Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents (2,498 times)
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- Gastroenterology
- Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children (2,396 times)
- Yu Kyung Cho, Jin Lee, Chang Nyol Paik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):377-383. Published online August 21, 2023
-
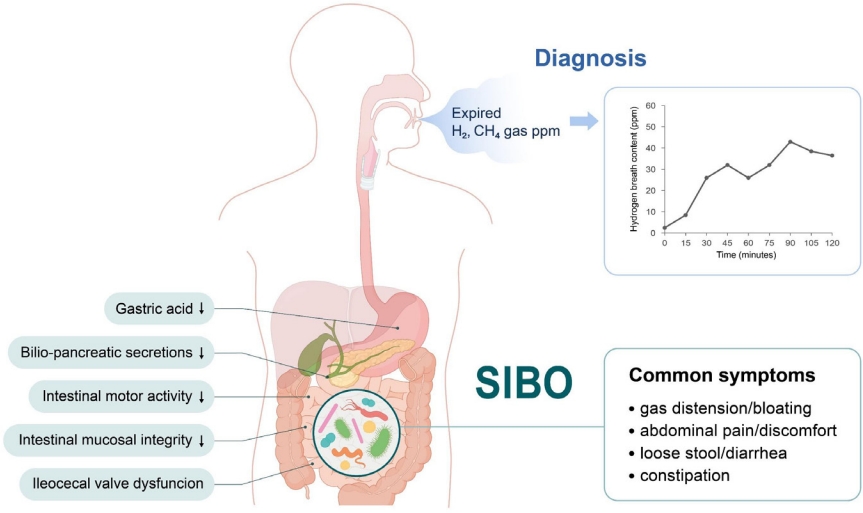
· Pediatric small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) manifestations range from nonspecific abdominal symptoms to malabsorption or malnutrition.
· SIBO is prevalent in children and adolescents with functional abdominal pain disorders.
· Predisposing factors include disturbed intestinal motility, altered anatomy, and/or abnormal body defense systems against intestinal bacteria.
· Breath tests are safe and noninvasive.
· Treatment principles include managing predisposing conditions, nutritional support, symptom control, and antibiotics.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric obesity: life cycle approach of pediatrician and society (2,380 times)
- Yong Hee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):29-30. Published online December 28, 2021
-
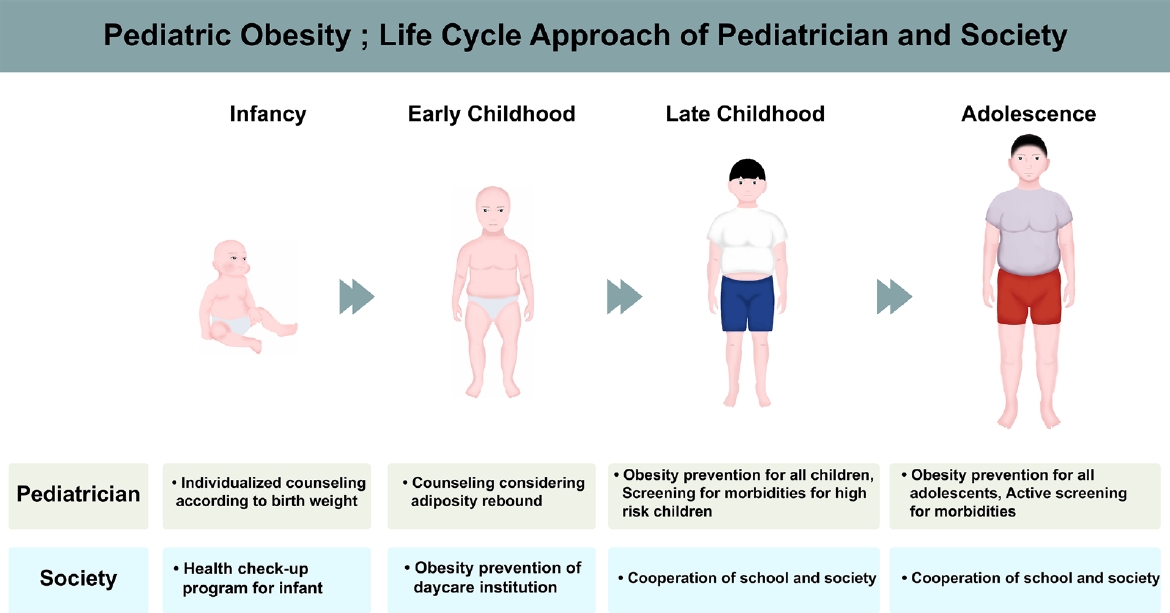
• With the emerging epidemic of pediatric obesity, many endocrine comorbidities classically seen in adulthood are surfacing much earlier in life.
• Appropriate obesity counseling and education should be provided from infancy to adolescence.
• Managing pediatric obesity may require school and society involvement.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy (2,377 times)
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):439-447. Published online December 23, 2021
-
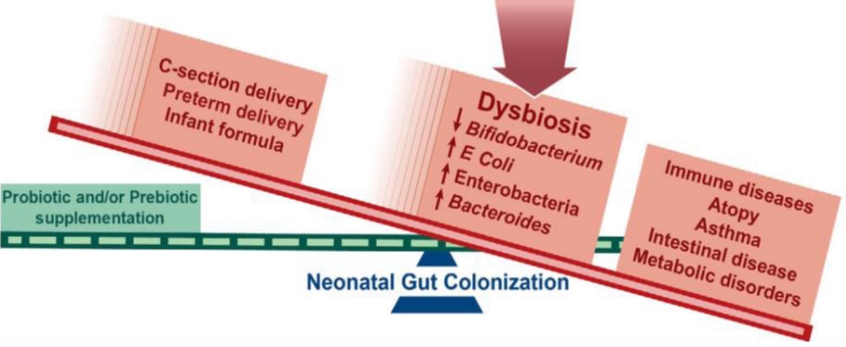
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism.
- Neurology
- Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system complications: clinicoradiological features and potential mechanisms (2,376 times)
- Kyung Yeon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):483-493. Published online February 7, 2022
-

∙ Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system (CNS) complications are fairly common in children.
∙ Common clinicoradiological features include benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis, acute encephalopathies/encephalitis, cerebellitis, and neonatal rotavirus-associated leukoencephalopathy.
∙ Possible mechanisms for CNS complications include direct viral invasion into the brain via several potential routes such as the blood-brain barrier and vagus nerve, and entry of various brain-damaging mediators and activated immune cells into the brain.
- Big data analysis and artificial intelligence in epilepsy – common data model analysis and machine learning-based seizure detection and forecasting (2,356 times)
- Yoon Gi Chung, Yonghoon Jeon, Sooyoung Yoo, Hunmin Kim, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):272-282. Published online November 26, 2021
-

· Big data analysis, such as common data model and artificial intelligence, can solve relevant questions and improve clinical care.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 0.887–0.996 areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for automated interictal epileptiform discharge detection.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 62.3%–99.0% accuracy for interictal-ictal classification in seizure detection and 75.0%– 87.8% sensitivity with a 0.06–0.21/hr false positive rate in seizure forecasting.
- Recent trends of healthcare information and communication technologies in pediatrics: a systematic review (2,356 times)
- Se young Jung, Keehyuck Lee, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):291-299. Published online December 15, 2021
-
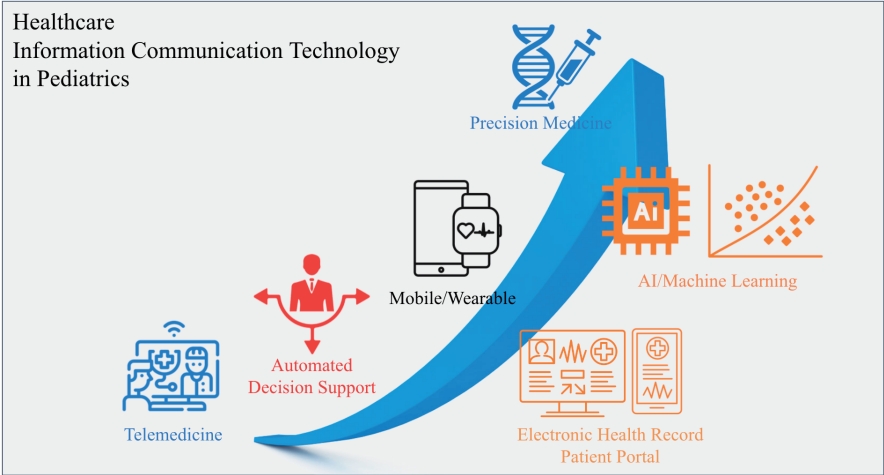
· The innovation of healthcare information communication technology (ICT) was accelerated with the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs).
· Telemedicine currently has no technical barriers.
· EHRs and personal health records are being connected, and mobile/wearable technologies are being integrated into them.
· Conventional rule-based clinical decision support systems have already been implemented and used in EHRs and PHRs. Artificial intelligence/machine learning improves precision and accuracy.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Early initiation of breastfeeding and factors associated with its delay among mothers at discharge from a single hospital (2,343 times)
- J. Jenifer Florence Mary, R. Sindhuri, A. Arul Kumaran, Amol R. Dongre
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):201-208. Published online October 18, 2021
-

Background: According to the National Family Health Survey– 4, in India, 78.9% of deliveries occur in institutions, although only 42.6% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding within 1 hour of delivery.
Purpose: To estimate the proportion of early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF) among new mothers at discharge from a tertiary care hospital and identify the determinants of delayed initiation of breastfeeding among...
- Review Article
- Other
- Hearing loss in neonates and infants (2,329 times)
- Goun Choe, Su-Kyoung Park, Bong Jik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):369-376. Published online January 9, 2023
-

· Congenital hearing loss is common, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns and affecting 1.2%–11% of preterm and 1.6%–13.7% of neonatal intensive care unit neonates.
· Etiologies vary, and up to 80% of cases are genetic.
· Newborn hearing screenings follow the 1-3-6 rule, and babies at high risk of hearing loss should be referred to otolaryngology for early detection and timely intervention.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Breastfeeding and vitamin D (2,277 times)
- Ju Sun Heo, Young Min Ahn, Ai-Rhan Ellen Kim, Son Moon Shin; for the Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):418-429. Published online December 14, 2021
-
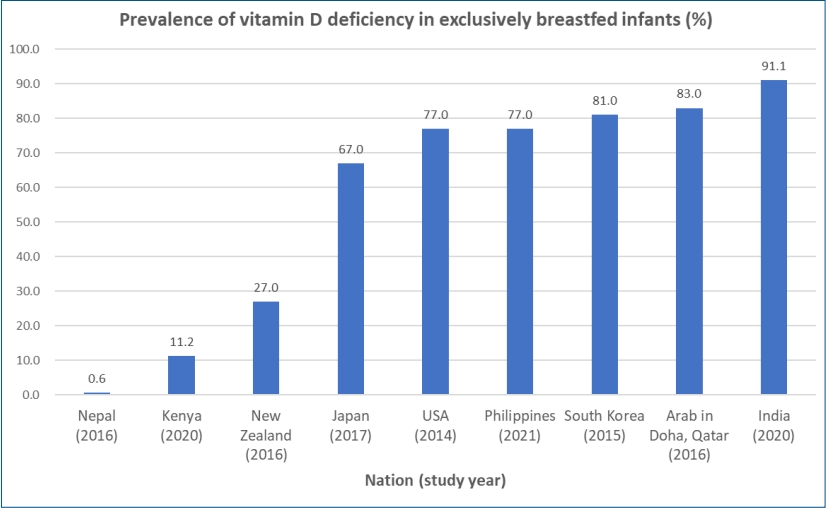
∙ Exclusively breastfed infants are at risk of developing vitamin D deficiency associated with hypocalcemia, rickets, and various health outcomes.
∙ The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants differs vastly between studies and nations at 0.6%–91.1%.
∙ The vitamin D content of breast milk does not meet the requirements of exclusively breastfed infants.
∙ Most international guidelines recommend that breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU/day of vitamin D during the first year of life.
∙ Vitamin D intake (milk+supplements) of 800 IU/day can be considered in preterm infants along with biochemical monitoring.
- Allergy
- Natural course of IgE-mediated food allergy in children (2,264 times)
- Kyunguk Jeong, Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):504-511. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Dendritic, regulatory T, and regulatory B cells significantly contribute to the natural course of food allergy.
· Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergies tend to resolve in earlier childhood but recent studies show that 50% of patients still persist into school age.
· The potential factors affecting the natural course of food allergy are age at diagnosis, symptom severity, sensitization status and its change rate, and external factors such as diet and interventions.
· There is a considerable possibility of food allergy outgrow if specific IgE levels are 2–5 kUA/L or less, but other factors such as age and recent symptoms should be considered together.
· With a clear understanding of the natural course of food allergy, pediatricians can provide appropriate assessment and interventions to our patients, and consequently can help patients overcome their food allergy and improve the social safety net.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review (2,201 times)
- Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
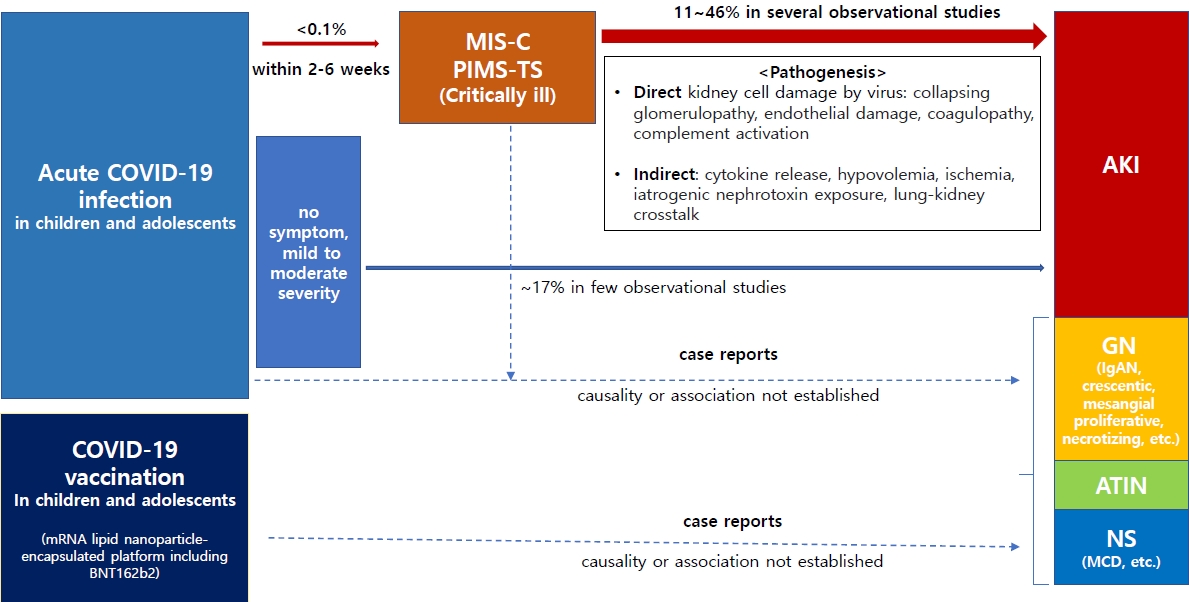
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention.
- Gastroenterology
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of Crohn disease: clinical implications in children and adolescents (2,135 times)
- Eun Sil Kim, Mi Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):21-28. Published online September 10, 2021
-

· Clinical manifestations of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract involvement in Crohn's disease (CD) are common but often clinically underestimated.
· Diagnosing CD by confirming inflammation of the UGI tract histologically is challenging because macroscopic and microscopic findings overlap with those of other diseases.
· Ongoing efforts are needed to enable a standardized assessment of UGI CD in the future.
- Neurology
- Worldwide national intervention of developmental screening programs in infant and early childhood (2,131 times)
- Seunghyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):10-20. Published online September 30, 2021
-

∙ Prevalence rate of developmental disabilities has been reported from 8% to 15% and its rate is increasing worldwide.
∙ The critical period of intervention for developmental delay is before the child reaches 3 years of age.
∙ All primary care pediatricians should conduct developmental surveillance and screening tests to infants and children at scheduled visits. Through this, they are liable for providing early identification and timely intervention.
- Gastroenterology
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children (2,131 times)
- Jisun Hwang, Hee Mang Yoon, Pyeong Hwa Kim, Ah Young Jung, Jin Seong Lee, Young Ah Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):12-21. Published online July 4, 2022
-
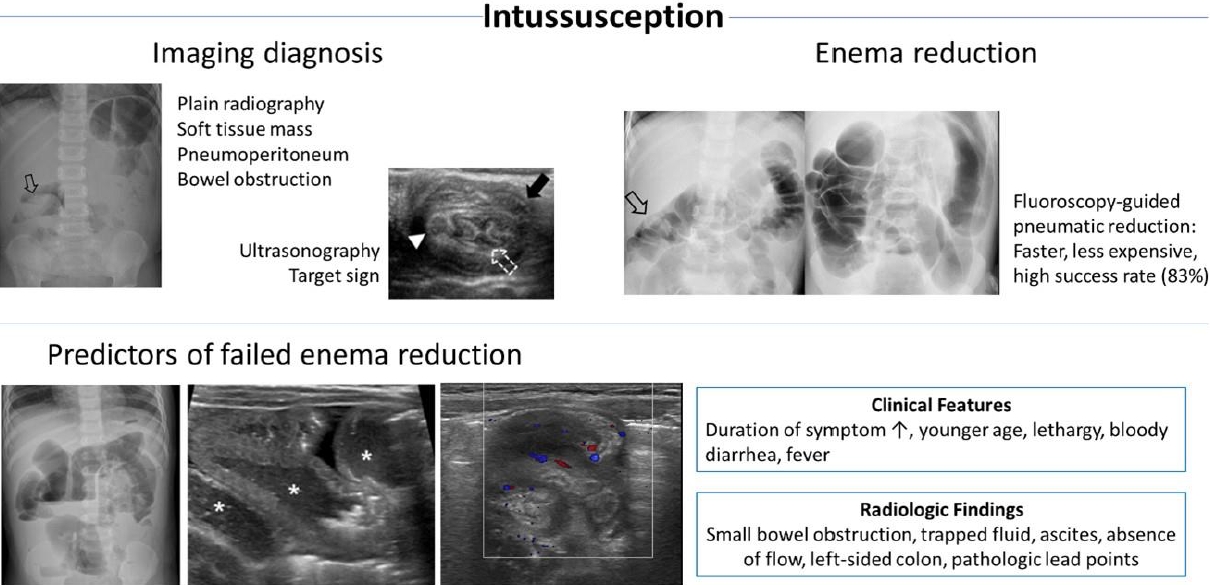
· Intussusception, the most common cause of small bowel obstruction in young children, has an overall incidence in Korea of 28.3 cases per 100,000 person-years.
· Its cause is idiopathic inmost cases, although viral or bacterial gastroenteritis has beenpostulated as a cause. Approximately 4% of children have pathological lead points for intussusception, and Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause.
· Intussusception in preterm infants is extremely rare. Older children (>5 years of age) are at increased risk of pathological lead points.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial (2,119 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Other
- Risk factors and screening timing for developmental dysplasia of the hip in preterm infants (2,082 times)
- Ga Won Jeon, Hye Jung Choo, Yong Uk Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):262-268. Published online November 5, 2021
-

Question: When is the best screening timing and what is the risk factor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in preterm infants?
Finding: Ultrasonography performed earlier than 38 weeks of postmenstrual age caused unnecessary subsequent ultrasonography. DDH did not occur predominantly on the left side or in breech infants.
Meaning: The screening timing, etiology, and risk factors for DDH in preterm infants are somewhat different from those in term infants.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Comparison of minimally invasive surfactant therapy with intubation surfactant administration and extubation for treating preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized clinical trial (2,081 times)
- Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Maryam Shokouhi, Sajad Ghahremani, Ali Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):188-193. Published online July 28, 2021
-
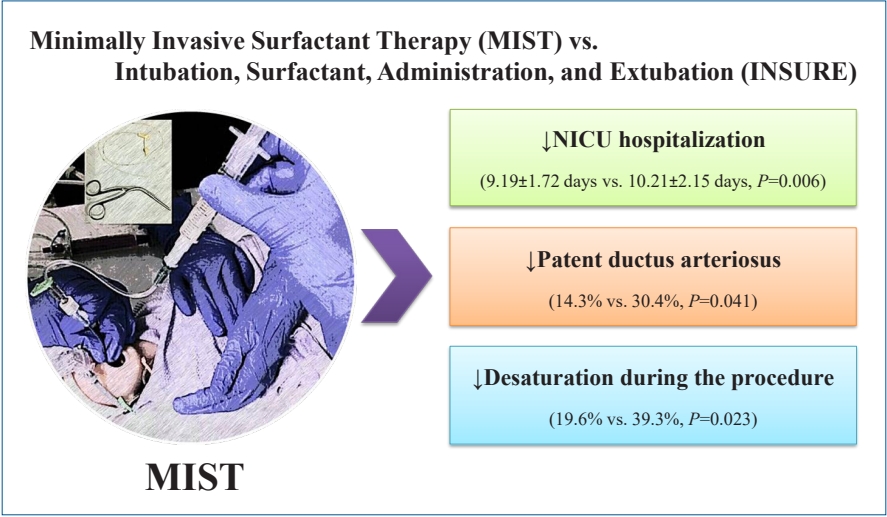
Question: Are the short-term outcomes of minimally invasive surfactant therapy (MIST) relatively superior to those of INtubation, SURfactant administration, and Extubation (INSURE) in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)?
Finding: MIST could be an appropriate substitution for INSURE in preterm infants with RDS since it reduced hospitalization time and number of side effects.
Meaning: MIST is recommended for surfactant administration for its proven advantages over the INSURE technique.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Four months of rifampicin monotherapy for latent tuberculosis infection in children (2,059 times)
- Chi Eun Oh, Dick Menzies
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):214-221. Published online October 29, 2021
-
· Recently, the importance of a short-term treatment regimen including rifamycin has been highlighted in the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI).
· Four prospective or retrospective studies in children consistently reported that a 4-month daily rifampicin regimen (4R) had a higher completion rate than and comparable safety to a nine-month daily isoniazid regimen.
· We suggest rifampicin 20–30 mg/kg/day for children aged 0–2 years and 15–20 mg/kg/day for children aged 2–10 years in 4R to treat LTBI.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial (2,032 times)
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-

Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Changes in age-specific seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus and impact of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Korea (2,028 times)
- Byung Ok Kwak, Young Jin Hong, Dong Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):108-114. Published online September 24, 2021
-
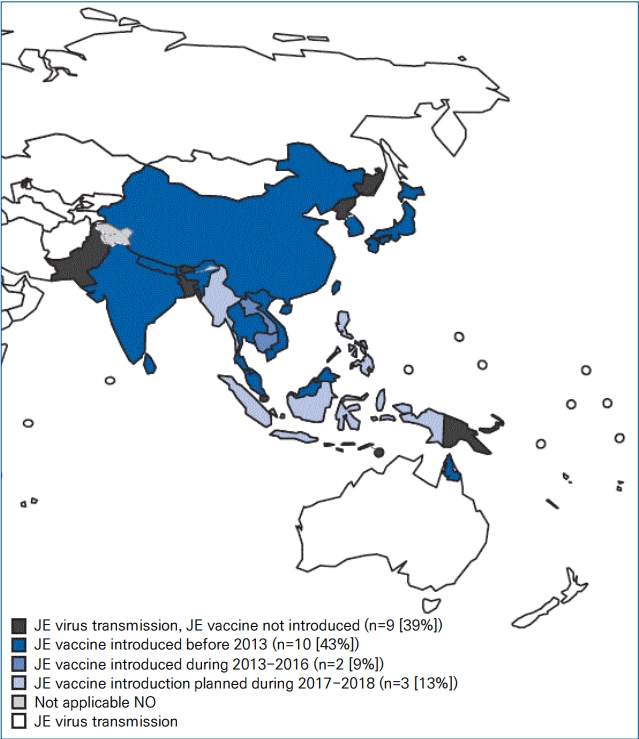
Since the introduction of a universal Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccination program and urbanization, the incidence of JE has dramatically decreased in Korea. However, recent JE cases have occurred, predominantly among unvaccinated adults and with a shift in age distribution. Continuous surveillance of the seroprevalence of JE is required to establish a proper immunization policy in Korea.
- Neurobehavior
- Psychological aspects in children and parents of children with chronic kidney disease and their families (1,999 times)
- Alemsungla Aier, Priya Pais, Vijaya Raman
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):222-229. Published online November 10, 2021
-

· Childhood chronic kidney disease (CKD) is complex and requires lifetime medical treatment.
· Children with CKD are at risk for emotional, behavioral, social, and academic difficulties that significantly affect their quality of life.
· Caring for children with CKD is stressful for families.
· These unique challenges are crucial and can negatively impact treatment outcomes.
· Awareness of and addressing these evolving psychosocial issues can foster their developing needs.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of maternal and child factors on stunting: partial least squares structural equation modeling (1,987 times)
- Agus Santosa, Essa Novanda Arif, Dinal Abdul Ghoni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):90-97. Published online May 4, 2021
-
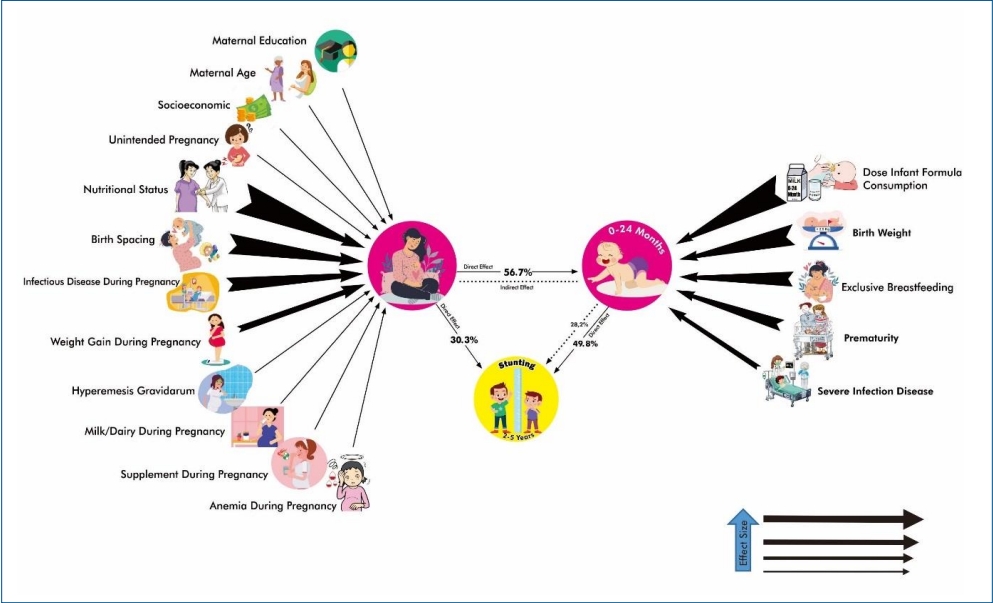
Question: What effects do maternal and child factors have on stunting? Are there significant indicators of stunting?
Finding: Child and maternal factors had 49.8% and 30.3% effects on stunting, respectively. The primary child factor was infant formula dose, while the primary maternal factor was nutritional status.
Meaning: More attention to nutritional status during pregnancy and ensuring the appropriate dose of infant formula at ages 6–24 months can prevent stunting.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children (1,981 times)
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-
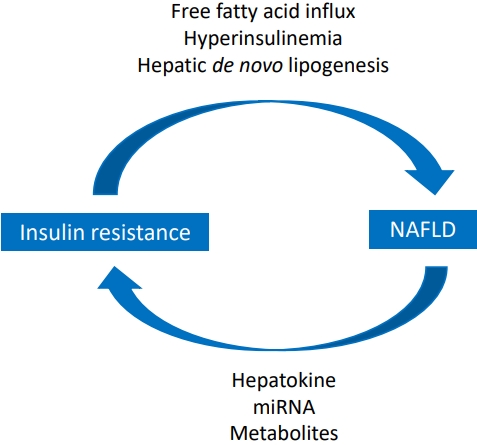
· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Neurology
- Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients (1,961 times)
- Seh Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):56-64. Published online August 23, 2021
-
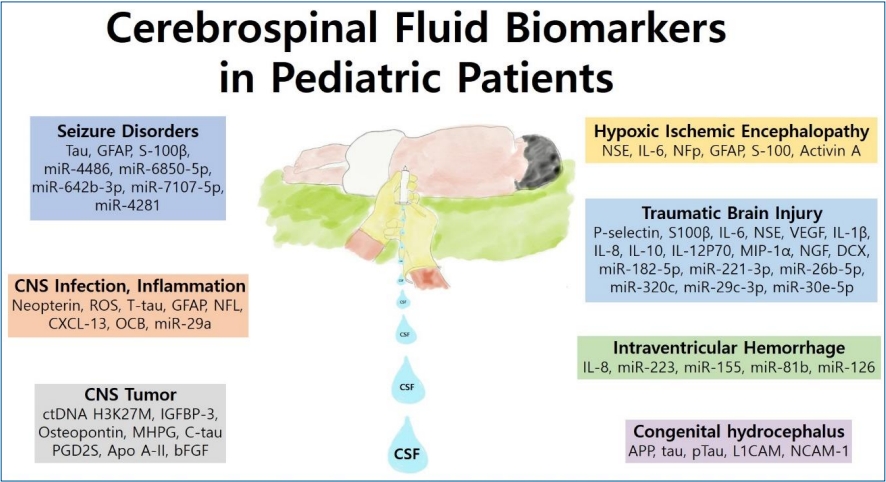
· Pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) components have been extensively evaluated as biomarkers of various neurologic diseases.
· Several promising candidate CSF biomarkers, including Tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, S100β, and interleukins, have been studied in pediatric patients with seizure disorders, central nervous system infections, inflammation, tumors, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injuries, intraventricular hemorrhage, and congenital hydrocephalus.
· Circulating microRNAs in the CSF are a promising class of biomarkers for various neurological diseases.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Telemedicine as progressive treatment approach for neonatal jaundice due to the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (1,960 times)
- Sukanya Sudhir Joshi, Bithiah Roy Benroy, Isabell Nelson Lawrence, Thanuja Jayasri Suresh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):269-271. Published online February 7, 2022
-
Question: How can the management of neonatal jaundice (NJ) be enhanced through telemedicine?
Finding: Teleconsultations, drive-through testing, and the use of an application to assess neonatal jaundice at home are being successfully used, but they must be further researched before being implemented on a larger scale.
Meaning: Recent technology allows for the treatment of NJ at home with an application that helps reduce hospital burden.
- Original Article
- Other
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study (1,958 times)
- Mahendra K. Pant, Abul. H. Ahmad, Manisha Naithani, Jayanti Pant
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):459-465. Published online May 19, 2022
-
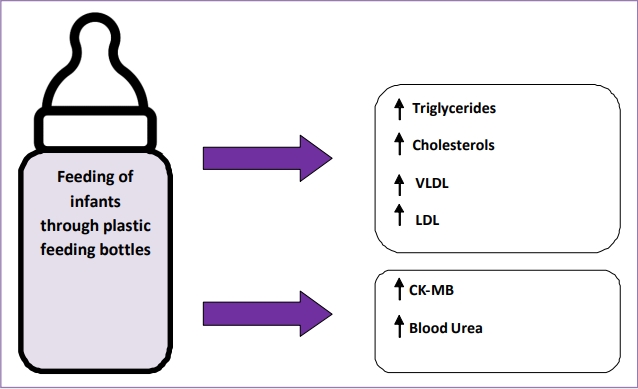
Question: Plastic feeding bottles are used commonly to feed infants who cannot be breastfeed. Does plastic bottle feeding produce biochemical changes in infants?
Finding: The plastic bottles leach out endocrine disruptors and affects bodily functions in terms of biochemical alterations like increased blood urea, raised creatine-kinase–MB levels, and altered lipid profile in infants exposed to bottle feeding.
Meaning: Plastic bottles feeding alters bodily functions in infants.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy (1,941 times)
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
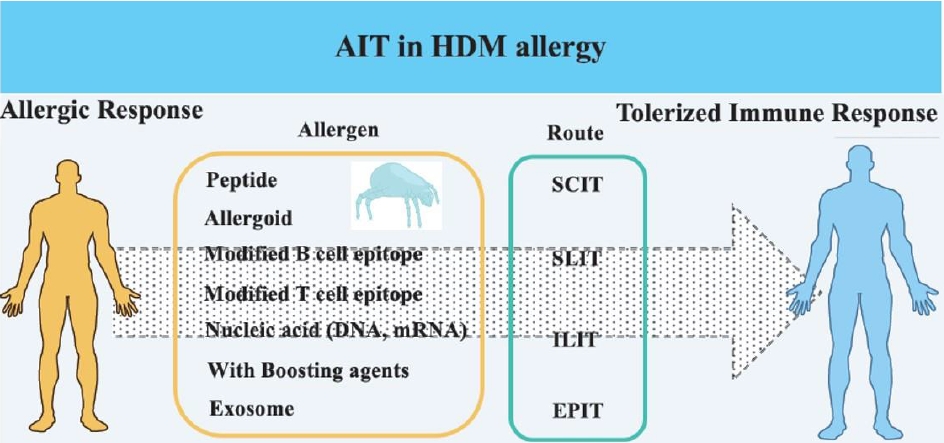
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Association between polycystic ovary syndrome and risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring: a meta-analysis (1,921 times)
- Azam Maleki, Saeid Bashirian, Ali Reza Soltanian, Ensiyeh Jenabi, Abdollah Farhadinasab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):85-89. Published online April 15, 2021
-
Question: Have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) increased risk of having an offspring with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
Finding: Six articles (3 cohort and 3 case-control studies; 401,413 total ADHD cases) met the study criteria. Maternal PCOS was associated with an increased risk of ADHD in the offspring based on odds ratio (OR) and relative ratio (RR) (OR, 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27–1.57) and (RR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.35–1.51), respectively.
Meaning: Our study showed that maternal PCOS is a risk factor for ADHD.
- Review Article
- Oncology
- Application of 3-dimensional printing implants for bone tumors (1,917 times)
- Jong Woong Park, Hyun Guy Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):476-482. Published online December 23, 2021
-

∙ The application of 3-dimensional (3D) printing in orthopedic oncology is summarized into bone and tumor modeling, patient-specific instruments (PSIs), custom-made implants, and tissue engineering.
∙ The 3D-printed customized implant is the most central application, while modeling and PSI often play adjunct roles.
∙ Short-term surgical outcomes of custom-made 3D-printed implants are promising.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







