Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms in children with primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Seham Mohamed Ragab, Wafaa Moustafa Abo ElFotoh, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy, Eman Abdelfatah Badr, Sara Khairat Ali Mostafa, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid
-
Background: The pathophysiology and susceptibility of children to primary immune thrombocytopenia are linked to polymorphisms of the interleukin (IL)-1B and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonist genes.
Purpose: To investigated the association between the susceptibility and severity of primary ITP in children and the IL-1B and IL-1R antagonist gene polymorphisms. Methods: This comparative case-control study was con-ducted at the Menoufia University Hospital Hematology and... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.00577 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Comprehensive evaluation of the child with global developmental delays or intellectual disability
- Abdullah Aldosari, Tahani Aldosari
-
Global developmental delay (GDD) and intellectual disability (ID) are relatively common neurodevelopmental disorders that significantly impact affected children, their families, and society. The etiology of GDD/ID is notably diverse, encompassing both genetic and acquired factors. Although the precise cause of most GDD/ID cases remains unclear, an estimated half of all cases can be attributed to genetic factors. Thus, a detailed... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01697 [Accepted]
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
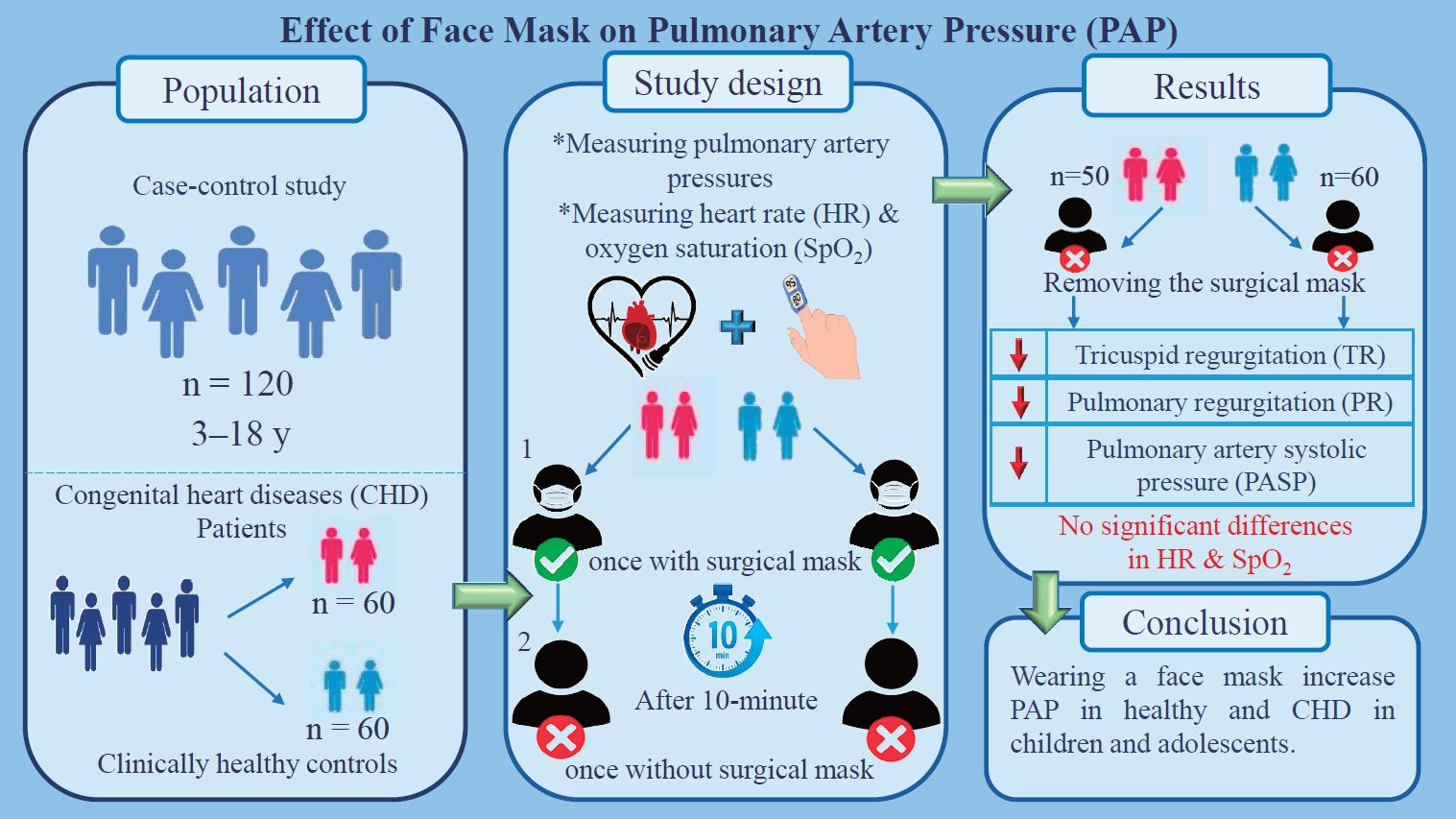
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Review article
- Evidence-based management guidelines for noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in children and adolescents
- Eun Lee, Kyunghoon Kim, You Hoon Jeon, In Suk Sol, Jong Deok Kim, Taek Ki Min, Yoon Ha Hwang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Dong In Suh, Hwan Soo Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Sung-Il Woo, Yong Ju Lee, Sungsu Jung, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Gwang Cheon Jang
-
Noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis is a chronic respiratory disease that carries high socioeconomic and medical burdens and is caused by diverse respiratory illnesses. To improve clinical outcomes, early recognition, active treatment of exacerbations, and prevention of further exacerbations are essential. However, evidence for the treatment and prevention of acute exacerbation of noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis, especially in children, is lacking. Therefore, the... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.00871 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
-
A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01039 [Epub ahead of print]
- Original Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-

Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Review Article
- Infection
- COVID-19 among infants: key clinical features and remaining controversies
- Nevio Cimolai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):1-16. Published online November 27, 2023
-
· Clinical studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in infants should be supported by rigorous laboratory diagnostic criteria.
· Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spreads to infants similarly to other viral respiratory infections.
· Among infants ≤1 year of age beyond the immediate postpartum period, COVID-19 is relatively mild, but even the low risk of severe disease requires prevention.
· Comorbidities increase infection vulnerability and complications in infants.
· Clinical and laboratory data do not sufficiently distinguish COVID-19 from other respiratory viral infections.
· Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 is uncommon among infants.
· Unique infection sequelae, including multi-inflammatory syndrome in children and neonates and long COVID require further study and refinement of diagnostic criteria.
· Infection control standards applied to mother-infant dyads should be tempered by standard preventive strategies, maternal input, accommodation potential, and overall safety.
· Maternal vaccination prevents disease in early infancy.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old
- Dedy Rahmat, Agus Firmansyah, Ina S. Timan, Saptawati Bardosono, Joedo Prihartono, Pramita Gayatri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):538-544. Published online November 16, 2023
-
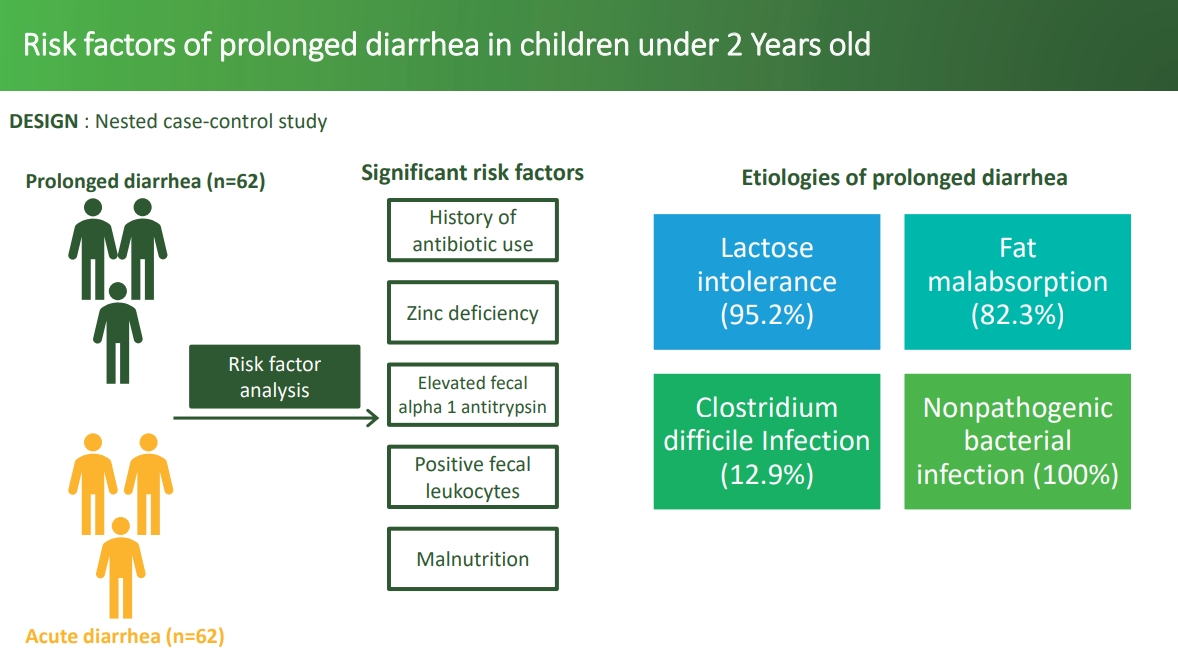
Question: What are the risk factors for prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old?
Finding: History of antibiotic use, zinc deficiency, and elevated fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels were the main risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Rational antibiotic usage is necessary as well as thorough testing of serum zinc level and fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children
- Yu Kyung Cho, Jin Lee, Chang Nyol Paik
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):377-383. Published online August 21, 2023
-
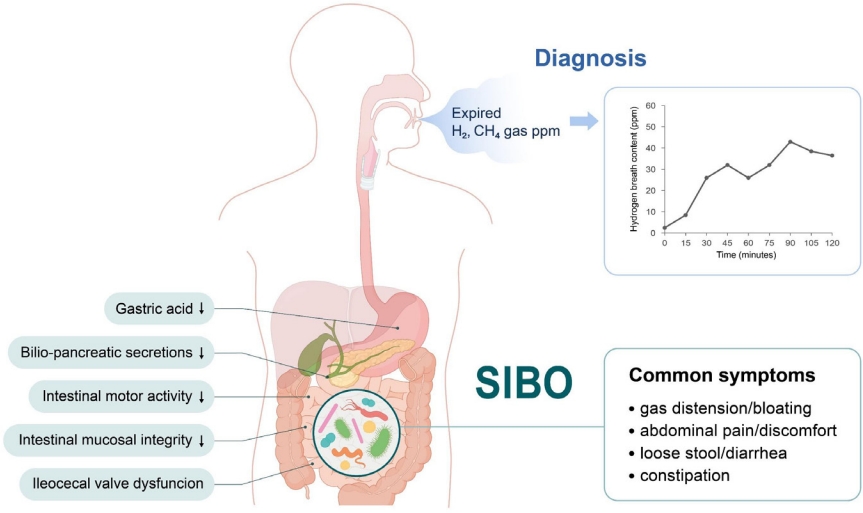
· Pediatric small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) manifestations range from nonspecific abdominal symptoms to malabsorption or malnutrition.
· SIBO is prevalent in children and adolescents with functional abdominal pain disorders.
· Predisposing factors include disturbed intestinal motility, altered anatomy, and/or abnormal body defense systems against intestinal bacteria.
· Breath tests are safe and noninvasive.
· Treatment principles include managing predisposing conditions, nutritional support, symptom control, and antibiotics.
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
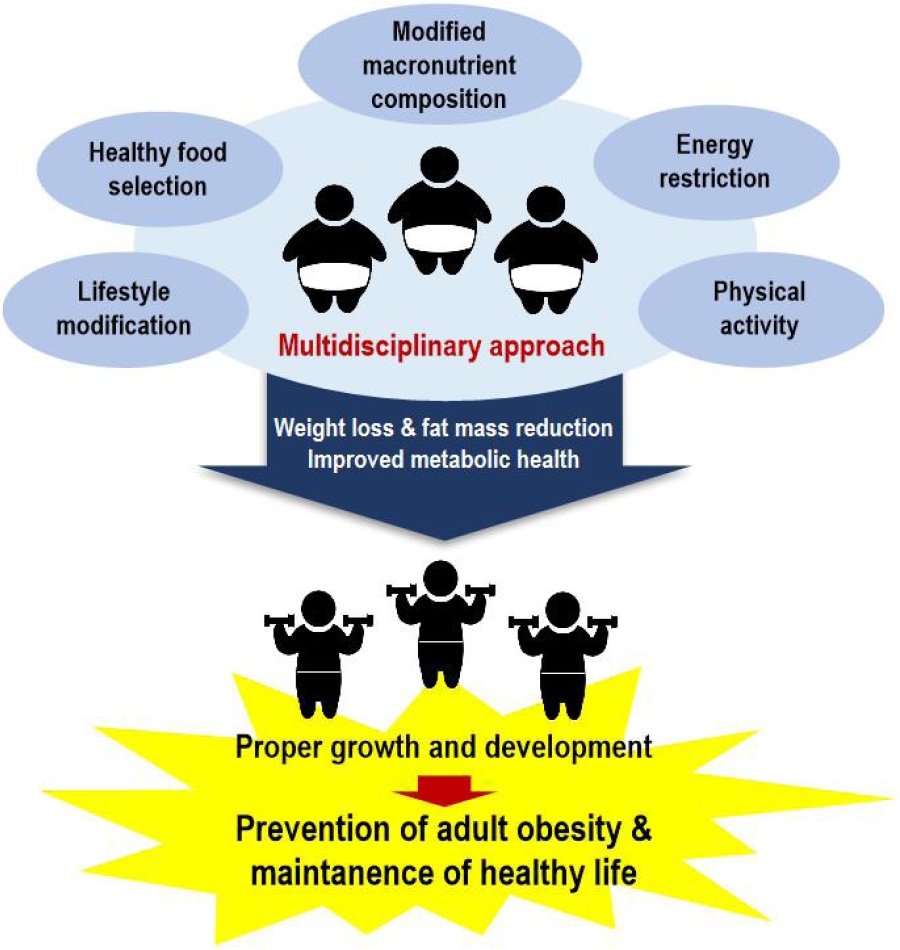
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
- Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
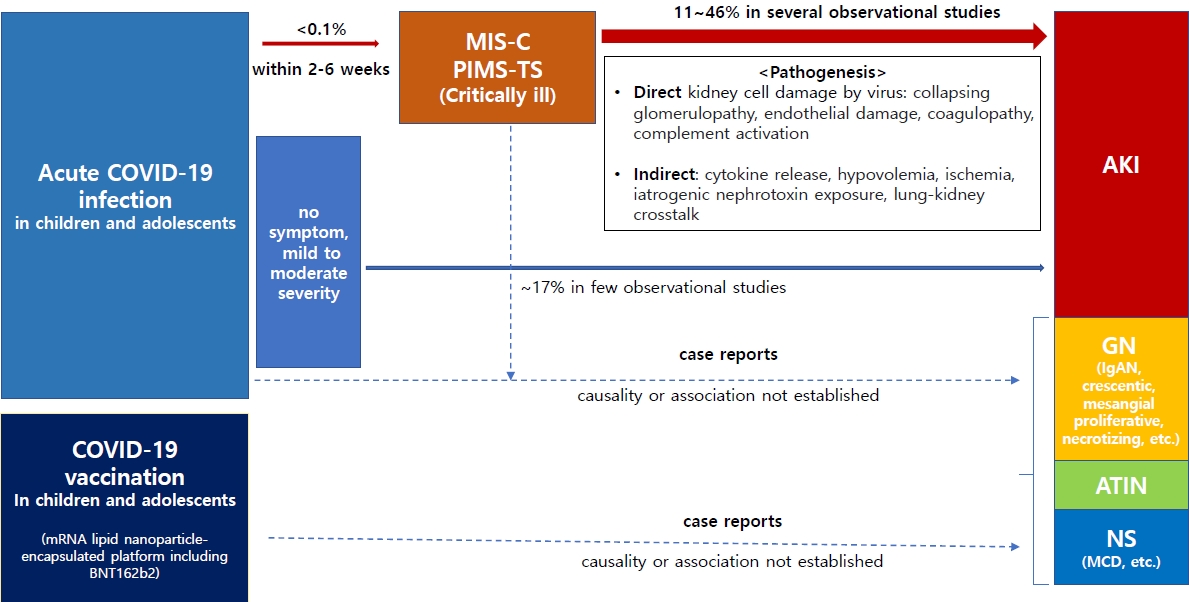
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
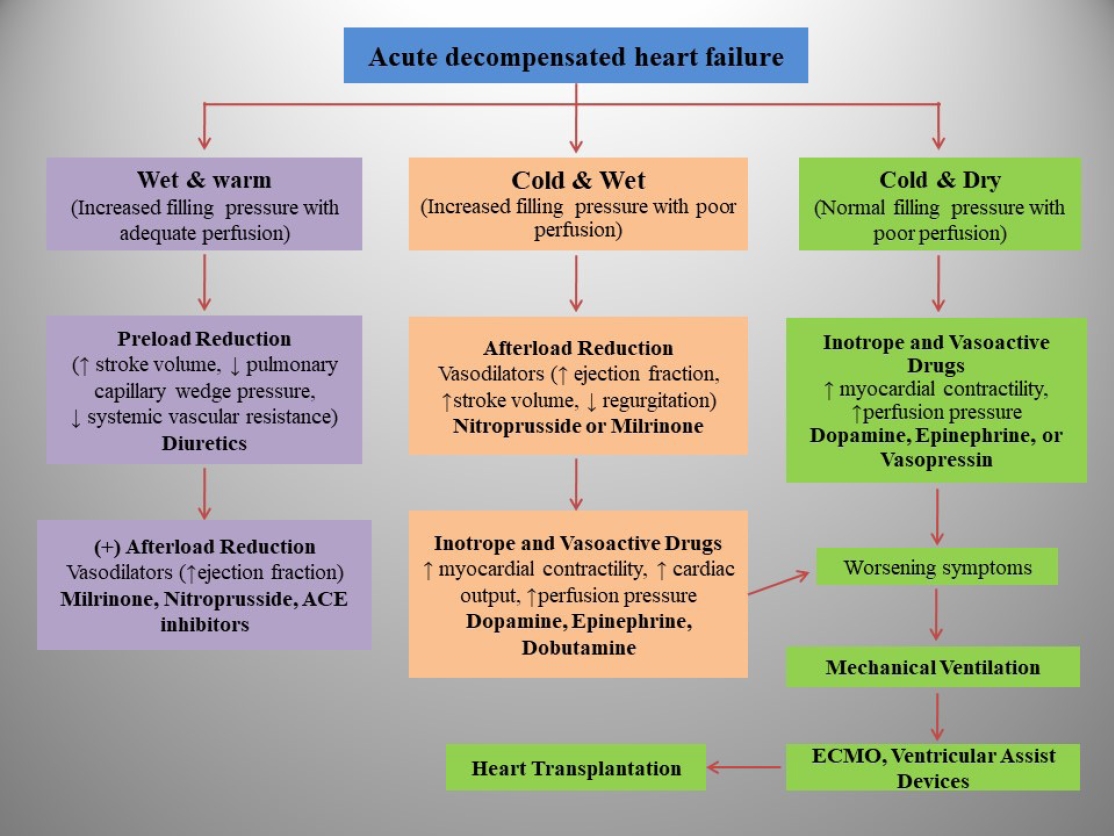
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Infection
- Community-acquired pneumonia in children: updated perspectives on its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment
- Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):80-89. Published online June 14, 2023
-
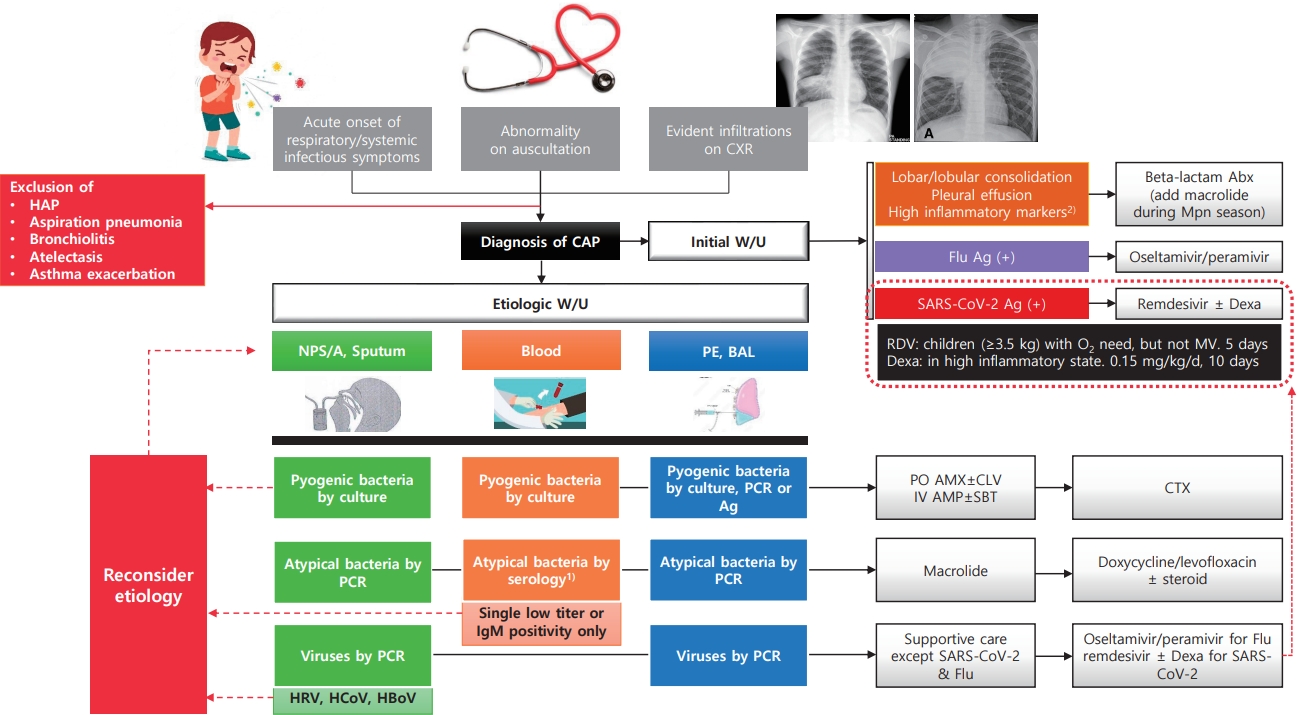
· Most commonly confirmed causes of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae (8%–40%) and respiratory syncytial virus (15%–20%).
· Pyogenic bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae (40%–50%) and Streptococcus pyogenes (10%–25%), are detected in 2%–5% of children hospitalized with CAP.
· CAP should be diagnosed conservatively according to clinical and radiological criteria.
· The etiology should be identified via appropriate test result interpretation.
- Allergy
- Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in children: focus on systemic Th2 cytokine receptor antagonists and Janus kinase inhibitors
- Jeong Hee Kim, Mona Salem Samra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):64-79. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized by a strong T helper (Th)2 response, although the extents of Th22, Th17/ interleukin (IL)-23, and Th1 responses vary among disease subtypes.
· Children with moderate to severe AD may require early systemic therapy to reduce the systemic inflammation caused by increased Th2 cytokine levels.
· Dupilumab, which blocks IL-4/IL-13 receptor, has equivalent efficacy for extrinsic and intrinsic AD and a favorable safety profile in infants and children aged 6 months and older.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration.
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
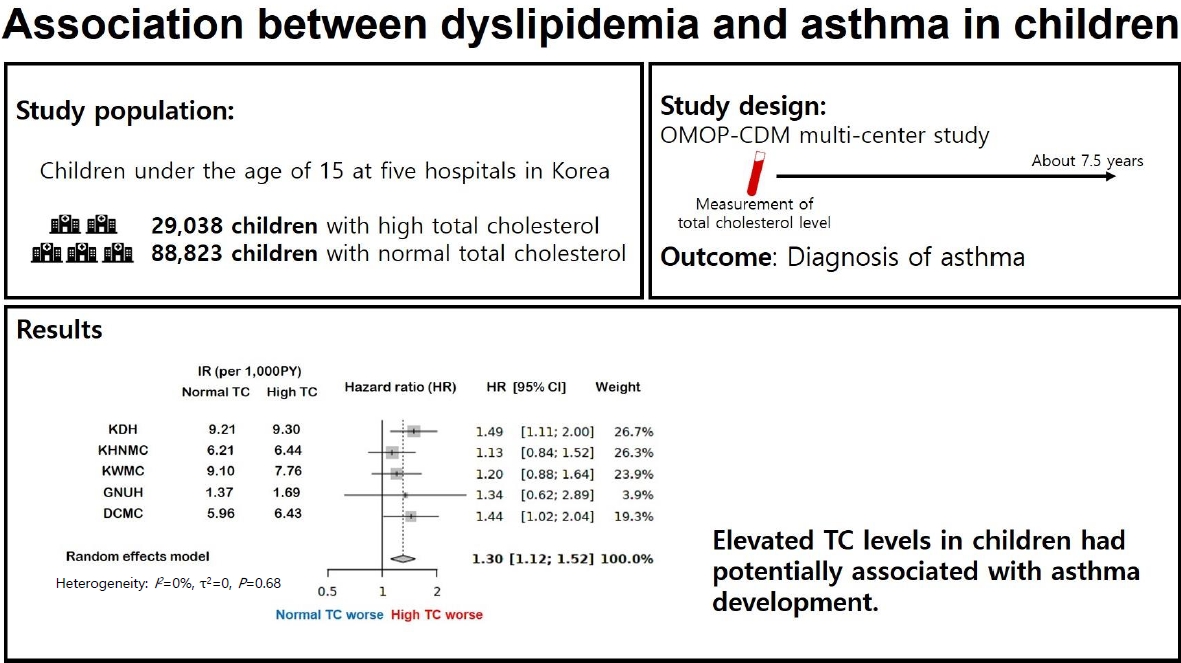
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Assessing indicators and clinical differences between functional and organic childhood constipation: a retrospective study in pediatric gastroenterology clinics
- Hasan M. Isa, Fatema A. Alkharsi, Fatema A. Salman, Maryam S. Ali, Zahra K. Abdulnabibi, Afaf M. Mohamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):296-306. Published online June 14, 2023
-
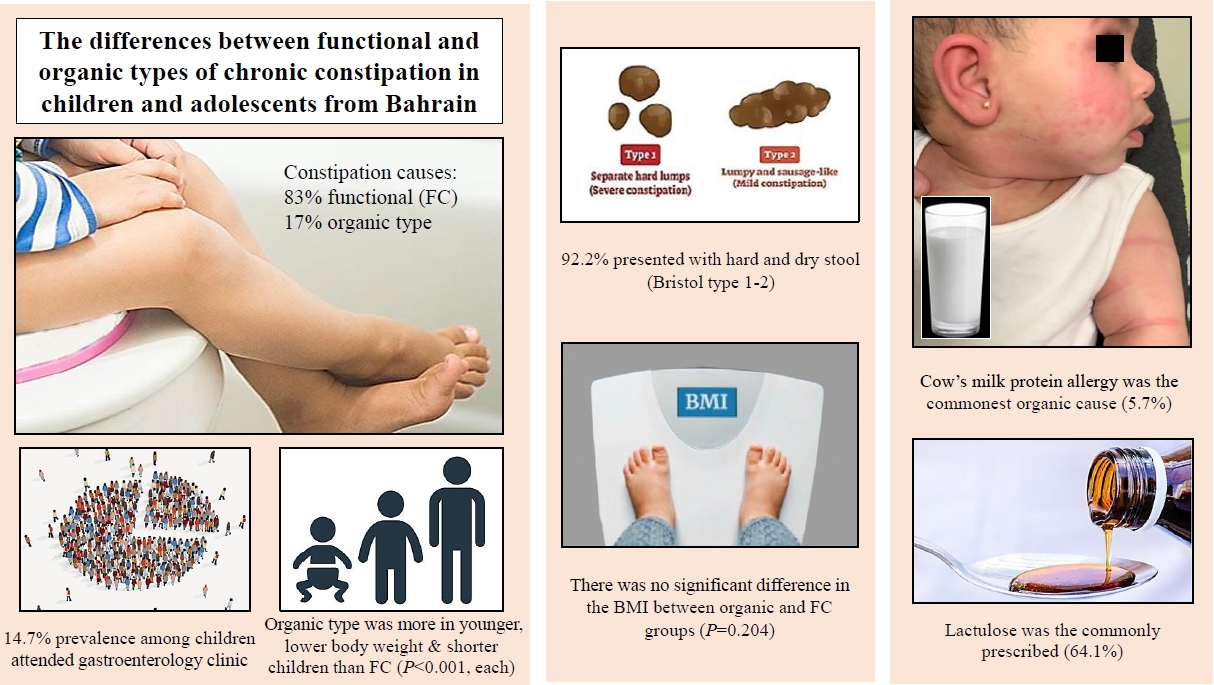
Question: What causes childhood constipation, and what can predict organic constipation?
Finding: Constipation represents 14.7% of gastroenterology visits. Functional constipation is more common among constipation types, while organic constipation is more common in young children and those with a low body weight, stunted growth, mucus in the stool, and associated diseases.
Meaning: Younger children and those with lower growth or mucus in the stool should be assessed for underlying organic causes of constipation.
- Review Article
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-
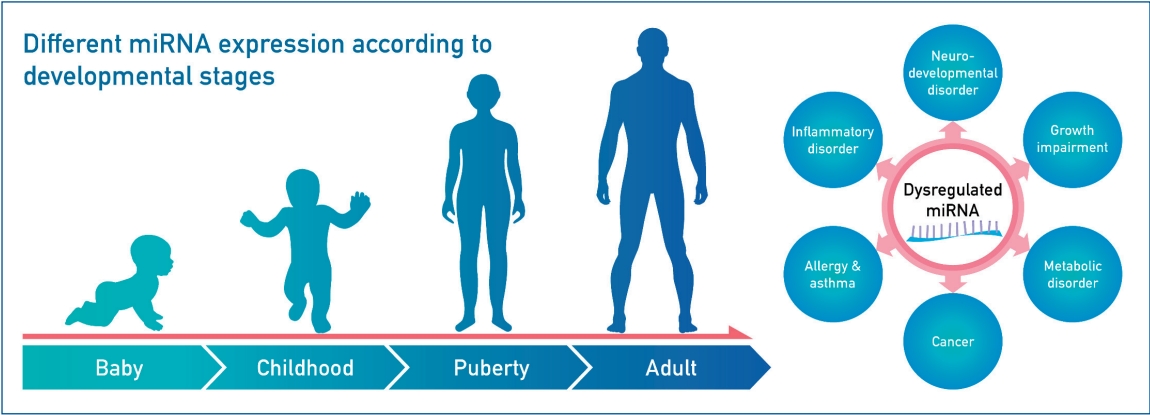
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Echocardiographic reference z scores of right ventricular dimension and systolic function of children aged 5–12 years
- Alaba Busola Oladimeji, Moriam Omolola Lamina, Peter Odion Ubuane, Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle, Omolara Adeolu Kehinde, Barakat Adeola Animasahun, Olisamedua FidelisNjokanma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):215-222. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Question: Z score reference values for right ventricular size and systolic function in children using echocardiography are available in several countries. Despite the high burden of diseases involving the right ventricle in Nigeria, these reference values have limited applicability.
Finding: The right ventricular sizes of Nigerian children differed from those published elsewhere.
Meaning: These reference values will aid the treatment, monitoring, and pre- and postintervention for Nigerian children.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
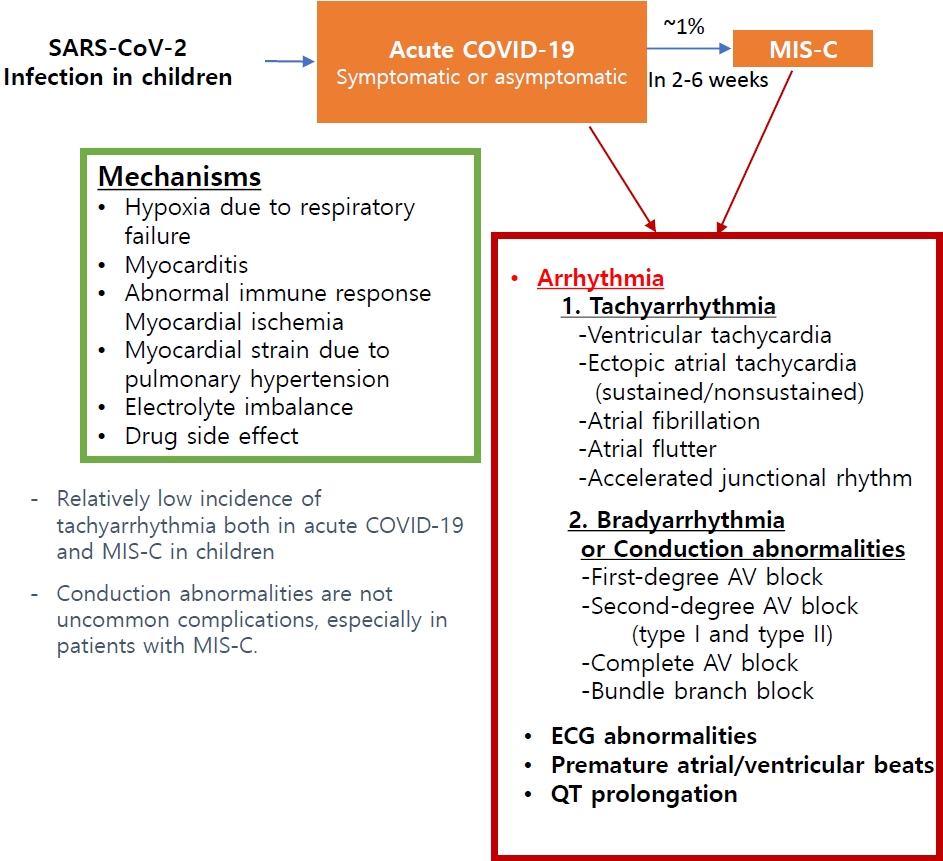
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Infection
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents
- Byung Ok Kwak, Byung Wook Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):182-189. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Most immunocompromised children and adolescents are not at increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19 outcomes for low- or medium-risk immunocompromised children are favorable, while more serious illness reportedly occurs in high-risk immunocompromised children by underlying disease, its treatments, and other factors. Therefore, the early detection and timely management of severe COVID-19 and treatment of underlying disease are important. Hospitalization and COVID-19 vaccination should be carefully considered.
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-
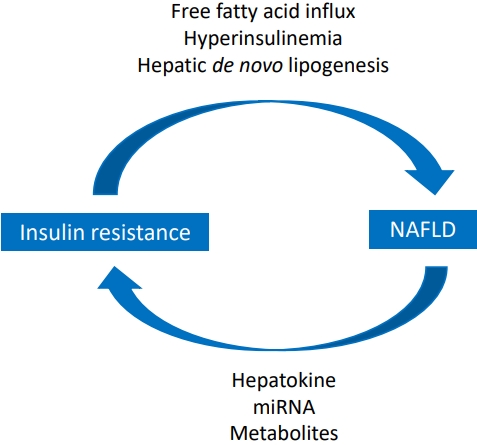
· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Other
- Hearing loss in neonates and infants
- Goun Choe, Su-Kyoung Park, Bong Jik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):369-376. Published online January 9, 2023
-

· Congenital hearing loss is common, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns and affecting 1.2%–11% of preterm and 1.6%–13.7% of neonatal intensive care unit neonates.
· Etiologies vary, and up to 80% of cases are genetic.
· Newborn hearing screenings follow the 1-3-6 rule, and babies at high risk of hearing loss should be referred to otolaryngology for early detection and timely intervention.
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-
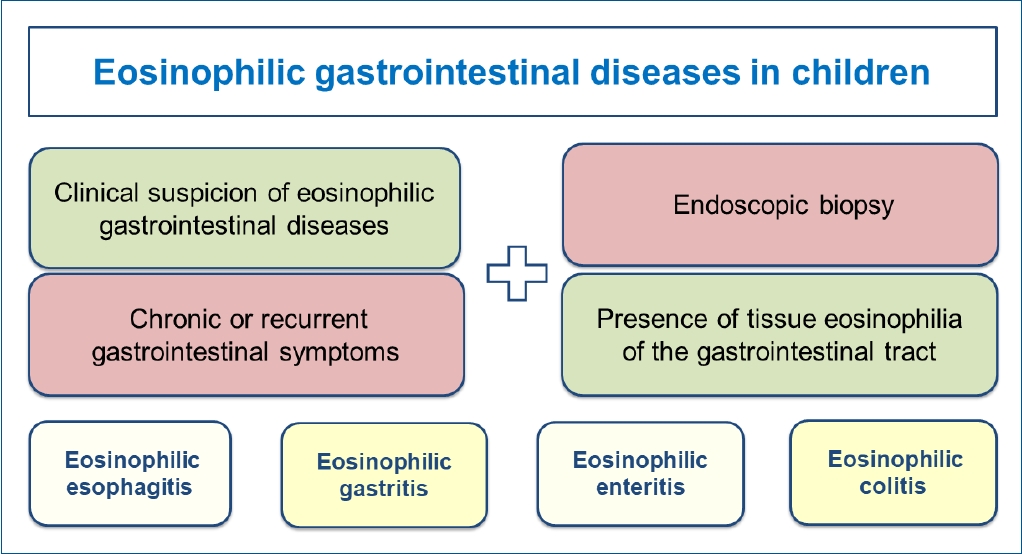
· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-
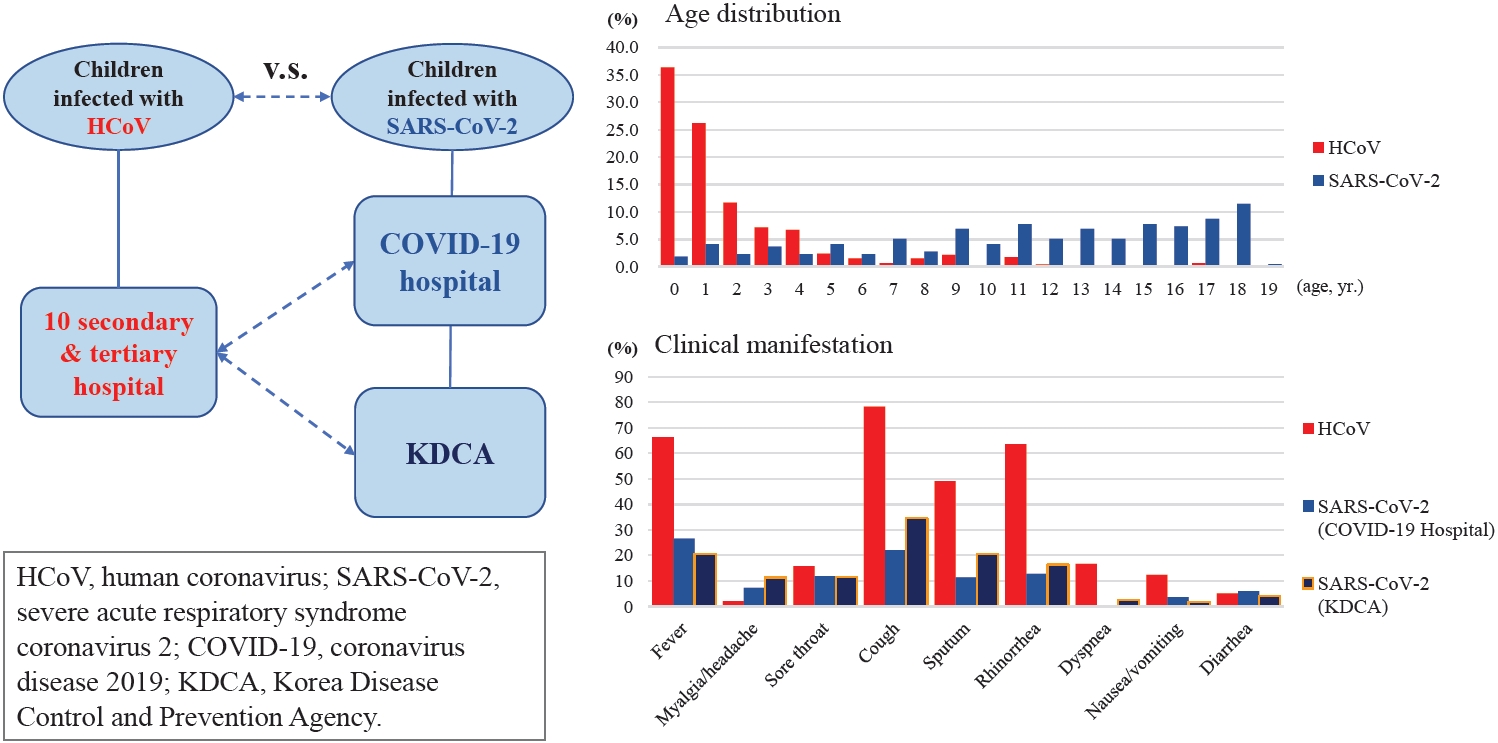
Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age
- Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-

Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94nd percentilePowered by







