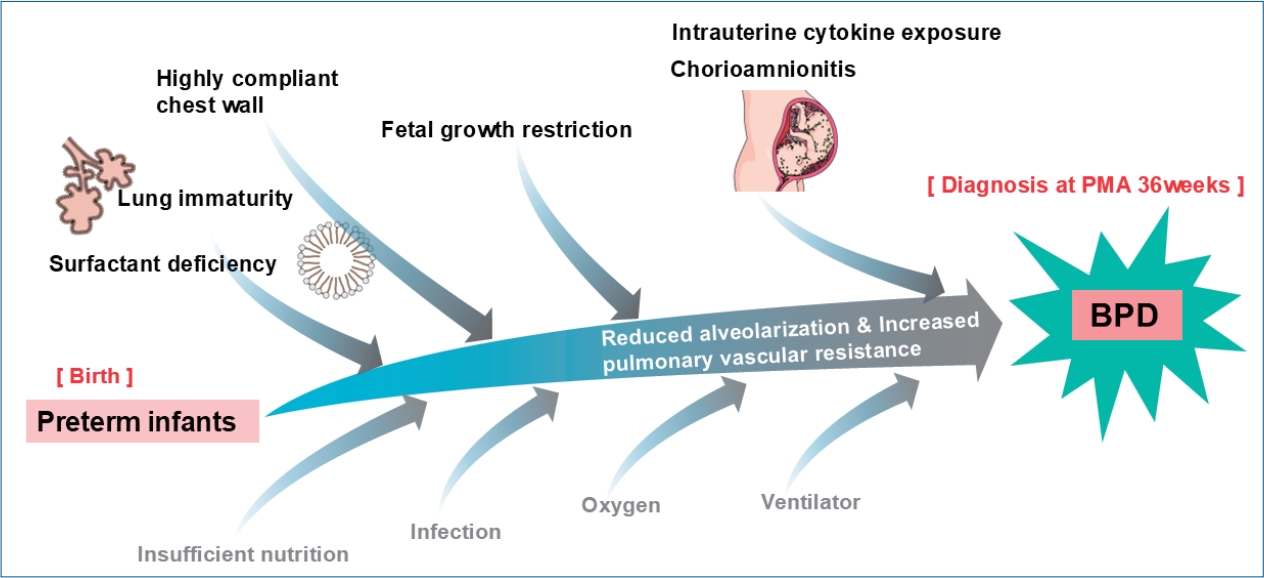
The definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) has continued to evolve. Recently, newer definitions based on respiratory support at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age better predict long-term outcomes but diagnose BPD relatively late. To address this limitation, the New Japanese Classification uses early postnatal factors, including small for gestational age and bubbly or cystic chest radiographic findings, to predict severe BPD and enable early targeted interventions.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Longitudinal analysis of gut microbiota dysbiosis and bacterial signatures predictive of postoperative enterocolitis in children with Hirschsprung disease
- Sireekarn Chantakhow, Chanon Kunasol, Jiraporn Khorana, Kanokkan Tepmalai, Nipon Chattipakorn, Siriporn C. Chattipakorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):214-227. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Question: Do gut microbiota differ between patients with Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) and healthy children, and can specific bacterial taxa predict postoperative HSCRassociated enterocolitis (HAEC)?
Finding: Patients with HSCR showed gut dysbiosis with reduced diversity. Postoperative microbial changes included increased alpha diversity. Certain taxa, such as Eubacterium and Collinsella, were associated with recovery or HAEC.
Meaning: Distinct microbial signatures may help identify HAEC risk and guide microbiota-based strategies to improve outcomes.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Discordance between antibiotic therapy and recurrent urinary tract infections in young children with third-generation cephalosporin-resistant infections
- Yusin Kim, Hyun A Lee, Gil Lee, Kyungseok Park, Ye Kyung Kim, Peong Gang Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):228-235. Published online November 26, 2025
-
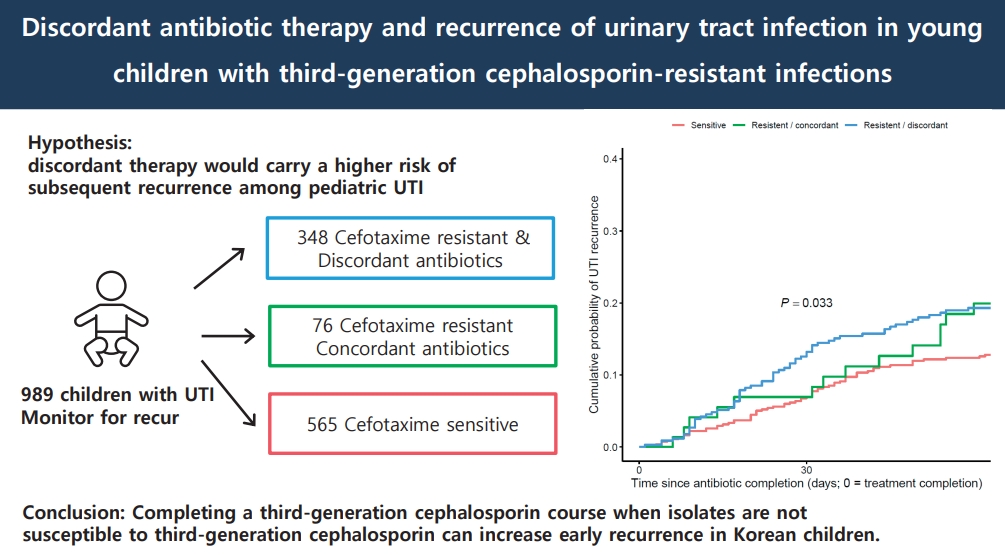
Question: Does completing a third-generation cephalosporin course, despite in vitro resistance, increase the early urinary tract infection recurrence rate in children?
Finding: Among 989 Korean children, discordant therapy increased the 2-month recurrence risk by 40% compared with concordant or susceptible therapy.
Meaning: Checking isolate susceptibility and switching to an active oral drug may curb recurrence and limit the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Hematology
- Granulocyte transfusion improves survival in pediatric febrile neutropenia: a 15-year cohort study
- Witsanu Phetsai, Kleebsabai Sanpakit, Jassada Buaboonnam, Kamon Phuakpet, Nassawee Vathana, Nattee Narkbunnam, Fon Kladed, Chayamon Takpradit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):236-246. Published online January 12, 2026
-

Question: Does granulocyte transfusion improve survival and clinical recovery in pediatric febrile neutropenia?
Finding: In this 15-year real-world cohort, granulocyte transfusion significantly increased 30-day survival (92.3 % vs. 65.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.105; P=0.020) and accelerated fever and neutrophil recovery without serious adverse events.
Meaning: Granulocyte transfusion may be an effective adjunctive therapy for severe neutropenic infections in children, particularly in low- and middle-income settings.
- Other
- Improvements in obesity-related measures among Asian patients with severe obesity following a structured lifestyle intervention
- Pei-Shan Chen, Shu-Mei Tsai, Chih-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ru Yang, Yen-Ju Huang, Hsiang-Yin Liu, Kai-Chi Chang, Huey-Ling Chen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):247-256. Published online December 22, 2025
-
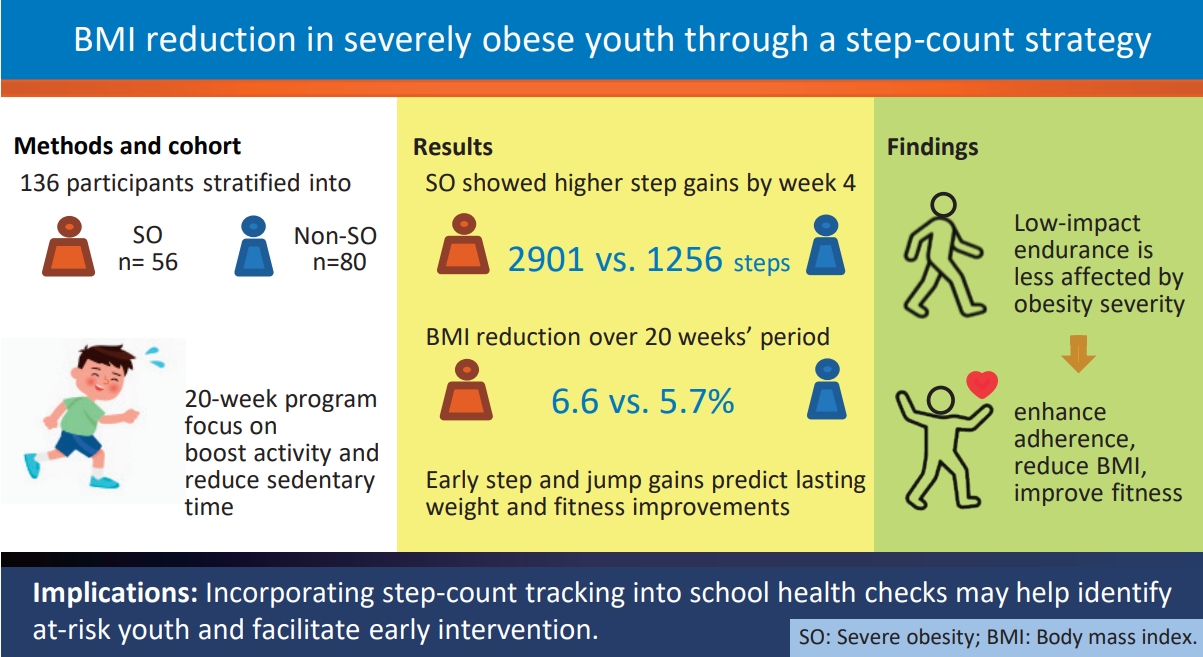
Question: How does obesity severity affect baseline fitness and improvements in key obesity-related measures following participation in a structured lifestyle modification program?
Finding: Severely obese youth showed poorer baseline physical fitness but greater improvements in key obesity-related measures following lifestyle interventions.
Meaning: Early targeted intervention may help prevent progression to more severe obesity and declines in physical fitness in patients with obesity.
- Allergy
- Can a basophil activation test of cord blood predict a cow's milk allergy?
- Dilara Fatma Kocacik Uygun, Durmuş Burgucu, Vedat Uygun, Gül Alkan Bulbul, Fulden Duyar, Cem Yasar Sahnal, Aysen Bingöl
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):257-265. Published online January 20, 2026
-
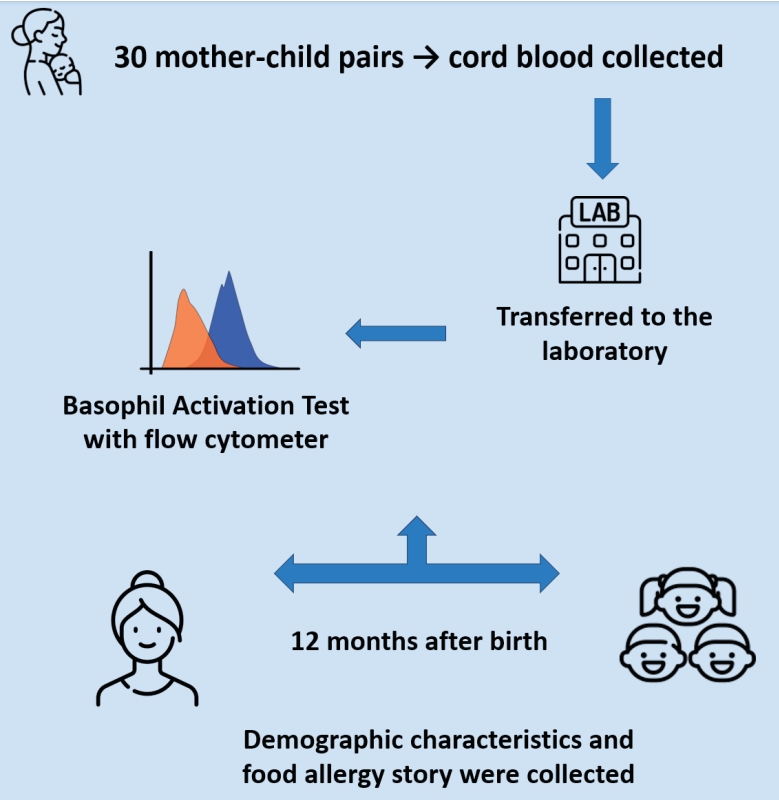
Question: Can a basophil activation test (BAT) of cord blood predict a cow's milk allergy?
Finding: Infants with a high casein-BAT value were more likely to develop food allergy symptoms in the first year, whereas cow’s milk BAT showed no predictive association.
Meaning: Cord blood casein BAT may help identify newborns at increased risk for early-life food allergies, enabling closer monitoring and preventive strategies, although larger studies are needed for validation.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Thrombocytopenia in preterm infants born to mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study
- Ru Xue, Guoqing Zhang, Xiafang Chen, Jun Bu, Lanlan Mi, Fei Bei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):266-273. Published online December 22, 2025
-
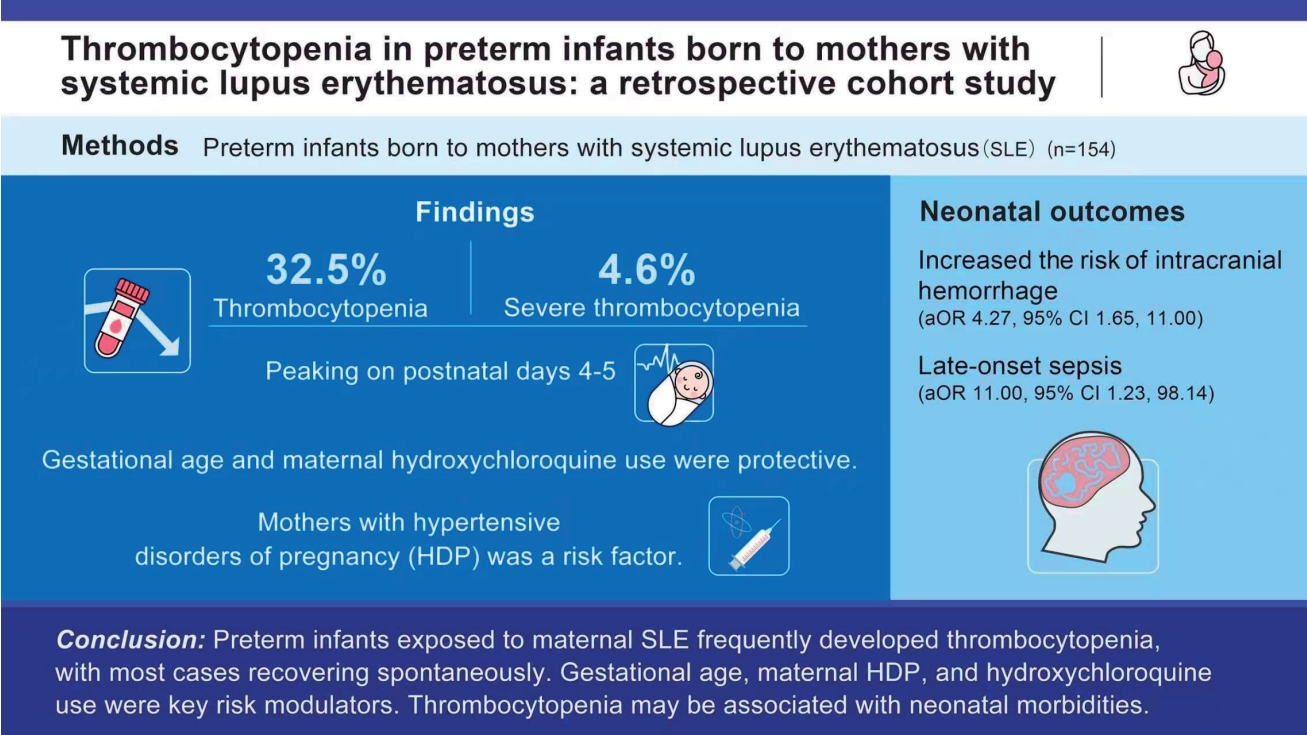
Question: What are the characteristics and clinical implications of thrombocytopenia in preterm neonates born to mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus?
Finding: Nearly one-third of preterm infants developed thrombocytopenia. Key modulators of this risk included gestational age, maternal hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and hydroxychloroquine use. Thrombocytopenia may be associated with neonatal morbidity.
Meaning: Platelet count should be monitored during the first week of life, and infants should be assessed for potential complications.
- Validation of a new Japanese classification for predicting severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Masato Ito, Shinya Hirano, Fumihiko Namba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(3):274-281. Published online January 20, 2026
-

Question: Can the revised Japanese classification predict severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) early in preterm infants?
Finding: Small for gestational age and bubbly/cystic chest radiographic patterns were independently associated with severe BPD, and subtypes I and III showed particularly strong associations.
Meaning: This classification may facilitate early risk stratification and guide timely supportive strategies to prevent progression to severe BPD.