- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial
-
Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
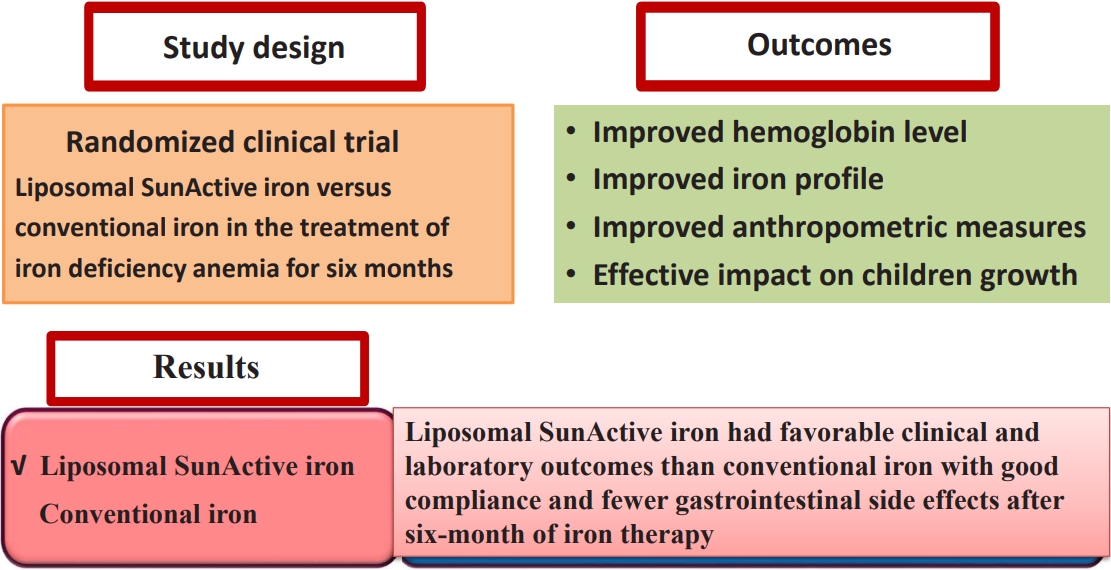
|
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years
Methods: This... |
-
-
- Oncology
- Prognostic role of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in predicting infection in pediatric cancer with febrile neutropenia
-
Seham M. Ragab, Sara Mahmoud El-Deeb, Ahmed Saeed, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):445-453. Published online January 13, 2025
-

|
· Infection remains a leading cause of death in febrile neutropenia (FN).
· Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-ProADM) levels are higher among patients with FN and a bacterial infection.
· A longer FN duration and hospital stay length as well as elevated C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and MR-ProADM levels are significant risk factors for mortality. |
-
-
- Other
- Role of neutrophil elastase in predicting infection among children with chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia
-
Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Doaa M. Elian, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Esraa T. Allam, Mariam S. Kandeel, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):801-807. Published online June 10, 2025
-

|
Question: Can neutrophil elastase (NE) levels predict infection— the primary cause of mortality—among children with hematological malignancies and febrile neutropenia (FN)?
Finding: Elevated levels of NE were found in children with chemotherapy-induced FN and a bacterial infection.
Meaning: Increased NE levels and prolonged FN are important factors associated with mortality risk. |
-
-
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial
-
Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-

|
Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration. |
-
-
|
















