Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (60)
- Cardiology (79)
- Critical Care Medicine (10)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (60)
- Gastroenterology (63)
- General Pediatrics (45)
- Genetics and Metabolism (24)
- Hematology (15)
- Immunology (14)
- Infection (72)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (119)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (52)
- Neurology (94)
- Nutrition (28)
- Oncology (16)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (30)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (35)
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pentraxin 3 as a marker of early-onset neonatal sepsis
- Safaa ELMeneza, Iman El-Bagoury, Hind Rayes, Amira Hassan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):312-314. Published online May 23, 2024
-

- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of online responsive teaching in young children with developmental disabilities: a pilot study
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jeongmee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):303-311. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Question: Does online responsive teaching (RT) impact children's and parents’ emotions and behaviors, and do parents find it satisfactory?
Finding: Online RT significantly improved children's pivotal and problem behaviors, decreased parenting stress, and enhanced parental interactive styles with high satisfaction.
Meaning: This pilot study's findings suggest that online RT can enhance child outcomes, offering accessible interventions amid challenges such as limited access and pandemics.
- Endocrinology
- Kisspeptin and DLK1 levels for monitoring treatment of girls with central precocious puberty
- Witchuwan Onsoi, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Vichit Supornsilchai, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):296-302. Published online May 21, 2024
-

Questions: Can the serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 be potential biomarkers for monitoring the treatments for central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Findings: There were no significant differences in the baseline serum kisspeptin and DLK1 levels in CPP girls compared to girls with premature thelarche (PT). After 6 months of GnRH analogue treatment in CPP girls, median serum kisspeptin levels decreased, while median serum DLK1 levels increased compared to baseline.
Meanings: Serum levels of kisspeptin and DLK1 may serve as novel biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of treatments for CPP.
- Editorial
- Neurobehavior
- Importance of pediatrician’s role in preventing positional plagiocephaly
- Hee-Jeong Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):294-295. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Plagiocephaly is characterized by the asymmetrical shape of a baby’s head.
· Since positional plagiocephaly is associated with developmental delay and further musculoskeletal problems, early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents worsening of the condition.
· Pediatricians can educate parents about proper head positioning and encourage supervised tummy time during awake hours.
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Iron deficiency in children with a focus on inflammatory conditions
- Na Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):283-293. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Iron deficiency has important effects on neurodevelopment and the immune system in children.
· Hepcidine plays an important role in iron homeostasis.
· Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic inflammatory disease are important for patients' quality of life and disease course.
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
- Allergy
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Oligohydramnios affects pulmonary functional/structural abnormalities in school-aged children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Jeong Eun Shin, Soon Min Lee, Mi-Jung Lee, Jungho Han, Joohee Lim, Haerin Jang, Ho Seon Eun, Min Soo Park, Soo Yeon Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Ji Ye Jung, Kyung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):257-266. Published online April 16, 2024
-
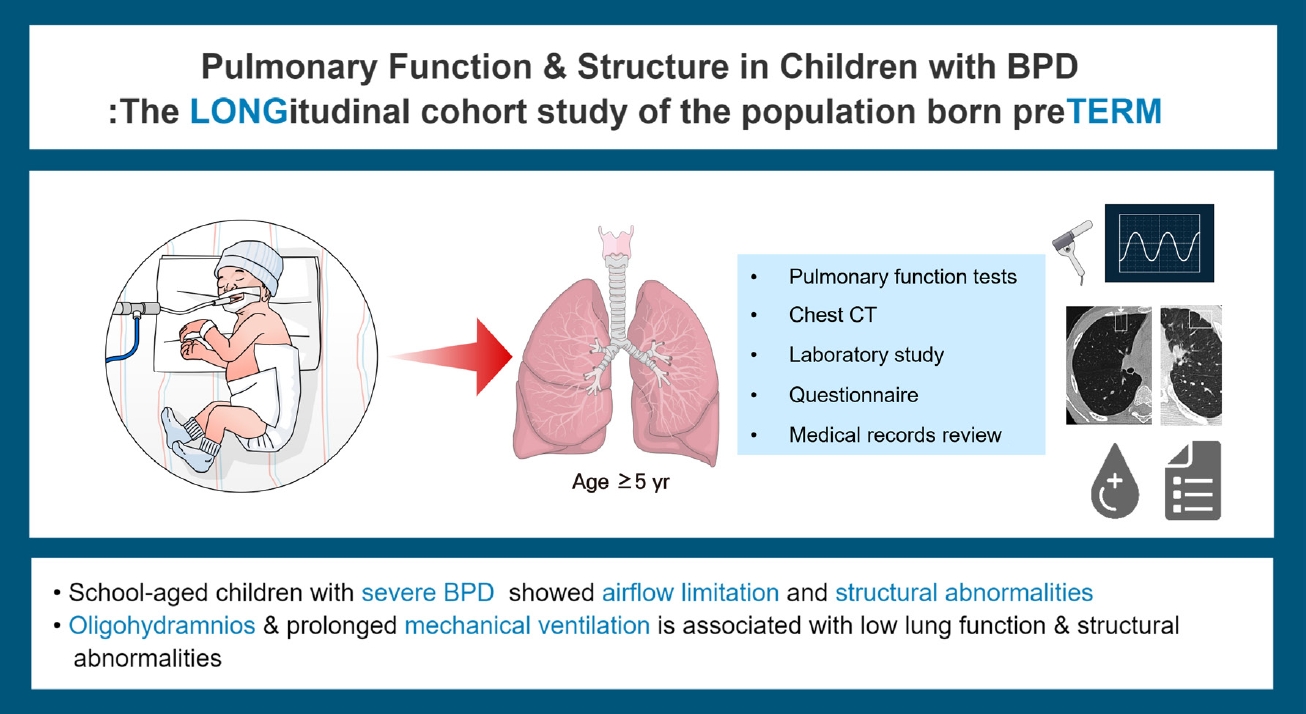
Question: Is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) associated with functional/structural abnormalities later in life?
Finding: School-aged children with severe BPD had abnormalities on pulmonary function tests and lung computed tomography despite no subjective respiratory symptoms; however, only prenatal oligohydramnios and prolonged ventilator use were associated with abnormal lung function.
Meaning: Long-term monitoring of preterm infants’ lung health is essential, especially for those with prenatal oligohydramnios or prolonged ventilator use.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-

Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Exploring the role of laryngeal masks in neonatal resuscitation
- Euiseok Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):247-248. Published online December 28, 2023
-
· Laryngeal masks (LMs) offer stable airway access and skill retention advantages, making them promising alternatives to positive-pressure ventilation in neonatal care.
· The ease of teaching LM insertion techniques to less experienced providers addresses the need for swift intervention and skill retention.
· Careful consideration of the benefits and challenges of LMs is essential in determining their effective integration into enhanced neonatal resuscitation protocols.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Updates in neonatal resuscitation: routine use of laryngeal masks as an alternative to face masks
- Eun Song Song, Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):240-246. Published online July 11, 2023
-

In neonatal resuscitation:
· Laryngeal masks are recommended when endotracheal intubation or positive-pressure ventilation fails.
· Laryngeal masks are useful even during chest compressions.
· Laryngeal masks aid neonates >34 weeks’ gestation and/or with a birth weight >2 kg.
· Main usage barriers include limited experience (81%), preference for endotracheal tubes (57%), and lack of awareness (56%).
· Second-generation laryngeal masks have a built-in esophageal drainage tube that prevents regurgitation into the glottis, and an orogastric tube can be inserted within the esophageal drainage tube to protect against gastric inflation.
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Influence of infant microbiome on health and development
- Noelle Younge
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):224-231. Published online August 21, 2023
-
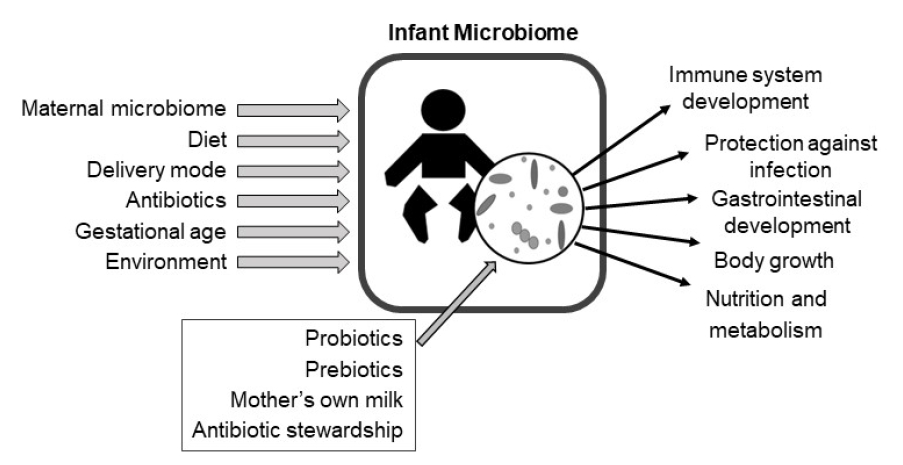
· The infant gut microbiome is highly dynamic and individualized.
· Microbes are vertically transmitted from mother to infant during delivery and throughout infancy.
· Delivery mode, gestational age, diet, and antibiotic use influence infant microbiome composition and function.
· In animal studies, the microbiome played critical roles in the structural and functional development of the infant gastrointestinal and immune systems.
· Microbiome-targeted therapies have great potential to reduce infant morbidity and mortality.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Assessment of iron status and red cell parameters in healthy term small for gestational age neonates at birth
- Arif Hossain, Shorna Rahman, Shahana Akter, Ismat Jahan, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):221-223. Published online March 19, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-

Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
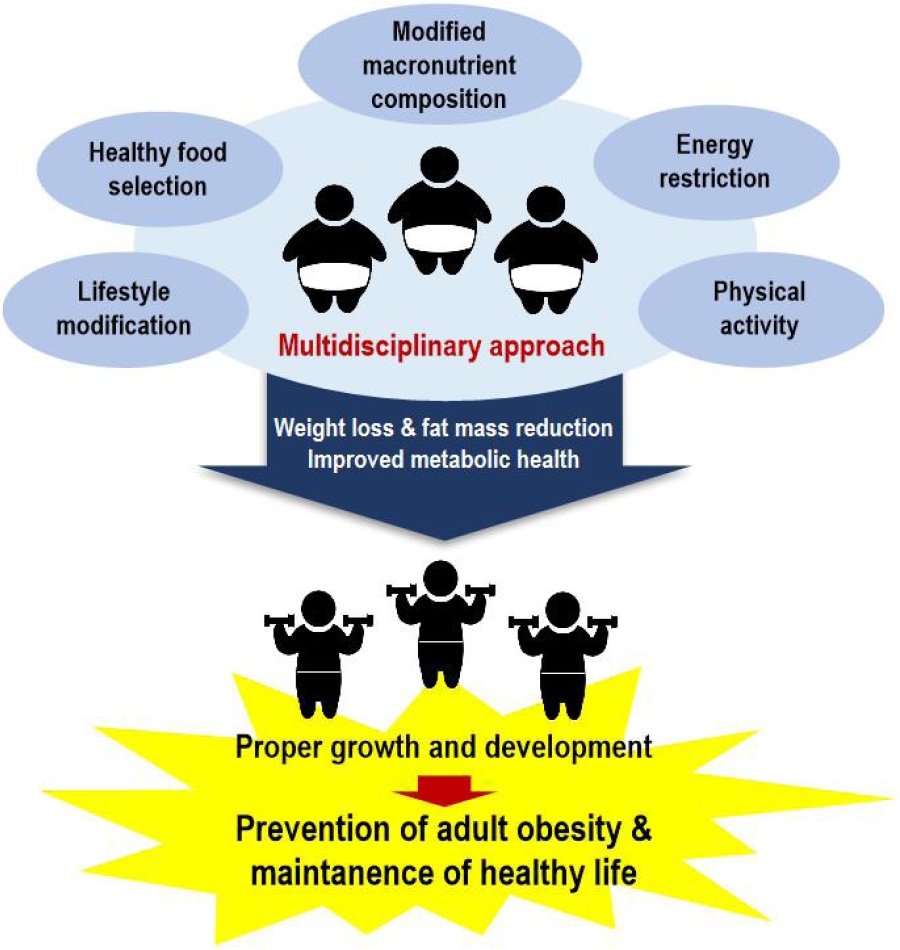
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
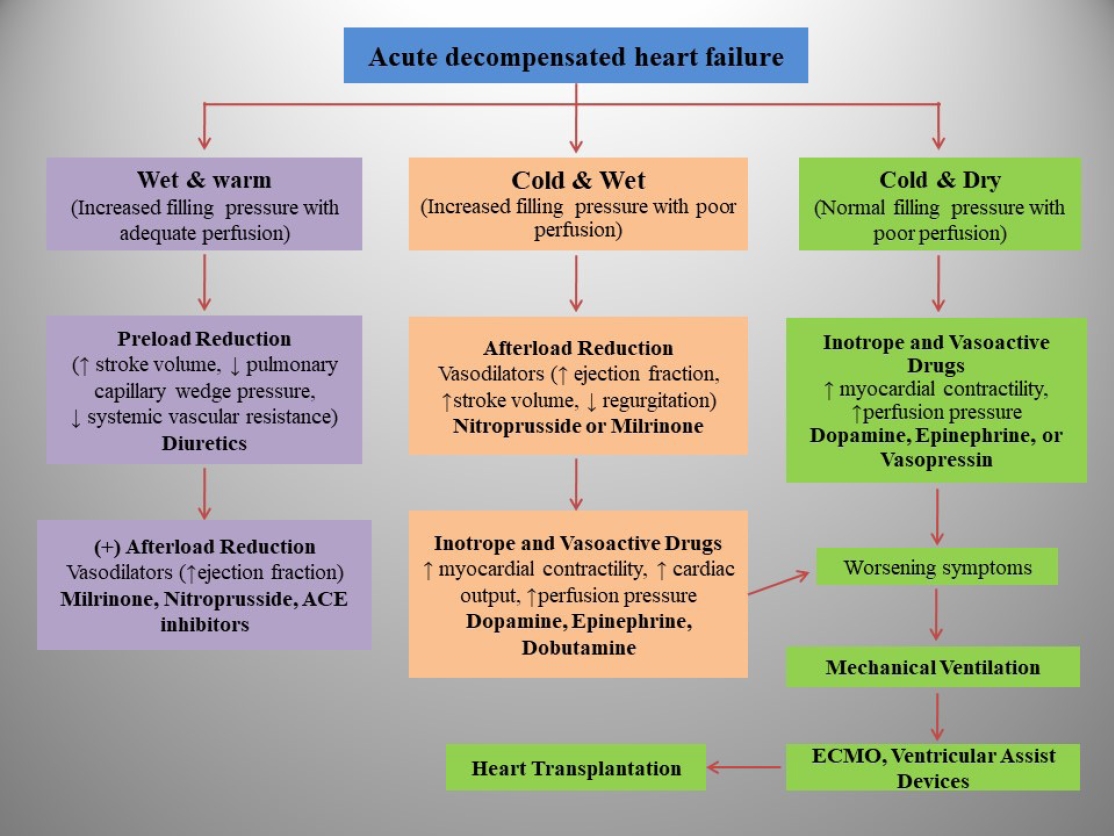
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
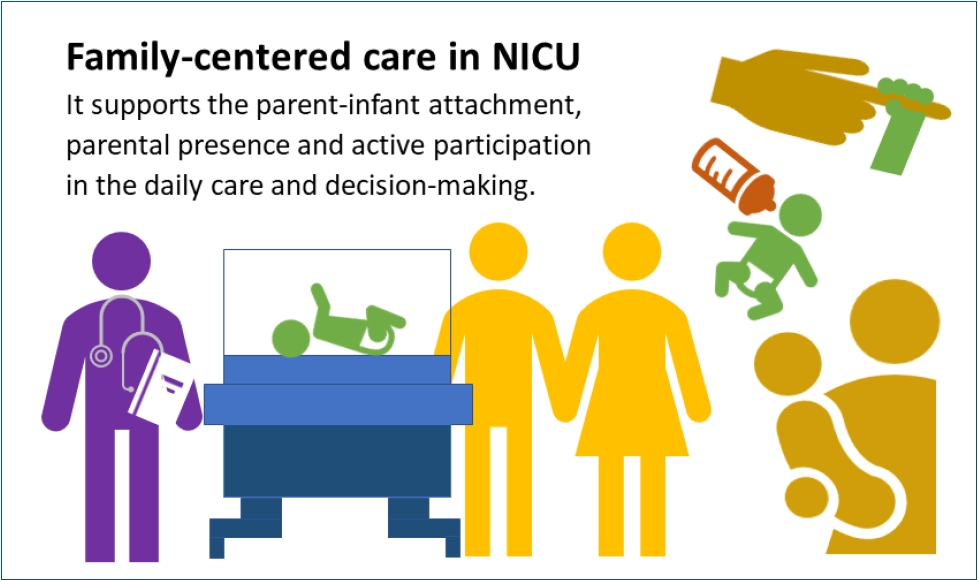
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
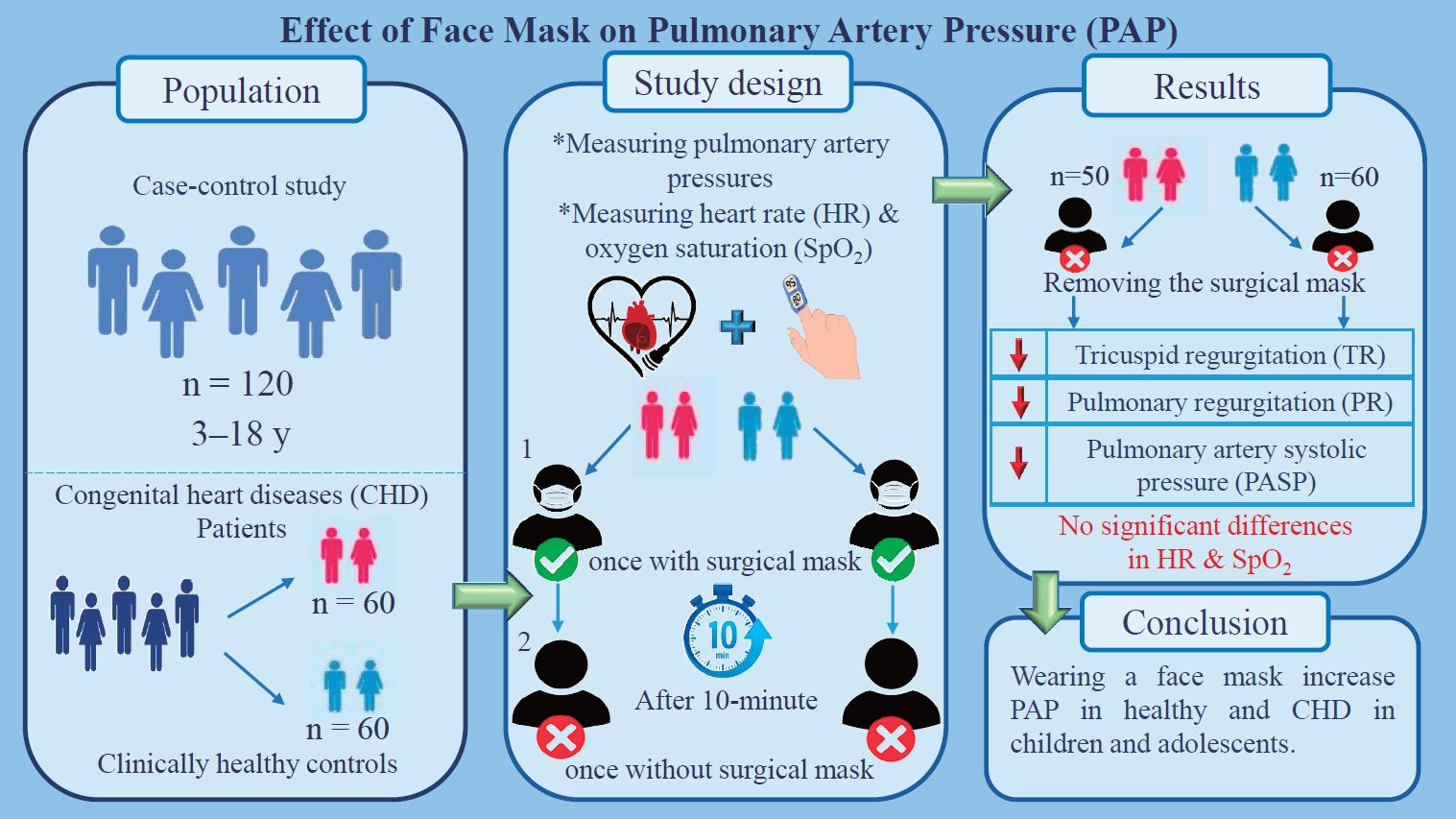
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates intestinal injury in necrotizing enterocolitis
- Yeong Seok Lee, Yong Hoon Jun, Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):152-160. Published online February 19, 2024
-
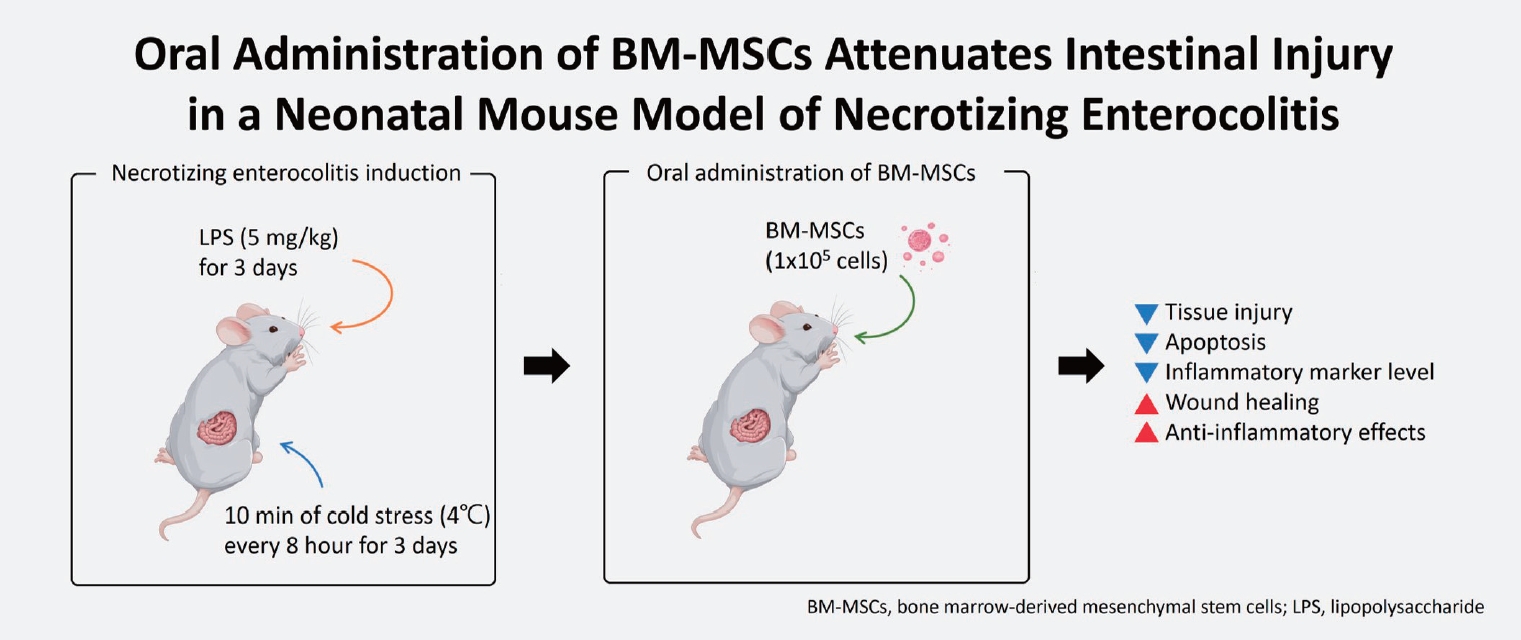
Question: What is the optimal dose of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) for treating necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and is orally administered BM-MSC effective?
Findings: High (1×106 cells) or multiple BM-MSC doses showed similar effects as low (1×105 cells) doses of intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs. Furthermore, orally administered BM-MSCs were as effective as intraperitoneally administered BM-MSCs.
Meaning: Orally administered low-dose BM-MSCs are a potential treatment for NEC.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Impacts of maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy on neonatal health and epidemiology
- Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):149-151. Published online December 28, 2023
-

Newborns born to mothers infected with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be closely monitored for respiratory disorders, such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, regardless of their COVID-19 test results. Further research is required of the development of infants born to mothers with COVID-19. The trends in Korea's birth rate and infant mortality rates have not been significantly affected by COVID-19.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-

· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Other
- Acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children: no valid rationale for controversy
- Lisa Zhao, John P. Jones, Lauren G. Anderson, Zacharoula Konsoula, Cynthia D. Nevison, Kathryn J. Reissner, William Parker
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):126-139. Published online June 14, 2023
-
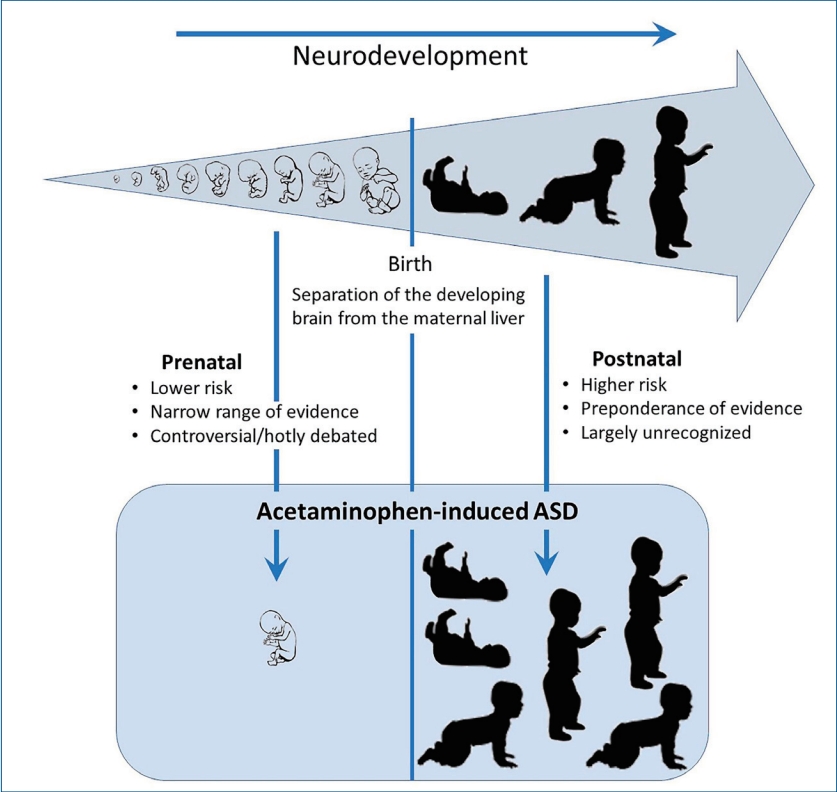
Despite worldwide acceptance of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in pediatric medicine, careful examination reveals no valid objections to the conclusion that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury in susceptible babies and children. Nevertheless, debate that early exposure to acetaminophen causes neurodevelopmental injury has centered around the prenatal period, evidence of which is relatively limited compared to that in the postnatal period, which is the time of greatest absolute and relative risk.
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-
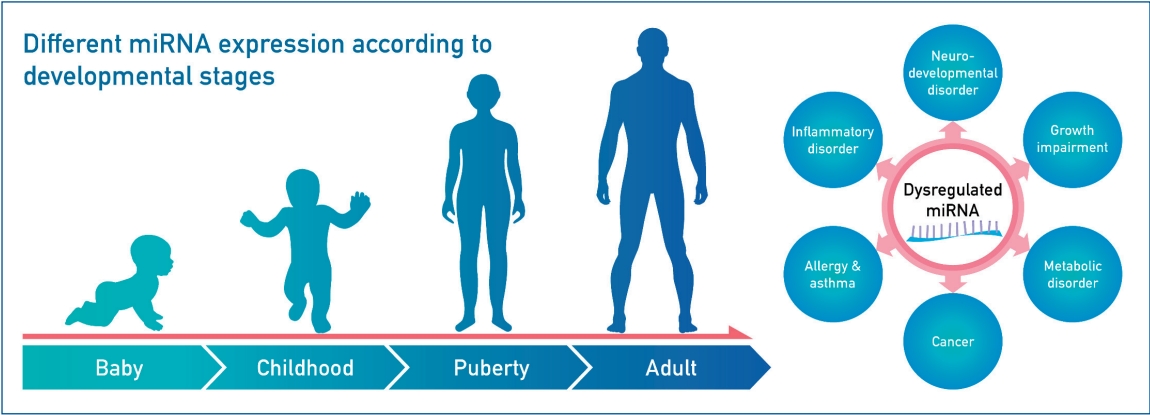
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in anemic children before versus after age 2 years: a form of hidden hunger in India
- Sahil Goel, Ruchika Bhatnagar, Anita Kumari, Brig Prem Lochan Prasad, Lahar Sahai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):116-118. Published online January 24, 2024
-
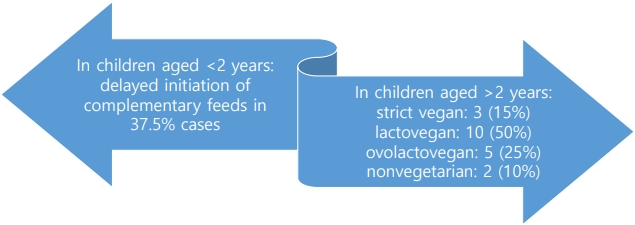
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
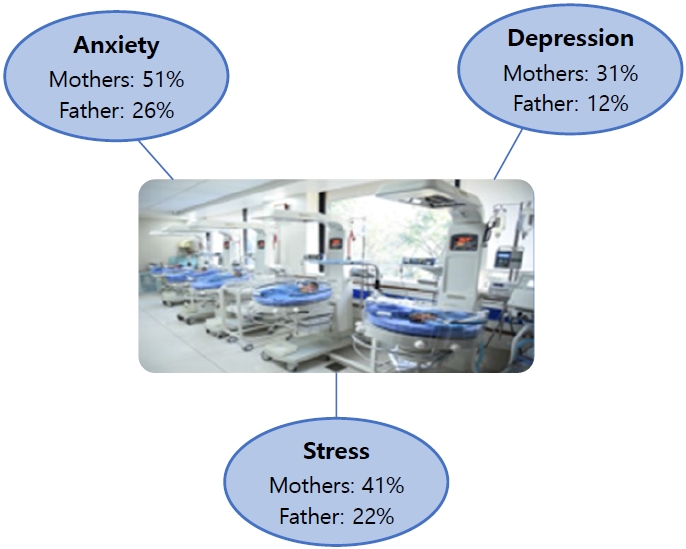
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Other
- Virtual, augmented, and mixed reality: potential clinical and training applications in pediatrics
- Suyoung Yoo, Meong Hi Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):92-103. Published online May 24, 2023
-
· Review of articles that investigated the applications of virtual, augmented, or mixed reality in pediatric clinical settings and in the training of pediatric medical professionals was conducted.
· A total of 89 studies were retrieved, with 36 randomized controlled trials.
· In most studies, intervention using the novel technology was at least as effective or more effective than the traditional method.
· Use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality has potential in pediatrics.
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











