Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Dual-strain probiotics Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates: a randomized controlled trial (4,576 times)
- Setthawut Sittiwong, Pornthep Tanpowpong, Pisut Pongchaikul, Pracha Nuntnarumit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):763-771. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: Can probiotics BB/LA reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates?
Finding: BB/LA supplementation induced more diverse beta diversity and increased relative abundances of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and decreased relative abundance Clostridium.
Meaning: Early BB/LA supplementation could reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review (4,571 times)
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (4,520 times)
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):454-462. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: What is the acceptance rate for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Finding: One-third of parents were hesitant to vaccinate their child. Parental willingness to vaccinate themselves, older patient age, and belief in the vaccine's potency were associated with vaccine acceptance.
Meaning: These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve vaccine acceptance among parents of children with SLE.
- Neurology
- Evaluation of pediatric migraine triggers: a single-center study (4,402 times)
- Hey-Joon Son, Joo-Ok Jin, Kon-Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):163-169. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: What are the primary triggers for pediatric migraines, and how do they impact clinical management?
Finding: Common triggers for pediatric migraines include sleep disturbances, academic stress, and motion sickness, with academic stress identified as the most intense.
Meaning: Recognizing and addressing specific triggers like sleep disturbance and academic stress is crucial to effectively managing pediatric migraines with emphasis on personalized care to improve outcomes.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children (4,369 times)
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-

· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Evaluation of Bak and Bcl-Xl gene expression among pediatric patients with acute primary immune thrombocytopenia (4,341 times)
- Amira Zaki Badawy, Samia Hassan Kandel, Iman Aly Ahmedy, Mahmoud Ahmed Elhawy, Sally Mohamed El-Hefnawy, Dina Fouad Sief El-Nasr Zidan, Hanan Hassan El-sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):901-908. Published online August 6, 2025
-

The B-cell lymphoma protein 2 family proteins Bak and Bcl- Xl, important markers of apoptosis, may contribute to primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Thus, their expression may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric ITP. Targeting these pathways may improve platelet survival, particularly in treatment-resistant cases. Personalized treatments based on apoptotic profiles can optimize therapy and reduce the unnecessary use of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations (4,280 times)
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers (4,210 times)
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty (4,141 times)
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents (3,984 times)
- Hae Sang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):90-91. Published online January 24, 2024
-
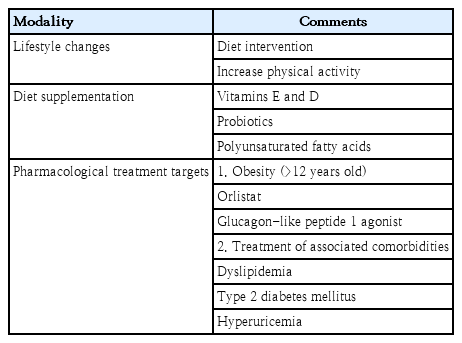
· With the increase in childhood obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a concern in recent years.
· NAFLD is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
· Lifestyle modifications are the mainstay treatment for NAFLD.
- Clinical Note
- Immunology
- Comparative analysis of rare periodic fever syndromes including the first Korean case of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome (3,973 times)
- Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Seo Kim, Jung Ok Shim, JungHwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):550-552. Published online September 24, 2024
-
- Editorial
- Neurobehavior
- Importance of pediatrician’s role in preventing positional plagiocephaly (3,955 times)
- Hee-Jeong Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):294-295. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Plagiocephaly is characterized by the asymmetrical shape of a baby’s head.
· Since positional plagiocephaly is associated with developmental delay and further musculoskeletal problems, early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents worsening of the condition.
· Pediatricians can educate parents about proper head positioning and encourage supervised tummy time during awake hours.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review (3,856 times)
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
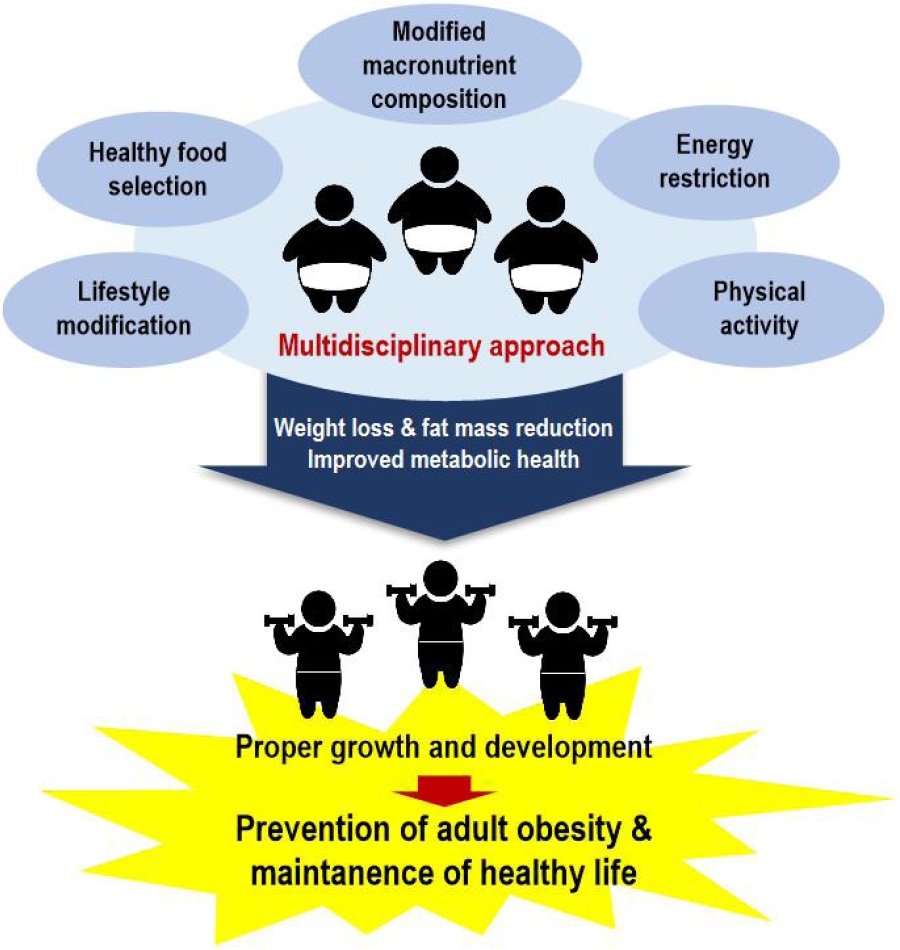
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review (3,839 times)
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia (3,789 times)
- Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children (3,780 times)
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-

Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Incidence, causative organisms, and risk factors of bloodstream infections in pediatric liver transplant patients: a systematic review (3,769 times)
- Mohamad Shieb, Rand Hasanain, Zara Arshad, Faisal A. Nawaz, Rahul Kashyap, Eric J. Stern
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):427-434. Published online April 5, 2024
-

The overall incidence of bloodstream infections was 23.5%. Gram-negative organisms occur at a much higher rate in pediatric liver transplant recipients then that the general pediatric population. However, when comparing pediatric and adult liver transplant recipients Gram-positive organisms occur with a much higher rate in the pediatric population highlighting the importance of early and broad spectrum antimicrobial coverage when bloodstream infections are suspected.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Exploring the role of laryngeal masks in neonatal resuscitation (3,706 times)
- Euiseok Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):247-248. Published online December 28, 2023
-
· Laryngeal masks (LMs) offer stable airway access and skill retention advantages, making them promising alternatives to positive-pressure ventilation in neonatal care.
· The ease of teaching LM insertion techniques to less experienced providers addresses the need for swift intervention and skill retention.
· Careful consideration of the benefits and challenges of LMs is essential in determining their effective integration into enhanced neonatal resuscitation protocols.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis (3,699 times)
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
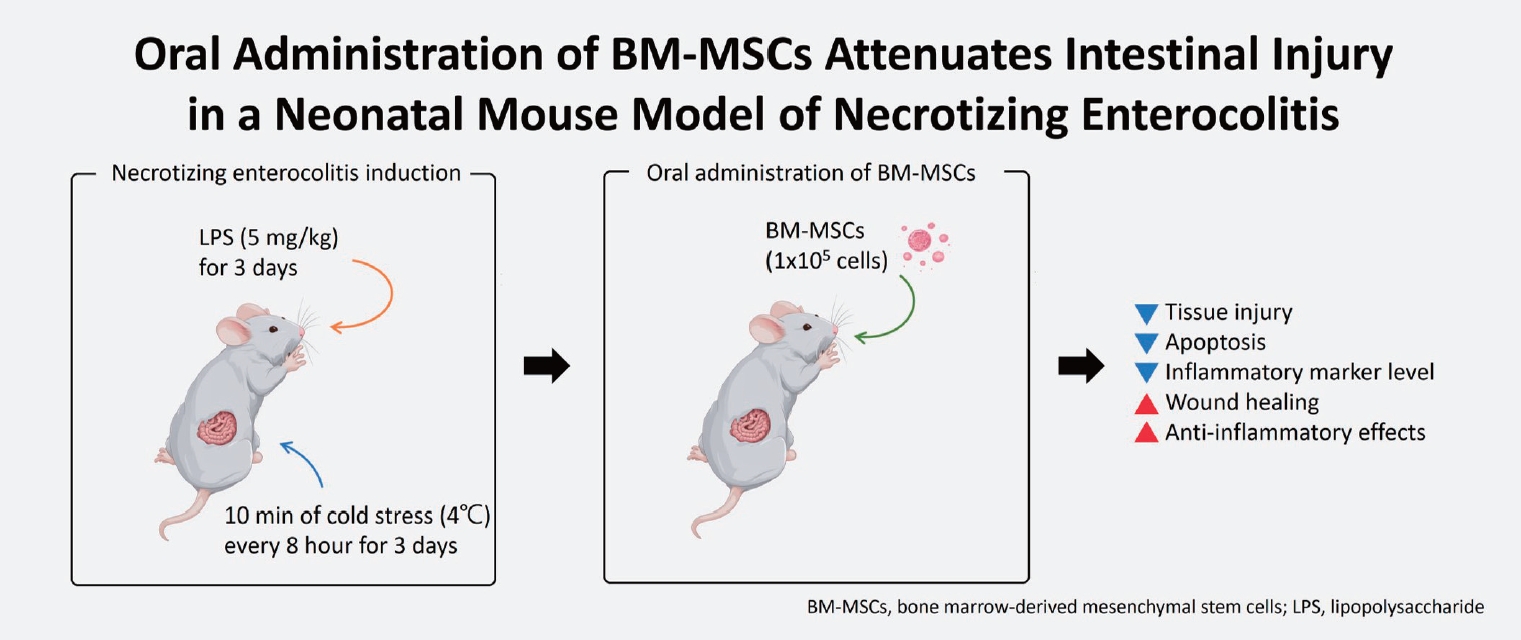
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study (3,694 times)
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (3,690 times)
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-
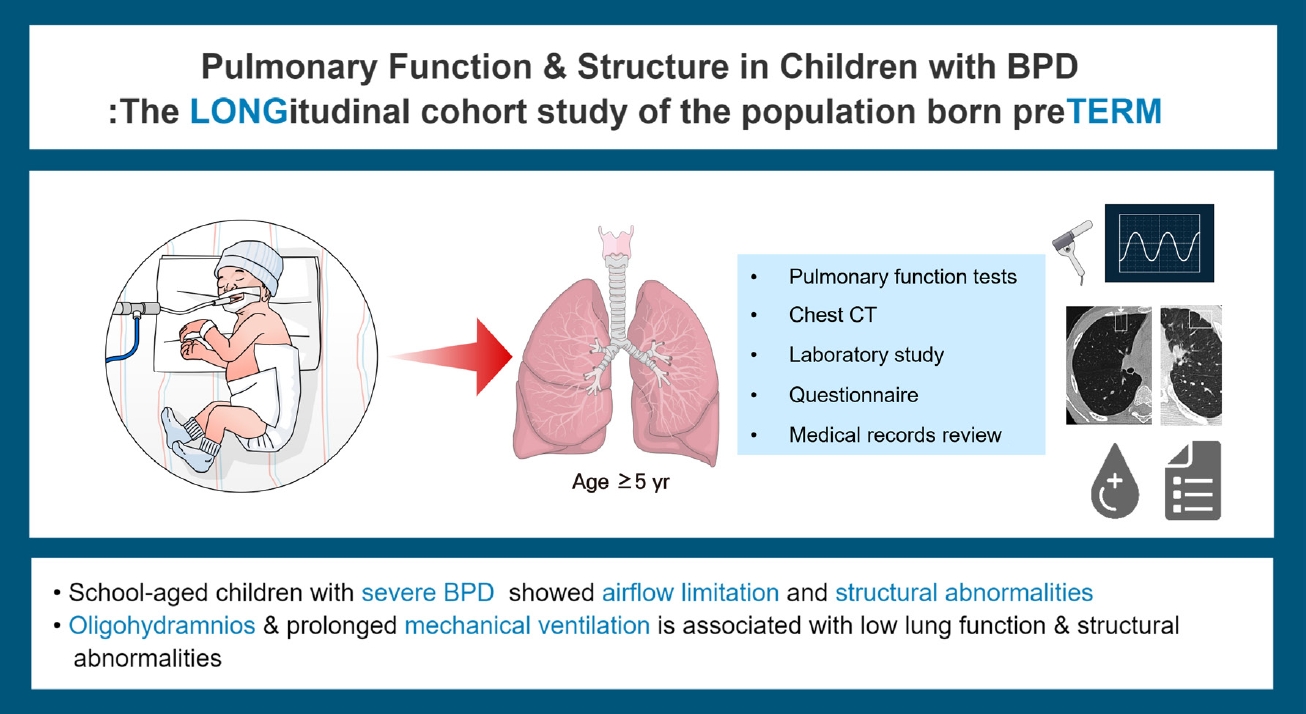
Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study (3,681 times)
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-

Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis syndrome caused by a novel CLDN1 mutation: a case report and literature review (3,656 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Varunvenkat M. Srinivasan, Rani Manisha, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Mayank Nilay, Harish Kumar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):858-867. Published online October 2, 2025
-

· Neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis (NISCH) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by cholestasis and manifestations such as generalized ichthyosis, alopecia, and dental anomalies.
· The clinical features of NISCH syndrome are distinct and necessitate an early genetic diagnosis.
· The disease phenotype can vary significantly, ranging from no liver involvement and transient neonatal cholestasis to end-stage liver disease.
· Management requires a multidisciplinary approach with long-term follow-up.
- General Pediatrics
- Bridging the gap: autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States and worldwide: a narrative review (3,626 times)
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Malika Goel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):852-857. Published online October 2, 2025
-

The prevalence of autism is increasing worldwide. The United States has the highest numbers, likely due to the availability of better treatment options. However, global disparities exist, especially in low-resource settings in which stigma, underdiagnosis, and limited services hinder care. A coordinated international approach emphasizing early screening, inclusive policies, and culturally sensitive support systems can bridge this gap and improve the outcomes for children with autism and their families worldwide.
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia (3,549 times)
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Saara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):465-473. Published online July 24, 2024
-

· Polymorphisms in interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonists may significantly affect the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
· IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms are correlated with severity and susceptibility to primary ITP in children.
- Infection
- Construction and validation of predictive models for intravenous immunoglobulin–resistant Kawasaki disease using an interpretable machine learning approach (3,515 times)
- Linfan Deng, Jian Zhao, Ting Wang, Bin Liu, Jun Jiang, Peng Jia, Dong Liu, Gang Li
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):405-414. Published online July 23, 2024
-

Question: Is there a reliable model to predict intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease (KD)?
Finding: We constructed 5 machine learning models to predict IVIG-resistant KD. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was superior to logistic, support vector machine, light gradient boosting machine and multiple layers perception models. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) value interpreted the contribution of each feature in XGBoost model.
Meaning: XGBoost model showed the excellent performance to predict IVIG-resistant KD with explainable and visualizable machine learning algorithm.
- Clinical, biochemical, and genetic study of TACE/TNF-α/ACE signaling pathway in pediatric COVID-19 infection (3,402 times)
- Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Sawsan M.A. Abuhamdah, Mohammed H. Hassan, Nagwan I. Rashwan, Eman A. Abd-Elmawgood, Haggagy Mansour, Hoda S. Sherkawy, Shymaa G. Rizk
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):704-717. Published online November 27, 2024
-

Question: Is the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (TNF-α-converting enzyme [TACE]/TNF-α/angiotensin converting enzyme [ACE]) involved in pediatric coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection?
Finding: Significantly increased circulating TACE/TNF-α and decreased ACE2 levels were noted. TNF-α-308G/A plays a significant role in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection among children. The ACE (I/D) (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) single nucleotide polymorphisms lack significant associations with pediatric COVID-19 infection.
Meaning: The TNF signaling pathway participates in pediatric COVID-19 infection.
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study (3,381 times)
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- Review Article
- Other
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the head and neck in patients with APC gene deletion mutations: a case report and scoping review of the literature (3,380 times)
- Koral M. Blunt, Monirah Albathi, Miriam Conces, Tendy Chiang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):428-433. Published online January 13, 2025
-

In this report, we describe our experience with a patient with an APC-related genetic syndrome who presented with a rare palatal lesion with characteristics of a schwannoma. We discuss the role of immunohistochemical staining in discerning the differential diagnosis.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- What we should know about pediatric heart failure: children are not small adults (3,272 times)
- Ja-Kyoung Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):62-64. Published online November 6, 2024
-
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) features high morbidity and mortality rates.
· Although adults and children can share a common diagnosis of heart failure, the underlying causes can differ significantly and require distinct therapeutic approaches.
· Treatments designed for adults are often applied to PHF despite the fundamental physiological and developmental differences between them.
· Child-specific data are vital for the development of tailored treatments to meet the unique needs of patients with PHF.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











