Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Effect of postoperative enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance in critically ill children
- Irene Yuniar, Kadek Apik Lestari, Antonius Hocky Pudjiadi, Fatima Safira Alatas, Yoga Devaera
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):790-800. Published online May 30, 2025
-

Question: Does high-protein enteral nutrition better increase the average nitrogen balance (NB) and decrease the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) level of critically ill postoperative children than standard-protein enteral nutrition?
Finding: The study demonstrated a significant increase in average NB but no significant decrease in I-FABP levels in the high- versus low-protein group.
Meaning: These findings suggest that high-protein enteral nutrition can improve NB in critically ill postoperative children, thereby supporting their recovery.
- Gastroenterology
- Adenosine deaminase and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genetic polymorphisms among obese children with versus without metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
- Hala M. Sakhr, Mohammed H. Hassan, Azza Mohamed Taha, Ali Helmi Bakri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):808-818. Published online May 29, 2025
-

Question: Is there an association between adenosine deaminase (ADA) G22A and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) genetic polymorphisms and pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)?
Finding: The GG genotype and G allele of ADA G22A were significantly associated with obesity but not pediatric MAFLD, while the *1/*2 genotype of the IL-1RN gene was significantly associated with obesity and pediatric MAFLD.
Meaning: The IL-1RN gene may contribute to pediatric MAFLD.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Navigating the complex behavioral landscape of children in foster care and adopted families
- Anisha Choi, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):620-623. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
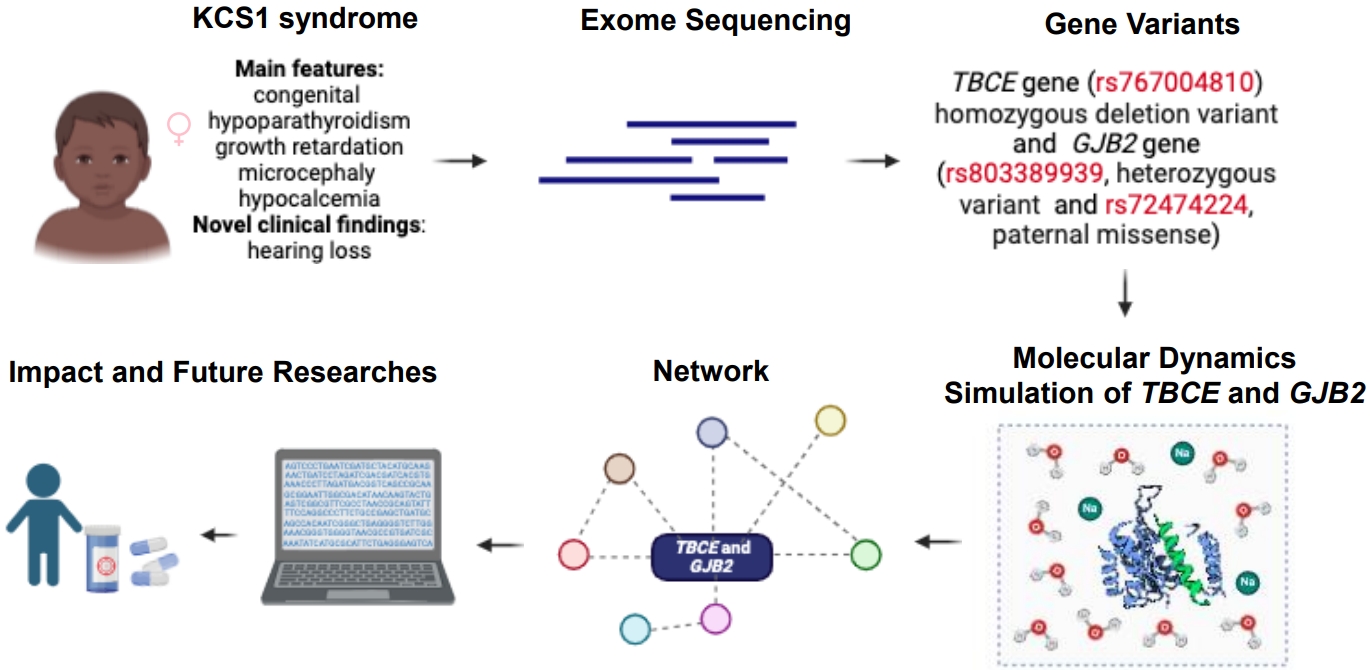
- Expanding genotype-phenotype correlation of Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1
- Manuela Lo Bianco, Federica Sipala, Xena Giada Pappalardo, Gaia Fusto, Roberta Rizzo, Federico Favata, Carla Cimino, Silvia Marino, Martino Ruggieri, Agnese Suppiej, Simone Ronsisvalle, Raffaele Falsaperla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):616-619. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Perspective
- Gastroenterology
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children: a practical update based on Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ISPGHAN) 2024 guidelines
- Ankit Agrawal, Arghya Samanta
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):546-550. Published online May 12, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Allergy
- Global burden of asthma among children and adolescents with projections to 2050: a comprehensive review and forecasted modeling study
- Tae Hyeon Kim, Hyunjee Kim, Jiyeon Oh, Soeun Kim, Michael Miligkos, Dong Keon Yon, Nikolaos G Papadopoulos
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):329-343. Published online April 22, 2025
-

Pediatric asthma can persist to adulthood and must be effectively managed. This review examined the prevalence of asthma among individuals younger than 20 years and revealed a decline from 1990 to 2021, higher rates in males, and a peak in children aged 5–9 years. Despite a projected continued decrease in prevalence by 2050, asthma will remain a significant health concern for children and adolescents.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study
- Phakwan Laohathai, Rathaporn Sumboonnanonda, Puthita Saengpanit, Chodchanok Vijarnsorn, Chatchawan Srisawat, Kwanjai Chotipanang, Sarawut Junnu, Supawan Kunnangja, Hathaichanok Rukprayoon, Phakkanan Phuangphan, Sompong Liammongkolkul, Arthima Phaokong, Narumon Densupsoontorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):666-672. Published online April 16, 2025
-
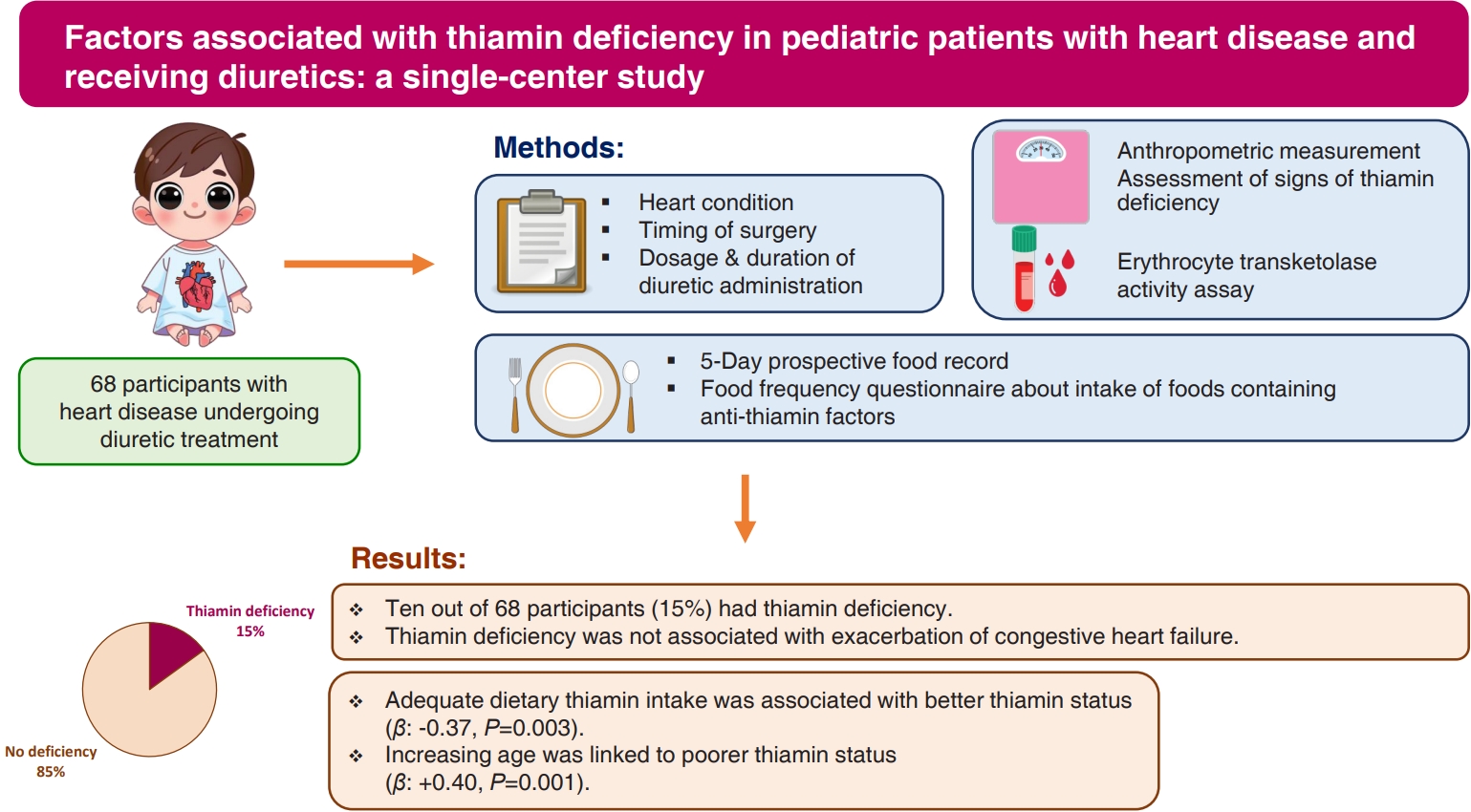
Question: Are pediatric patients with heart disease who are receiving diuretics at risk of thiamin deficiency (TD)?
Finding: Fifteen percent of the patients had TD. TD was associated with inadequate dietary thiamin intake and increasing age.
Meaning: The thiamin pyrophosphate effect should be assessed in those with high risk of TD. Dietary counseling should be emphasized to ensure adequate dietary thiamin intake.
- Review Article
- Other
- Cost-effectiveness of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: a systematic review
- Rezwanul Rana, Syed Afroz Keramat, Moin Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):628-640. Published online April 16, 2025
-
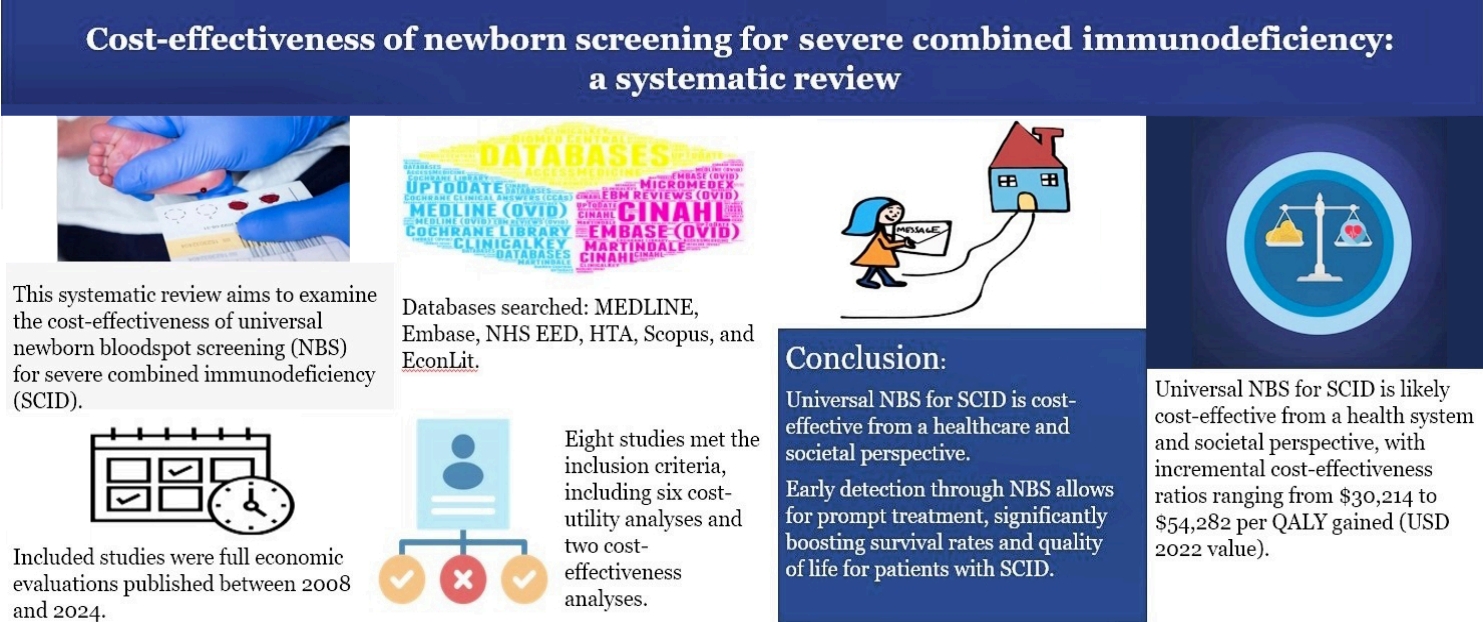
Universal newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) demonstrates robust cost-effectiveness across diverse high-income healthcare systems, both from healthcare and societal standpoints. Early detection yields substantial savings. While uncertainties persist, impacting precise cost-effectiveness, the overall finding is positive. Future research must prioritize enhanced data collection and statistical rigor to refine our understanding of SCID's economic impact within the Australian context.
- Correspondence
- Infection
- A commentary on "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus"
- Hinpetch Daungsupawong, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):624-625. Published online April 16, 2025
-
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Treatment and clinical outcomes of pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia: real-world single-center data from Korea
- Young Dai Kwon, Eun Sun Jung, Yeon Jung Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):522-529. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Question: Can pediatric autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) be effectively managed using first-line steroids?
Finding: In this single-center study, pediatric patients with AIHA achieved normal hemoglobin levels within 16.5 days (range, 9.0–22.0 days) of first-line steroid treatment and maintained effective responses for 2 months.
Meaning: These outcomes highlight the efficacy of steroid treatment in pediatric versus adult AIHA and underscore the need for multicenter trials to establish standardized treatment guidelines.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Intermittent sigh breaths during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation among newborn infants
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):486-488. Published online April 16, 2025
-

Intermittent sigh breaths during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation can improve ventilation and oxygenation by enhancing lung recruitment. Although research on this approach in newborn infants is limited, some published studies suggest that sigh breaths are generally applied at a rate of 2–3 breaths/min with an inspiratory time of 0.5–1 second and pressure of current mean airway pressure + 5 cmH2O (maximum, 30 cmH2O).
- Original Article
- Infection
- Role of miRNA-146a and miRNA-125b in Helicobacter pylori
- Nashwa Farouk Mohamed, Ola G.A. Behairy, Manal S. EL-Defrawy, Mona Mahmoud Elsayed, Naglaa F. Alhusseini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):781-789. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Why is the early detection of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis in children important?
Finding: The early detection of H. pylori-related gastritis is crucial for its effective management, especially in pediatric patients with dyspepsia.
Meaning: The use of miRNA signatures could detect early gastritis, enabling timely H. pylori eradication treatment to mitigate growth delays and cancer risk.
- Pulmonology
- Effect of vitamin C supplement in treatment of childhood pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a randomized controlled trial
- Chutima Phuaksaman, Katechan Jampachaisri, Klaita Srisingh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):690-699. Published online April 1, 2025
-
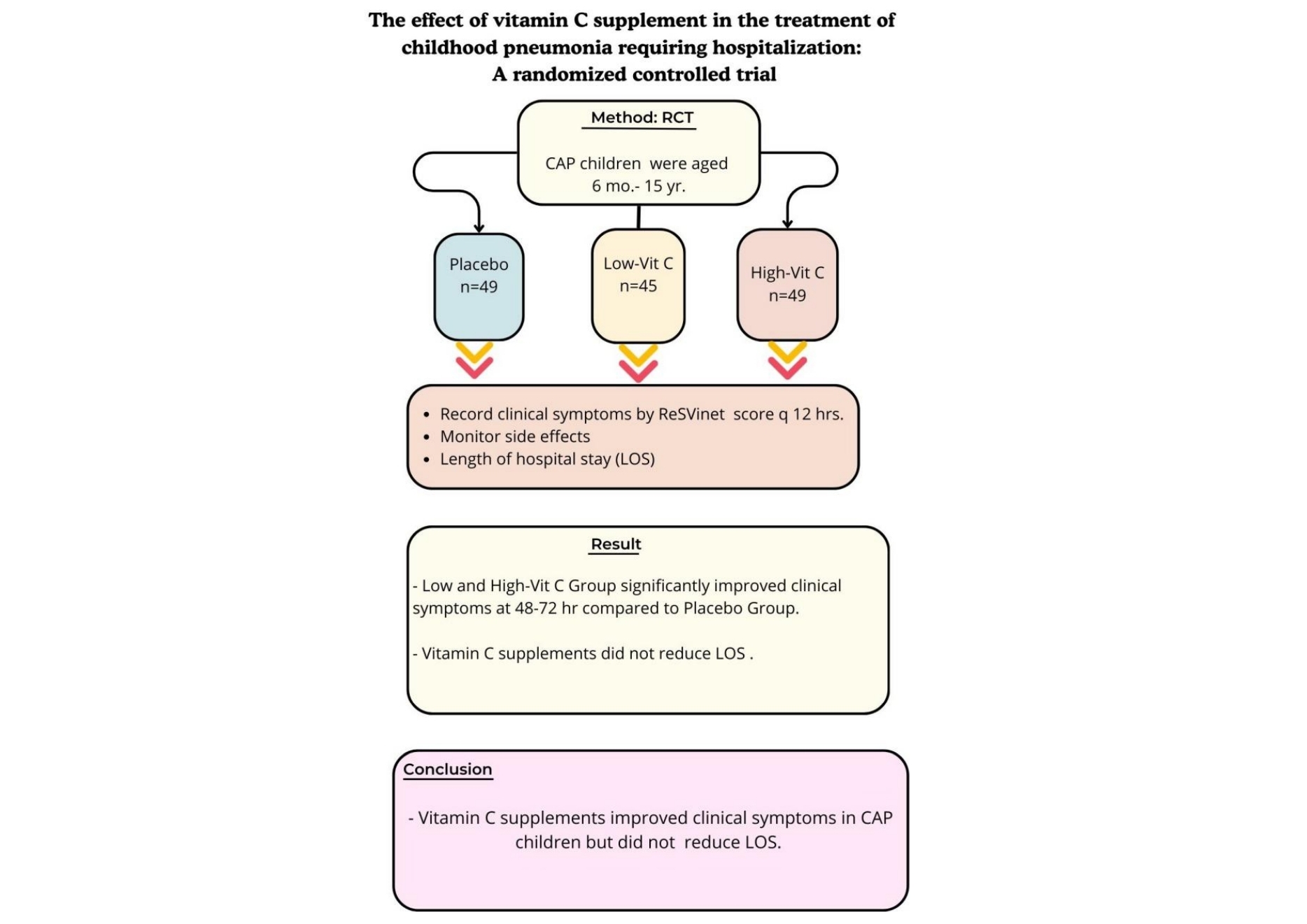
This study assessed the effects of vitamin C on children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Vitamin C supplementation improved clinical symptoms within 48–72 hours compared to placebo but did not reduce the length of hospital stay (LOS). These findings suggest that vitamin C is beneficial for managing CAP severity, but does not affect LOS.
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-
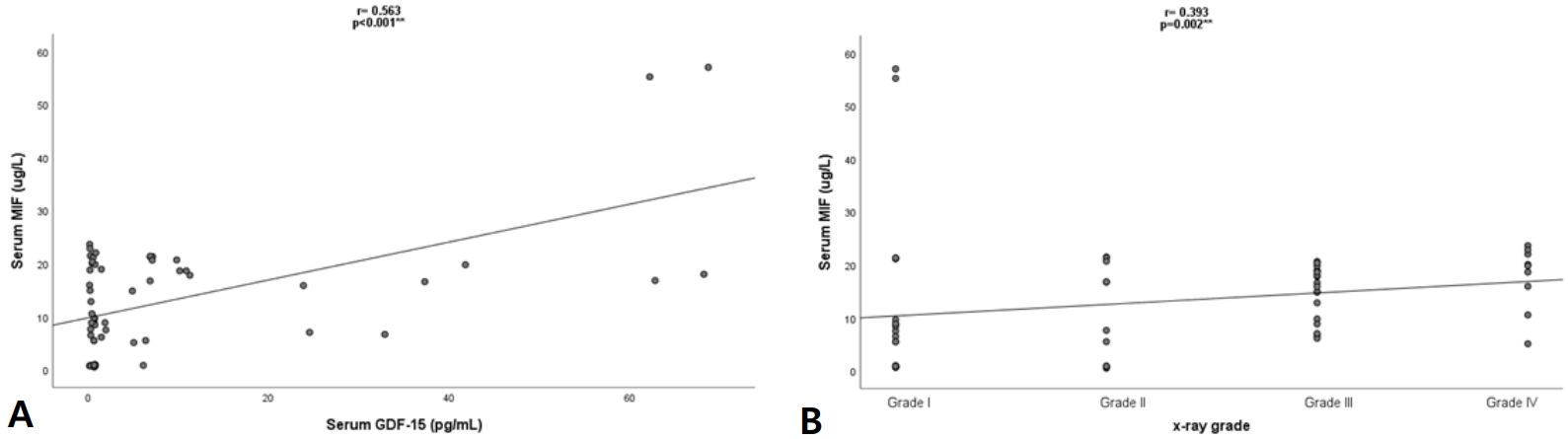
Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
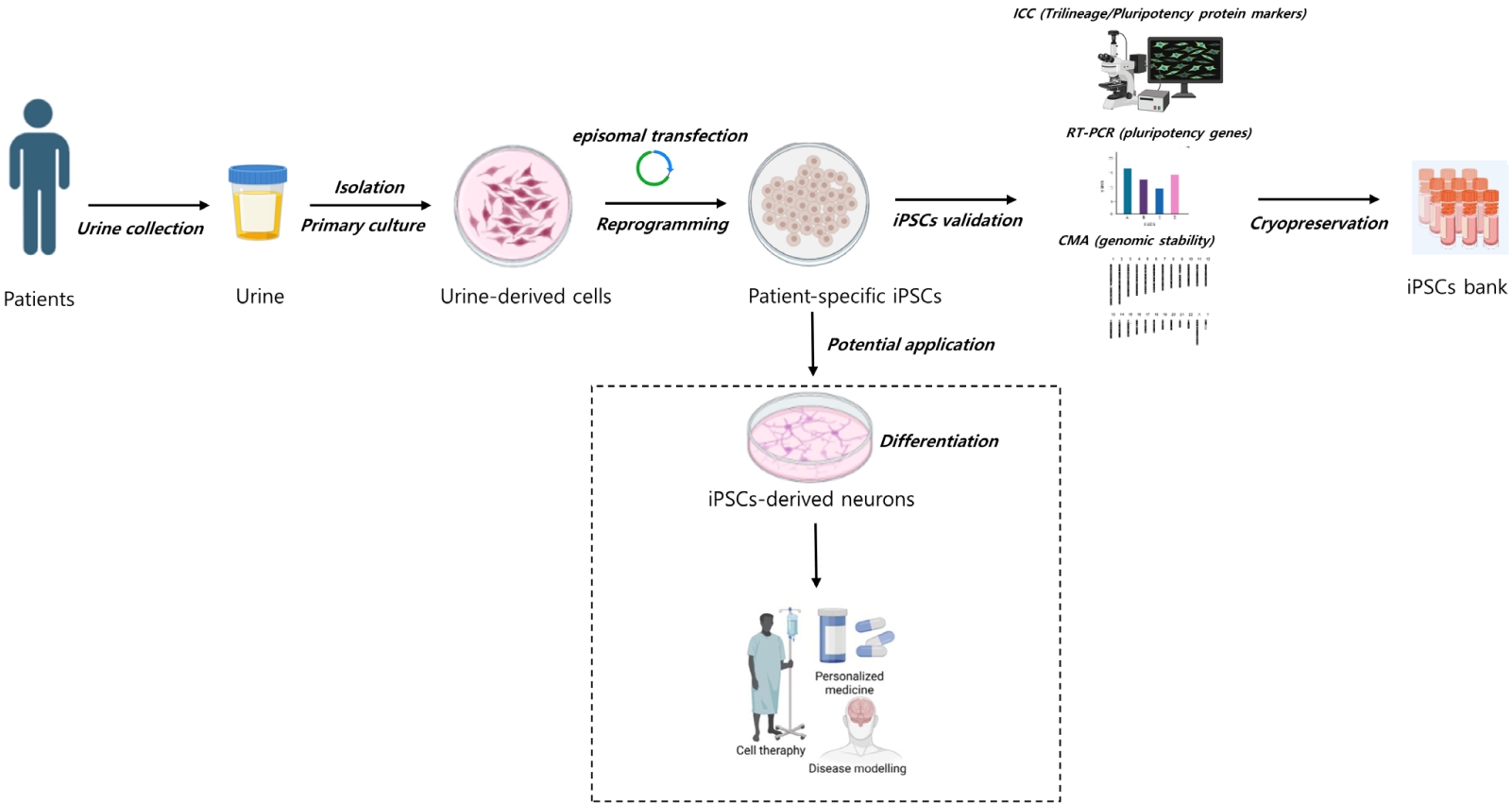
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- Review Article
- Other
- Myopia: a review of current concepts, association with nonophthalmological conditions, and treatment strategy in children and adolescents
- Yeon Woong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):554-565. Published online April 1, 2025
-
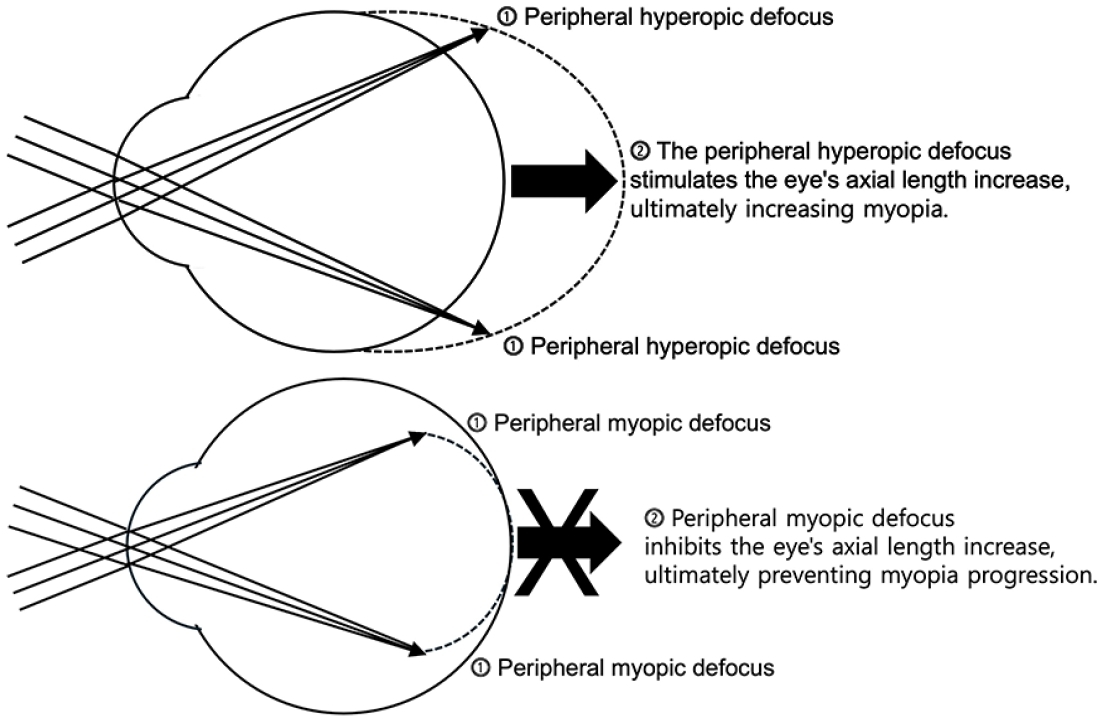
Myopia is a major ophthalmological disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide, particularly in East Asia. Evidence indicates that its development involves complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Body stature, sleep patterns, and nutritional status significantly influence the progression of myopia during childhood and adolescence. Its treatment and prevention strategies include optical correction, atropine therapy, increased outdoor activity, decreased near work, and regular retinal monitoring.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Pulmonology
- Clinical course of children with postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans with versus without comorbid bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Lamia Medghoul, Julien Grosjean, Christophe Marguet, Hortense Petat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):497-502. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans (PIBO) is a chronic respiratory disease that typically develops in children after a severe respiratory infection. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is often comorbid in patients with PIBO.
Finding: Corticosteroid pulse therapy effectively manages PIBO with or without comorbid BPD, significantly reducing exacerbations and decreasing the daily requirement for inhaled corticosteroids.
Meaning: Therapeutic effects of corticosteroid pulses are rapid and sustained over time, in both groups.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis
- Vedat Uygun, Koray Yalçın, Hayriye Daloğlu, Seda Öztürkmen, Suna Çelen, Suleimen Zhumatayev, Gülsün Karasu, Akif Yeşilipek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):601-607. Published online March 11, 2025
-
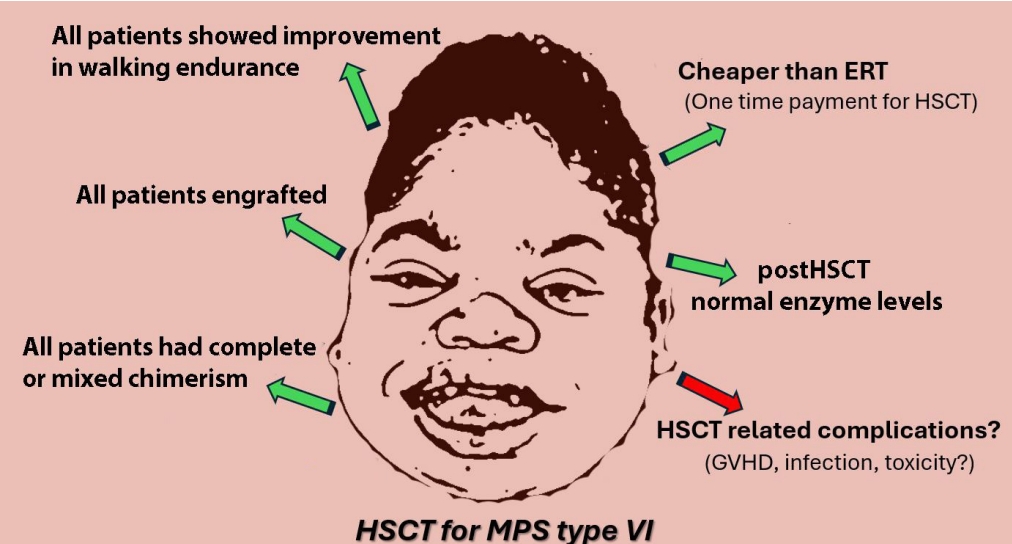
Question: Could hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) be an alternative to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS VI)?
Finding: HSCT is generally not offered due to reports of high toxicity and mortality. However, we detected fewer complications and graft-versus-host disease cases and no deaths with HSCT.
Meaning: HSCT is both less expensive than ERT and permanent; thus, it should be considered an alternative treatment for MPS VI.
- Gastroenterology
- Efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide versus room-air insufflation in pediatric colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial
- Ajay Aravind, Ujjal Poddar, Anshu Srivastava, Moinak Sen Sarma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):594-600. Published online March 11, 2025
-
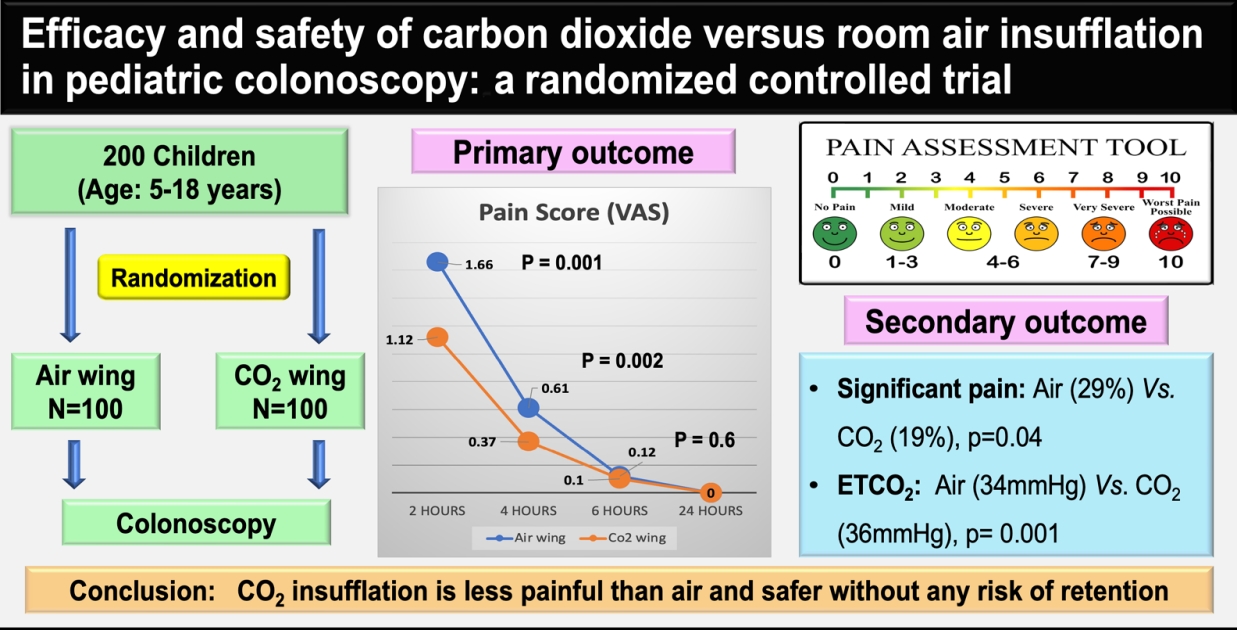
CO2 insufflation has been used instead of air insufflation to reduce postprocedure pain and discomfort in adults; however, adequately powered studies in children are scarce. This randomized controlled trial of 200 children showed that CO2 insufflation reduces postprocedure pain and discomfort during pediatric colonoscopy with no signs of CO2 retention. CO2 insufflation is safe and causes less pain in children.
- Somatic symptom severity during acute illnesses among children with functional gastrointestinal disorders
- Rattanachart Sirinil, Anundorn Wongteerasut
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):587-593. Published online March 11, 2025
-
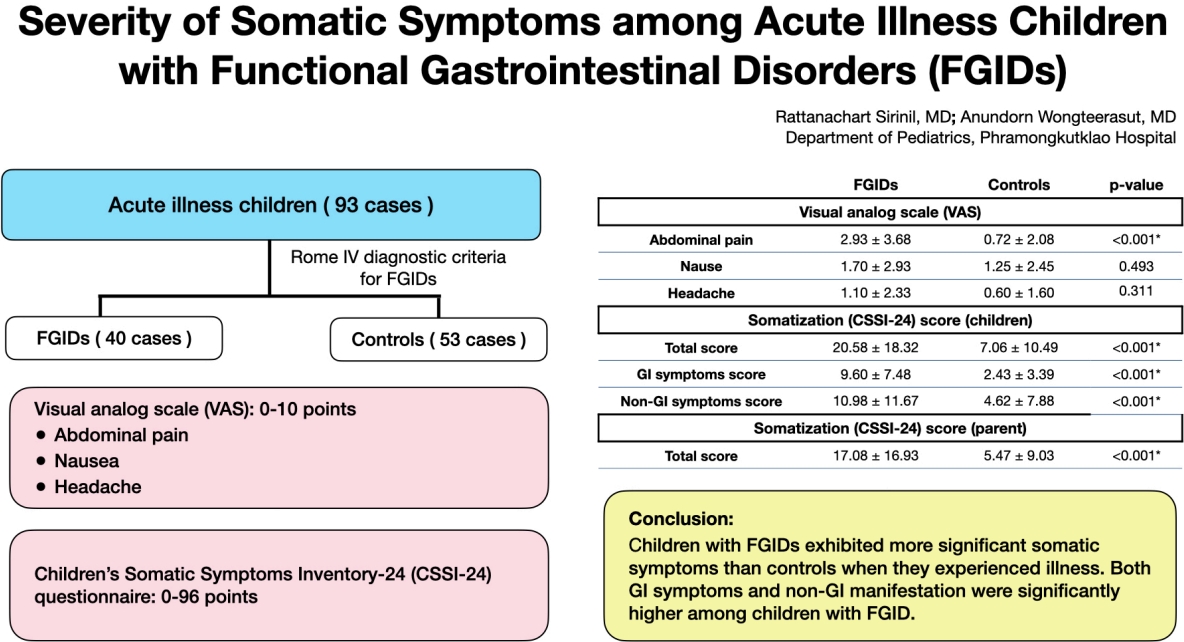
Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are associated with various somatic symptoms measured using a visual analogue scale and the Children’s Somatic Symptoms Inventory-24 questionnaire. Children with FGIDs exhibited more significant somatic symptoms than controls during acute illnesses. Gastrointestinal (GI) and non-GI manifestations are significantly more common in children with FGIDs.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Clinical Note
- General Pediatrics
- Aplasia cutis congenita with unique vascular malformation and cranial hypoplasia: a case in a preterm infant
- Yasufumi Sakata, Natsumi Fujii, Sadahiro Nomura, Yoshihiro Azuma, Hiroki Hamano, Hidenobu Kaneyasu, Seigo Okada, Kazumasa Takahashi, Shunji Hasegawa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):472-474. Published online March 11, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Abdominal pain in a young girl: a twist in the tale
- Upasana Ghosh, Ankit Agrawal, Umesh Shukla, Vikas Jain, Deeksha Bhalla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):395-397. Published online March 11, 2025
-

· Chronic abdominal pain caused by a gastric trichobezoar is extremely rare among children.
· An indentable epigastric mass is characteristic and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is diagnostic of a gastric trichobezoar.
· Symptomatic large trichobezoars usually require surgery.
· Neuropsychiatric disorders are often associated with gastric trichobezoar, making a psychiatric evaluation of paramount importance.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Wafaa M. Abo El Fotoh, Mona S. Habib, Salem E. Deraz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):578-586. Published online February 26, 2025
-
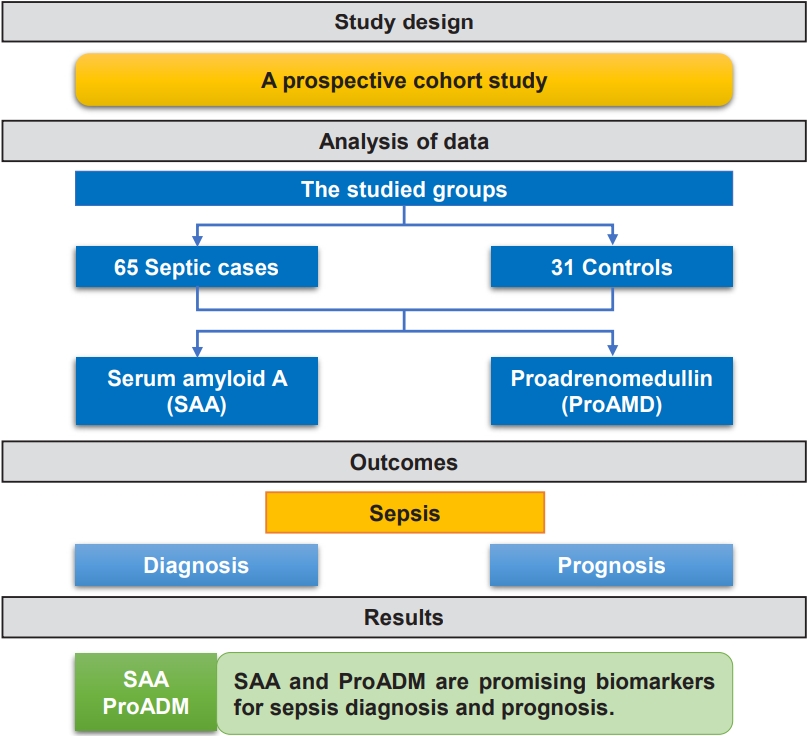
Question: Are serum amyloid A (SAA) and proadrenomedullin (proADM) levels early markers in critically ill children with sepsis?
Finding: This prospective case-control study included 65 critically ill children with sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and 31 controls. SAA and proADM levels were significantly higher in patients versus controls.
Meaning: SAA and proADM are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in pediatric sepsis.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of total serum bilirubin thresholds for discontinuing phototherapy in jaundiced neonates: a randomized study
- Ajay Kumar, Nidhi Jain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):539-545. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: What are the outcomes of jaundiced neonates when phototherapy is discontinued at 2 different total serum bilirubin (TSB) thresholds?
Findings: The study involved 80 neonates, comparing a recommended TSB threshold and a lower threshold for phototherapy discontinuation. Results showed a 14.3% reinstitution rate of treatment, with no adverse outcomes.
Meaning: Careful posttreatment monitoring is essential when discontinuing phototherapy, and future research should consider updated guidelines like those from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Role of microRNA-498 and microRNA-410 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Eman Salah Eldeen Arafat, Hasnaa Hesham Abotaleb, Dina Abdel Razek Midan, Abdel Hamid Abdo Ismail, Zeinab Sabri Abouzouna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):512-521. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Is it role of microRNA-410 (miRNA-410) and microRNA-498 (miRNA-498) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Findings: miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 can be auxiliary diagnostic and prognostic tools for neonatal HIE.
Meaning: we can use miRNA-498 and miRNA-410 as markers and indicator for HIE.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











