Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on clinical features of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (2,559 times)
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(9):456-458. Published online March 25, 2024
-

· The frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) was not significantly influenced by the pandemic.
· The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has further diversified the etiologic enteric viral pathogens of CwG.
- Basic Research
- Stem cell mining: urine cells to biobanking (2,496 times)
- Yong Joo Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):761-762. Published online September 24, 2025
-

· A safe and accessible source of somatic cell generating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in pediatric neurogenic disorders
· A noninvasive and simple method for isolating urine cells, which can effectively reprogram into pluripotent stem cells using episomal vectors
· Establishing a urine-derived iPSC bank as a reliable and scalable resource for disease modeling, therapeutic testing, and personalized medicine in pediatric neurogenic disorders.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- HLA‒B*58:01 and skin reactions in pediatric hematology and oncology patients treated with allopurinol (2,362 times)
- Parisa Maneechai, Cholada Ratanatharathron, Jassada Buaboonam, Kleebsabai Sanpakit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):974-980. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Question: Does human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–B*58:01 increase the risk of cutaneous reactions in pediatric patients with hematological and oncological diseases receiving allopurinol?
Finding: : Of 108 patients, 17.6% carried HLA–B*58:01 but none developed skin reactions. The only rash occurred in an HLA-B*58:01–negative patient.
Meaning: Short-duration allopurinol may mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reaction risk regardless of genotype. Routine HLA-B*58:01 screening may be unnecessary in pediatric patients with hematological and oncological diseases briefly receiving allopurinol.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Impact of screen exposure during pediatric ages including multifaceted aggravating factors: a literature review (2,336 times)
- Daniel González-Pérez, David Sebastián Huertas-Moreno, Manuela Granados-Pinilla, Sofía Hernandez-Rojas, Laura González-Rincon, Geraldine Hurtado-Garcia, Simón Grisales-Calle, María José González-Mariño, Luz Dary Gutierrez-Castañeda, Jhon Camacho-Cruz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):751-760. Published online September 24, 2025
-

Excessive screen time in children is linked to obesity, overweight, sedentary behavior, depression and mood disorders, myopia, behavioral changes, sleep disturbances, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among others. Polymorphisms in genes like FTO, CACNA1D, and DRD2 could further increase these risks. Implementing strategies such as limiting screen use, creating screen-free zones, and monitoring content is essential to mitigate adverse physical and mental health effects in the pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- High-dose methylprednisolone and tocilizumab improve survival of patients with high-risk pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy (2,264 times)
- Chaonan Fan, Fei Li, Kechun Li, Zheng Li, Yiyang Mao, Lijuan Wang, Gang Liu, Yingchao Liu, Quan Wang, Suyun Qian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):56-64. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Which immunomodulatory strategies can reduce mortality in children with acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE)?
Finding: High-dose methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg/day) significantly improved the survival of high-risk patients, particularly when combined with tocilizumab.
Meaning: These findings support the use of a severity-based immunotherapy approach to optimize the outcomes of pediatric ANE.
- Review Article
- Oncology
- Breaking the barrier: a guidelines-based review of antiangiogenesis drug resistance in pediatric cancer therapy (2,148 times)
- Nader Shakibazad, Mahdi Shahriari, Mani Ramzi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):952-962. Published online November 24, 2025
-

Antiangiogenic therapy resistance in pediatric cancers involves alternative angiogenic pathways, microenvironmental support, hypoxia-driven signaling, metabolic reprogramming, and structural adaptations such as vascular co-option. Metabolic adaptation highlights tumor plasticity. Effective treatments combine immunotherapy with biomarkers. To address vascular endothelial growth factor limitations, emerging targets include hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, endoglin, CXCR4, angiopoietin/Tie2, and bispecific antibodies. In resource-constrained settings, the guidelines recommend low-dose chemotherapy plus oral multiantiangiogenic agents to ensure improved accessibility and treatment outcomes.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical outcomes and healthcare utilization of hospitalized children with influenza versus COVID-19 (1,755 times)
- David Chun-Ern Ng, Chuin-Hen Liew, Kah Kee Tan, Joanne Pereira, Muhammad Ihsan Roslan, Xiang Lin Cheng, Hui Yi Lim, Farah Nuruliayana A. Nazri, Asuwani Maran, Wan Fei Wong, Yasothai Chandran, Syaniza Shaharudin, Pon Ling Lau, Naveen Nair Gangadaran, Marlindawati Mohd Ali
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1007-1014. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Question: How do clinical presentations, healthcare resource utilization, and outcomes differ between children hospitalized with influenza versus coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: Patients with influenza were older, were more symptomatic, and required greater healthcare resources, including intravenous fluids, empirical antibiotics, respiratory support, and pediatric intensive care unit admission.
Meaning: Influenza involves greater severity and a higher healthcare burden than COVID-19, highlighting the need for preventive strategies such as vaccination and hospital resource planning during seasonal outbreaks.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Exploring nutritional screening tools for hospitalized children: a narrative review (1,734 times)
- Pankaj Soni, Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):963-970. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Malnutrition is frequently identified in hospitalized children, and the use of nutritional screening tools is crucial for assessing their nutritional status during their hospital admission and stay. Common tools include the Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score, Screening Tool for Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics, and Screening Tool for Risk of Nutritional Status and Growth. However, these tools have varying sensitivities and specificities, and none is recommended for all hospitalized children.
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and subsequent risk of allergic diseases in Japanese children: the TMM BirThree Cohort Study (1,729 times)
- Ami Uematsu, Masatsugu Orui, Mami Ishikuro, Keiko Murakami, Aoi Noda, Genki Shinoda, Taku Obara, Shinichi Kuriyama
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):36-45. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Associations have been made between maternal sleep disorders during pregnancy and allergic diseases including bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever in their children.
Finding: In the crude model, sleep disorders during pregnancy were associated with all examined allergic diseases in children. After adjustment, significant associations remained for atopic dermatitis and allergic conjunctivitis/rhinitis/hay fever.
Meaning: The study highlights associations between maternal sleep and child allergic diseases.
- Other
- Comparing ethyl chloride and 10% lignocaine spray for pediatric intravenous cannulation pain relief (1,713 times)
- Susmitha Vellanki, Malavika Kulkarni, H.D. Arun Kumar, Deepali Shetty, Nikhil Karthik B, Mathew Tom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):65-72. Published online November 21, 2025
-
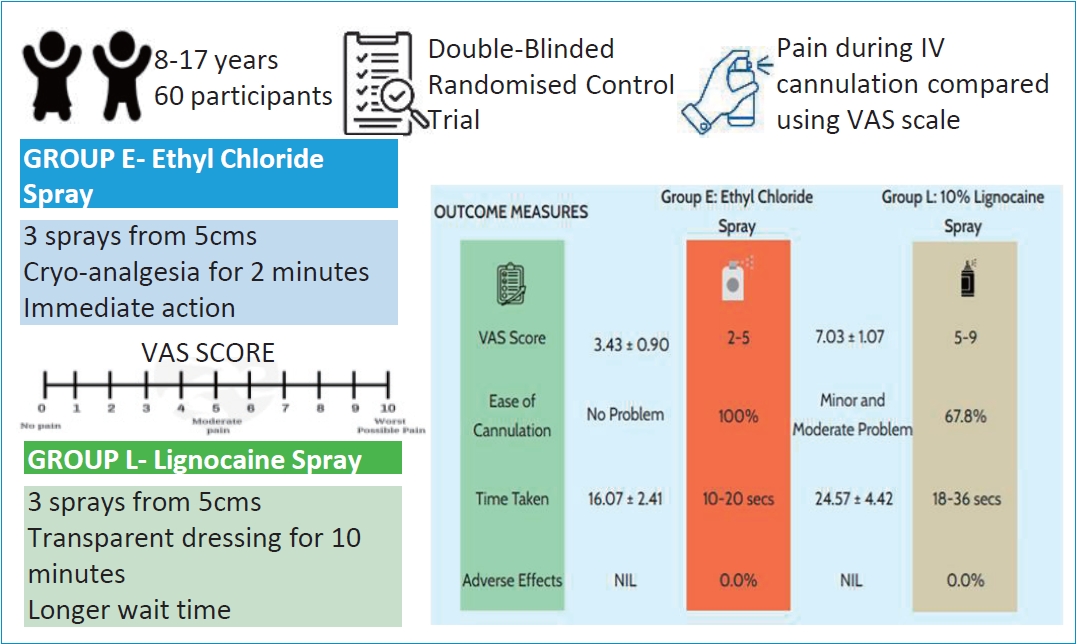
Background: Intravenous cannulation (IVC) is a routine yet distressing procedure in pediatric patients, often provoking significant anxiety and procedural pain. Although eutectic mixtures such as eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream are widely used, their delayed onset limits their applicability in time-sensitive settings. Ethyl chloride vapocoolant spray and 10% lignocaine spray have been proposed as rapid-onset alternatives, yet direct comparative...
- Pulmonology
- Ciclesonide shows a lung-protective effect in neonatal hyperoxia-exposed rats (1,644 times)
- Victoria Mielgo, Miguel A. Gomez-Solaetxe, Lara Olazar, Begoña Loureiro, Carmen Rey-Santano
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1023-1030. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Question: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most prevalent chronic lung disease of prematurity. Numerous nonpharmacological/pharmacological interventions have been investigated without clear consensus. Can ciclesonide, a new synthetic glucocorticoid, effectively treat BPD?
Finding: Ciclesonide mitigated hyperoxia-induced lung injury and right ventricular hypertrophy in newborn rats.
Meaning: These findings suggest that postnatal ciclesonide may be an alternative to existing corticosteroids for the treatment of BPD.
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota and metabolomic alterations in newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus (1,618 times)
- Wan-Hsin Su, Yi-Wei Wang, Chien-Chang Chen, Ming-Wei Lai, Hsun-Chin Chao, Ming-Chou Chiang, Ren-Huei Fu, Pai-Jui Yeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):26-35. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Does maternal gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affect newborn gut microbiota and metabolomic profiles?
Finding: Neonates born to mothers with diet-controlled GDM exhibited reduced gut microbiota α-diversity, altered β-diversity, and metabolic shifts, including changes in fumarate and succinate levels, with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and adipocytokine signaling pathway activation.
Meaning: Maternal GDM affects early microbial colonization and metabolism in newborns and may have long-term health implications.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Parenting principles to combat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and form resilient young minds (1,593 times)
- Jandy Le, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):838-841. Published online September 22, 2025
-

The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and other related behavioral problems is increasing among children, likely due to less interaction with their parents and the real world and more time spent on screens, on social media, and in the virtual world. This article highlights several simple, basic parenting principles to facilitate the growth of healthy, resilient minds and combat the symptoms of opposition, hyperactivity, and distractibility.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Association between vitamin D polymorphisms and binding protein and COVID-19 risk and severity in children (1,402 times)
- Victoria Giatraki, Helen Dimitriou, Georgia Martimianaki, Christos Tsatsanis, Emmanouil Galanakis, Chrysoula Perdikogianni
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):998-1006. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: Addressing crucial genetic variants within the vitamin D pathway and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility, the vitamin D receptor, vitamin D binding protein, and CYP27B1-1260 polmorphisms might be associated with COVID-19 occurrence and severity in children.
Finding: The FokI FF genotype might be an independent risk factor for COVID-19 severity in childhood.
Meaning: This research may further elucidate genetic susceptibility to multisystem viral infections and establish genetic markers for severe clinical outcomes.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Successful rescue after catastrophic bleeding of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm following button battery ingestion in a toddler (1,374 times)
- Manjit Kaur, Ujjal Poddar, Basant Kumar, Abdul Muzil Munshi, Rajanikant R. Yadav, Moinak Sen Sarma, Anshu Srivastava
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1041-1044. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Button battery (BB) ingestion is an increasing hazard. Catastrophic gastrointestinal bleeding due to pseudoaneurysm rupture following BB impaction is often fatal. Here we report the case of an unwitnessed BB ingestion in an 18-month-old boy who presented with repeated massive UGIB due to a left CCA pseudoaneurysm that was successfully managed multidisciplinarily. BB ingestion should be considered in toddlers presenting with hematemesis.
- Original Article
- Rheumatology
- Recurrent immunoglobulin A vasculitis in children and adolescents: prevalence and associated risk factors (1,340 times)
- Nootsara Atchariyaphuk, Maynart Sukharomana, Thanaporn Chaiyapak, Sirirat Charuvanij
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):46-55. Published online October 22, 2025
-

Question: What can predict immunoglobulin A vasculitis (IgAV) recurrence, and when does it occur? How do childhood- and adolescent-onset IgAV compare?
Finding: The IgAV recurrence rate was 35.6%. It usually occurred within 12 months and was associated with corticosteroids treatment.
Meaning: Childhood-onset IgAV more commonly featured gastrointestinal and musculoskeletal manifestations and required hospitalization. Adolescent-onset IgAV more commonly featured renal involvement. Vigilant monitoring for recurrence is necessary, particularly with corticosteroids treatment.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins? (1,277 times)
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-
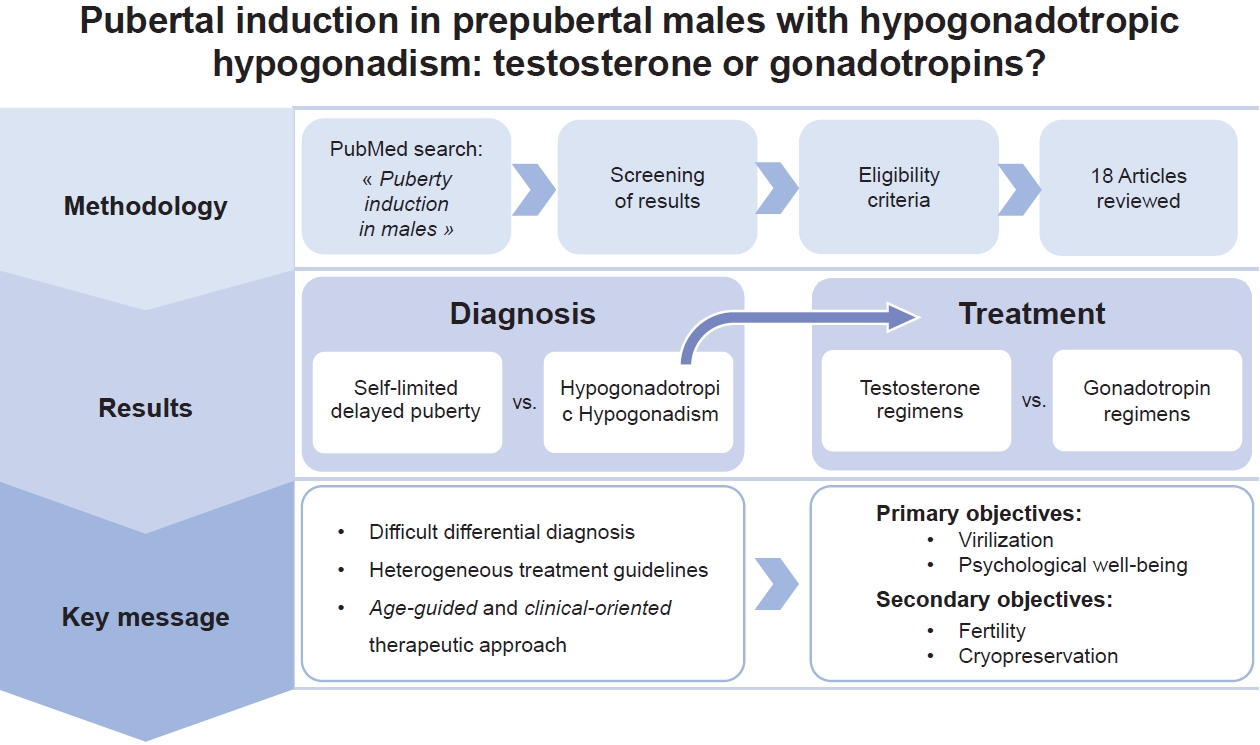
The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Gastroenterology
- Ingestion of foreign bodies and caustic substances in children: a narrative review on clinical evaluation and management update (1,258 times)
- Maria Rogalidou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):11-21. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Foreign body and caustic substance ingestion in children aged 1–5 years can feature to severe and, sometimes life-threatening complications. High-risk items include batteries, magnets, and corrosive chemicals. Severity depends on object type, location, and ingestion timing. Prompt diagnosis and early endoscopic intervention are crucial. Individualized management, high clinical suspicion, and parental education are essential to improving outcomes and preventing immediate and long-term complications affecting a child’s quality of life.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Beyond COVID-19: meeting the challenge of evolving pediatric invasive group A streptococcal disease (1,175 times)
- Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):971-973. Published online November 26, 2025
-
Pediatric for invasive group A Streptococcus has resurged globally with increasing severity and toxin-mediated presentations. Beta-lactams remain the first-line treatment, but linezolid has emerged as a safe alternative in cases refractory to β-lactams. Early intravenous immunoglobulin use may improve outcomes in severe streptococcal toxic shock syndrome cases, while C-reactive protein and procalcitonin aid early risk stratification. Integrating global surveillance and individualized therapy is crucial in the postpandemic era.
- Clinical Note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- External tracheal compression and mucosal injury in a neonate with cervical teratoma: a rare airway challenge (981 times)
- Rhodora Guillen, Arijit Lodha, Prashanth Murthy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):73-75. Published online December 4, 2025
-
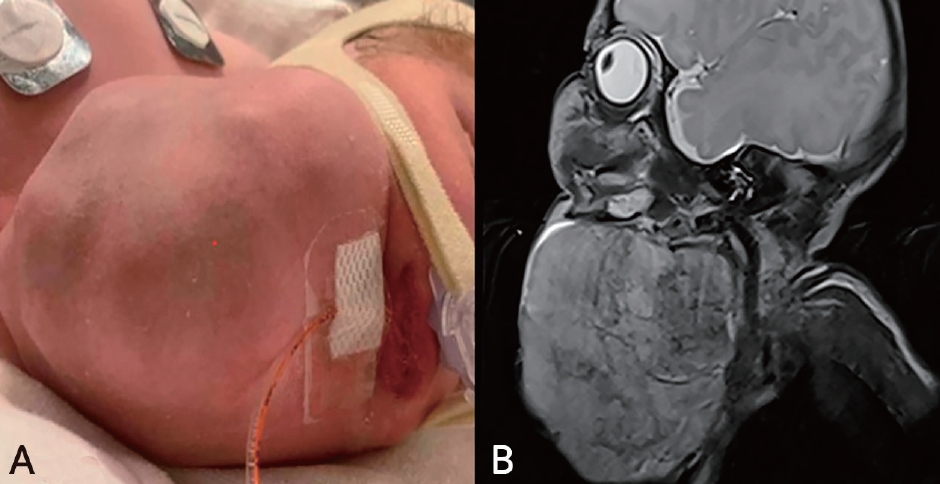
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Prioritizing maternal sleep: a public health strategy for preventing childhood allergic diseases (865 times)
- Eunchae Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):22-25. Published online December 18, 2025
-
Sleep disorders affect more than half of pregnancies worldwide and can harm maternal health and offspring outcomes. Prioritizing maternal sleep as a public health strategy may help prevent prenatal and pediatric allergic diseases and reduce their burden. Other maternal health strategies may also reduce the burden of offspring allergic diseases, while adequate maternal sleep is associated with other offspring outcomes, underscoring its importance as a key public health strategy.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











