- Editorial
- Allergy
- Effect of metabolic syndrome on pulmonary dysfunction in children with asthma
-
Hyo-Bin Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):136-137. Published online November 13, 2024
-
|
|
· The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increased in Korean children during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic owing to reduced physical activity resulting from social distancing.
· Metabolic syndrome impacts pulmonary dysfunction in childhood asthma.
· Further studies are needed to understand the mechanism linking asthma and metabolic syndrome and develop interventions. |
-
-
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview
-
Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

|
· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
-
In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-
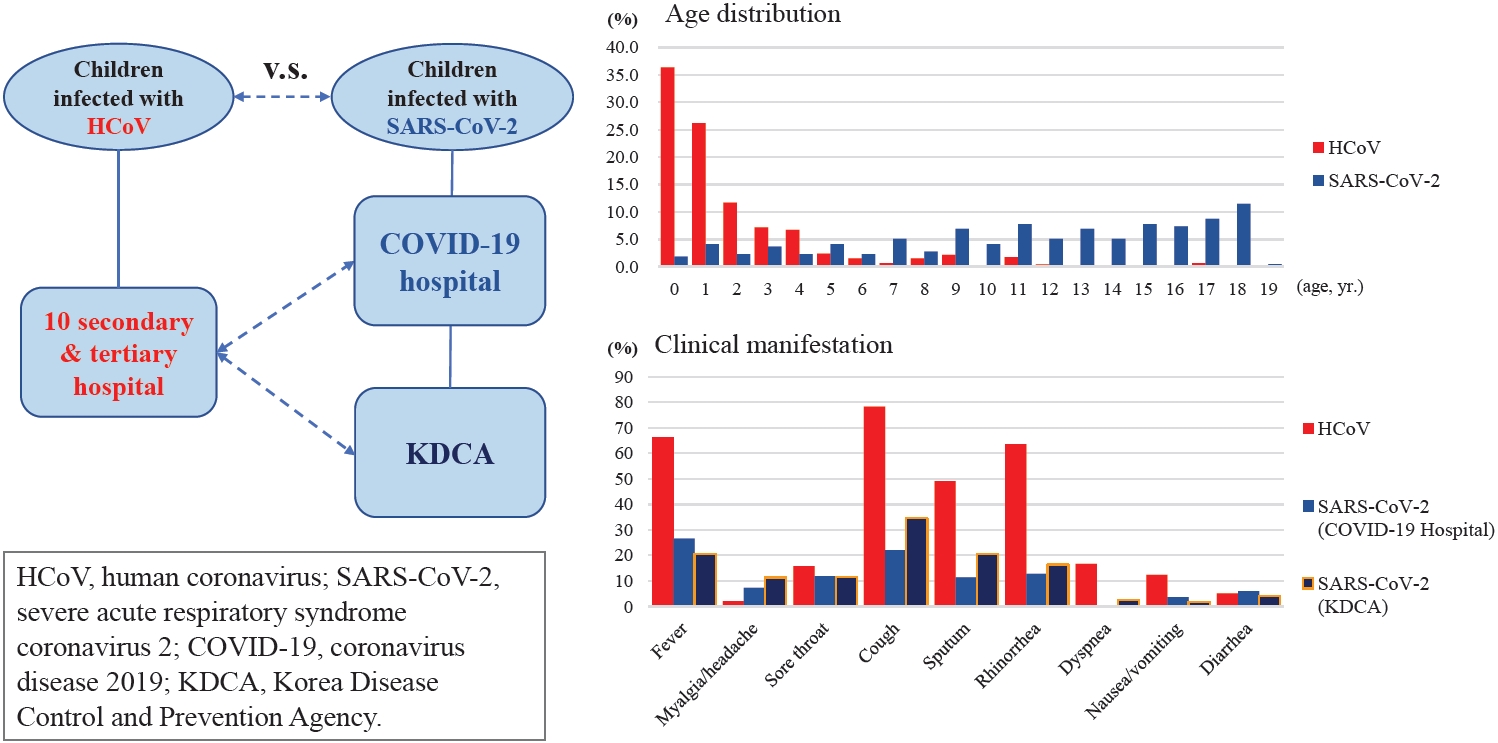
|
Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Influence of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on respiratory health in children
-
Hyo-Bin Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):348-349. Published online May 3, 2022
-
|
|
· Practicing hand hygiene, wearing a mask, maintaining social distancing, and other lockdown measures were implemented to reduce the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a worldwide disaster that started in 2019.
· The advent of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic resulted in positive secondary effects, such as reduced respiratory viral infections in children and decreased degrees of air pollution. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Asthma predictive index as a useful diagnostic tool in preschool children: a cross-sectional study in Korea
-
Dong Hyeon Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Hyo-Bin Kim, So-Yeon Lee, Gwang-Cheon Jang, Dae-Jin Song, Woo Kyung Kim, Young-Ho Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Jung Yeon Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):104-109. Published online November 8, 2019
-

|
Question: Is physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children associated with the asthma predictive index, atopic sensitization, or pulmonary function test?
Finding: Physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children was associated with the asthma predictive index, but not with spirometry, methacholine provocation test, fractional expiratory nitric oxide level, and atopic sensitization.
Meaning: Physician-diagnosed asthma in preschool children may be different from classic atopic asthma in school children or adolescents. |
-
-
- Case Report
- Allergy
- Drug eruption by antihistamine mistaken for chronic urticaria in a child
-
Gun Moo Lee, Shou-Yu Chu, Sung Yeon Kang, Hyo-Bin Kim, Jin-Sung Park, Ja Kyoung Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(2):75-78. Published online October 30, 2018
-

|
Although rare, antihistamines can cause adverse effects, including drug-induced eruptions or anaphylaxis. A 4-year-old child visited the pediatric department of a hospital for skin eruptions after administration of antihistamines, (e.g., ucerax [hydroxyzine] or leptizine [levocetirizine]), for cholinergic rashes; he did not have pruritus. Skin prick, intradermal, and drug provocation tests were performed to determine the relationship between the antihistamines and... |
-
-
- Original Article
- Association between cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and respiratory tract infections in the first 6 months of age in a Korean population: a birth cohort study (COCOA)
-
Youn Ho Shin, Jinho Yu, Kyung Won Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Seo-Ah Hong, Eun Lee, Song-I Yang, Young-Ho Jung, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Ji-Won Kwon, Byoung-Ju Kim, Hyo-Bin Kim, Jung Yeon Shim, Woo Kyung Kim, Dae Jin Song, So-Yeon Lee, Soo Young Lee, Gwang Cheon Jang, Dong In Suh, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Bong Sung Kim, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-Young Oh, Ja-Young Kwon, Kyung-Ju Lee, Hee Jin Park, Pil Ryang Lee, Hye-Sung Won, Soo-Jong Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):439-445. Published online October 31, 2013
-
|
|
Purpose Previous studies suggest that the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] in cord blood may show an inverse association with respiratory tract infections (RTI) during childhood. The aim of the present study was to examine the influence of 25(OH)D concentrations in cord blood on infant RTI in a Korean birth cohort. MethodsThe levels of 25(OH)D in cord blood obtained from 525 Korean... |
-
-
- Nationwide surveillance of acute interstitial pneumonia in Korea
-
Byoung-Ju Kim, Han A Kim, Young-Hwa Song, Jinho Yu, Seonguk Kim, Seong Jong Park, Kyung Won Kim, Kyu-Earn Kim, Dong Soo Kim, June Dong Park, Kang Mo Ahn, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hyang-Min Jung, Chun Kang, Soo-Jong Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):324-329. Published online March 15, 2009
-
|
|
Purpose : Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) is a rare disease, but its prognosis is fatal because of lack of efficient treatment modality. Recently, it has been reported that there was epidemic AIP in Korea. This study aims to investigate the past and current status of AIP in Korea.
Methods : We performed a nationwide survey and a prospective study. From August... |
-
-
- Airway Compression or Airway Anomaly Causing Respiratory Symptoms in Infants and Children with Cardiovascular Diseases
-
Ja-Hyeong Kim, So-Yeon Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, So-Eun Koo, Sung-Jong Park, Young-Hui Kim, In-Suk Park, Jae-Kon Ko, Dong-Man Seo, Soo-Jong Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(7):737-744. Published online July 15, 2005
-
|
|
Purpose : Infants and children with cardiovascular diseases often present with respiratory symptoms. However, missed or delayed evaluation for potential airway problem may complicate overall prognosis. The aim of this study is to determine the clinical characteristics of these patients and explore the cause of airway problem.
Methods : We reviewed the medical records of 64 patients(M : F=33:31, mean... |
-
-
- Clinical Outcome and Prognostic Factors of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Children
-
Jung-Min Ko, Eun-Ju Ha, Eun-Hee Lee, So-Youn Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Soo-Jong Hong, Seong-Jong Park
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(6):599-605. Published online June 15, 2005
-
|
|
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to examine the causes, clinical courses and outcomes in children with acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS), and evaluate the physiologic variables as prognostic factors in the patients.
Methods : Retrograde medical chart review was carried out in 24 patients who were diagnosed with ARDS at the pediatric intensive care unit(PICU) during 20-month period.
Results... |
-
-
- Airway Expandible Metallic Stent Implantation in Children with Tracheal or Bronchial Stenosis
-
Ju Young Jang, Hyo-Bin Kim, So Yeon Lee, Ja Hyung Kim, Seong Jong Park, Ji Hoon Shin, Soo-Jong Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(5):512-517. Published online May 15, 2005
-
|
|
Purpose : In adults, endoscopic tracheobronchial balloon dilatation and stenting have become valuable methods to establish and maintain an adequate airway lumen when tracheomalacia or neoplastic growth compromise the airways. But in children, only a few cases were reported due to technical problems. We report six children who were treated with stent implantation and describe the use and safety of... |
-
-
- Clinical Study of Children Using Home Mechanical Ventilation
-
Young Joon Ahn, Seung Hyeon Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Seong Jong Park, Tae Sung Ko, Soo-Jong Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):401-405. Published online April 15, 2005
-
|
|
Purpose : The use of mechanically-assisted ventilators at home reduces morbidity and improves the quality of life in children with chronic respiratory failure. But in Korea there is no clinical data of children with home mechanical ventilation. We investigated ventilator types, duration, the causes of failure or death, and the cost needed for care.
Methods : We retrospectively analyzed the medical... |
-
-
- Outcome after Discontinuation of Antiepileptic Drugs in Well Controlled Epileptic Children - Recurrence and Related Risk Factors
-
Hyo-Bin Kim, Su Jeong You, Tae-Sung Ko
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):66-75. Published online January 15, 2004
-
|
|
Purpose : There has been no exact criteria established for when to discontinue antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in epileptic children who had been well controlled for a long period. This study was undertaken to evaluate the recurrence rate and predictive risk factors of relapse after discontinuation of AEDs in epileptic children who had been seizure-free.
Methods : We retrospectively studied 294 children... |
-
-
|
















