Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2023 during the last six months.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development (43 times)
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of online infant care training and postpartum counseling based on Meleis' transition theory on mothers' readiness for care and breastfeeding: a randomized controlled trial (42 times)
- Fatma Şule Bilgiç, Gülçin Bozkurt
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):521-530. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Question: Do interventions based on Meleis' transition theory affect mothers' readiness for baby care and breastfeeding?
Findings: We found a statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups in mothers' readiness for newborn care and breastfeeding (P<0.001).
Meaning: This intervention increased breastfeeding rates while ensuring that mothers were ready to care for their babies and prepared for the role of motherhood.
- Clinical Note
- Gastroenterology
- Congenital antral web: rare cause of gastric outlet obstruction successfully managed with endoscopic balloon dilatation (42 times)
- Upasana Ghosh, Ujjal Poddar, Srinivas Srinidhi Vadlapudi, Moinak Sen Sarma, Anshu Srivastava
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):266-268. Published online January 13, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review (42 times)
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children (41 times)
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-
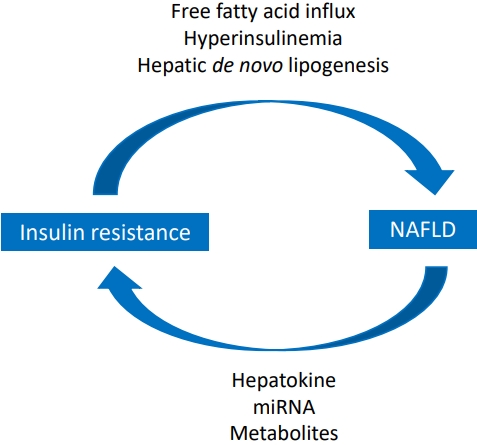
· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review (41 times)
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
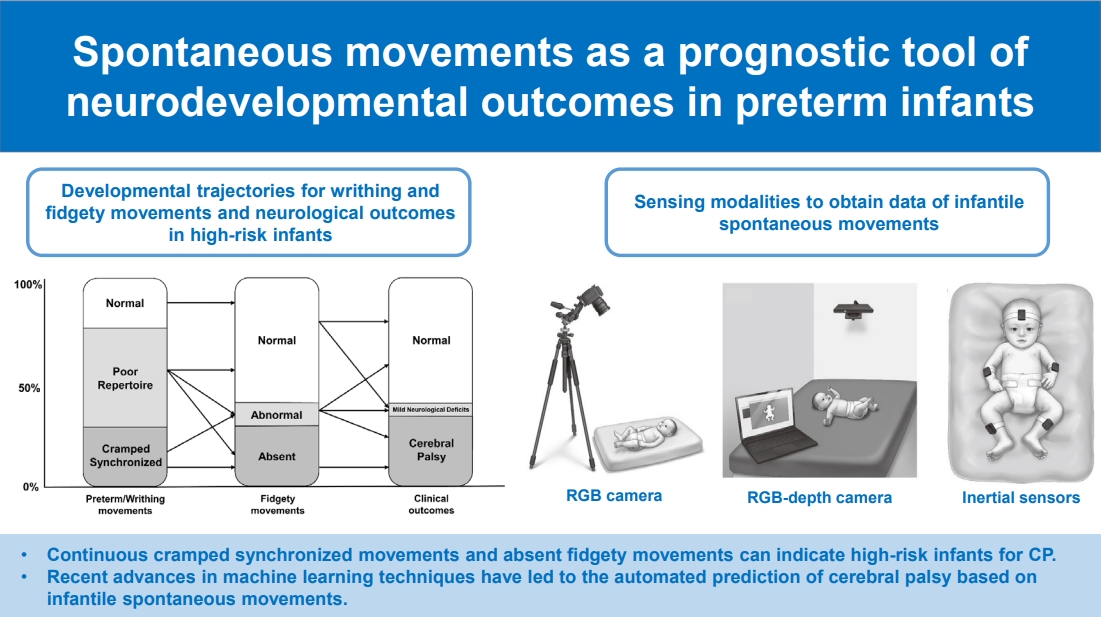
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children (40 times)
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-
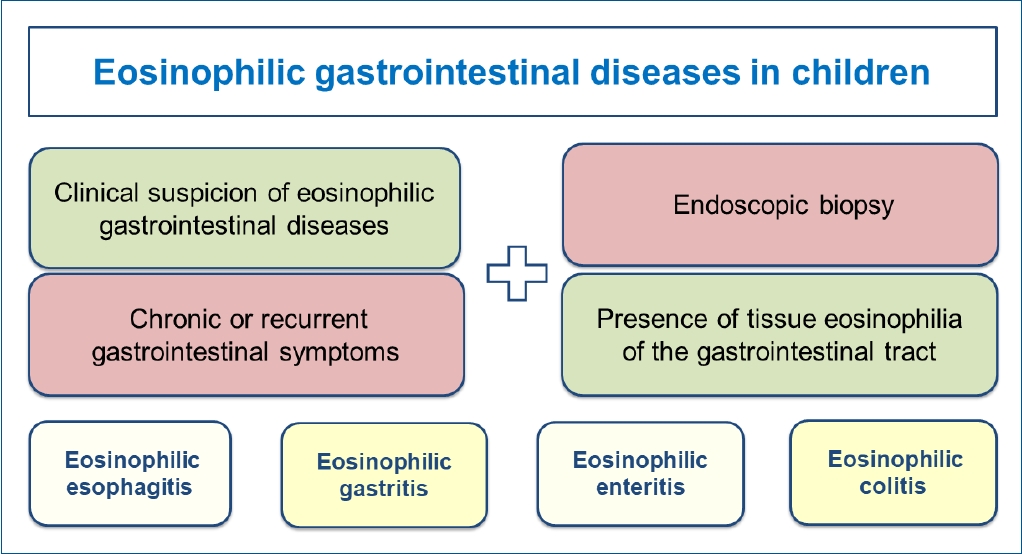
· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors (40 times)
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Review Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents (40 times)
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy (39 times)
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
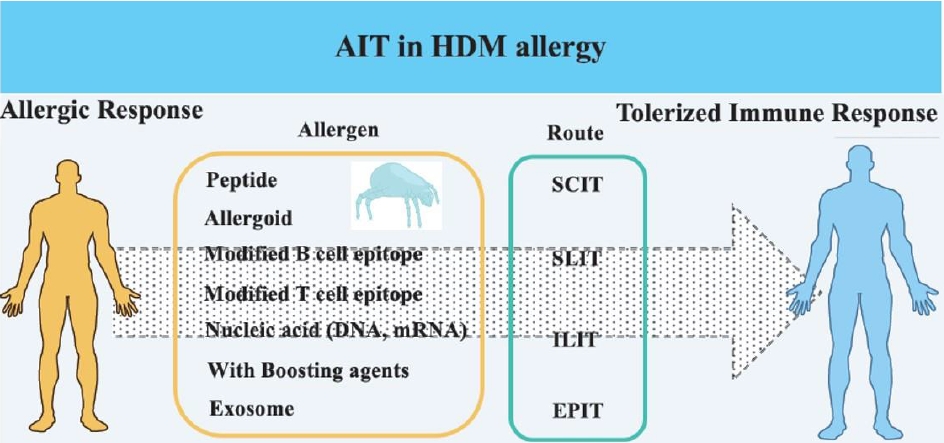
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Other
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: implications for South Korea (39 times)
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):16-29. Published online November 11, 2024
-

· The 24-hour movement behavior paradigm provides an important framework for future pediatric health promotion efforts.
· Policy priorities should include advancing surveillance and monitoring assessments related to 24-hour movement behaviors, evaluating their implementation in school and government policies, and building preparedness for future pandemics and natural disasters, including climate change, by promoting healthy 24-hour movement behaviors.
· Future research should advocate for the promotion of 24- hour movement behaviors.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh (39 times)
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Editorial
- Other
- Further research on impact of microplastics on children's health is essential to protecting future generations (38 times)
- Jongin Lee, Dong-Wook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):359-361. Published online November 13, 2024
-
· The ecological impacts of microplastics have been documented. It was recently recognized that they can directly or indirectly cause diseases in humans.
· There are few established methods for assessing human exposure to microplastics.
· Standardization of exposure assessments and large-scale epidemiological studies are required to explore the human effects of microplastics.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers (37 times)
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- What we should know about pediatric heart failure: children are not small adults (37 times)
- Ja-Kyoung Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):62-64. Published online November 6, 2024
-
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) features high morbidity and mortality rates.
· Although adults and children can share a common diagnosis of heart failure, the underlying causes can differ significantly and require distinct therapeutic approaches.
· Treatments designed for adults are often applied to PHF despite the fundamental physiological and developmental differences between them.
· Child-specific data are vital for the development of tailored treatments to meet the unique needs of patients with PHF.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of total serum bilirubin thresholds for discontinuing phototherapy in jaundiced neonates: a randomized study (37 times)
- Ajay Kumar, Nidhi Jain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):539-545. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: What are the outcomes of jaundiced neonates when phototherapy is discontinued at 2 different total serum bilirubin (TSB) thresholds?
Findings: The study involved 80 neonates, comparing a recommended TSB threshold and a lower threshold for phototherapy discontinuation. Results showed a 14.3% reinstitution rate of treatment, with no adverse outcomes.
Meaning: Careful posttreatment monitoring is essential when discontinuing phototherapy, and future research should consider updated guidelines like those from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Pulmonology
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study (37 times)
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury (37 times)
- Cagla Kiser, Ilkcan Ercan, Defne Engur, Sermin Genc
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):475-485. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is the major cause of neonatal brain injury. NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation leads to neuroinflammation, which significantly affects newborn mortality. The establishment of preventive and therapeutic strategies against brain damage requires a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation and inflammasome activation in the neonatal brain.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Effects of diethylene glycol contamination of pharmaceutical products on unexplained acute kidney injury in children: a systematic review (36 times)
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Muhammad Luthfi Adnan, Hilmi Ardian Sudiarto, Satria Bintang Mahathma, Alya Ayu Tazkia, Hana Afifah Firdaus, Alfreda Amelia Khotijah, Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas, Emi Azmi Choironi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):395-402. Published online January 4, 2024
-

A recent unexplained acute kidney injury (AKI) outbreak due to pharmaceutical product contamination with diethylene glycol (DEG) raises public attention. Our study revealed that DEG-contaminated paracetamol causes unexplained AKI in children. However, paracetamol is not the only contaminated drug. Other drugs, such as cough expectorants, antihistamines, and sedatives, can also be affected. Other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, can also contribute to poisonings.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens in an Iranian hospital: high prevalence of OXA-type carbapenemase genes (36 times)
- Setareh Mamishi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Sadaf Sajedi Moghaddam, Babak Pourakbari, Shiva Poormohammadi, Maryam Sotoudeh Anvari, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):65-72. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What is the prevalence of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria and associated carbapenemase genes?
Findings: This study identified a notable prevalence of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative isolates, with Escherichia coli being the predominant contributor, follow ed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, while bla OXA48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase gene.
Meaning: These findings highlight the urgent need for proactive measures including the rapid detection of carbapenemase- producing isolates and effective infection control.
- Editorial
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders: autoinflammatory and autoimmune disorders (35 times)
- Young Dae Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):439-440. Published online July 4, 2023
-
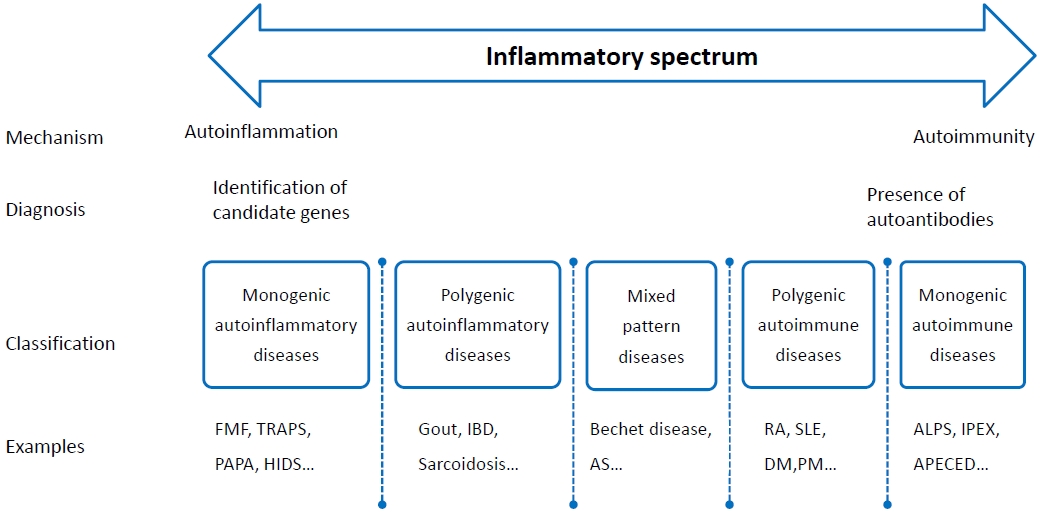
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAIDs) typically have an early onset in life, and may have close relatives may have similar disease.
· SAIDs should be suspected in any patient, especially children, who experience persistent or recurrent inflammatory episodes that fail to fit the pattern of other established diseases.
· Advancements in the understanding of autoinflammation will provide novel diagnostic and therapeutic options for SAIDs patients.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents (35 times)
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-

· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Neurology
- Gut microbiota affects brain development and behavior (34 times)
- Gun-Ha Kim, Jung-Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):274-280. Published online November 8, 2022
-
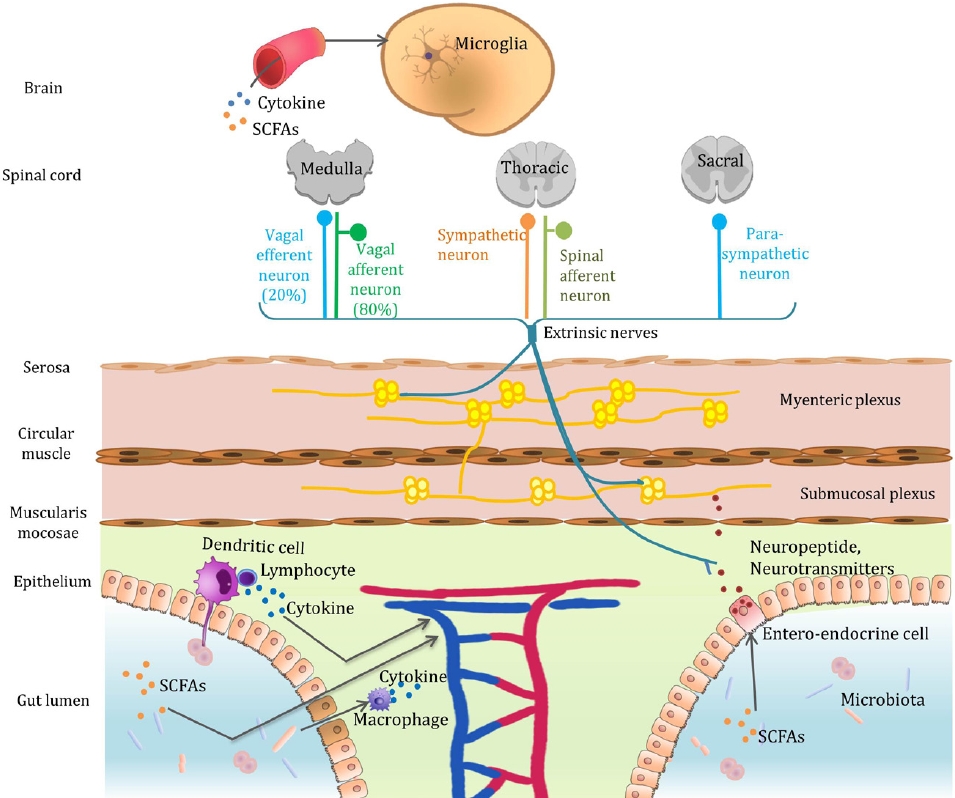
· The gut microbiota can alter a host’s brain development and behavior.
· Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
· Fecal microbial transplantation is a promising treatment strategy for autism spectrum disorder.
- Nutrition
- Association of gut microbiota with obesity in children and adolescents (34 times)
- Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):148-154. Published online November 16, 2022
-

The gut microbiota is an emerging factor in the development of pediatric obesity, which is affected by renowned risk factors such as diet, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status. This review aimed to describe the association between the gut microbiota and childhood obesity.
- General Pediatrics
- Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST): development, applications, and implications for future early childhood development interventions (34 times)
- Dooyoung Kim, Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, EunYoung Kim, Junghye Byeon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):288-293. Published online December 22, 2022
-

· This review discusses the development and application of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) for ensuring early childhood development.
· Various studies have demonstrated the integral role of the K-DST in facilitating the detection of developmental delays and delivery of timely interventions.
· The tailoring of the K-DST to Korean infants and children suggests that other countries may further translate and adapt it.
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies (34 times)
- Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-

· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms.
- Neurology
- Role of nonpharmacological concussion management in children: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (34 times)
- Andre Marolop Pangihutan Siahaan, Alvin Ivander, Rr. Suzy Indharty, Steven Tandean, Anastasia Grace Milenia Ginting, Masrini Ginting, Felix Khosasi, Elbert
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):569-579. Published online October 28, 2024
-

The long-term effects of concussion for pediatric patient remains unclear. Children and teenagers do not experience or recover from concussion in the same manner as adults do. Concussions can cause a variety of anatomical and functional alterations. Nonpharmacological approach in pediatric concussion management is an understudied field of research with significant ability to affect prognosis and quality of life. Active rehabilitation and occupational therapy were especially promising.
- General Pediatrics
- Protecting our future: environmental hazards and children’s health in the face of environmental threats: a comprehensive overview (34 times)
- Jungha Lee, Hyo-Bin Kim, Hun-Jong Jung, Myunghee Chung, So Eun Park, Kon-Hee Lee, Won Seop Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Jung Won Lee, Jae Won Shim, Sang Soo Lee, Yunkoo Kang, Young Yoo; The Environmental Health Committee of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):589-598. Published online October 31, 2024
-

· Exposure to air pollutants cause allergic and respiratory diseases as well as chronic kidney disease.
· Adequate physical activity and proper nutrition are essential for children to maintain good health.
· We must educate people about the harmful effects of noise, blue light, heavy metals and smoke.
· Government and society must actively decrease environ-mental hazards.
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review (33 times)
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Other
- Use of virtual reality in children in a broad range of medical settings: a systematic narrative review of recent meta-analyses (33 times)
- Emily Antonovics, Grammatina Boitsios, Thomas Saliba
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):274-282. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· Virtual reality (VR) is becoming increasingly common for entertainment and in medical settings.
· VR is useful for treating children with cerebral palsy.
· VR can help with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms.
· VR can decrease pain perception in children undergoing burn wound care.
· VR can reduce preoperative anxiety.
· VR can reduce fear and pain during needle-involving procedures.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











