Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Lifelong medical challenges and immunogenetics of Turner syndrome (5,589 times)
- Won Kyoung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):560-568. Published online July 31, 2024
-
· This summary emphasizes the importance of the early diagnosis of Turner syndrome (TS) and presents a multidisciplinary approach to its prevention and management, high-lighting the need for customized care.
· Advancements in immunogenetic research may improve our understanding of TS and improve its outcomes.
· TS encompasses a wide array of medical challenges, including cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune, and mental health issues, as well as a heightened cancer risk.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Differences in immune cells and gene expression in human milk by parity on integrated scRNA sequencing (5,570 times)
- Dae Yong Yi, Hong-Jai Park, Min Sun Shin, Hyoungsu Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Insoo Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):141-152. Published online January 10, 2025
-

Question: Is there a difference in immune cells in human breast milk by parity?
Finding: There were higher proportions of monocytes and T/B cells in the primiparous and multiparous group, respectively. The expression of genes with a direct role in the infant immune system and immune response-related genes were highest in the primiparous group
Meaning: There were parity-dependent differences in the expression of genes between innate and adaptive immune cells.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- C3 glomerulopathy in children: experience at a resource-limited center (5,528 times)
- Soumya Reddy, Abhishek Ghante, Mahesha Vankalakunti, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):311-318. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: What are the clinicopathological features and outcomes of pediatric C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) in resource-limited settings?
Finding: Children with C3G in resource-limited settings have significant morbidities, and most experience kidney sequelae despite treatment. Electron microscopy was performed in only 50% of our patients, while none received complement assays or genetic testing.
Meaning: Pediatric C3G presentation, management, and kidney outcomes vary. Its thorough evaluation and management are challenging in resource-limited settings.
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study (5,484 times)
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy (5,476 times)
- You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient.
- Rheumatology
- Double-negative T cells in pediatric rheumatic diseases (5,471 times)
- Dimitri Poddighe, Tilektes Maulenkul, Kuanysh Dossybayeva, Gulsamal Zhubanova, Zaure Mukusheva, Lyudmila Akhmaltdinova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):632-640. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Double-negative T (DNT) cells appear to be increased in several pediatric rheumatic diseases and this finding may be correlated with disease activity to some extent. However, due to significant heterogeneity in several methodological aspects, further investigations in rheumatic children are needed to assess the potential relevance of DNT cells as biomarkers and clarify their immunopathological role.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in anemic children before versus after age 2 years: a form of hidden hunger in India (5,423 times)
- Sahil Goel, Ruchika Bhatnagar, Anita Kumari, Brig Prem Lochan Prasad, Lahar Sahai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):116-118. Published online January 24, 2024
-
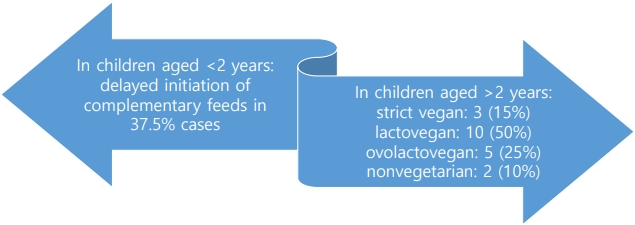
- Review Article
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases (5,349 times)
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-
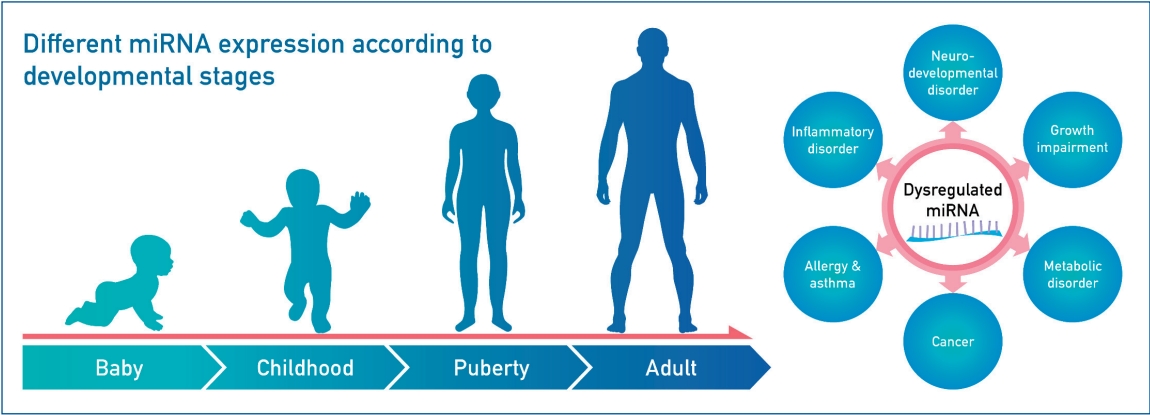
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes (5,329 times)
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Recent advances in understanding pathophysiology of non-nutritional stunting in very preterm infants (5,275 times)
- Eduardo Cuestas, Alina Rizzotti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):287-297. Published online December 23, 2024
-

· Previous reviews of extrauterine growth restriction focused mainly on weight growth restriction caused by nutritional factors or pathological conditions.
· This review summarizes recent developments in the pathophysiology of nonnutritional length growth restriction in very preterm infants with focus on the impact of sustained neonatal inflammation on their short- and long-term outcomes.
· Further research is needed to investigate optimal strategies to improve length growth restriction in very preterm infants.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Comparative analysis of goal attainment for helmet therapy versus conservative management for positional plagiocephaly in infants (5,270 times)
- Bjoern Vogt, Ariane Deutschle, Georg Gosheger, Adrien Frommer, Andrea Laufer, Henning Tretow, Robert Roedl, Gregor Toporowski
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):892-900. Published online October 2, 2025
-
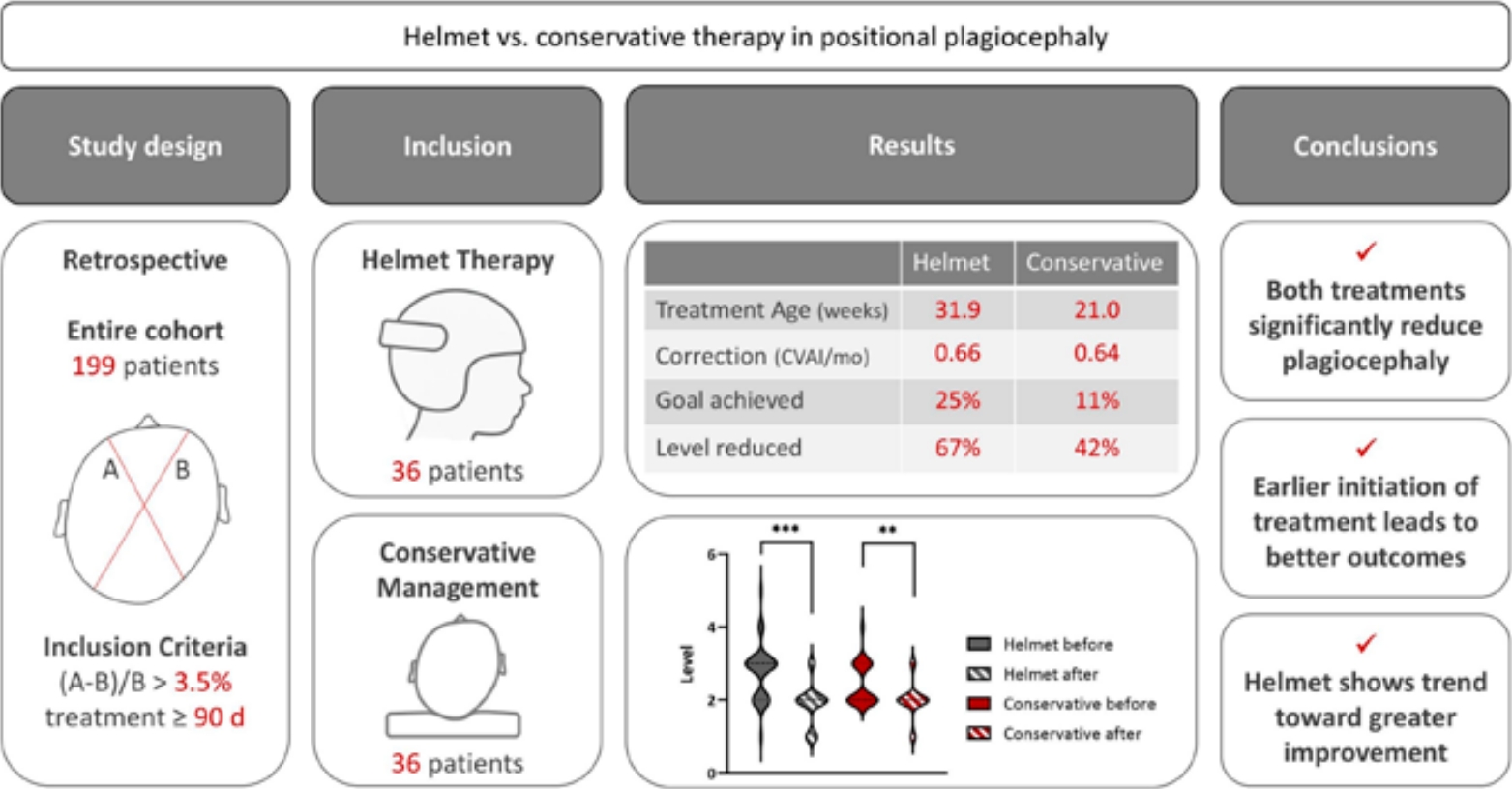
Question: Is helmet therapy more effective than conservative management in treating positional plagiocephaly?
Finding: Both approaches reduced cranial asymmetry with comparable correction speed. Helmet therapy showed a trend toward greater severity reduction.
Meaning: Early treatment initiation was the strongest predictor of improvement. Helmet therapy may offer additional benefit in more severe cases.
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life (5,261 times)
- Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings.
- Pulmonology
- Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: an impulse oscillometry study (5,258 times)
- Anuvat Klubdaeng, Kanokporn Udomittipong, Apinya Palamit, Pawinee Charoensittisup, Khunphon Mahoran
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):319-325. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: Does obesity in preschool children affect lung function, and which obesity indices can predict such alterations?
Finding: Preschool children with obesity exhibit impaired lung function characterized by elevated total and peripheral airway resistance. Waist-to-height ratio was the strongest predictor of such changes.
Meaning: Early obesity prevention and treatment are needed. Monitoring waist-to-height ratio, body weight, and body mass index may help identify children at risk of altered lung function.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Effect of postoperative enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance in critically ill children (5,243 times)
- Irene Yuniar, Kadek Apik Lestari, Antonius Hocky Pudjiadi, Fatima Safira Alatas, Yoga Devaera
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):790-800. Published online May 30, 2025
-

Question: Does high-protein enteral nutrition better increase the average nitrogen balance (NB) and decrease the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) level of critically ill postoperative children than standard-protein enteral nutrition?
Finding: The study demonstrated a significant increase in average NB but no significant decrease in I-FABP levels in the high- versus low-protein group.
Meaning: These findings suggest that high-protein enteral nutrition can improve NB in critically ill postoperative children, thereby supporting their recovery.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury (5,228 times)
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Screen time and neurodevelopment in preschoolers: addressing a growing concern in pediatric practice (5,222 times)
- Soongang Park, Hyewon Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):434-436. Published online January 13, 2025
-
· Excessive screen time in preschoolers is associated with neurodevelopmental delays, particularly during the early years of life.
· Parental supervision and national guidelines are critical in mitigating the negative impacts of excessive screen time and fostering healthy media habits in preschoolers.
- Hematology
- Absolute versus functional iron deficiency (5,176 times)
- Hye Lim Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):138-140. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· Iron deficiency (ID), the most common cause of anemia, can be classified into absolute and functional types. Absolute ID is a state of low total body iron, while functional ID is a state of imbalance between iron demand and iron availability due to inflammation and/or infection.
· ID is diagnosed by serum ferritin and transferrin saturation levels.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Role of nonpharmacological concussion management in children: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (5,091 times)
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Alvin Ivander, Rr. Suzy Indharty, Steven Tandean, Anastasia Grace Milenia Ginting, Masrini Ginting, Felix Khosasi, Elbert
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):569-579. Published online October 28, 2024
-

The long-term effects of concussion for pediatric patient remains unclear. Children and teenagers do not experience or recover from concussion in the same manner as adults do. Concussions can cause a variety of anatomical and functional alterations. Nonpharmacological approach in pediatric concussion management is an understudied field of research with significant ability to affect prognosis and quality of life. Active rehabilitation and occupational therapy were especially promising.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Parental support and exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months in West Java, Indonesia: a mixed-methods approach (5,081 times)
- Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fadila Wirawan, Wawan Gunawan, Primasti Nuryandari Putri, Nurul Husna Mohd Shukri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):358-367. Published online June 21, 2024
-

Question: Does paternal support affect exclusive breastfeeding failure?
Finding: Exclusive breastfeeding failure by 3 months was affected by paternal support.
Meaning: Fathers should be included in breastfeeding education and antenatal care.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis (5,034 times)
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Impact of Xmn1 polymorphism on hydroxyurea therapy in children with HbE-β non-transfusion dependent thalassemia: a cohort study (5,028 times)
- Saheli Roy, Paramita Bhattacharya, Atanu Kumar Dutta, Mrinal Kanti Das
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):437-444. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: Does the T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influence hydroxyurea efficacy in children of Eastern descent with fetal hemoglobin (HbE)-β nontransfusion dependent thalassemia (NTDT)?
Finding: Decrease in transfusion requirement and increase in height following hydroxyurea therapy was noted in both groups, however, change in CT was more critical than that in CC genotype.
Meaning: T allele of Xmn1 polymorphism favorably influences hydroxyurea efficacy in children with HbE-β NTDT.
- Perspective
- Other
- Telemedicine in pediatrics: things to consider (4,948 times)
- Sandhya J. Kadam, Archana Reddy Bongurala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):326-328. Published online February 3, 2025
-

This article highlights the benefits, challenges, and current significance of telemedicine. Future research is needed, primarily to address the challenges of optimizing the implementation of telehealth. To use telemedicine effectively and efficiently for the timely diagnosis and management of patients, an evaluation of current telemedicine practice is needed. Analysis of shortcomings and advantages can help enhance healthcare delivery to pediatric patients, making it more accessible for future use.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Quantifying myelin in neonates using magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic literature review (4,931 times)
- Nabila Hanem Arshad, Hasyma Abu Hassan, Nur Farhayu Omar, Zurina Zainudin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):371-385. Published online December 6, 2023
-

Question: This systematic review attempts to discover the best magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for myelin quantification in neonates by evaluating various MRI parameters and their reproducibility.
Finding: Since the benefits of using synthetic MRI for quantifying myelin in neonates outweigh the very minor draw- backs, it is recommended.
Meaning: The findings suggest the importance of identifying noninvasive MRI techniques available to assess myelin tissue in neonates, which aid in diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Original Article
- Immunology
- Serum bactericidal activity against meningococcus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (4,865 times)
- Soyoung Lee, Kyung-Hyo Kim, Ji Hyen Lee, Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):362-369. Published online January 13, 2025
-

Question: What is the level of immunity against meningococcal infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) under the age of 19, and is vaccination against meningococcus necessary for these patients, given their susceptibility to infections due to immunosuppressive treatments and disease characteristics?
Finding: Although some of our study patients exhibited serum bactericidal activity against meningococci, most remained seronegative.
Meaning: These findings suggest that patients with SLE who are at risk of meningococcal infection receive appropriate vaccinations.
- Other
- Balance assessment with decreased base of support for children with disabilities (4,799 times)
- Guilherme M. Cesar, Madison Giebler, Thad W. Buster, Judith M. Burnfield
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):718-724. Published online November 11, 2024
-

Question: Can a balance task with narrowed base of support indicate overall functional balance control in children with disabilities?
Finding: While single-limb standing could explain overall balance control for children with disabilities, it was unrelated with balance control for typically developing children.
Meaning: One balance task with narrowed base of support can be used as practical assessment of balance abilities for children with disabilities when allocated session time is of concern.
- Hematology
- Hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia: links to vitamin cofactor deficiencies and oxidative stress (4,793 times)
- Arzu Dadashova, Gunay Aliyeva, Rana Rahimova, Gulnara Azizova, Khayala Mammadova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):819-830. Published online July 8, 2025
-

Question: What are the biochemical and clinical correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia, and how does it relate to vitamin status, oxidative stress, and splenectomy?
Finding: Most pediatric β-thalassemia patients exhibited severe hyperhomocysteinemia, which was strongly associated with folate and B12 deficiencies and influenced oxidative stress patterns, particularly in splenectomized individuals.
Meaning: These findings suggest that routine monitoring and correction of B-vitamin deficiencies may mitigate hyperhomocysteinemia-related risks in pediatric thalassemia.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status (4,742 times)
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum in preterm neonates: a double-blind placebocontrolled randomized trial (4,724 times)
- Ameneh Lamsehchi, Maryam Shokouhi Solgi, Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Elahe Talebi Ghane, Kiana Kimiaei Asadi, Sina Azadnajafabad
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):73-79. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What are the short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum (OAC) in preterm neonates?
Finding: This study demonstrated the significantly lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis, clinically suspected sepsis, shorter hospital stay, period to full enteral feeding, and antibiotic therapy period in the OAC group.
Meaning: This trial may further expand the clinical application of OAC in premature infants to reduce their length of hospital stay and complications.
- Endocrinology
- Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone score changes in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (4,708 times)
- Pattara Wiromrat, Yutapong Raruenrom, Phanpaphorn Namphaisan, Nantaporn Wongsurawat, Ouyporn Panamonta, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):238-246. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of an impaired trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone microarchitecture, in adolescents with 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD)? Do prednisolone and hydrocortisone affect TBS differently in this patient population?
Finding: Impaired TBS was observed in 18% of participants. Prednisolone use negatively impacted TBS change.
Meaning: Impaired TBS is prevalent among adolescents with 21OHD. Prednisolone impairs trabecular bone microarchitecture development.
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents (4,583 times)
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
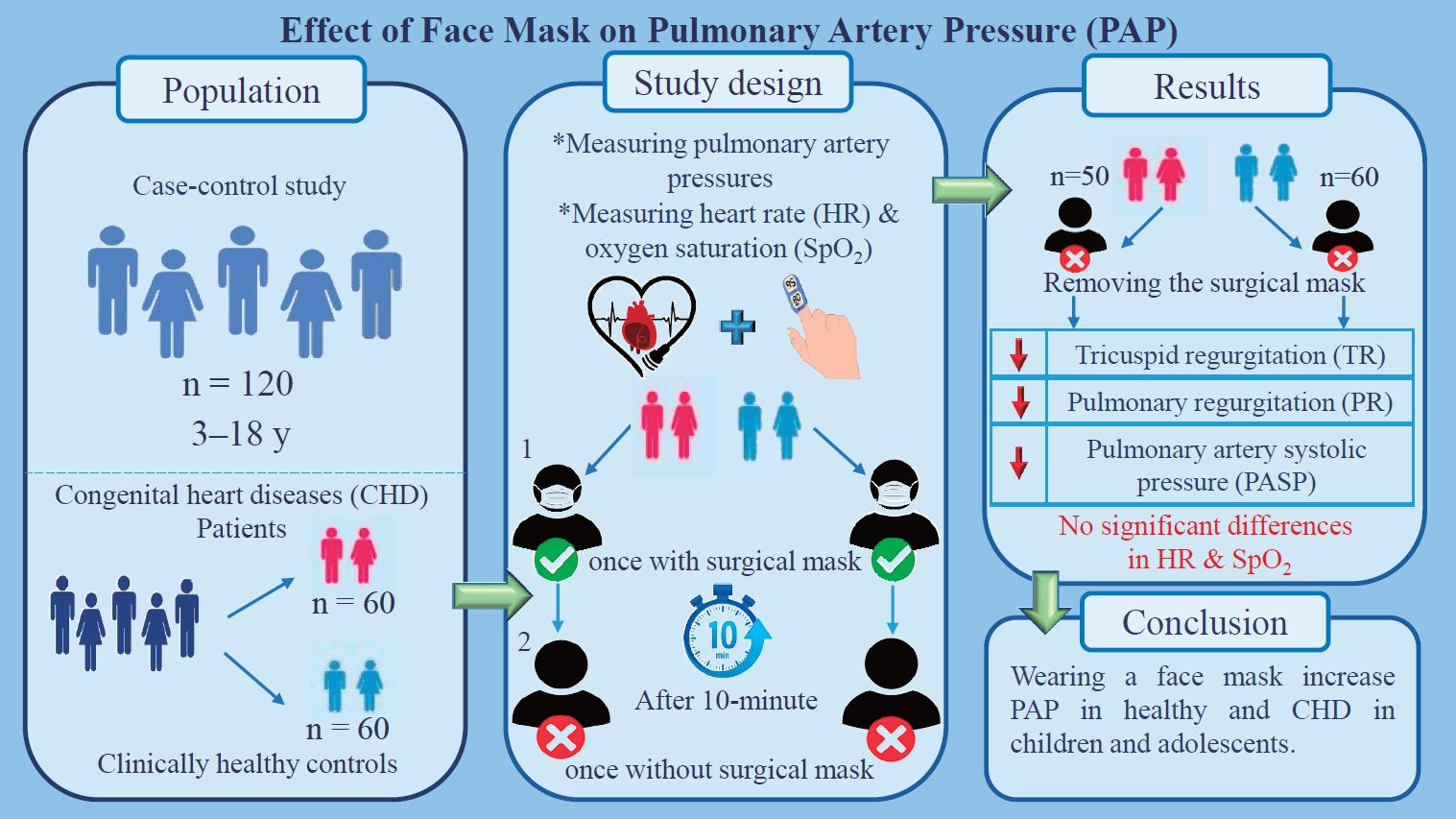
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











