Editorial
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Understanding the usefulness of electroencephalography source localization
- Bo Lyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):210-211. Published online April 18, 2023
-
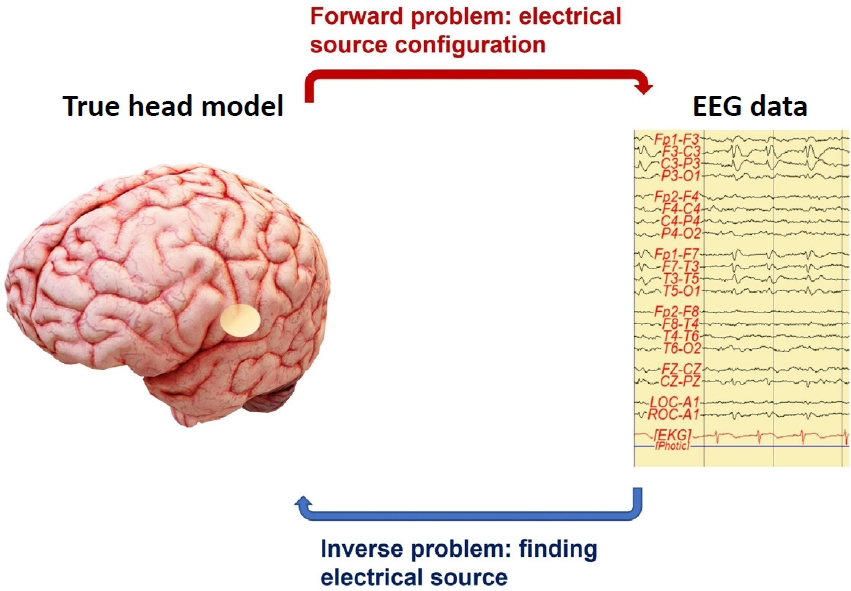
· Electroencephalography (EEG) records brain activity with high temporal resolution.
· EEG source localization, combined with other functional or structural imaging methods, provides information about brain network and connectivity in clinical neuroscience.
· EEG source localization identifies brain location from electrical current sources in several neuropsychiatric diseases such as epilepsy, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and anxiety disorders.
- Other
- Advancing pediatric health: the multifaceted scope of Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics
- Jin Hee Oh, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):171-172. Published online March 29, 2023
-
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics (CEP) is a journal that specializes in pediatric research topics. It covers a wide range of research areas, including basic research, translational research, and research related to improving pediatric health and diseases. CEP also focuses on the coordination of societal structures and processes that orchestrate pediatric health and disease throughout society, and the parallel relationship between regional characteristics and globalization. The journal intends to continue promoting pediatric health through relentless efforts and the discovery of new research areas.
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children?
- Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Optimal hemodialysis treatment for pediatric kidney failure patients
- Yo Han Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):125-126. Published online February 15, 2023
-
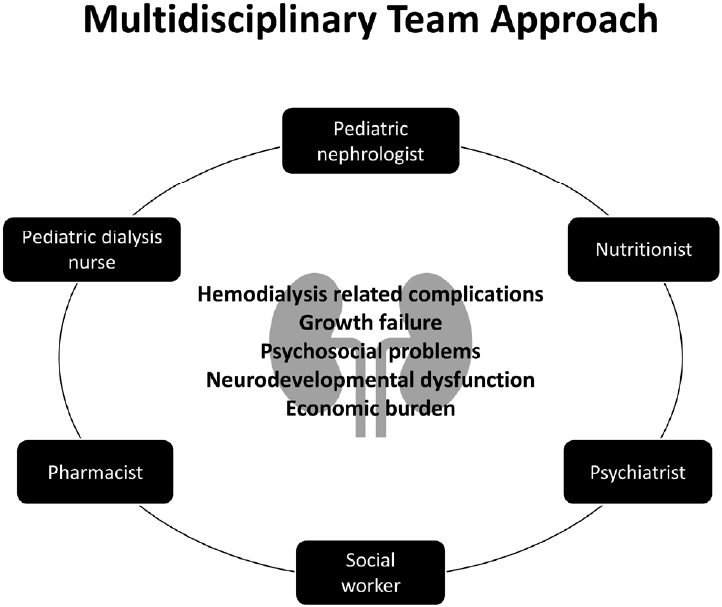
· Although the basic concept of hemodialysis (HD) is similar in adults and children, specific factors must be considered in the latter, including the small dialyzer and circuit, difficult vascular access, and frequent complications.
· HD-associated complications include catheter-related problems, hemodynamic instability, and neurodevelopmental and cognitive dysfunction.
· Pediatric HD is challenging, and steady efforts are needed to perform it safely and reduce its complications, thereby improving clinical outcomes.
- Neurology
- Lumbar puncture or not: when does febrile seizure require a neurodiagnostic evaluation?
- Seung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):68-69. Published online December 9, 2022
-
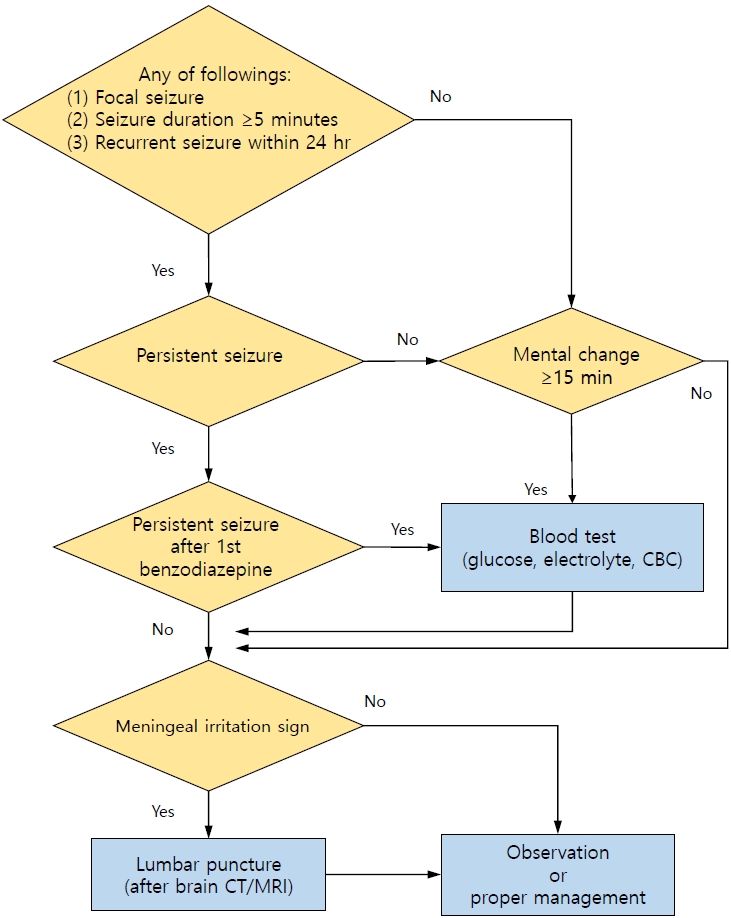
· A neurodiagnostic evaluation (lumbar puncture, blood tests, electroencephalography, and neuroimaging) is not indicated in most patients with simple febrile seizures.
· A lumbar puncture is indicated when a central nervous system infection is suspected in any patient with febrile seizures.
· Blood tests (glucose, electrolytes, and complete blood count) are indicated in patients with persistent seizure after benzodiazepine treatment, prolonged loss of consciousness, poor general condition, or signs of dehydration.
- Emergency Medicine
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children: teamwork approach
- Ji-Hyun Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):66-67. Published online September 1, 2022
-
· The successful and safe enema reduction of intussusception depends primarily on the experience and preference of the radiologists and the availability of resources.
· The establishment of a standardized manual or protocol for reduction and pre-reduction treatment of intussusception, along with the collaboration of pediatricians, radiologists, and surgeons, is expected to improve the treatment success rate.
- Pulmonology
- Wheezing in infants and preschoolers: phenotypes and treatment options
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):26-27. Published online December 6, 2022
-
· Knowing who will develop into asthma or who will not is important to impose proper treatment and early intervention in a child with the first episode of wheezing.
· Phenotypes of severe bronchiolitis in less than 2-year-old children with first episode of wheezing were suggested for different treatment options
· RV-induced and/or atopy-associated severe wheezing in preschool children may benefit from early intervention of asthma treatment.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Does cord blood cortisol have a mediating effect on maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight?
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):24-25. Published online November 30, 2022
-
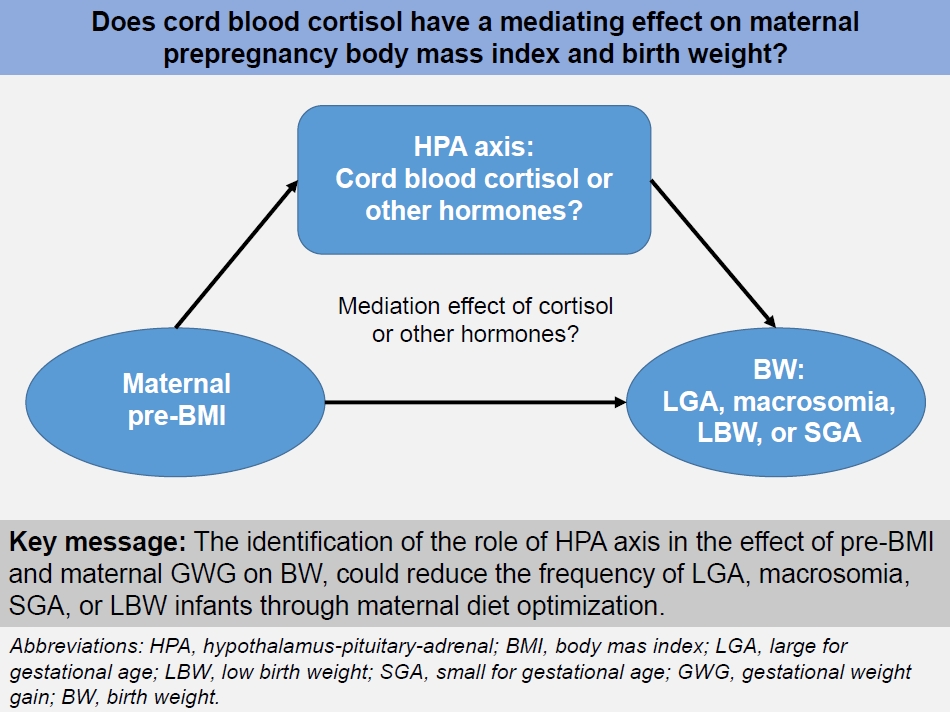
· A high prepregnancy body mass index (pre-BMI) is associated with large for gestational age (LGA) and macrosomia, whereas a low pre-BMI is associated with small for gestational age (SGA) and low birth weight (LBW).
· The identification of the role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in the effect of pre-BMI and maternal gestational weight gain on birth weight could reduce the frequency of LGA, macrosomia, SGA, or LBW through maternal diet optimization.
- Pulmonology
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
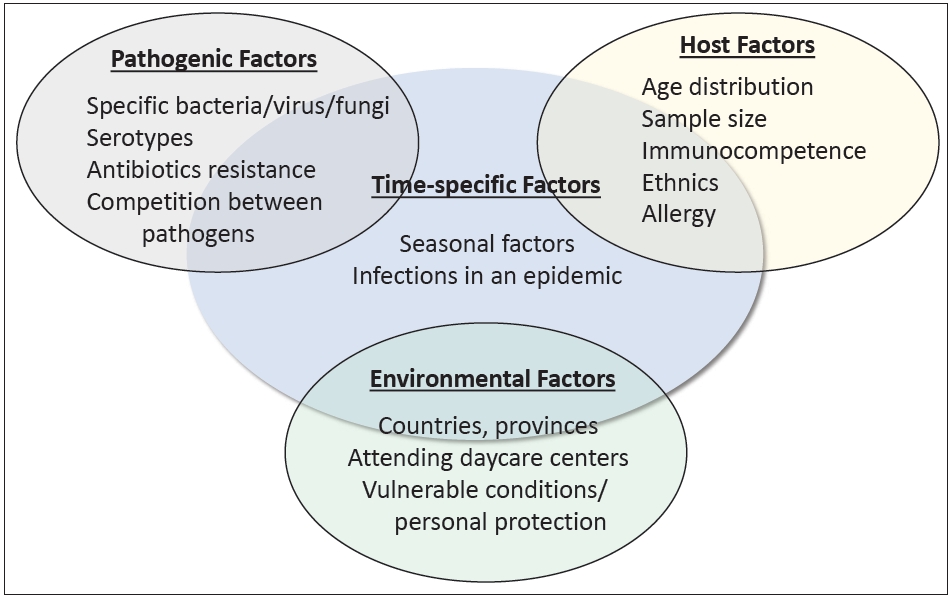
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Allergy
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of allergic diseases in COVID-19 era
- Sungsu Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):587-588. Published online November 29, 2022
-
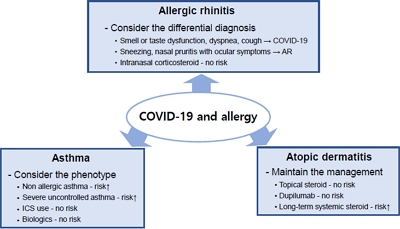
The risk of sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes is not elevated in patients with the type 2 phenotype and well-controlled asthma. Inhaled corticosteroids, intranasal corticosteroids, and topical steroids can be safely used in COVID-19 patients. Biologics can be safely used by patients with allergic diseases without concern about antibody responses.
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of probiotics to reduce functional abdominal pain in children
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):585-586. Published online October 6, 2022
-
· The ability of probiotics to relieve pain caused by functional abdominal pain disorders (FAPD) in children is unclear.
· Lactobacillus reuteri may effectively reduce pain caused by childhood FAPD.
· Since the routine use of probiotics cannot be recommended due to a lack of clinical evidence, research into probiotic mixtures or symbiotics remains necessary.
- Cardiology
- Recent research trends in Kawasaki disease-related infection
- Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):538-539. Published online July 22, 2022
-
The incidence of Kawasaki disease has reportedly decreased since the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) quarantine. However, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children has reportedly occurred more frequently in areas where COVID-19 was prevalent than in previous years. Research into the etiology of childhood and adolescent systemic vasculitis in infection-related immune responses during the COVID-19 pandemic has increased accordingly.
- Neurology
- Increasing our understanding of rotavirus-induced central nervous system manifestations
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):536-537. Published online May 6, 2022
-
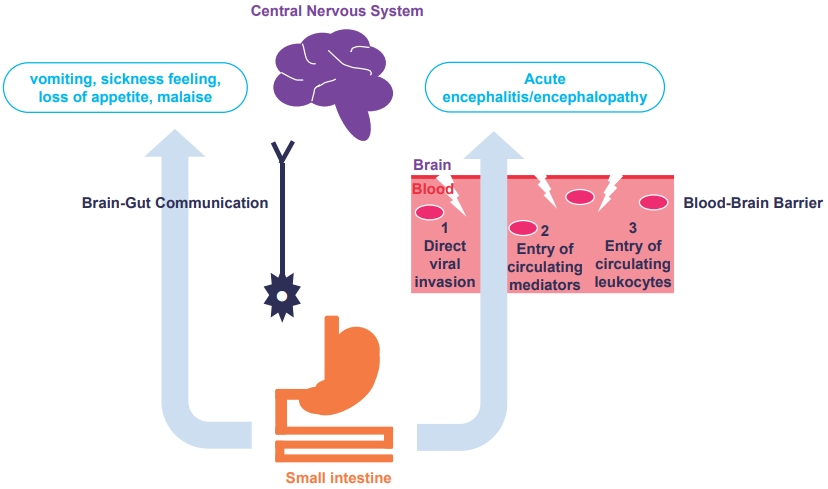
· Diverse clinicoradiological features of central nervous system (CNS) complications in rotavirus infection can be identified with the rapid and wide use of various brain magnetic resonance imaging protocols.
· An increased understanding of the various pathophysiological mechanisms of rotavirus-induced CNS manifestations will enable precise management in the future.
- Neurobehavior
- Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on children’s health
- Joon Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):498-499. Published online September 16, 2022
-
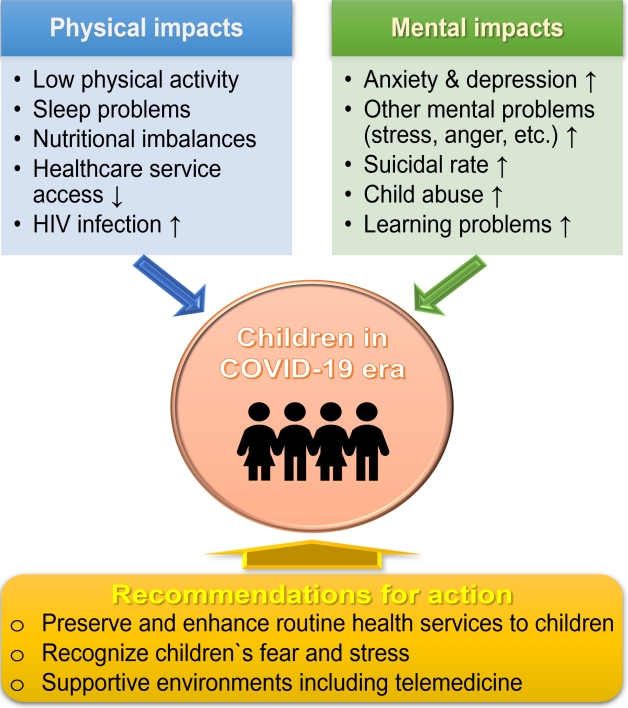
· Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has had an enormous impact on mental health and other aspects of children’s health.
· The prevalence of anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents have increased in the COVID-19 era.
· Cooperation among parents, guardians, academic societies, and the government is needed to maintain the mental health of children and adolescents.
- Other
- Three-dimensional printing technolgy in orthopedic oncology
- Yongsung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):496-497. Published online May 11, 2022
-
Orthopedic oncology is one of the most active fields in applying 3-dimensional printing technology from preoperative planning to intraoperative procedures such as accurate resection of tumors and reconstruction of huge bone defects.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Hypertension in adulthood is programmed during the perinatal period
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):494-495. Published online August 12, 2022
-
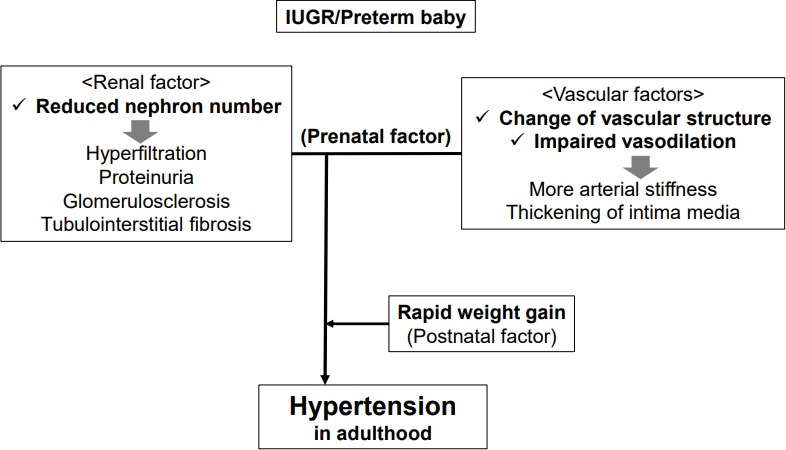
∙ Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and preterm birth can be significant risk factors for the development of adult hypertension.
∙ Several perinatal factors of hypertension are related to IUGR, including renal, vascular, and rapid catch-up growth.
- Endocrinology
- Bisphenol A leaching from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food causes potential health issues
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):450-452. Published online July 25, 2022
-
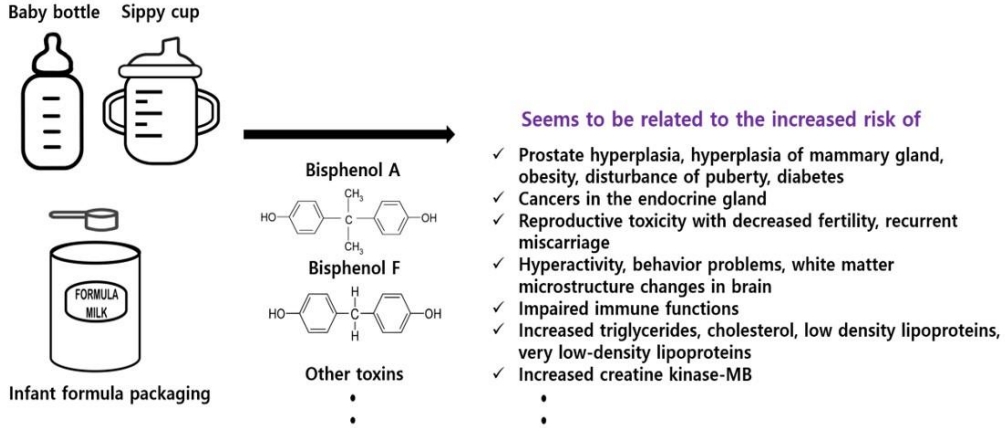
Can bisphenol A (BPA) leach out from polycarbonate baby bottles into baby food? BPA and other toxic materials can leach out from baby bottles and increase the risk of various health problems, including endocrine disturbances. Although the use of BPA in baby bottles has been banned, many developing countries still use it, which can cause health issues. Thus, public awareness of this issue is required.
- Cardiology
- Characteristics of z score systems for diagnosing coronary abnormalities in Kawasaki disease
- Gyeong-Hee Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):448-449. Published online March 14, 2022
-
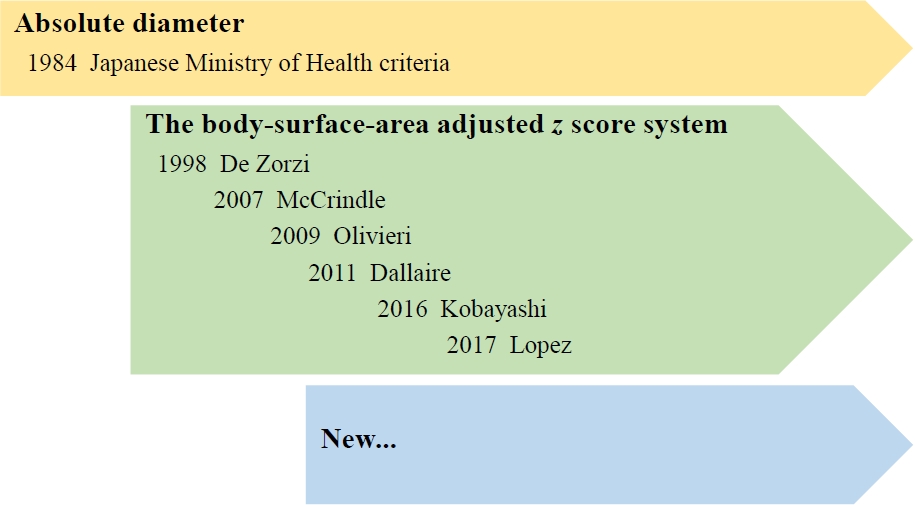
Because of the various body sizes of children with Kawasaki disease (KD), coronary artery diameter requires normalization to the body surface area as a z score.
In updated guidelines, coronary artery abnormalities are important criteria in the diagnosis of KD, and z score systems have been accepted to define coronary artery abnormalities.
However, the z score formula should be selected carefully because each yields different results.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Factors to consider before implementing telemedicine protocols to manage neonatal jaundice
- Heui Seung Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):403-404. Published online April 12, 2022
-
In the rapidly changing environmental situation during the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak, neonatal centers have developed telemedicine systems with extended coverage for neonatal monitoring and high-risk follow-up programs including neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. At this point, electronic health technology and noncontact medical system increase the effectiveness of rather than replacing the face-to-face visit and the opinions of experienced neonatologists.
- Pulmonology
- Now lung ultrasound has been established as a fundamental examination in pediatric respiratory diseases
- Kyunghoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):401-402. Published online July 13, 2022
-
· Several studies demonstrated the usefulness of lung ultrasound in pediatric respiratory diseases including coronavirus disease 2019.
· Knowledge of lung ultrasound is increasing, and lung ultrasound has been established as a fundamental diagnostic examination for pediatric respiratory diseases.
- Cardiology
- Early echocardiographic screening for subclinical myocardial dysfunction in children and adolescents with dyslipidemia: why and when?
- Hyun Gyung Lee, Hwa Jin Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):398-400. Published online March 7, 2022
-
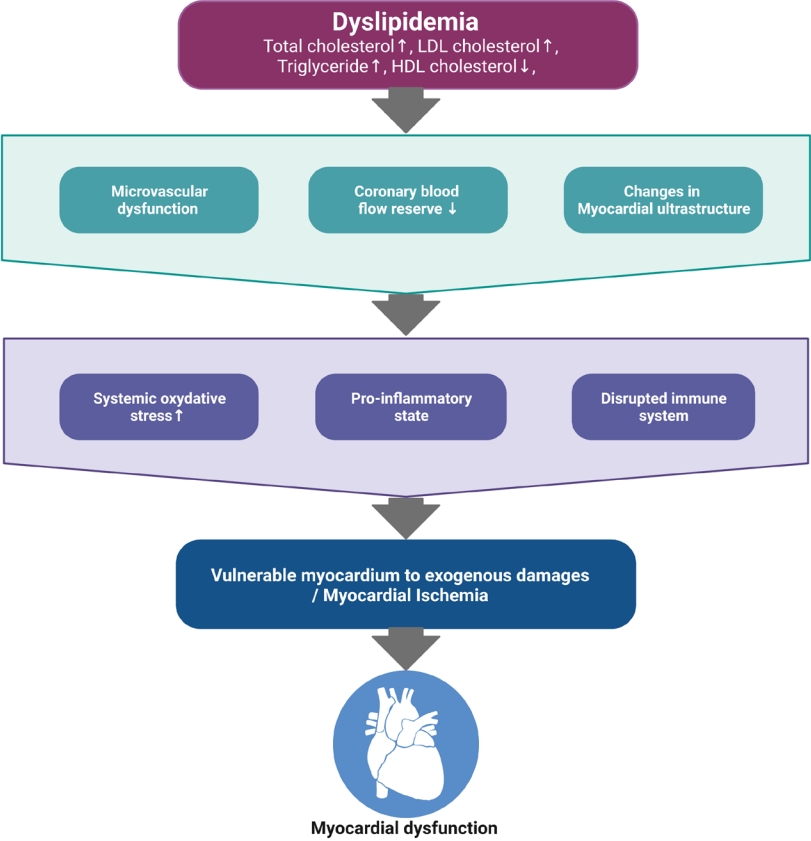
Dyslipidemia contributes to early atherosclerosis, premature cardiovascular disease, and subclinical ventricular dysfunction in children. This paper highlights the need for echocardiographic evaluation for impaired diastolic function of both ventricles and narrowing of the aortic valve and sinus of Valsalva. Therefore, early echocardiographic screening of children with primary hyperlipidemia should be considered.
- Pulmonology
- Influence of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on respiratory health in children
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):348-349. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Practicing hand hygiene, wearing a mask, maintaining social distancing, and other lockdown measures were implemented to reduce the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a worldwide disaster that started in 2019.
· The advent of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic resulted in positive secondary effects, such as reduced respiratory viral infections in children and decreased degrees of air pollution.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Ideal timing for aggressive screening to detect developmental dysplasia of the hip in term and preterm infants
- Won-Ho Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):346-347. Published online March 14, 2022
-
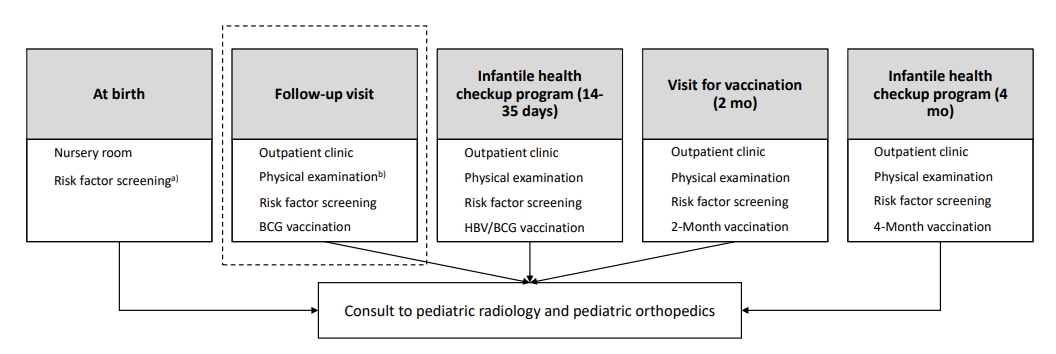
The risk factors and pathogenesis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) are unclear. Moreover, no universal screening method can entirely eliminate the risk of DDH. However, its incidence is significant and its early detection is critical for improving patient prognosis. Although the ideal evaluation time and risk factors, especially for premature infants, are unclear, the necessity for DDH screening programs for term and preterm infants is emerging.
- Nutrition
- Human milk oligosaccharides as immunonutrition key in early life
- Jung Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):344-345. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Human milk is a major source of immunonutrients for neonates and infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) act as prebiotics and promote the growth of commensal bacteria.
· HMOs inhibit microorganism adhesion to the gut mucosa through interactions with the commensal microbiome and improve gut barrier function by increasing short-chain fatty acid mediated by bifidobacteria and immunomodulation.
· Several randomized controlled trials recently reported on HMOs.
- Cardiology
- Coronavirus disease 2019 and mRNA vaccines: what’s next – miRNA?
- Joon Kee Lee, Heon-Seok Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):302-303. Published online March 28, 2022
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small single-stranded noncoding RNA molecules that function in RNA silencing and the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. The potential role of miRNAs as biomarkers of myocarditis is promising, and miRNAs are expected to be utilized in various clinical fields in the future.
- Endocrinology
- Low bone mineral density can occur in children after shortterm systemic glucocorticoid treatment
- Moon Bae Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):300-301. Published online April 27, 2022
-

Osteoporosis diagnosed in children with chronic diseases is a major endocrine complication triggered by the disease itself or its treatment. Although age upon starting osteotoxic agents and the their duration of use are vital contributors, spontaneous recovery of bone mass following treatment completion is a privilege of this specific age group. For any patients short-term glucocorticoid therapy, bone health screening is the next step.
- Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children?
- Minsun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):252-253. Published online March 29, 2022
-
· Evidence shows that patients with type 1 diabetes have been severely affected by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in various ways.
· Although there is no reliable evidence that COVID-19 worsens or induces diabetes, it can impair β-cell insulin secretion and glucose control by inducing inflammation and cytokine production.
· A study is needed of the short- and long-term relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 in the Korean pediatric population.
- Infection
- Effects of nonpharmaceutical interventions for coronavirus disease 2019
- Jae Hong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):250-251. Published online March 22, 2022
-
∙ Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have decreased the incidence of various infectious diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
∙ During the 2-year COVID-19 pandemic, NPIs changed patients’ daily lives, and the impact on mental health was notable.
∙ The effects of NPIs were evaluated in detail, considering both infections and mental health.
- Endocrinology
- Clinical and diagnostic importance of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):129-130. Published online January 14, 2022
-
∙ Because childhood lipid concentrations continue into adulthood, early evaluation and treatment are needed, but dyslipidemia awareness is low.
∙ For the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in childhood and adolescence, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in adulthood, lifestyle modifications, appropriate exercise, and drug treatment are required.
∙ A large-scale study of the prevalence and therapeutic effects of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents in Korea is needed.
- Infection
- Importance of maintaining a high childhood vaccination rate and surveillance program against Japanese encephalitis in Korea
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):127-128. Published online February 16, 2022
-
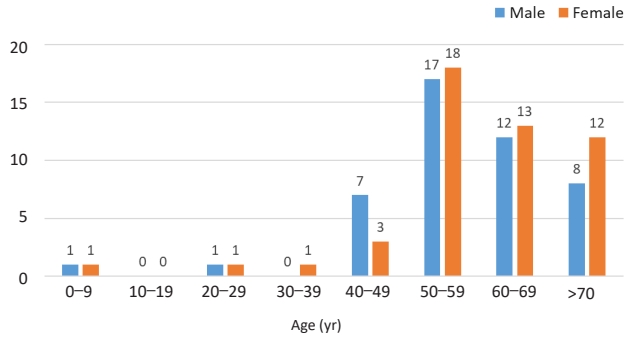
∙ Recent epidemiologic changes of Japanese encephalitis (JE) in Korea are area (rural to urban or suburban) and age shift (children to adult).
∙ Although the main factors contributing to recent epidemiologic changes of JE are not well identified, maintaining high vaccination rates of JE appear to be important in preventing of JE in all age groups.
∙ Continuous surveillance for epidemiology and seroprevalence should be carried out.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











