Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
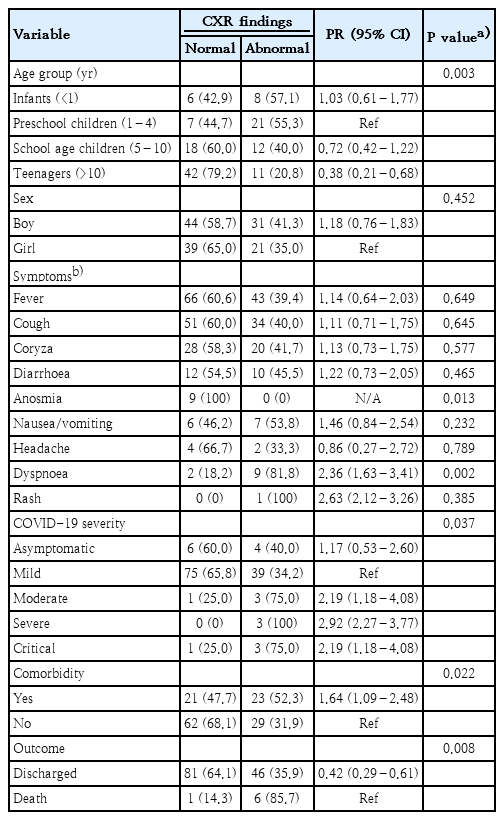
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Echocardiographic reference z scores of right ventricular dimension and systolic function of children aged 5–12 years
- Alaba Busola Oladimeji, Moriam Omolola Lamina, Peter Odion Ubuane, Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle, Omolara Adeolu Kehinde, Barakat Adeola Animasahun, Olisamedua FidelisNjokanma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):215-222. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Question: Z score reference values for right ventricular size and systolic function in children using echocardiography are available in several countries. Despite the high burden of diseases involving the right ventricle in Nigeria, these reference values have limited applicability.
Finding: The right ventricular sizes of Nigerian children differed from those published elsewhere.
Meaning: These reference values will aid the treatment, monitoring, and pre- and postintervention for Nigerian children.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Impact and role of vitamins as immunonutrition in children during COVID-19 pandemic
- Yoo Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):212-214. Published online April 18, 2023
-
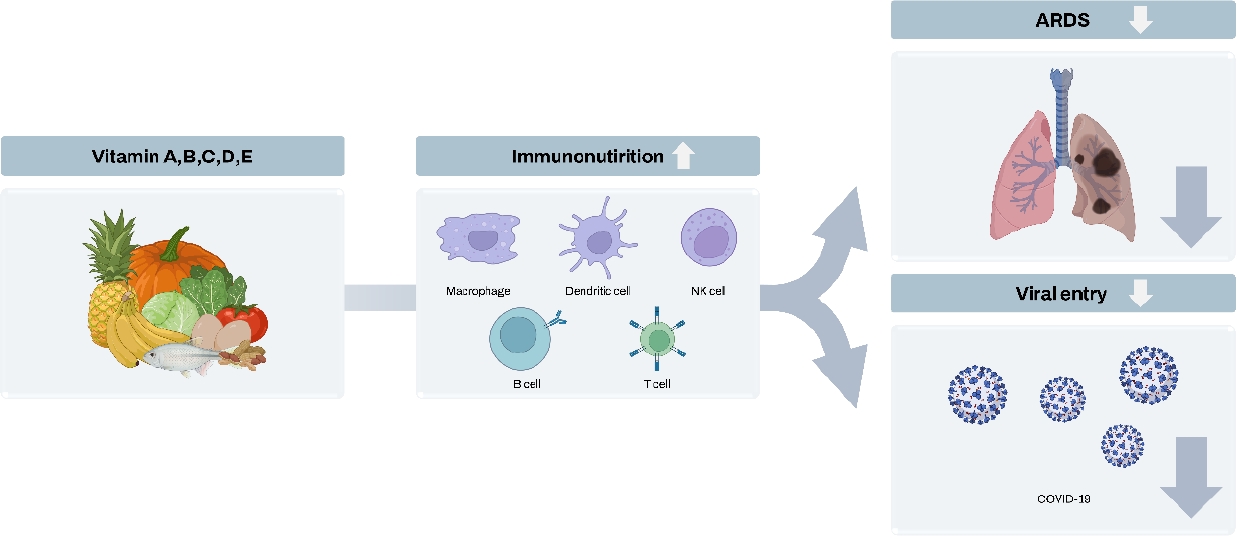
· Vitamins have effector mechanisms in the innate and adaptive immune systems and potential roles in preventing and reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
· Vitamins may be immunonutrients in the treatment of COVID-19 infections and prevention of patient deterioration due to critical illness, thus demonstrating the significance of a nutritious, well-balanced diet.
- Neurology
- Understanding the usefulness of electroencephalography source localization
- Bo Lyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):210-211. Published online April 18, 2023
-
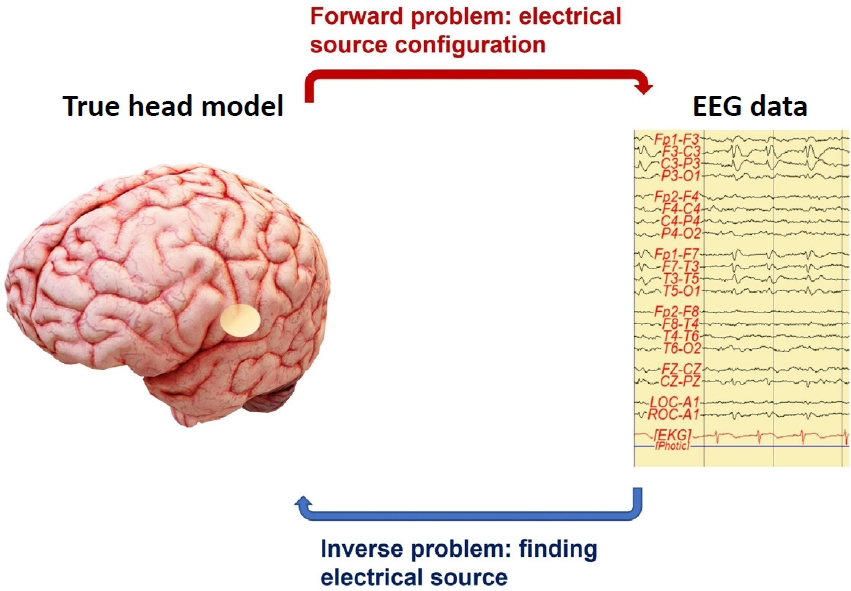
· Electroencephalography (EEG) records brain activity with high temporal resolution.
· EEG source localization, combined with other functional or structural imaging methods, provides information about brain network and connectivity in clinical neuroscience.
· EEG source localization identifies brain location from electrical current sources in several neuropsychiatric diseases such as epilepsy, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and anxiety disorders.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-

· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Infection
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents
- Byung Ok Kwak, Byung Wook Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):182-189. Published online April 18, 2023
-

Most immunocompromised children and adolescents are not at increased risk of developing severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19 outcomes for low- or medium-risk immunocompromised children are favorable, while more serious illness reportedly occurs in high-risk immunocompromised children by underlying disease, its treatments, and other factors. Therefore, the early detection and timely management of severe COVID-19 and treatment of underlying disease are important. Hospitalization and COVID-19 vaccination should be carefully considered.
- Perspective
- Other
- New public-centered child protection system in Korea
- We Sun Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):179-181. Published online April 18, 2023
-
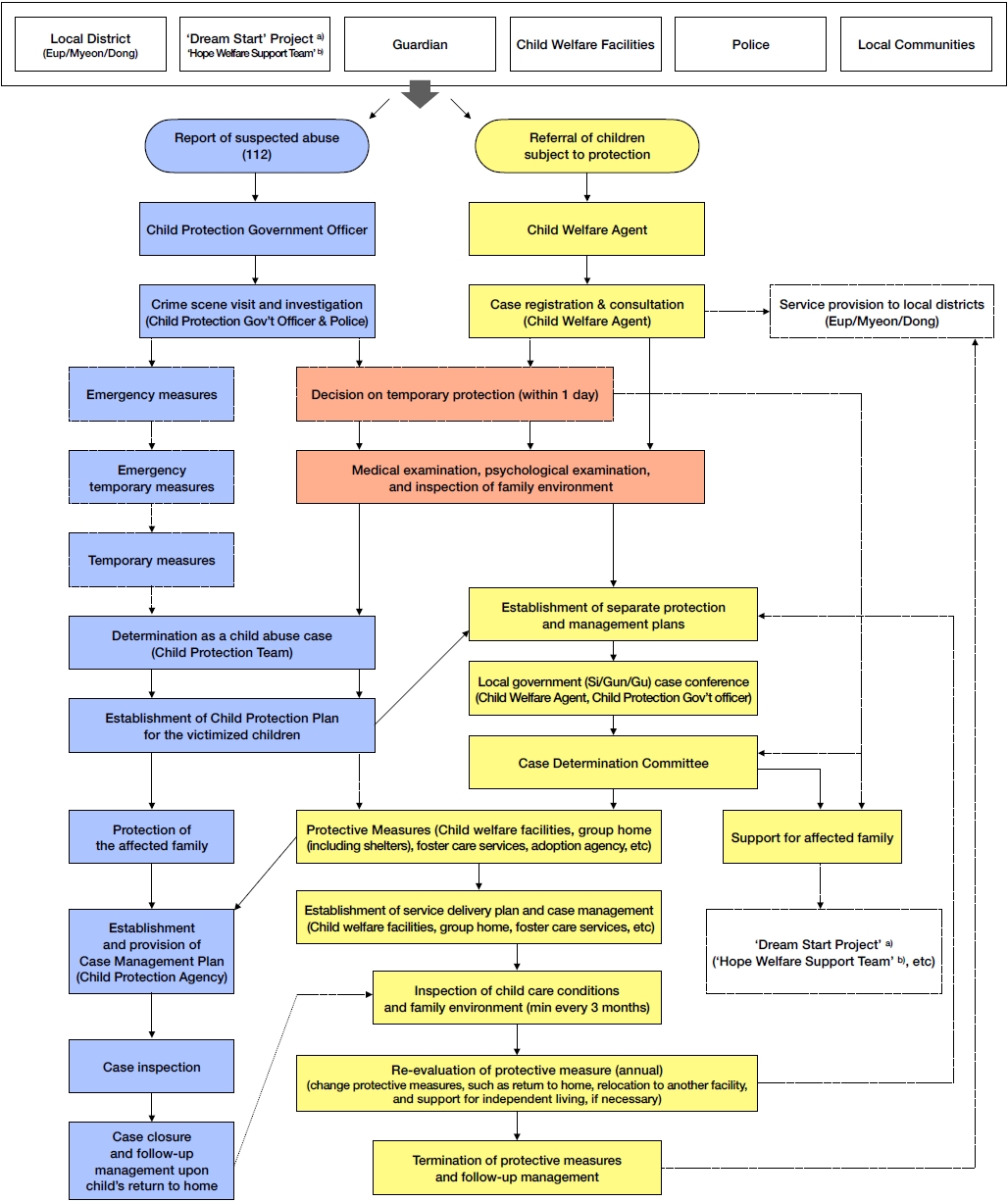
Korea’s child abuse response system was transformed under policy change in April 2020, from what was previously operated on a private-centered basis to a focus on the public sector with expanded role of local governments. Promising outcomes are expected with new system as greater governmental intervention will effectively protect at-risk children with acceleration in institutional collaboration and expertise in information management and administration.
- Editorial
- Other
- Advancing pediatric health: the multifaceted scope of Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics
- Jin Hee Oh, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):171-172. Published online March 29, 2023
-
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics (CEP) is a journal that specializes in pediatric research topics. It covers a wide range of research areas, including basic research, translational research, and research related to improving pediatric health and diseases. CEP also focuses on the coordination of societal structures and processes that orchestrate pediatric health and disease throughout society, and the parallel relationship between regional characteristics and globalization. The journal intends to continue promoting pediatric health through relentless efforts and the discovery of new research areas.
- Clinical Note
- Other
- Novel PTRH2 gene variant causing IMNEPD (infantile-onset multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease) in 2 Saudi siblings
- Dalal K. Bubshait
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):223-225. Published online March 23, 2023
-

- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children?
- Hae Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Changes and correlations of T-cell coinhibitory molecule programmed death-1 and interferon-γ in pediatric immune thrombocytopenia
- Fady Mohamed El-Gendy, Amira M.F. Shehata, Esam Awad Abd El-Kawy, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):127-133. Published online February 24, 2023
-
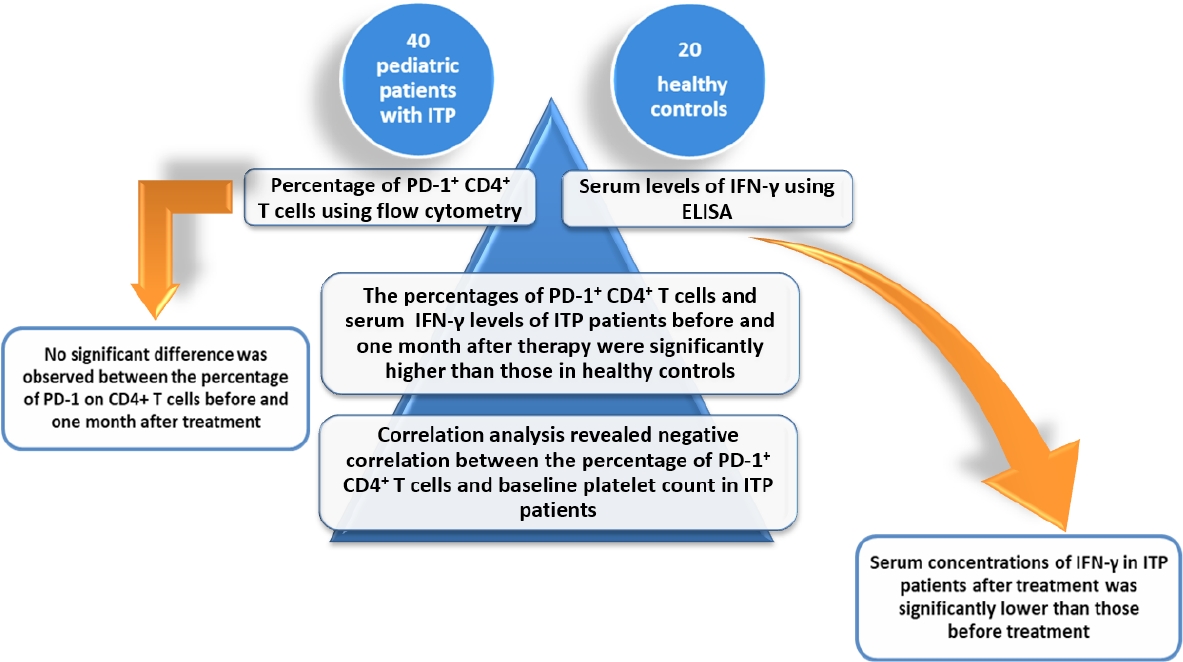
Question: What are the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and serum interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels of pediatric patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)?
Finding: Compared with healthy controls, the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in ITP patients before and 1 month after therapy.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that PD-1+ CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are involved in the pathophysiological process of ITP.
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Optimal hemodialysis treatment for pediatric kidney failure patients
- Yo Han Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):125-126. Published online February 15, 2023
-
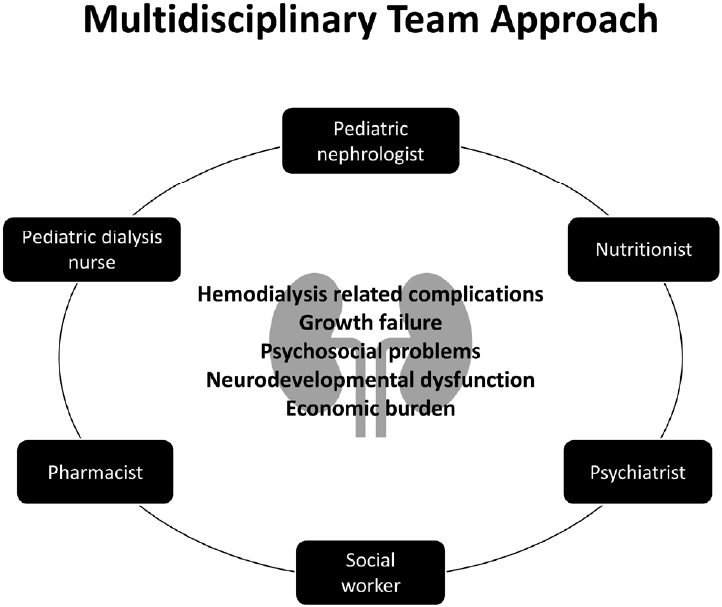
· Although the basic concept of hemodialysis (HD) is similar in adults and children, specific factors must be considered in the latter, including the small dialyzer and circuit, difficult vascular access, and frequent complications.
· HD-associated complications include catheter-related problems, hemodynamic instability, and neurodevelopmental and cognitive dysfunction.
· Pediatric HD is challenging, and steady efforts are needed to perform it safely and reduce its complications, thereby improving clinical outcomes.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Pediatric syncope: pearls and pitfalls in history taking
- Jung Sook Yeom, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):88-97. Published online February 15, 2023
-
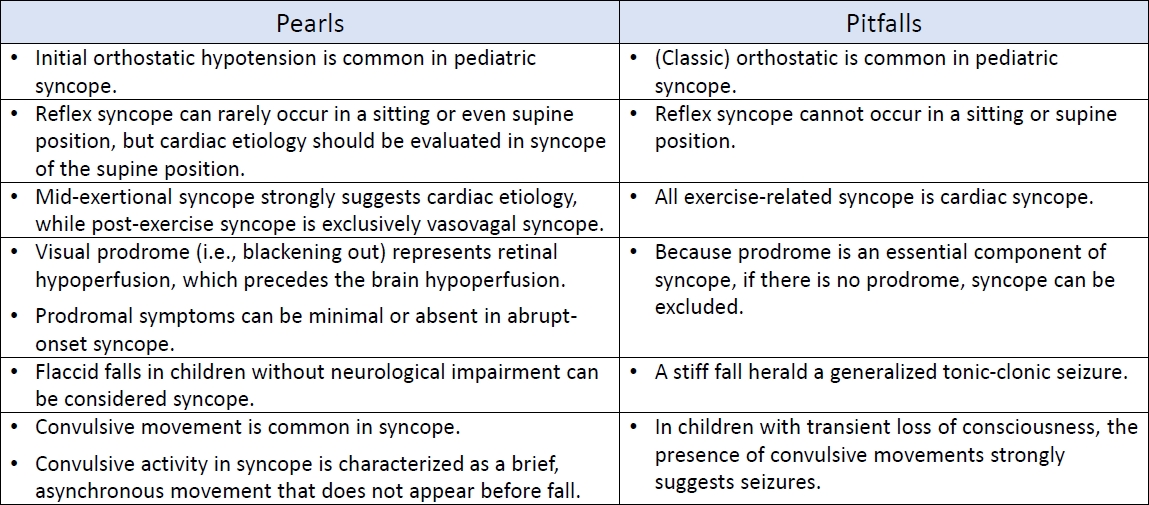
An accurate diagnosis depends on correct history taking and its interpretation. An in-depth understanding of the symptoms of syncope in connection with its pathophysiology can lead to avoiding critical pitfalls in the diagnostic process of history taking.
- Letter to the Editor
- Endocrinology
- Accuracy of predicted adult height using the Greulich-Pyle method and artificial intelligence medical device
- Dongho Cho, Yun Sun Choi, Hayun Oh, Young min Ahn, Ji-Young Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):145-147. Published online January 25, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Infection
- Pathogenetic and etiologic considerations of febrile seizures
- Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):46-53. Published online January 13, 2023
-

· Inflammatory responses accompanying fever increase neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, which in turn provokes seizures.
· Fever in children with febrile seizures is usually caused by common respiratory viruses, the distributions of which match those of seasonal community-acquired respiratory tract infections.
· Several genetic variations in ion channels seem associated with neuronal hyperexcitability in children with febrile seizures.
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-
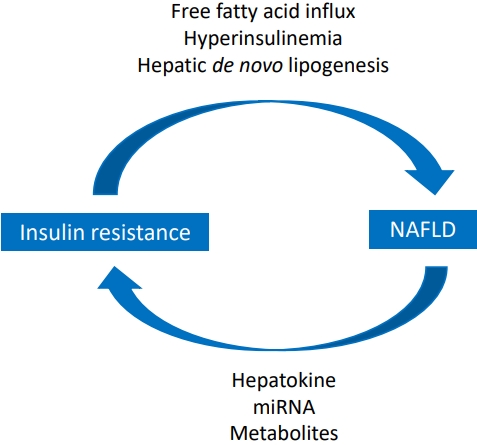
· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Other
- Hearing loss in neonates and infants
- Goun Choe, Su-Kyoung Park, Bong Jik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):369-376. Published online January 9, 2023
-

· Congenital hearing loss is common, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns and affecting 1.2%–11% of preterm and 1.6%–13.7% of neonatal intensive care unit neonates.
· Etiologies vary, and up to 80% of cases are genetic.
· Newborn hearing screenings follow the 1-3-6 rule, and babies at high risk of hearing loss should be referred to otolaryngology for early detection and timely intervention.
- Allergy
- Recent topics on gastrointestinal allergic disorders
- Yoshiyuki Yamada
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):240-249. Published online January 9, 2023
-
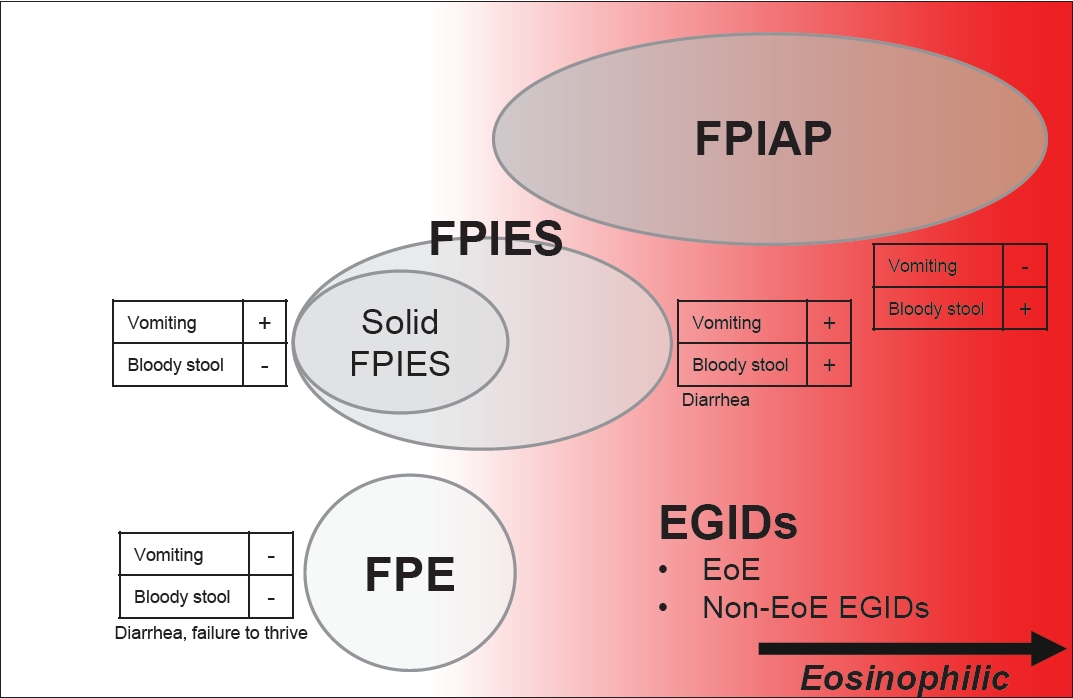
Gastrointestinal (GI) allergies are divided into immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed types. In addition to non-IgE-mediated, overlapping eosinophilic GI disorders (EGIDs) have increased in Japan. EGIDs, a mixed-type allergy category, include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and non-EoE EGIDs. The number of EoE cases has increased in Western countries, followed by Asian countries. Recent GI allergies may also be associated with type 2 inflammation.
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-
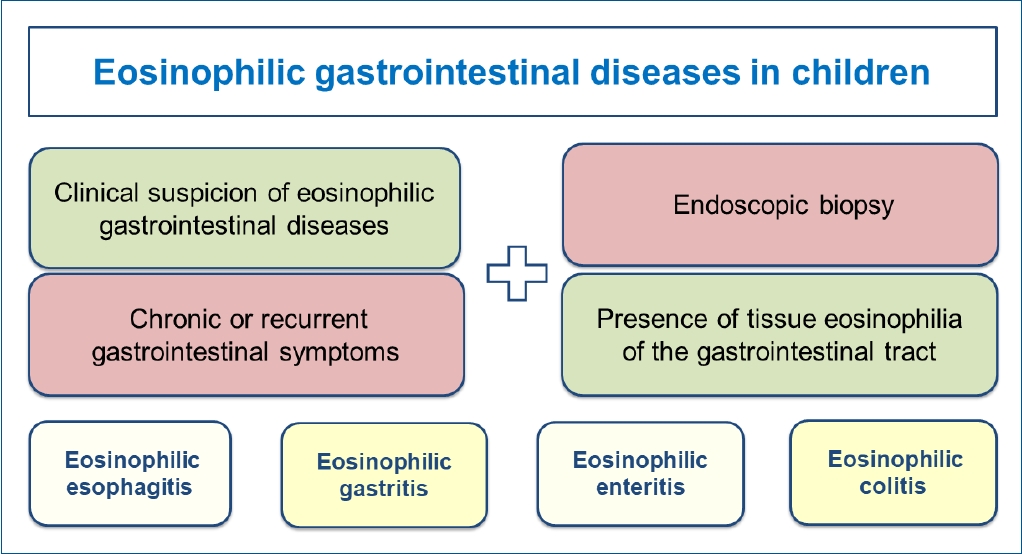
· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Cardiology
- Environmental changes surrounding congenital heart disease
- Eun-Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):332-338. Published online January 2, 2023
-
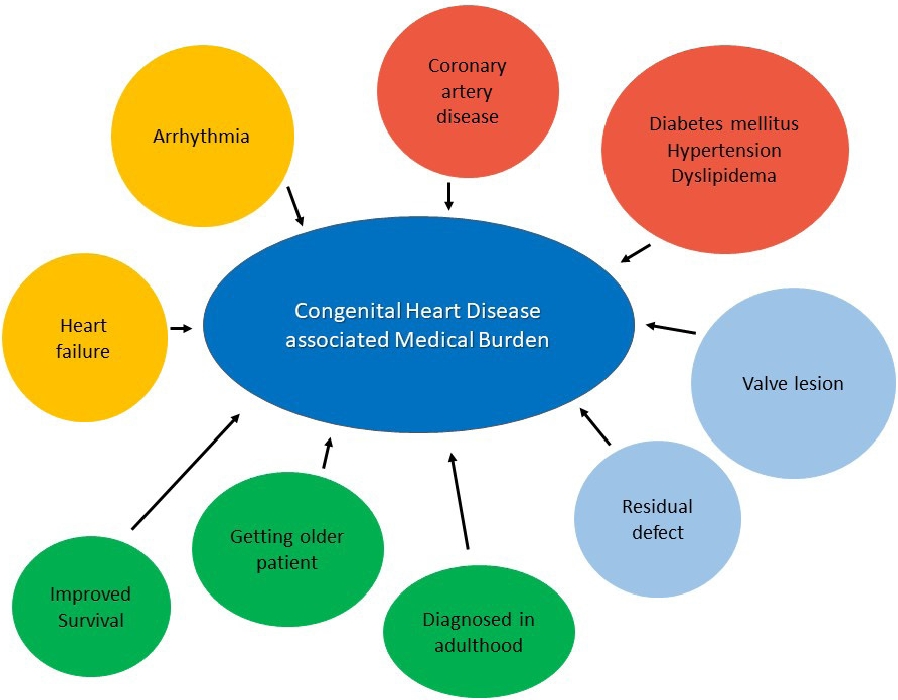
· As the number of patients with congenital heart disease increases, the medical burden increases.
· Various fusion imaging techniques using percutaneous procedures have been introduced.
· With advances in technology, convenient ambulatory devices have been introduced.
· A well-organized team approach is required to resolve advanced heart failure in patients with congenital heart disease.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- In Gyu Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):281-287. Published online December 30, 2022
-
· Among survivors, 60.9% of infants born at 22 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments, whereas 50.3% born at 23 weeks’ and 42.2% at 24 weeks’ gestation had moderate to severe impairments.
· Moderate and late preterm infants reportedly have less severe disease than very preterm infants, but they still experience adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
· The careful follow-up and early detection of developmental problems in these patients are required.
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Biallelic POLR3A variants cause Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch syndrome with atypical brain involvement
- Byungseung Moon, Minhye Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Jae So Cho, Hey Joon Son, Byung Chan Lim, Ki Joong Kim, Jong Hee Chae, Soo Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):142-144. Published online December 30, 2022
-

- Review Article
- Neurology
- Electroencephalography source localization
- Tae-Hoon Eom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):201-209. Published online December 29, 2022
-

· Electroencephalography (EEG) directly images the electrical activity of neurons at a higher temporal resolution than other neuroimaging techniques.
· EEG is still widely used in brain function research due to its advantages.
· Forward and inverse problems of EEG analyses require solutions.
· Methods such as the dipole and distributed source models have been introduced.
· Applications of EEG are expanding with the integration of other technologies and large-scale data.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):384-394. Published online December 28, 2022
-
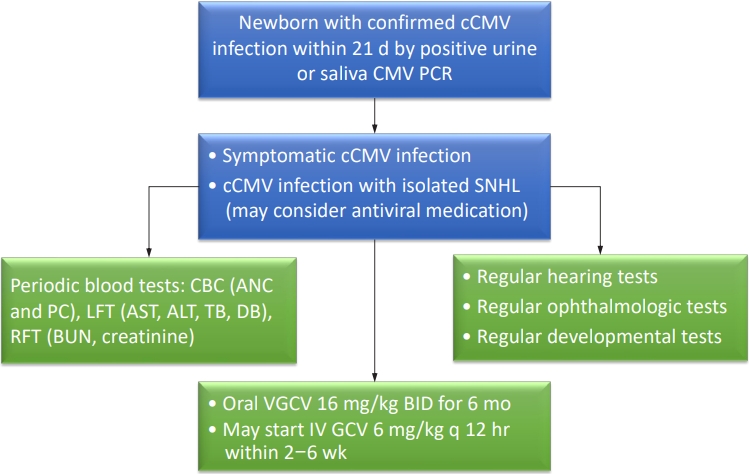
· Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is among the most common causes of nongenetic sensorineural hearing loss.
· Congenital CMV is initially treated with intravenous ganciclovir for 2–6 weeks and switched to oral valganciclovir, or with oral valganciclovir for the entire 6-month period.
· Infants with congenital CMV require periodic monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, platelet count, and blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function tests, audiological, ophthalmological, and developmental tests during antiviral medication.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
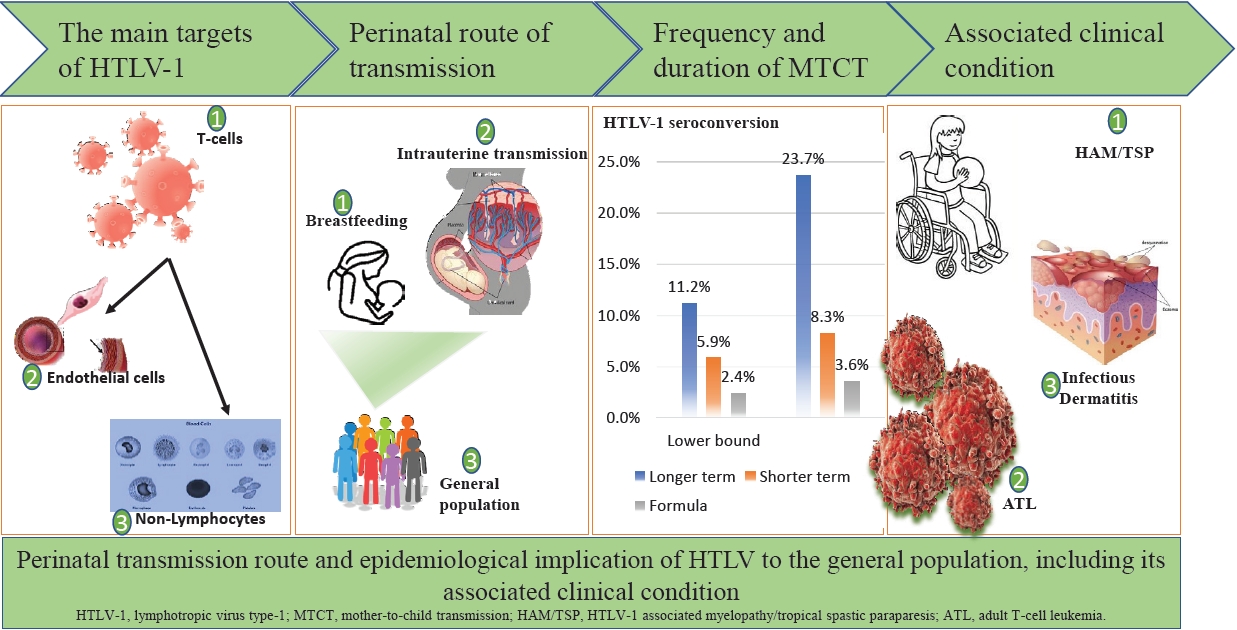
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Predicting COVID-19 transmission in a student population in Seoul, South Korea, 2020–2021
- Young Hwa Lee, Han Ho Kim, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):173-178. Published online December 22, 2022
-
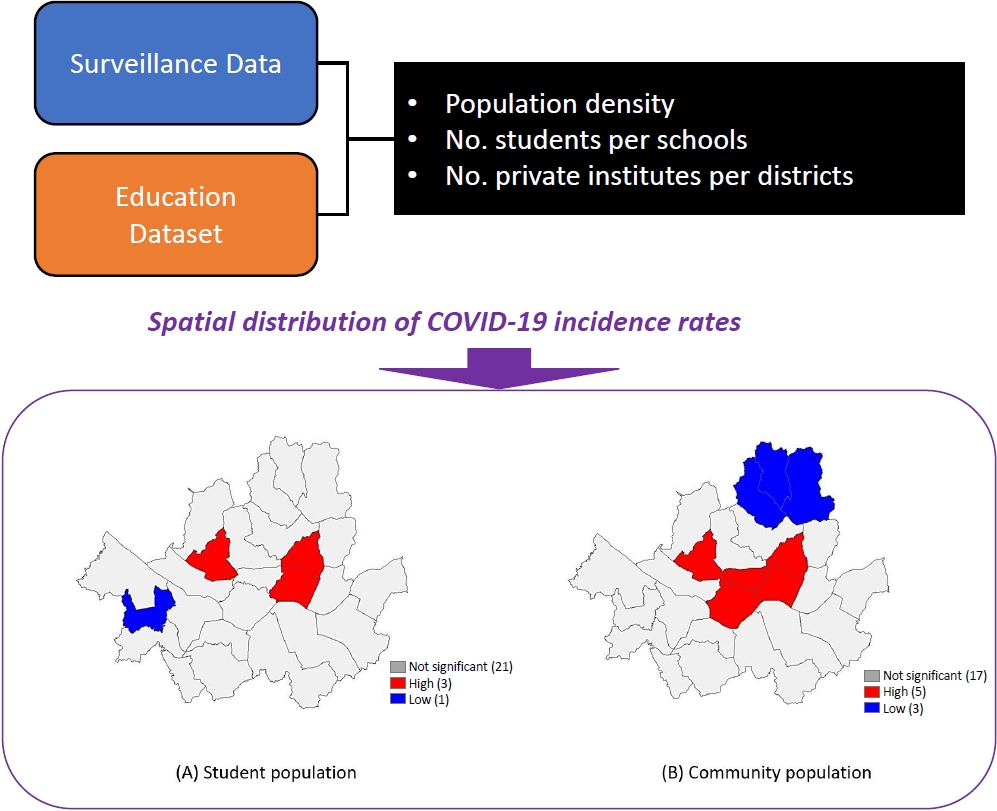
Question: What is the spatial distribution and determinants of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection among students in Korea?
Finding: The community population was closely associated with the risk of COVID-19, and the number of students per school class were inversely associated with COVID-19 rates in students.
Meaning: Our finding suggests that controlling the community-level burden of COVID-19 can help prevent sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in school-aged children.
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-
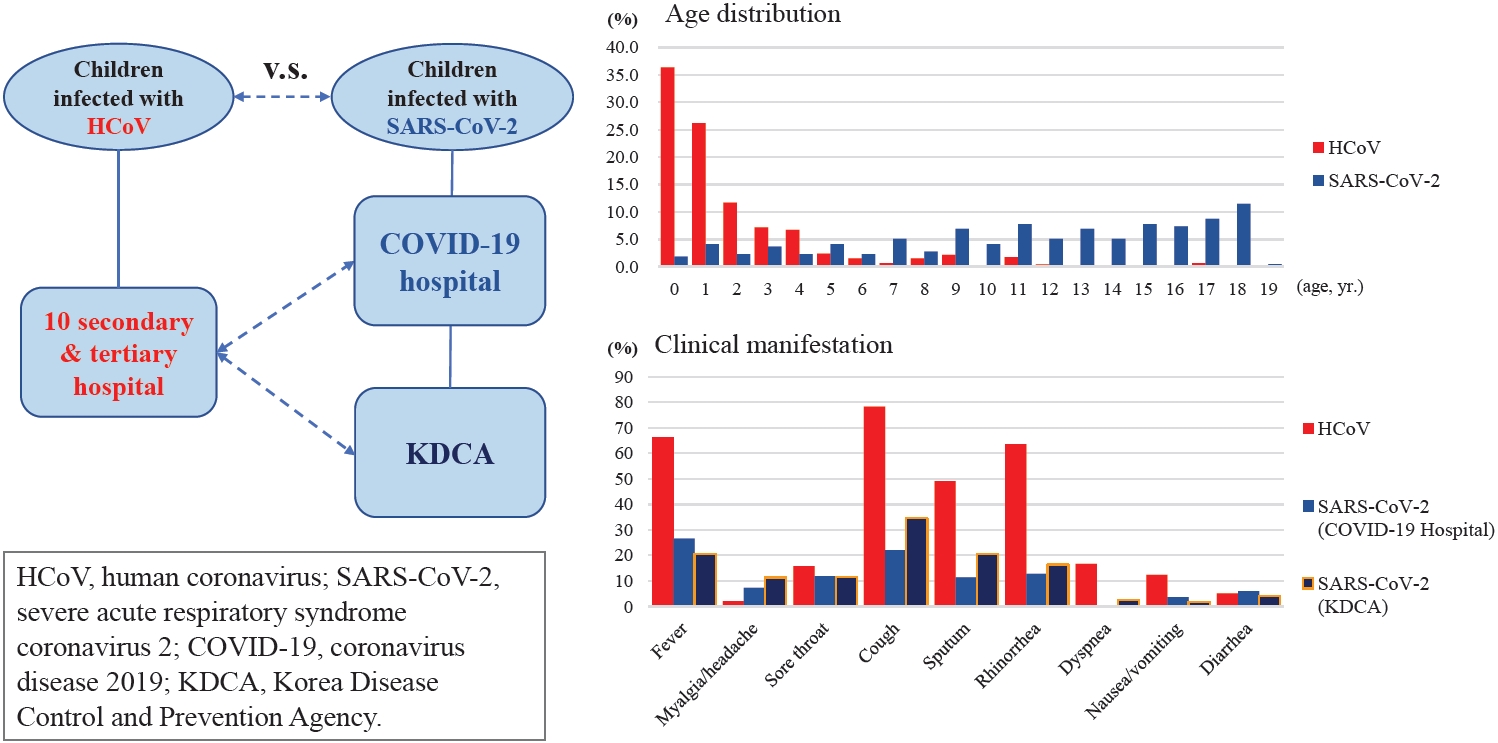
Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
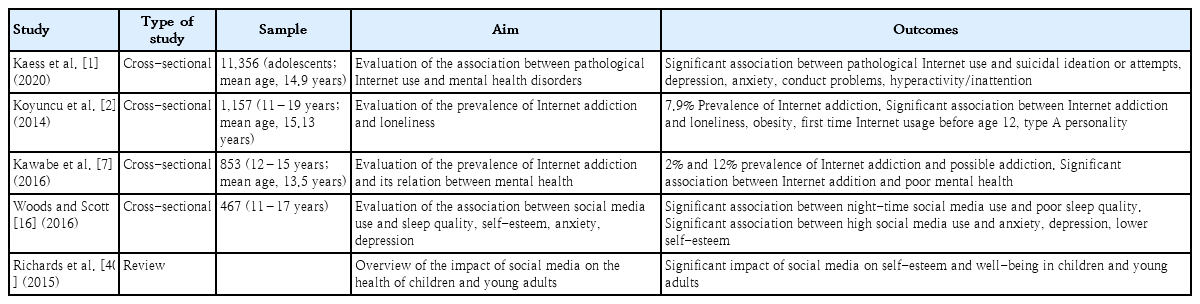
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Liver fibrosis in children: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy
- Elif Ozdogan, Cigdem Arikan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):110-124. Published online December 19, 2022
-
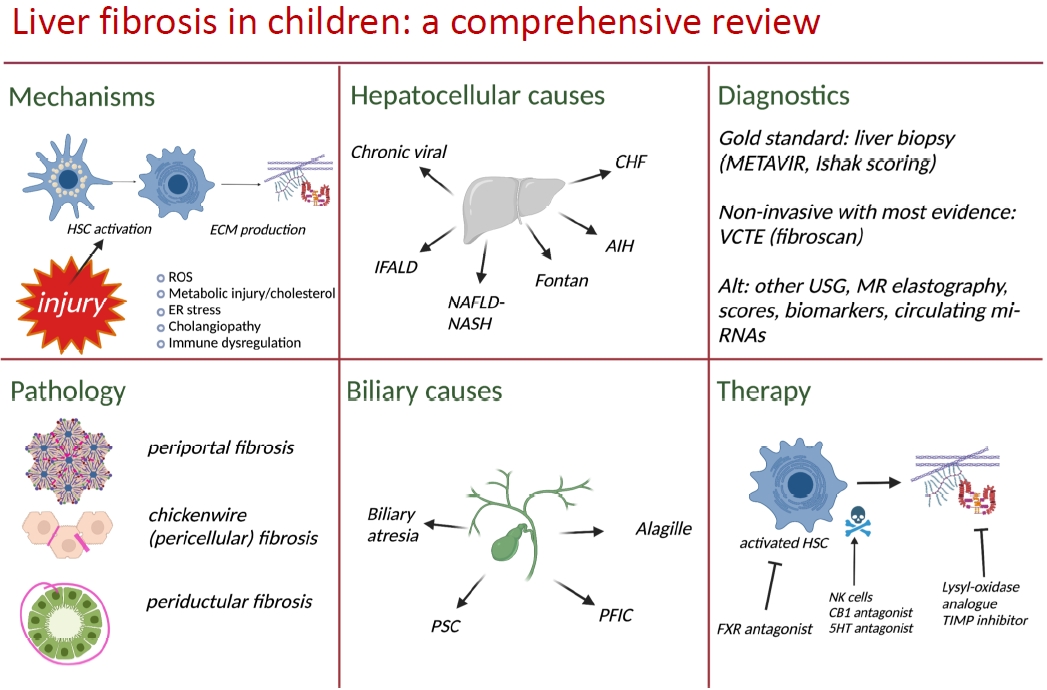
· Chronic liver diseases in children are heterogenous but converge in the common pathway of fibrosis.
· Much of the literature on mechanisms of fibrogenesis focus on adults but pediatric physiology has documented differences.
· Understanding of these distinctions are necessary to define, treat, and prevent fibrosis.
· Current management of liver fibrosis relies heavily on liver biopsy. Multiple tools have shown high diagnostic performance in pediatric and adult populations. Large, multicenter studies are needed for validation.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











