- Review Article
- Other
- Cost-effectiveness of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: a systematic review
- Rezwanul Rana, Syed Afroz Keramat, Moin Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):628-640. Published online April 16, 2025
-
Universal newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) demonstrates robust cost-effectiveness across diverse high-income healthcare systems, both from healthcare and societal standpoints. Early detection yields substantial savings. While uncertainties persist, impacting precise cost-effectiveness, the overall finding is positive. Future research must prioritize enhanced data collection and statistical rigor to refine our understanding of SCID's economic impact within the Australian context.
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-
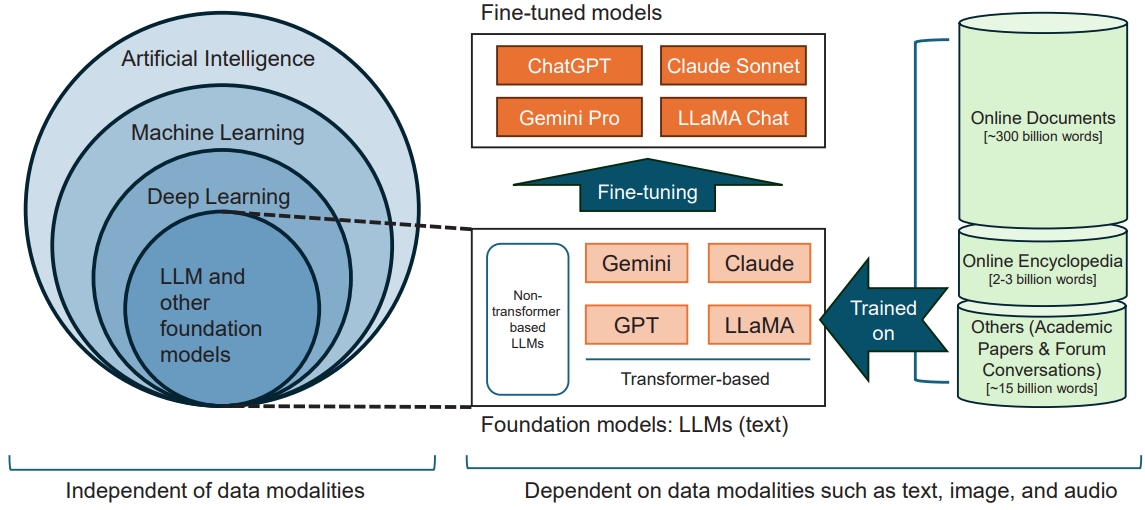
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: bridging potential, clinical practice, and ethical considerations
- Yoon Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):652-655. Published online August 28, 2025
-
· Artificial intelligence (AI) holds transformative potential for pediatric healthcare, with applications spanning prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up across diverse subspecialties; however, ethical concerns, scarcity of pediatric- specific data, and limited funding remain significant challenges.
· International consensus on pediatric AI guidelines, expanding child-specific datasets, and incorporating explainable AI are essential to ensure safety and trust.
· Multicenter collaboration and increased investment can address these gaps, enabling equitable, reliable, and pediatric- centered AI solutions.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Respiratory severity score-guided postnatal systemic corticosteroid therapy for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants
- Gyeong Eun Yeom, Ju Sun Heo, Baek Sup Shin, Seh Hyun Kim, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):656-665. Published online July 8, 2025
-
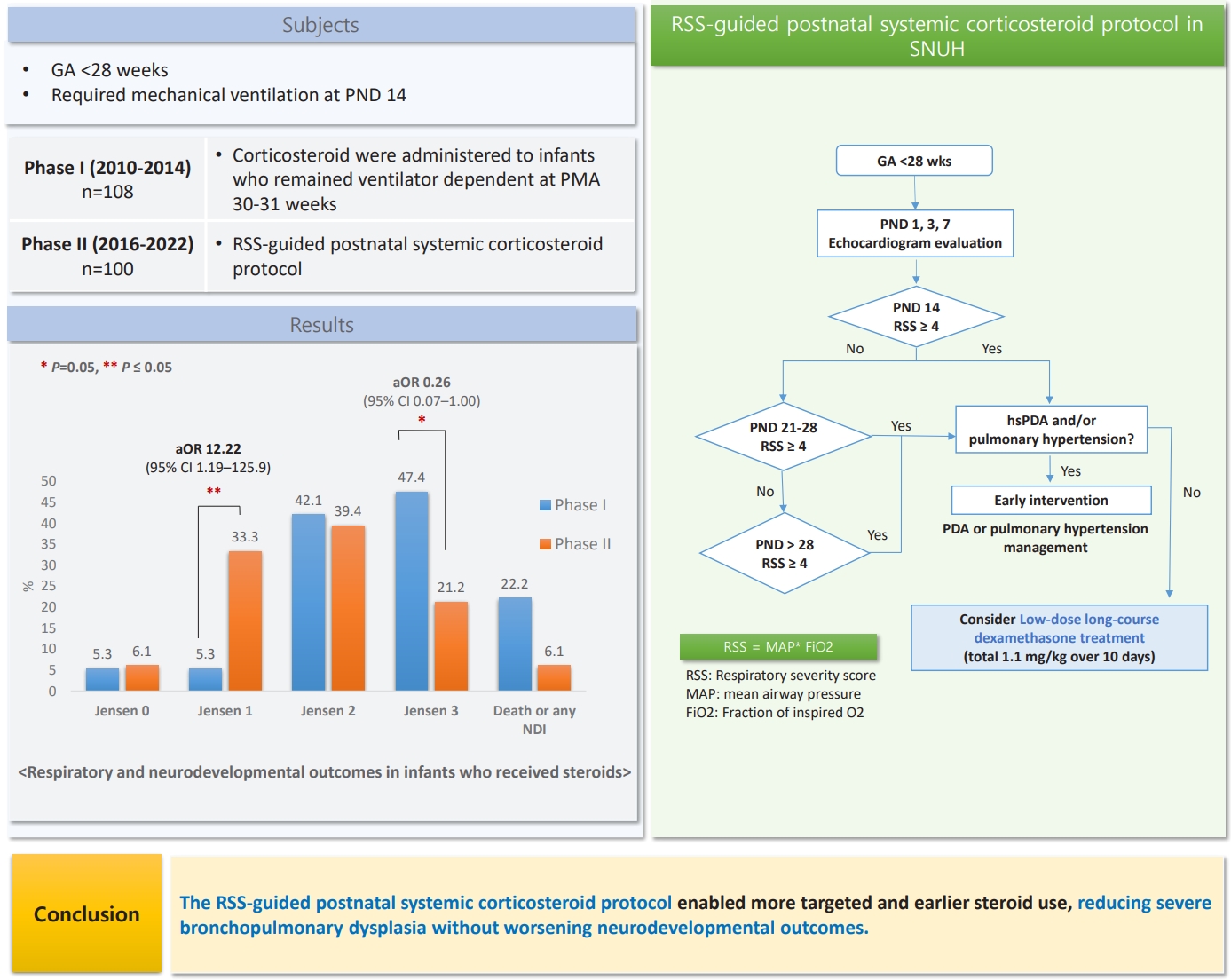
Question: Does a respiratory severity score (RSS)-guided postnatal corticosteroid protocol improve respiratory outcomes of extremely preterm (EP) infants without worsening neurodevelopmental outcomes?
Finding: The protocol enabled targeted and early steroid use, thereby reducing severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia without affecting mortality or causing neurodevelopmental impairments.
Meaning: The RSS-guided protocol may offer a more precise and individualized postnatal corticosteroid therapy for EP infants.
- Nutrition
- Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study
- Phakwan Laohathai, Rathaporn Sumboonnanonda, Puthita Saengpanit, Chodchanok Vijarnsorn, Chatchawan Srisawat, Kwanjai Chotipanang, Sarawut Junnu, Supawan Kunnangja, Hathaichanok Rukprayoon, Phakkanan Phuangphan, Sompong Liammongkolkul, Arthima Phaokong, Narumon Densupsoontorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):666-672. Published online April 16, 2025
-
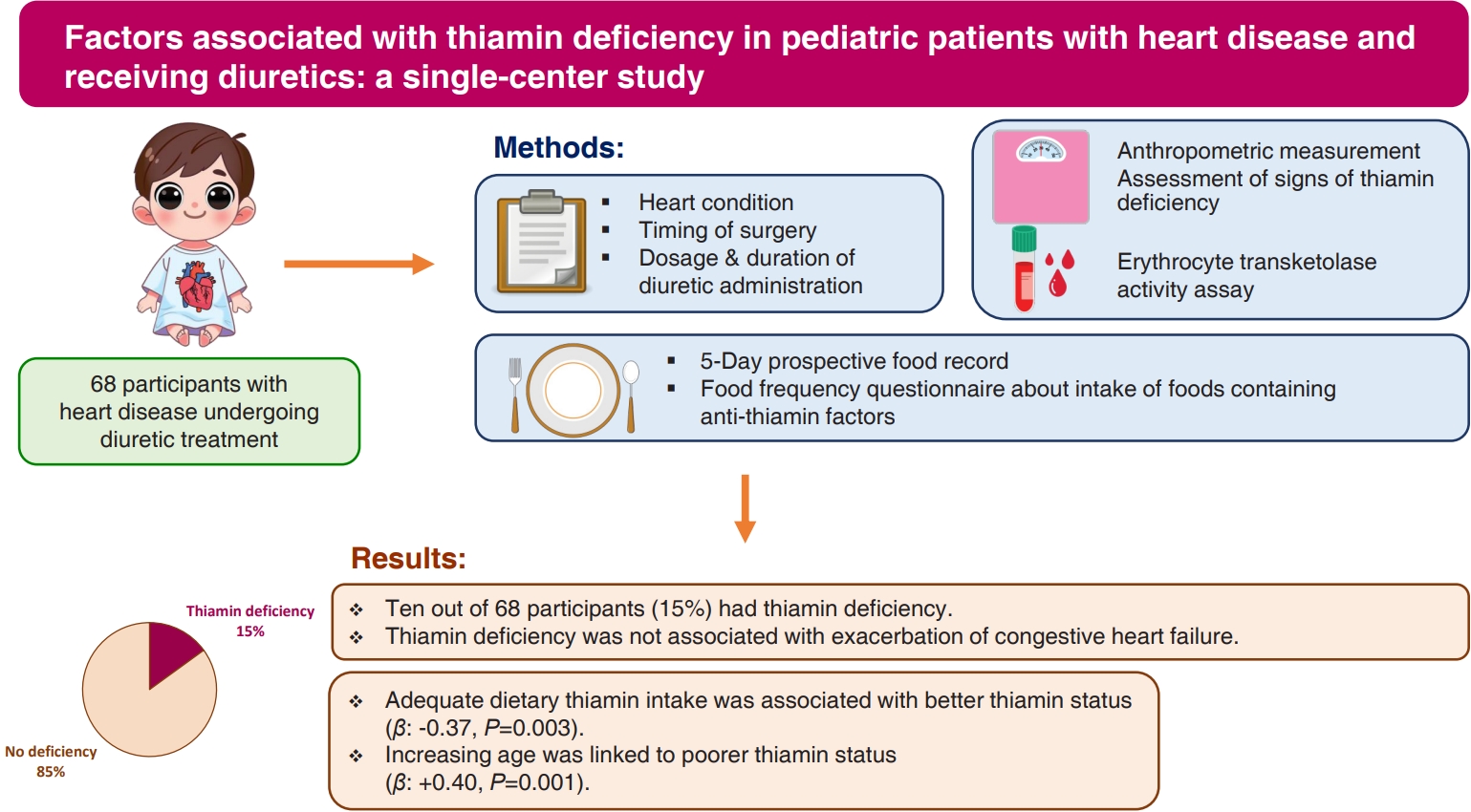
Question: Are pediatric patients with heart disease who are receiving diuretics at risk of thiamin deficiency (TD)?
Finding: Fifteen percent of the patients had TD. TD was associated with inadequate dietary thiamin intake and increasing age.
Meaning: The thiamin pyrophosphate effect should be assessed in those with high risk of TD. Dietary counseling should be emphasized to ensure adequate dietary thiamin intake.
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in adolescents: transcranial doppler versus autonomic function test results
- Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):673-679. Published online August 6, 2025
-
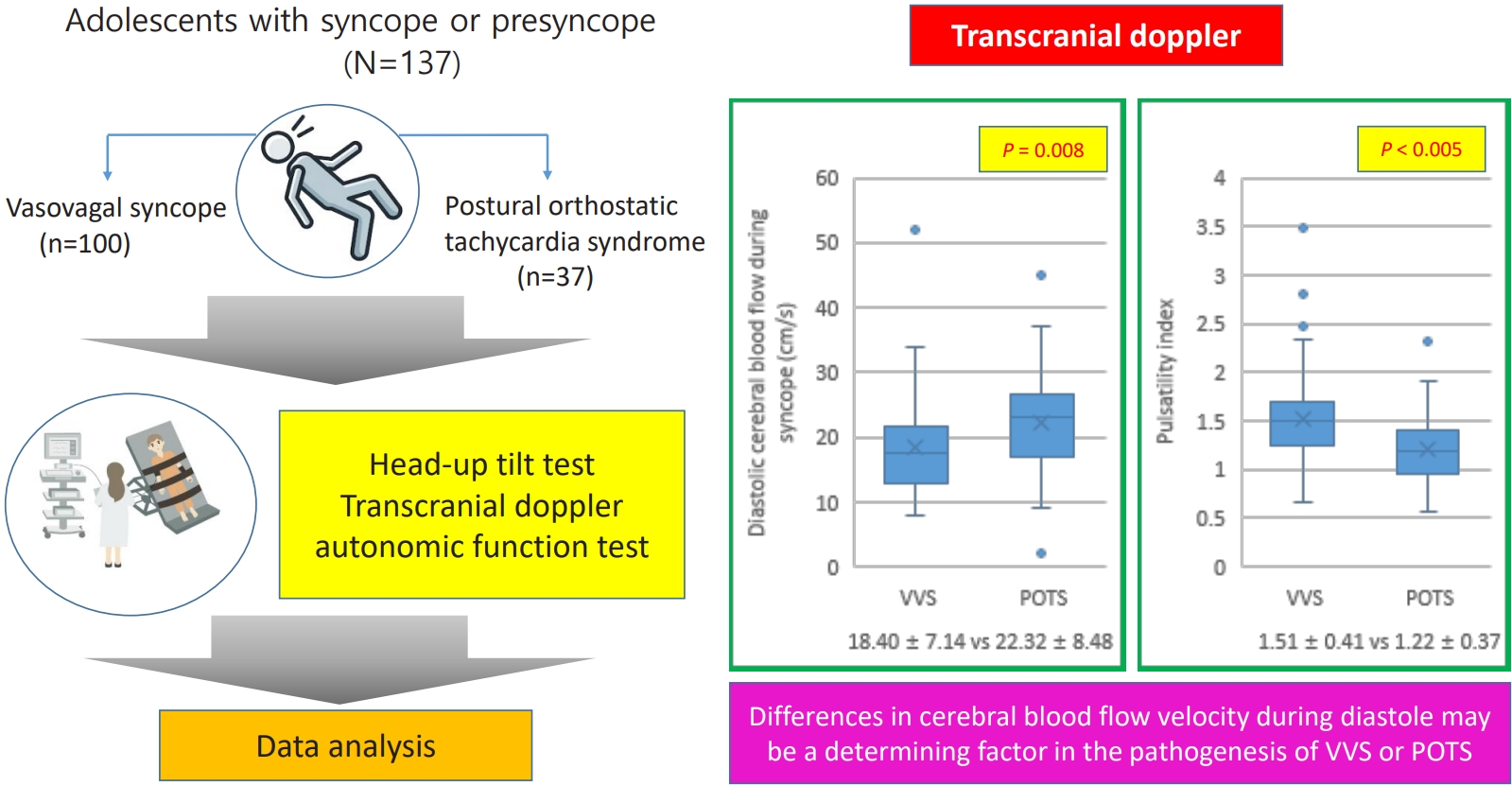
Question: Vasovagal syncope (VVS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) are representative forms of neurally mediated syncope. What influences the occurrence of each?
Finding: Autonomic function test results did not differ, but cerebral blood flow during diastole on transcranial doppler differed between VVS and POTS.
Meaning: Differences in diastolic cerebral blood flow velocity play an important role in VVS and POTS.
- Pulmonology
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-
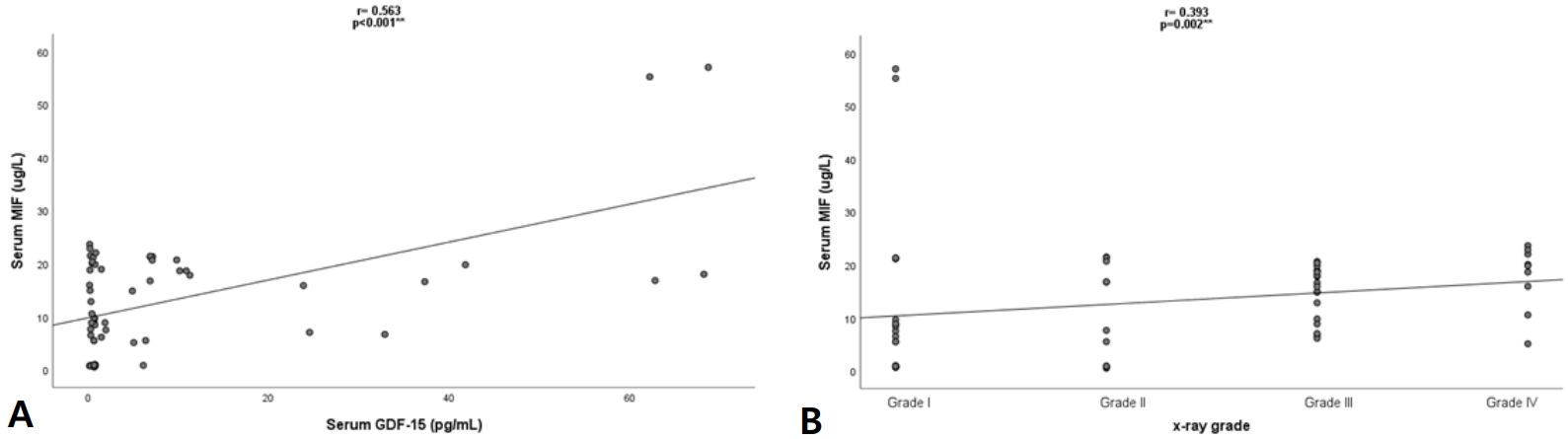
Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Effect of vitamin C supplement in treatment of childhood pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial
- Chutima Phuaksaman, Katechan Jampachaisri, Klaita Srisingh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):690-699. Published online April 1, 2025
-
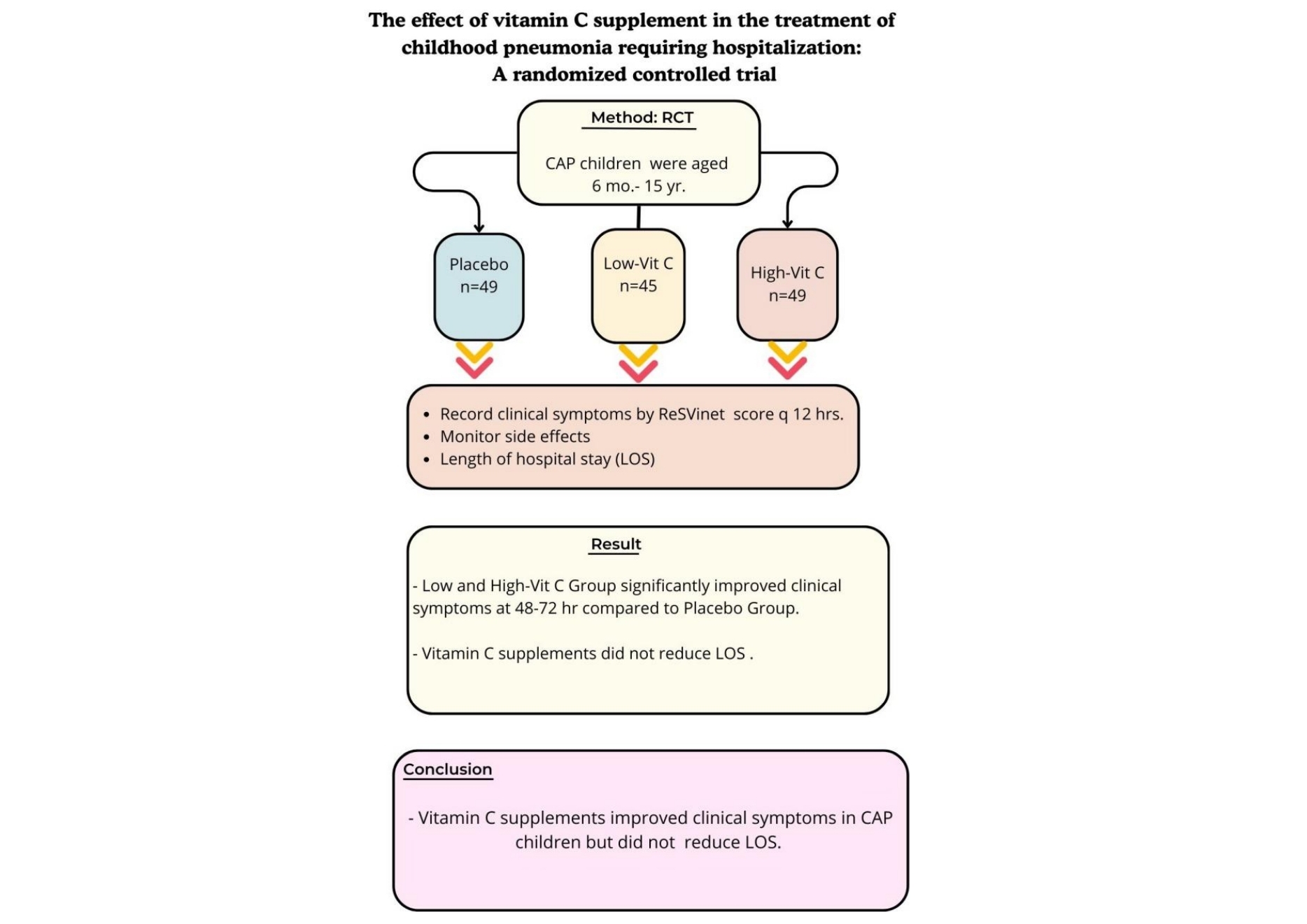
This study assessed the effects of vitamin C on children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Vitamin C supplementation improved clinical symptoms within 48–72 hours compared to placebo but did not reduce the length of hospital stay (LOS). These findings suggest that vitamin C is beneficial for managing CAP severity, but does not affect LOS.
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-
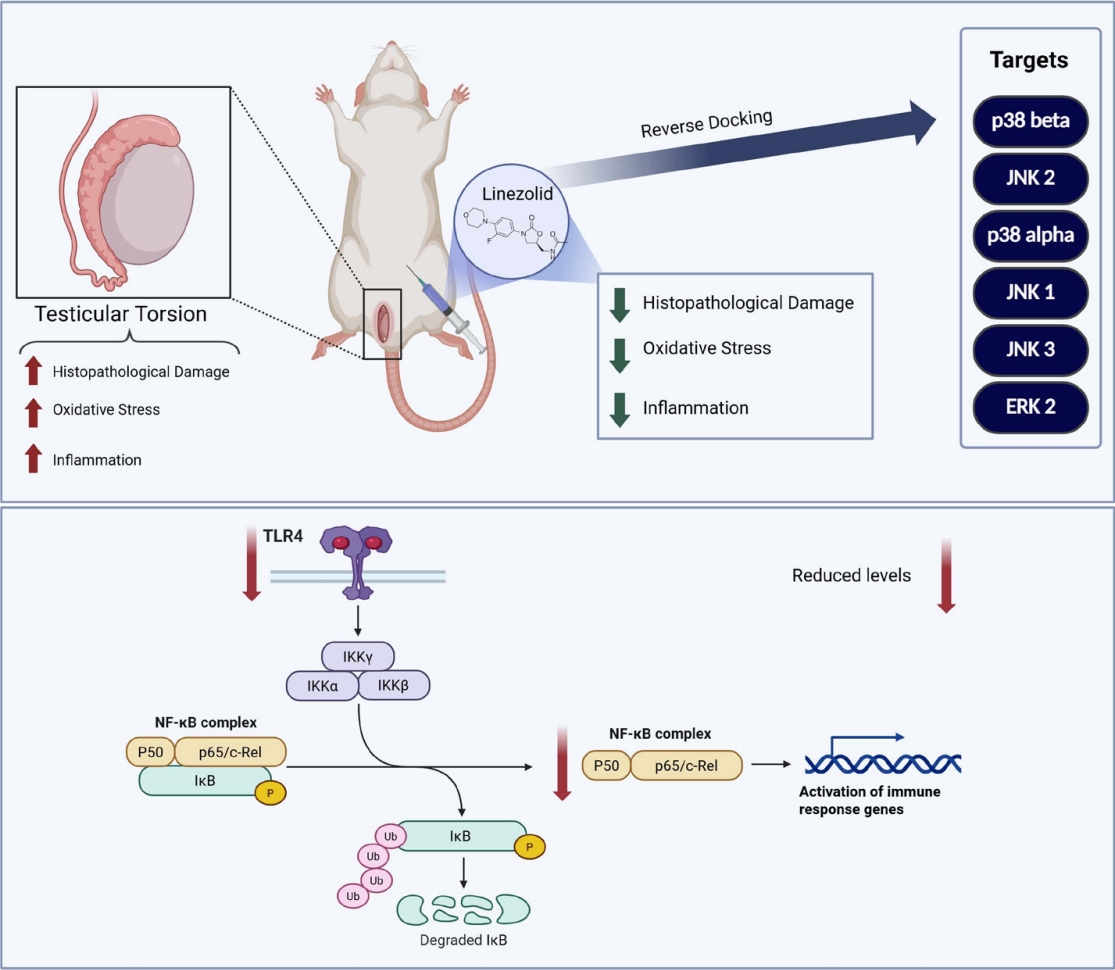
Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Oncology
- Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for treatment of relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancy in children and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ghea Mangkuliguna, Edi Setiawan Tehuteru, Reganedgary Jonlean, Nicholas Adrianto, Stella Kallista
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):712-721. Published online July 4, 2025
-
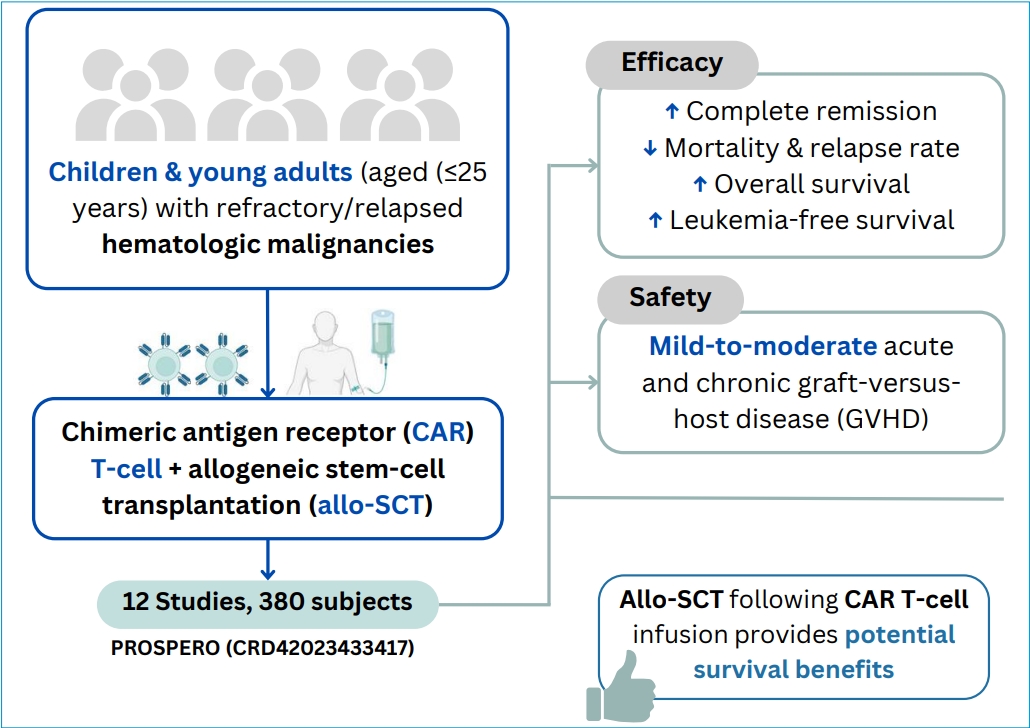
Question: Does consolidative allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy improve outcomes of children and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies?
Finding: The meta-analysis showed reduced relapse rates and favorable survival trends with allo-SCT despite low evidence quality.
Meaning: Consolidative allo-SCT after CAR T-cell therapy may enhance survival; however, further clinical studies are needed.
- Gastroenterology
- Treatment targeting pediatric inflammatory bowel disease-associated anemia: experience from a single tertiary center
- Ana S.C. Fernandes, Sara Azevedo, Ana Rita Martins, Ana Isabel Lopes
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):722-731. Published online June 10, 2025
-
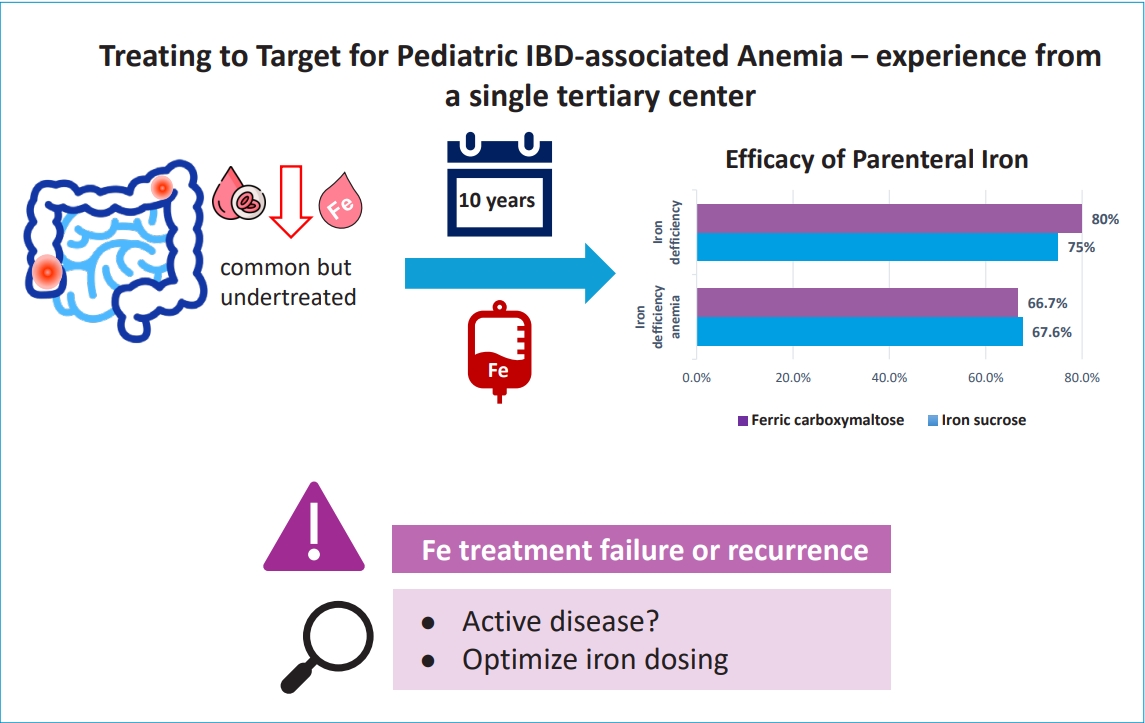
Question: Does treating iron deficiency (ID) using intravenous iron in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) feature long-term safety and efficacy?
Finding: Intravenous iron supplementation was safe and effective. However, the ID recurrence rate was higher than expected.
Meaning: Proactive screening and treatment of ID in pediatric IBD are essential. The Ganzoni formula likely underestimates the iron requirements of pediatric patients. Prospective trials are needed to optimize iron treatment dosing.
- Cardiology
- Unsustainable and overworked: unpacking the challenges faced by pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea
- Soo In Jeong, GI Beom Kim, Sung Hye Kim, Jae Yoon Na, Hong Ju Shin, Sin Weon Yun, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Sang Yun Lee, Chang-Ha Lee, Kwang Ho Choi, Seul Gi Cha, Mi Young Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):732-741. Published online August 6, 2025
-
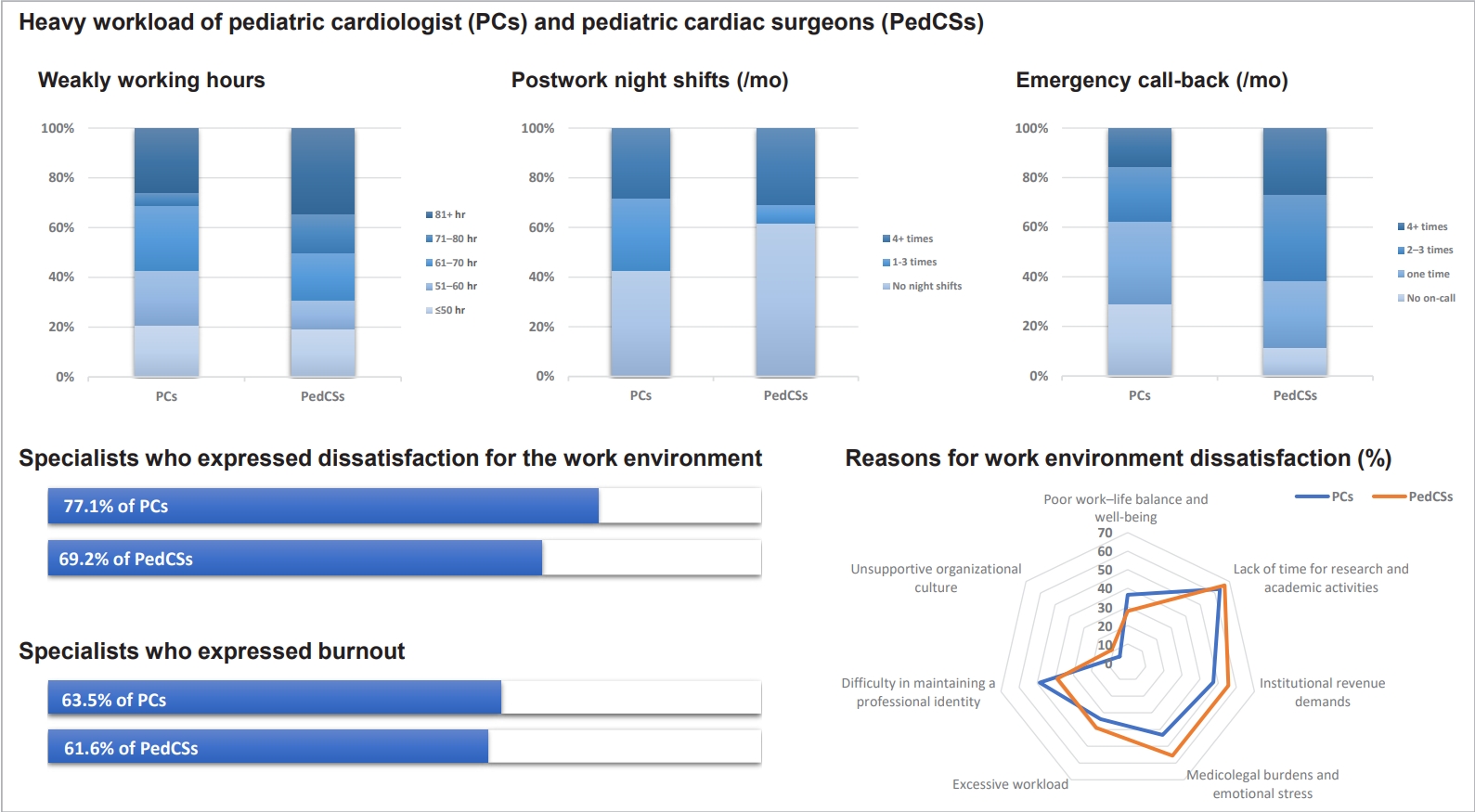
Question: What are the key challenges affecting pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea?
Finding: Excessive workloads, low procedural volumes, and legal risks contribute to high burnout. Regional disparities limit skill maintenance and threaten workforce sustainability.
Meaning: Targeted policies ensuring fair workloads, legal protections, and regional support are essential to stabilizing the pediatric cardiac workforce and maintaining high-quality care.














