Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six month.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide versus room-air insufflation in pediatric colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial (10,539 times)
- Ajay Aravind, Ujjal Poddar, Anshu Srivastava, Moinak Sen Sarma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):594-600. Published online March 11, 2025
-
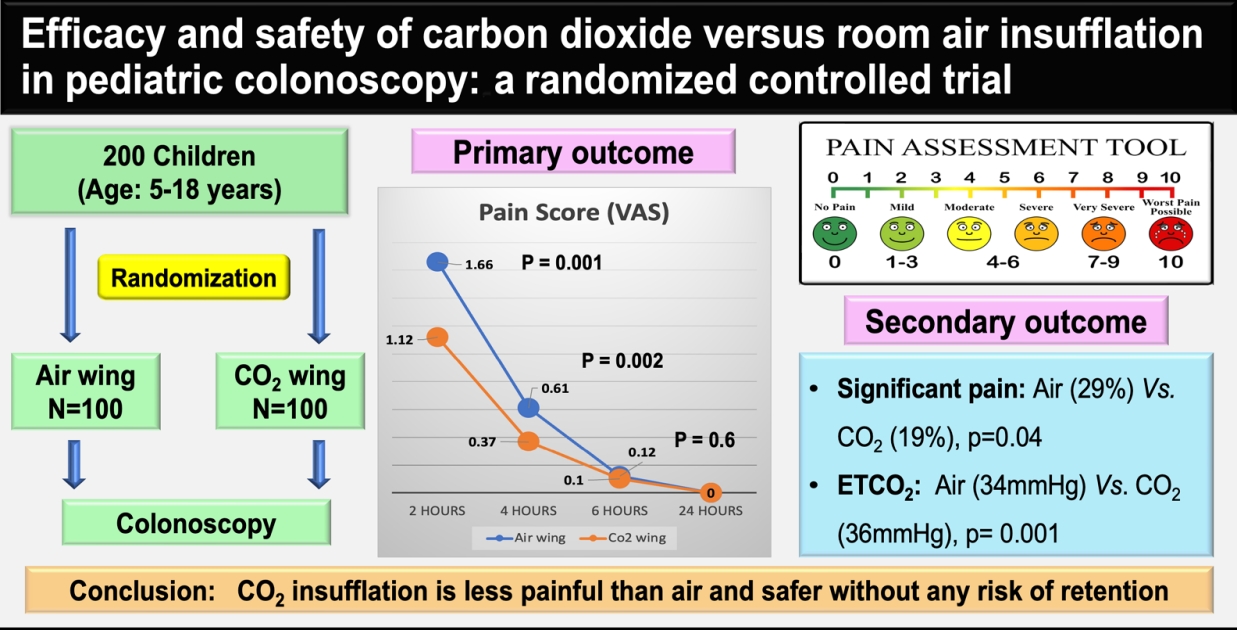
CO2 insufflation has been used instead of air insufflation to reduce postprocedure pain and discomfort in adults; however, adequately powered studies in children are scarce. This randomized controlled trial of 200 children showed that CO2 insufflation reduces postprocedure pain and discomfort during pediatric colonoscopy with no signs of CO2 retention. CO2 insufflation is safe and causes less pain in children.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Updates in neonatal resuscitation: routine use of laryngeal masks as an alternative to face masks (10,492 times)
- Eun Song Song, Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):240-246. Published online July 11, 2023
-

In neonatal resuscitation:
· Laryngeal masks are recommended when endotracheal intubation or positive-pressure ventilation fails.
· Laryngeal masks are useful even during chest compressions.
· Laryngeal masks aid neonates >34 weeks’ gestation and/or with a birth weight >2 kg.
· Main usage barriers include limited experience (81%), preference for endotracheal tubes (57%), and lack of awareness (56%).
· Second-generation laryngeal masks have a built-in esophageal drainage tube that prevents regurgitation into the glottis, and an orogastric tube can be inserted within the esophageal drainage tube to protect against gastric inflation.
- Endocrinology
- A review of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in endocrine-related disorders (10,472 times)
- Nur Faten Hafizah Rosli, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Rose Adzrianee Adnan, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):30-52. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is high among children and adolescents and mainly attributed to changes in environmental factors.
· Vitamin D hormone-like properties are associated with many endocrine-related disorders.
· The effect of vitamin D is modulated by the vitamin D receptor, polymorphisms of which are reportedly associated with an increased risk of disease development in children and adolescents.
- Nutrition
- The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey (KIPGroS): a study protocol (10,174 times)
- Jong Woo Hahn, MinSoo Shin, Jin Gyu Lim, Yoon-Joo Kim, Ki Soo Kang, Narae Lee, Seong Hee Jeong, Mun Hui Jeong, Yeoun Joo Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Jung Ok Shim, Jee Yoon Park, Chan-Wook Park, Joo Young Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Young Hwa Jung, Jaehyun Kim, Chang Won Choi, Ju Whi Kim, Seung Han Shin, Yun Jeong Lee, Young Ah Lee, Choong-Ho Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Young Eun Kim, Youn Ha Kang, Kyungwon Oh, Sungha Yun, Jae Sung Ko, Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):352-358. Published online February 13, 2025
-
The suitability of World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts for assessing the growth of children under 3 years of age in all countries remains controversial, and their applicability must be evaluated based on country-specific growth data. The Korea Infant Physical Growth Examination Survey evaluated the suitability of WHO growth charts to contribute to the next revision of growth charts in Korea.
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses (10,034 times)
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis (10,000 times)
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review (9,746 times)
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis (9,566 times)
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Wafaa M. Abo El Fotoh, Mona S. Habib, Salem E. Deraz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):578-586. Published online February 26, 2025
-
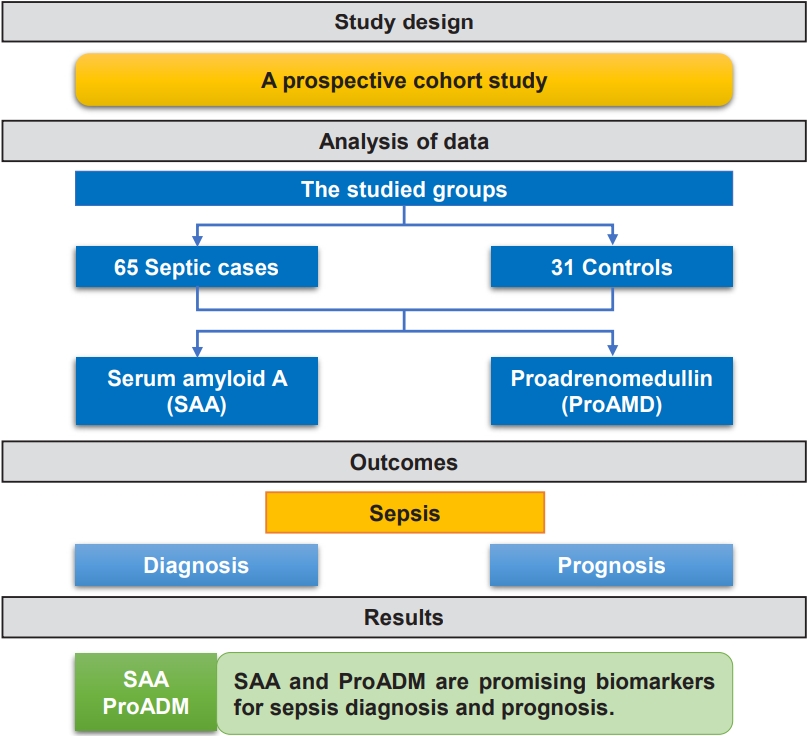
Question: Are serum amyloid A (SAA) and proadrenomedullin (proADM) levels early markers in critically ill children with sepsis?
Finding: This prospective case-control study included 65 critically ill children with sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and 31 controls. SAA and proADM levels were significantly higher in patients versus controls.
Meaning: SAA and proADM are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in pediatric sepsis.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation and sedation requirements in the pediatric intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis (9,461 times)
- Ambrus Szemere, Alíz Fazekas, Anna Réka Sebestyén, Rani Ezzeddine, Veronika Upor, Marie Anne Engh, Péter Hegyi, Zsolt Molnár, Klára Horváth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):406-416. Published online February 19, 2025
-
Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation requirements, pediatric intensive care unit length of stay, and sedative exposure. However, it may increase the likelihood of unplanned extubation, highlighting the importance of incorporating preventive measures to mitigate this risk.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis (9,439 times)
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (9,406 times)
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):601-607. Published online March 11, 2025
-
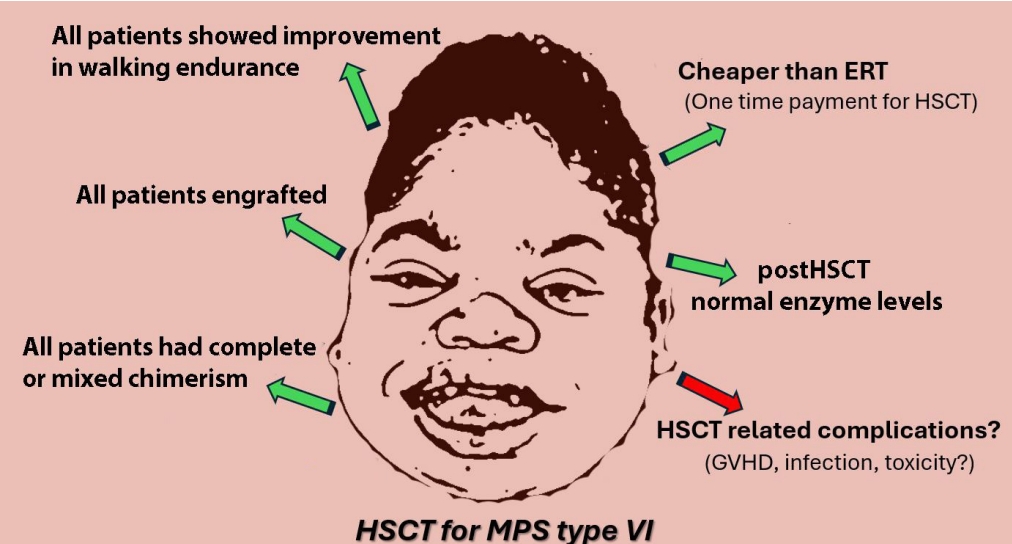
Question: Could hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) be an alternative to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI)?
Finding: HSCT is generally not offered due to reports of high toxicity and mortality. However, we detected fewer complications and graft-versus-host disease cases and no deaths with HSCT.
Meaning: HSCT is both less expensive than ERT and permanent; thus, it should be considered an alternative treatment for MPS VI.
- Review Article
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea (9,199 times)
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents (8,916 times)
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-

· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Occurrence of stroke in children and young adults in Indonesia: a multicenter private hospital study (8,827 times)
- Jeanne Leman, Veli Sungono, Yosua Timotius Haryono, Muhammad Adam Mudzakir, Dewi Lestari Rahmawati, Callistus Bruce Henfry Sulay, Gilbert Sterling Octavius
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(4):303-310. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Question: What is the occurrence of pediatric stroke in Indonesia?
Finding: This multicenter study identified 1,074 stroke cases, predominantly hemorrhagic (83.4%), with males and older children at higher risk. Accidents were the primary cause (73.2%).
Meaning: Pediatric stroke in Indonesia shows critical epidemiological trends, highlighting the need for targeted prevention efforts, particularly for high-risk groups like males and accident victims.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Practical concepts and strategies for early diagnosis and management of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in East-Asian children (8,815 times)
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):185-198. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) often coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other IgE or non-IgE mediated GI diseases. Diagnosing EGIDs requires a high index of suspicion and a comprehensive approach to differentiate them from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Tests such as fecal calprotectin and biopsies aid in severe cases. Maintaining a food diary helps identify triggers for long-term elimination. Awareness and education are key to effective management.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Somatic symptom severity during acute illnesses among children with functional gastrointestinal disorders (8,744 times)
- Rattanachart Sirinil, Anundorn Wongteerasut
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):587-593. Published online March 11, 2025
-
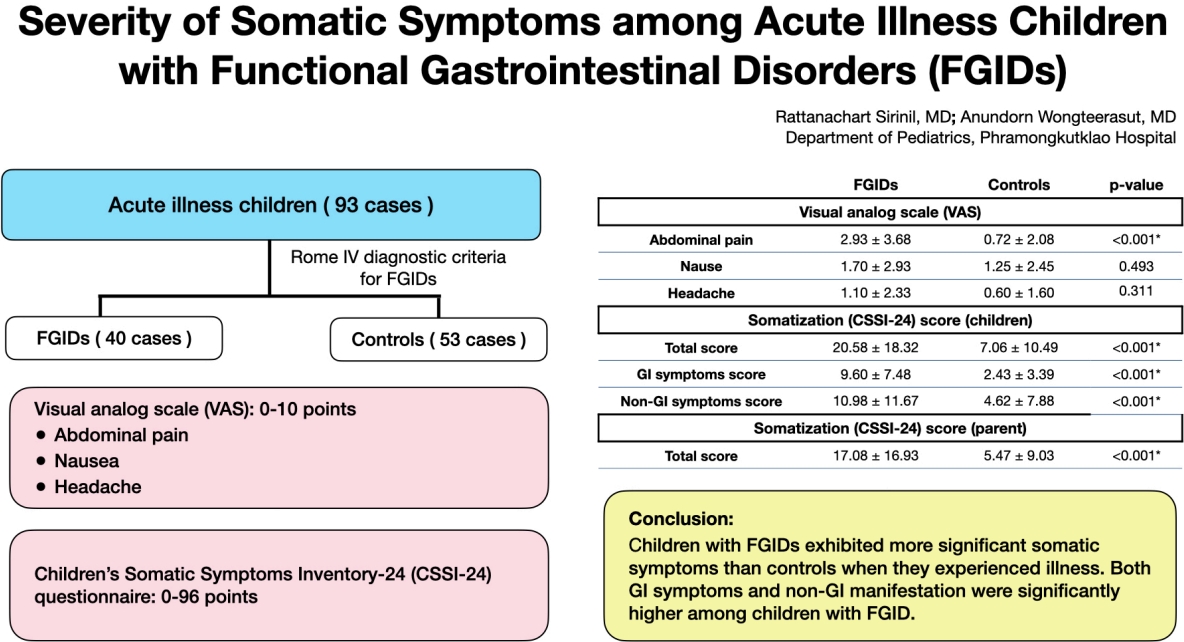
Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are associated with various somatic symptoms measured using a visual analogue scale and the Children’s Somatic Symptoms Inventory-24 questionnaire. Children with FGIDs exhibited more significant somatic symptoms than controls during acute illnesses. Gastrointestinal (GI) and non-GI manifestations are significantly more common in children with FGIDs.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Navigating the complex behavioral landscape of children in foster care and adopted families (8,553 times)
- Anisha Choi, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):620-623. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review (8,480 times)
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Enteric pathogens implicated in acute infectious diarrhea among young children in resource-limited region with rapidly growing population: a hospital-based cross-sectional study (8,478 times)
- Aseel Mahmood Ibrahim Al-Mashahedah, Randa Mohammed Dhahi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):379-387. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: What are the most common enteric pathogens in acute diarrhea among children younger than 5 years of age, and which age group is most susceptible?
Finding: Bacteria were the most common causative microorganisms of diarrhea, followed by viruses, parasites, and fungi. The 1–2-year age group was the most commonly affected.
Meaning: There is a need to formulate preventive strategies targeting children exposed to enteric pathogens to limit diarrhea.
- Letter to the Editor
- Hematology
- Neutropenia following metamizole use in pediatric patients: a multicenter retrospective study (8,250 times)
- Meraj Alam Siddiqui, Arzu Akyay, Fatma Burcu Belen Apak, Özgür Carti, Canan Albayrak, Melek İşik, Zühre Kaya, Sevgi Yetgin, Lale Olcay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):415-417. Published online July 23, 2024
-

- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Expanding genotype-phenotype correlation of Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1 (8,166 times)
- Manuela Lo Bianco, Federica Sipala, Xena Giada Pappalardo, Gaia Fusto, Roberta Rizzo, Federico Favata, Carla Cimino, Silvia Marino, Martino Ruggieri, Agnese Suppiej, Simone Ronsisvalle, Raffaele Falsaperla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):616-619. Published online May 12, 2025
-
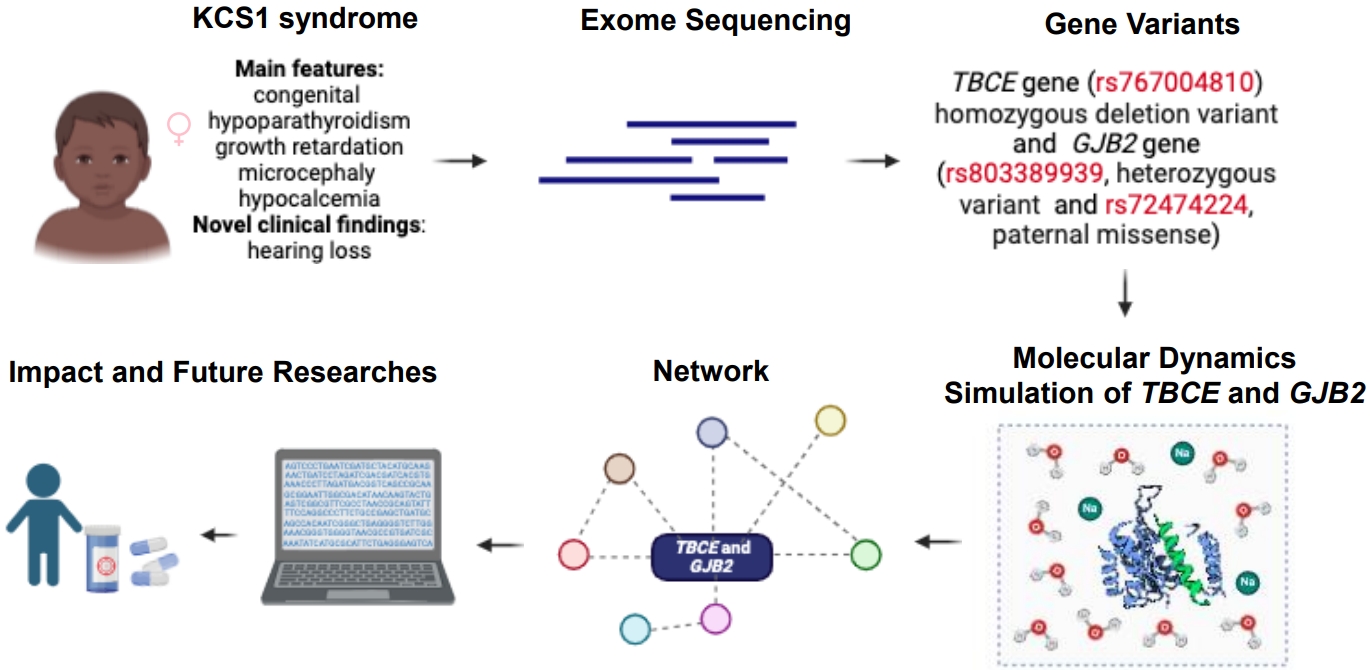
- Correspondence
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Authors' reply: a commentary on “COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus” (7,923 times)
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):626-627. Published online July 18, 2025
-
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021): a nationwide study using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children (7,900 times)
- Minwoong Kang, Eui Kyung Choi, Jeung Min Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Son Moon Shin; Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):772-780. Published online July 4, 2025
-

Question: What are the recent trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea?
Finding: Breastfeeding rates in South Korea declined significantly from 2007 to 2021, with lower rates observed in preterm, low-birthweight, and multiple-birth infants as well as rural or lower-income households.
Meaning: Targeted interventions, including prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based programs, are required to address disparities and improve breastfeeding rates.
- Editorial
- Nutrition
- Zinc as a treatment modality for acute infectious diarrhea in children (7,880 times)
- Ji Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):223-224. Published online October 31, 2024
-
· Prevention and management of dehydration is the major goal of treatment in acute infectious diarrhea in children.
· Zinc could be effective as an adjuvant therapy in reducing the duration of acute infectious diarrhea in malnourished children.
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Role of microRNA-498 and microRNA-410 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (7,867 times)
- Eman Salah Eldeen Arafat, Hasnaa Hesham Abotaleb, Dina Abdel Razek Midan, Abdel Hamid Abdo Ismail, Zeinab Sabri Abouzouna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):512-521. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Is it role of microRNA-410 (miRNA-410) and microRNA-498 (miRNA-498) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Findings: miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 can be auxiliary diagnostic and prognostic tools for neonatal HIE.
Meaning: we can use miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 as markers and indicator for HIE.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Practical issues of oral immunotherapy for egg or milk allergy (7,860 times)
- Sukyung Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):140-148. Published online June 19, 2023
-

· Oral immunotherapy should be supervised by pediatricians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing allergic reactions.
· Food allergen intake is gradually increased and maintained for years.
· Patients may experience allergic reactions and psychological problems.
· Adjunctive therapies (biologics, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists) may improve efficacy and safety.
· Contraindications include uncontrolled asthma, malignancy, active autoimmune disorders, and beta-blocker usage.
- Correspondence
- Infection
- A commentary on "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus" (7,822 times)
- Hinpetch Daungsupawong, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):624-625. Published online April 16, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Value of transabdominal ultrasonography for diagnosing functional constipation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis (7,796 times)
- Duc Long Tran, Phu Nguyen Trong Tran, Paweena Susantitaphong, Phichayut Phinyo, Palittiya Sintusek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):127-135. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Transabdominal ultrasonography is increasingly used as a novel modality for detecting pediatric functional constipation (FC). This systematic review and metaanalysis aimed to assess the diagnostic parameters of FC including rectal diameter (RD) and anterior rectal wall thickness. A systematic search was conducted of the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and PubMed databases through September 29, 2023, to identify studies comparing RD...
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Nonpharmacological interventions for managing postoperative pain and anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial (7,786 times)
- Edlin Glane Mathias, Mamatha Shivananda Pai, Vijay Kumar, Dinesh Narayanakurup, Malavika Kulkarni, Vasudeva Guddattu, Ann-Cathrine Bramhagen, Baby S Nayak, Anice George
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):677-685. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the effect of nonpharmacological interventions on postoperative pain and anxiety among children.
Finding: Nurse-provided distraction interventions reduce pain and anxiety among pediatric surgical patients.
Meaning: The findings suggest that nonpharmacological interventions provided postoperatively to children reduce their pain and anxiety levels.
- Allergy
- Regional differences in diagnosis and management of cow's milk allergy (7,769 times)
- Fabian Hendricx, Emma Robert, Jaime A. Ramirez-Mayans, Karen Rubi Ignorosa Arellano, Erick M. Toro Monjaraz, Yvan Vandenplas
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):601-607. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· Although there is broad consensus on many aspects regarding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cow's milk allergy, the impact of geographical, cultural, and socioeconomic factors remains unestablished.
· Availability and cost of formula for the management of cow's milk allergy have a major impact on the therapeutic choice.
· Region-specific guidelines for the treatment of cow's milk allergy are required.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











