Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Continuous glucose monitoring in Korean pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: current landscape and clinical implications
- Hwa Young Kim, Jaehyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):842-851. Published online October 2, 2025
-

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has transformed pediatric type 1 diabetes care by facilitating tighter glycemic control, reducing hypoglycemia, and improving quality of life.
Recent advances in CGM technology and the expansion of insurance coverage in Korea have led to its broader adoption.
Emerging metrics such as time in tight range offer refined tools for individualized glycemic assessment, highlighting CGM’s evolving role in personalized pediatric diabetes management.
- Editorial
- Basic Research
- Stem cell mining: urine cells to biobanking
- Yong Joo Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):761-762. Published online September 24, 2025
-

· A safe and accessible source of somatic cell generating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in pediatric neurogenic disorders
· A noninvasive and simple method for isolating urine cells, which can effectively reprogram into pluripotent stem cells using episomal vectors
· Establishing a urine-derived iPSC bank as a reliable and scalable resource for disease modeling, therapeutic testing, and personalized medicine in pediatric neurogenic disorders.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Impact of screen exposure during pediatric ages including multifaceted aggravating factors: a literature review
- Daniel González-Pérez, David Sebastián Huertas-Moreno, Manuela Granados-Pinilla, Sofía Hernandez-Rojas, Laura González-Rincon, Geraldine Hurtado-Garcia, Simón Grisales-Calle, María José González-Mariño, Luz Dary Gutierrez-Castañeda, Jhon Camacho-Cruz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):751-760. Published online September 24, 2025
-

Excessive screen time in children is linked to obesity, overweight, sedentary behavior, depression and mood disorders, myopia, behavioral changes, sleep disturbances, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among others. Polymorphisms in genes like FTO, CACNA1D, and DRD2 could further increase these risks. Implementing strategies such as limiting screen use, creating screen-free zones, and monitoring content is essential to mitigate adverse physical and mental health effects in the pediatric population.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
- Parenting principles to combat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and form resilient young minds
- Jandy Le, Sandhya J. Kadam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):838-841. Published online September 22, 2025
-

The prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and other related behavioral problems is increasing among children, likely due to less interaction with their parents and the real world and more time spent on screens, on social media, and in the virtual world. This article highlights several simple, basic parenting principles to facilitate the growth of healthy, resilient minds and combat the symptoms of opposition, hyperactivity, and distractibility.
- Original Article
- Other
- Impact of thyroid hormones and serum endothelin levels on pediatric asthma control: a case-control study of an Indian population
- Murugaiyan Sathishbabu, Sathiya Ramasamy, Niranjjan Ramachandran, Soundararajan Palanisamy, Arulvijayavani Subramaniam
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):831-837. Published online September 22, 2025
-

Question: What are the roles of thyroid hormones and endothelin in South Indian children with asthma?
Finding: Thyroid hormone and endothelin levels were significantly elevated in South Indian children with asthma; poorly controlled cases exhibited the highest levels. Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone and endothelin levels were correlated with asthma severity.
Meaning: Serum endothelin is a potential surrogate marker for asthma severity that could aid the assessment and management of childhood asthma.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cytokine profile of Post–cardiopulmonary bypass in children
- Kantara Saelim, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Jirayut Jarutach, Pongsanae Duangpakdee, Smonrapat Surasombatpattana, Pharsai prasertsan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1015-1022. Published online September 19, 2025
-

Question: Can cytokine levels predict low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS) in children post–cardiopulmonary bypass?
Finding: Elevated interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were associated with LCOS, with an increase in IL-8 of >56 pg/mL from baseline to immediately postoperative being the strongest predictor.
Meaning: Monitoring immediately postoperative IL-8 levels may help identify pediatric patients at risk of LCOS, enabling timely interventions to improve outcomes.
- Hematology
- Assessment of natural killer cell subpopulations in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major
- Fathia Ibrahim Elbassal, Mohamed Abdel Rehim Soliman, Nourhan Hossam Eldin Mohamed, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Hanan Hassan El-Sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):981-990. Published online September 12, 2025
-

Question: How does iron overload affect immunity in pediatric patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major?
Finding: Iron overload in these patients is associated with disrupted natural killer (NK) cell subpopulations, reflecting impaired innate immunity.
Meaning: This highlights the need to monitor immune profile alongside iron status during thalassemia management.
- General Pediatrics
- Effectiveness of Kinder Lebensqualität Fragebogen (KINDL) and Children’s Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) for measuring postacute sequelae of COVID-19 in children: a diagnostic validation study
- Lawrence Shih-Hsin Wu, Pei-Chi Chen, Xiao-Ling Liu, Shu-Tsen Liu, Chi-Hung Wei, Yu-Lung Hsu, Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Huan-Cheng Lai, Chien-Heng Lin, Chieh-Ho Chen, An-Chyi Chen, I-Ching Chou, Wen-Jue Soong, Hui-Ju Tsai, Chung-Ying Lin, Jiu-Yao Wang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):944-951. Published online September 12, 2025
-

Question: Although children with postacute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (PASC) may experience persistent symptoms that affect their quality of life (QoL), a screening tool for identifying high-risk children is lacking.
Finding: Kinder Lebensqualität fragebogen (KINDL) and Children's Somatic Symptom Inventory-24 (CSSI-24) were significantly correlated. An optimal KINDL cutoff score (74.75) detected those at high risk of a reduced QoL.
Meaning: Integrating KINDL and CSSI-24 into routine pediatric outpatient care may enable timely identification and interventions for children at risk of PASC-related impairments.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of a long-acting monoclonal antibody to prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and young children
- Soo-Han Choi, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Ki Wook Yun, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):742-750. Published online September 3, 2025
-

To prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-associated lower respiratory tract infections, a single dose of nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, is recommended for all neonates born during the RSV season (October to March) and all infants younger than 6 months old at the start of the RSV season. Nirsevimab should be administered shortly after birth to neonates and just before or early in the season to infants entering their first RSV season.
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: bridging potential, clinical practice, and ethical considerations
- Yoon Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):652-655. Published online August 28, 2025
-
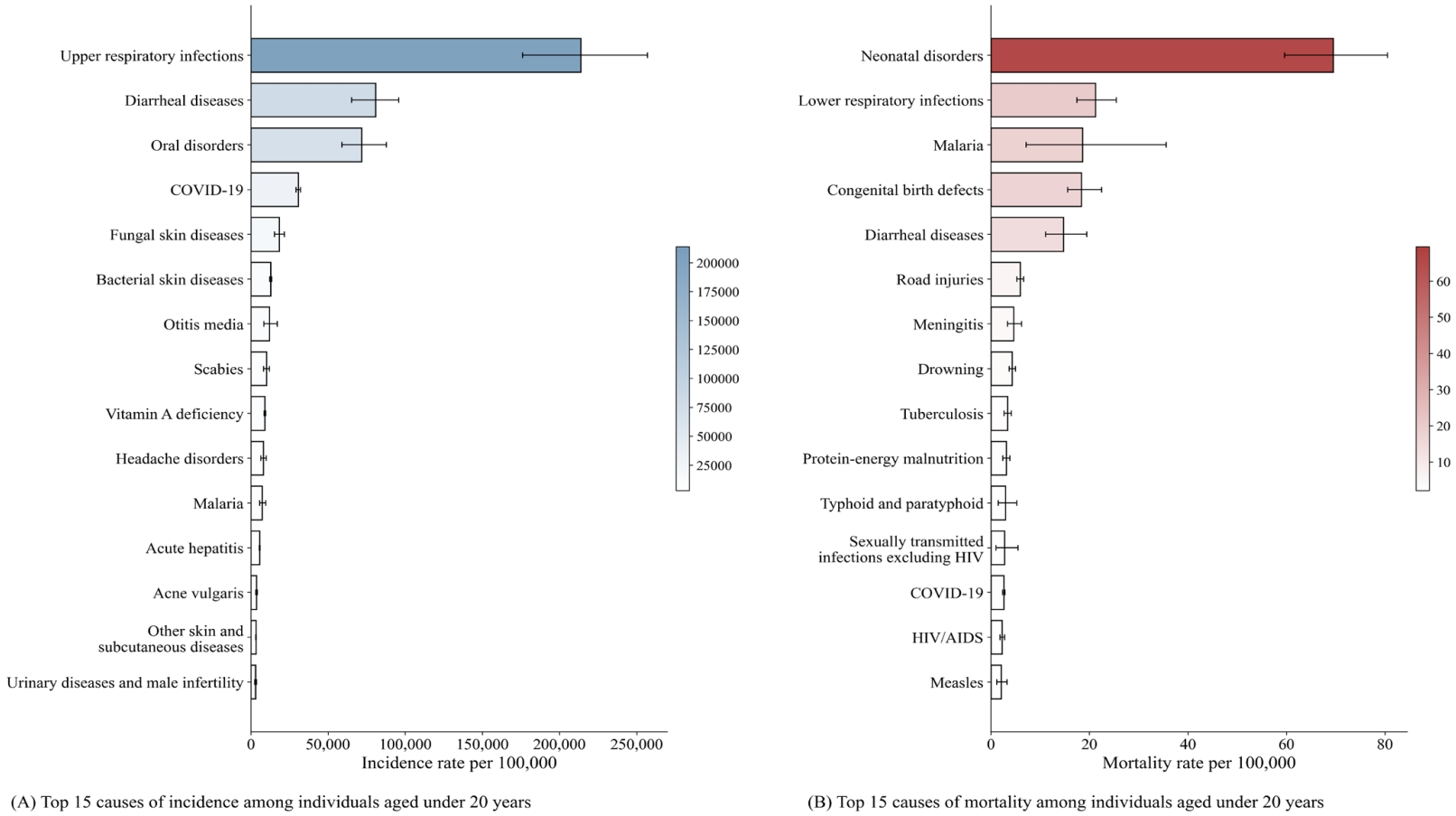
· Artificial intelligence (AI) holds transformative potential for pediatric healthcare, with applications spanning prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up across diverse subspecialties; however, ethical concerns, scarcity of pediatric- specific data, and limited funding remain significant challenges.
· International consensus on pediatric AI guidelines, expanding child-specific datasets, and incorporating explainable AI are essential to ensure safety and trust.
· Multicenter collaboration and increased investment can address these gaps, enabling equitable, reliable, and pediatric- centered AI solutions.
- Original Article
- Basic Research
- Linezolid mitigates tissue injury in experimental model of pediatric testicular torsion: TLR-4/MAPK/NF-κB involvement
- Moein Ghasemi, Abolfazl Basiri, Houman Kazemzadeh, Mohammad Amin Manavi, Seyed Mohammad Tavangar, Ahmad Reza Dehpour, Hamed Shafaroodi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):700-711. Published online August 26, 2025
-
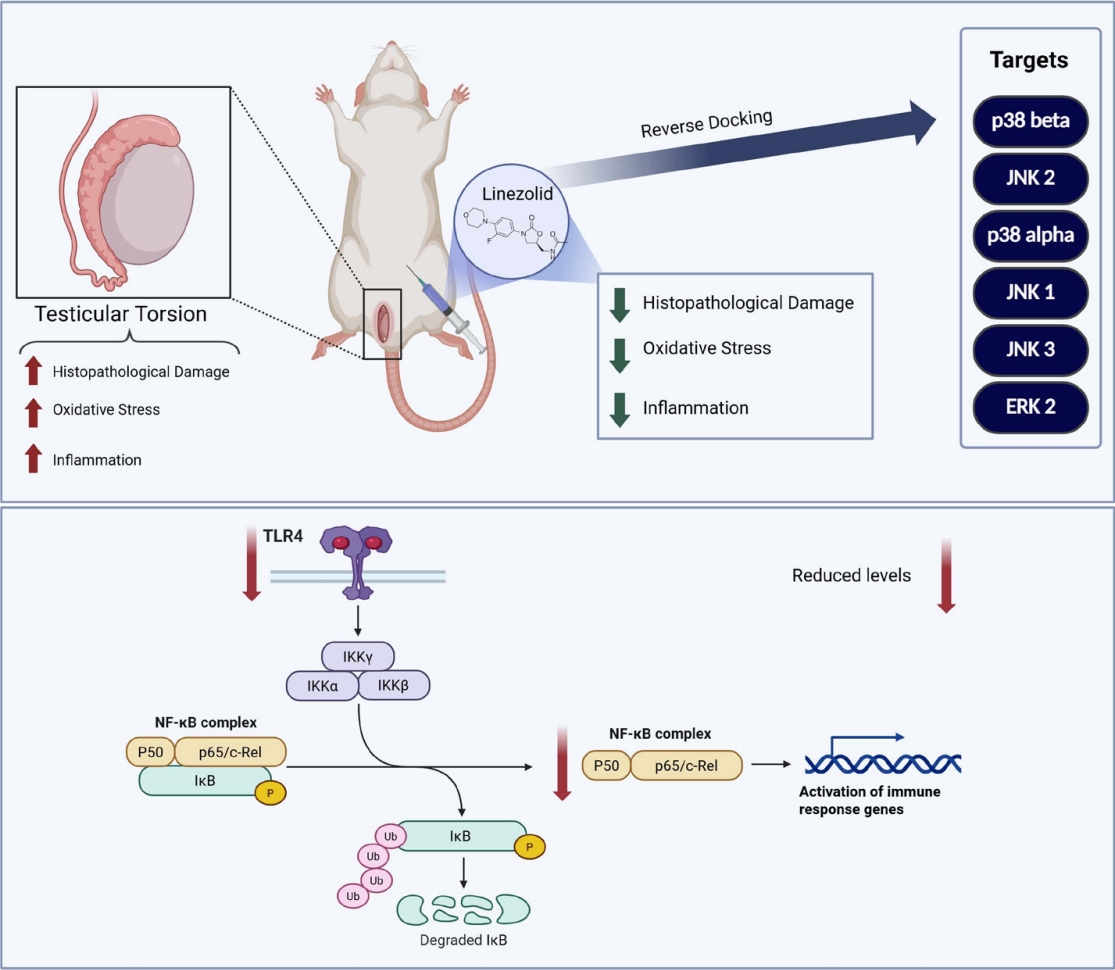
Question: What pharmacological strategies can limit ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric patients with testicular torsion?
Finding: In a rat model of testicular torsion, linezolid reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue injury via the Toll-like receptor 4/mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa beta pathway.
Meaning: Linezolid may offer a pharmacological approach to attenuate testicular damage in pediatric patients with testicular torsion, warranting further clinical investigation.
- Gastroenterology
- Fecal microbiome profiles in infants with biliary atresia versus nonbiliary atresia cholestasis: a pilot study
- Nur Azizah, Fadilah Fadilah, Silvia Werdhy Lestari, Muzal Kadim, Fithriyah Sjatha, Hanifah Oswari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):932-943. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: How does the gut microbiota profile of infants with biliary atresia (BA) differ from that of infants with non-BA cholestasis and healthy infants in the Indonesian population?
Finding: The unique fecal microbiome composition of the BA group differed significantly from that of the other 2 groups.
Meaning: There is an urgent need to improve dysbiosis in BA and non-BA cholestasis to prevent worsening liver injury in cholestasis.
- Endocrinology
- Long-term epidemiological insights into rickets: a nationwide population-based retrospective study
- Chun-Hao Chu, Ying-Chuan Chen, Pei-Yao Liu, Chun-Chieh Hu, Yu-Lung Lin, Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Tzu-Ju Hsu, Yu-Tung Hung, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Chien-Ming Lin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):879-891. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: What are the nationwide trends and mortality risk factors of nutritional versus hereditary rickets among children in Asia?
Finding: In 2012–2018, the incidence of rickets steadily increased, whereas mortality rates declined. Mortality is associated with a low household income, anemia, chronic kidney disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and a prolonged hospital stay.
Meaning: Early diagnosis and targeted interventions addressing social and medical vulnerabilities are critical to reducing ricket-related mortality.
- Infection
- Evolving treatment strategies for invasive Streptococcus pyogenes in children in the postpandemic era
- Laura Buricchi, Giuseppe Indolfi, Marco Renni, Elisabetta Venturini, Luisa Galli, Elena Chiappini
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):921-931. Published online August 11, 2025
-

Question: What are the roles of linezolid, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and corticosteroids in pediatric invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS)? Can any improve outcomes beyond beta-lactams and clindamycin?
Finding: Two of 46 patients with iGAS died. Nearly all received beta-lactams plus clindamycin. Linezolid was effective in refractory cases. IVIG and corticosteroids had variable efficacies.
Meaning: Linezolid may be valuable in refractory cases. IVIG may be considered in severe presentations. The role of corticosteroids remains less clearly defined.
- Serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels as biomarkers reflecting liver fibrosis in children with autoimmune hepatitis
- Salma Abdel Megeed Nagi, Mai Ibrahim Elashmawy, Amany E. Elashkar, Mohamed Zaeim Hafez, Ashraf A.E. Emara, Osama Mohammad Abdelhay, Albayoumi A.B. Fouda, Mohamed AbdelAziz Doma, Ahmad Mohamed Awad, Ahmed Mohammed Saba, Hesham Abdelrahman Ahmed, Ahmed Mohamed Gad Allah, Fatma Mahmoud Abdelraheem, Mohamed A. Gad, Mohamad A. Soliman, Tamer I. Abdalrhman, Khaled Hassaan Awad, Ismael A.K.M. El-lebedy, Mostafa M. Abdelnaser, Mohammed Z. Abdel Kareem, Marwa Fekry Hassan, Shymaa Sobhy Menshawy Khalifa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):909-920. Published online August 6, 2025
-

· A total of 159 children with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH; 60.3% female, 13.2% type 2 AIH) were identified. According to a global study, the estimated annual incidence of AIH in Egypt is 1.28 cases per 100,000 inhabitant-years.
· No studies to date have examined the serum levels of copper or ceruloplasmin in children with AIH. Therefore, here we investigated whether serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels are useful for identifying liver fibrosis in children with AIH.
· Serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels may provide important information for the identification of advanced liver fibrosis in children with AIH.
- Hematology
- Evaluation of Bak and Bcl-Xl gene expression among pediatric patients with acute primary immune thrombocytopenia
- Amira Zaki Badawy, Samia Hassan Kandel, Iman Aly Ahmedy, Mahmoud Ahmed Elhawy, Sally Mohamed El-Hefnawy, Dina Fouad Sief El-Nasr Zidan, Hanan Hassan El-sheity
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):901-908. Published online August 6, 2025
-

The B-cell lymphoma protein 2 family proteins Bak and Bcl- Xl, important markers of apoptosis, may contribute to primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Thus, their expression may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric ITP. Targeting these pathways may improve platelet survival, particularly in treatment-resistant cases. Personalized treatments based on apoptotic profiles can optimize therapy and reduce the unnecessary use of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Nutrition
- Success rates of conservative treatment and optimal surgical timing for pediatric chylothorax
- Pakwan Kaewchusen, Narumon Densupsoontorn, Supaluck Kanjanauthai, Puthita Saengpanit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):871-878. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: What is the success rate of conservative treatment for pediatric chylothorax, and when should surgical intervention be employed?
Finding: Overall success rate of conservative treatment was 83.3%. Surgically related etiologies and lower peak pleural fluid drainage rates were significantly associated with successful conservative management of pediatric chylothorax.
Meaning: If chylous drainage persists at ≥10 mL/kg/day beyond 2 weeks of optimal conservative treatment, surgical intervention should be considered.
- Gastroenterology
- Dual-strain probiotics Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates: a randomized controlled trial
- Setthawut Sittiwong, Pornthep Tanpowpong, Pisut Pongchaikul, Pracha Nuntnarumit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):763-771. Published online August 6, 2025
-

Question: Can probiotics BB/LA reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates?
Finding: BB/LA supplementation induced more diverse beta diversity and increased relative abundances of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and decreased relative abundance Clostridium.
Meaning: Early BB/LA supplementation could reverse gut dysbiosis in preterm neonates.
- Cardiology
- Unsustainable and overworked: unpacking the challenges faced by pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea
- Soo In Jeong, GI Beom Kim, Sung Hye Kim, Jae Yoon Na, Hong Ju Shin, Sin Weon Yun, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Sang Yun Lee, Chang-Ha Lee, Kwang Ho Choi, Seul Gi Cha, Mi Young Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):732-741. Published online August 6, 2025
-
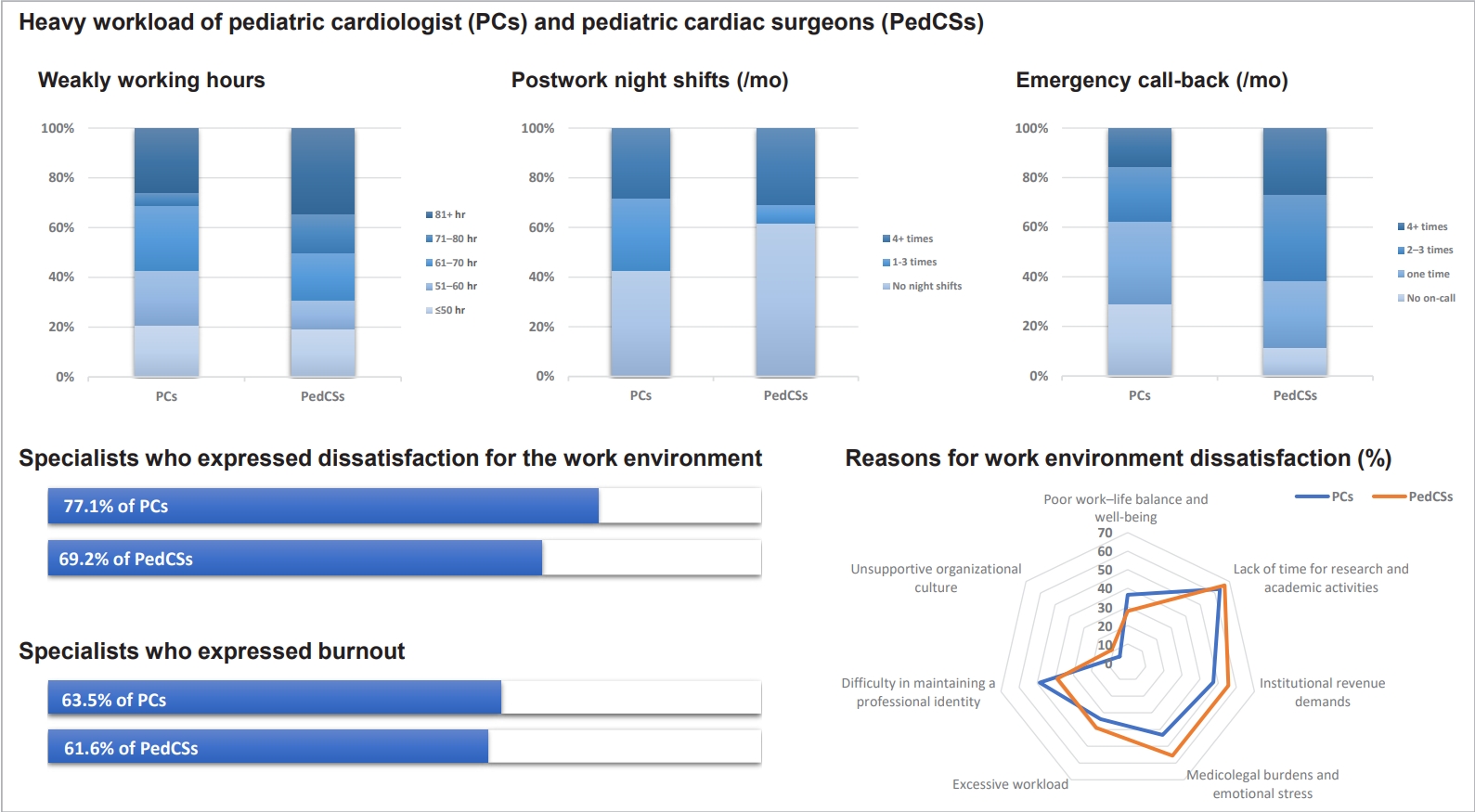
Question: What are the key challenges affecting pediatric cardiologists and cardiac surgeons in Korea?
Finding: Excessive workloads, low procedural volumes, and legal risks contribute to high burnout. Regional disparities limit skill maintenance and threaten workforce sustainability.
Meaning: Targeted policies ensuring fair workloads, legal protections, and regional support are essential to stabilizing the pediatric cardiac workforce and maintaining high-quality care.
- Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in adolescents: transcranial doppler versus autonomic function test results
- Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):673-679. Published online August 6, 2025
-
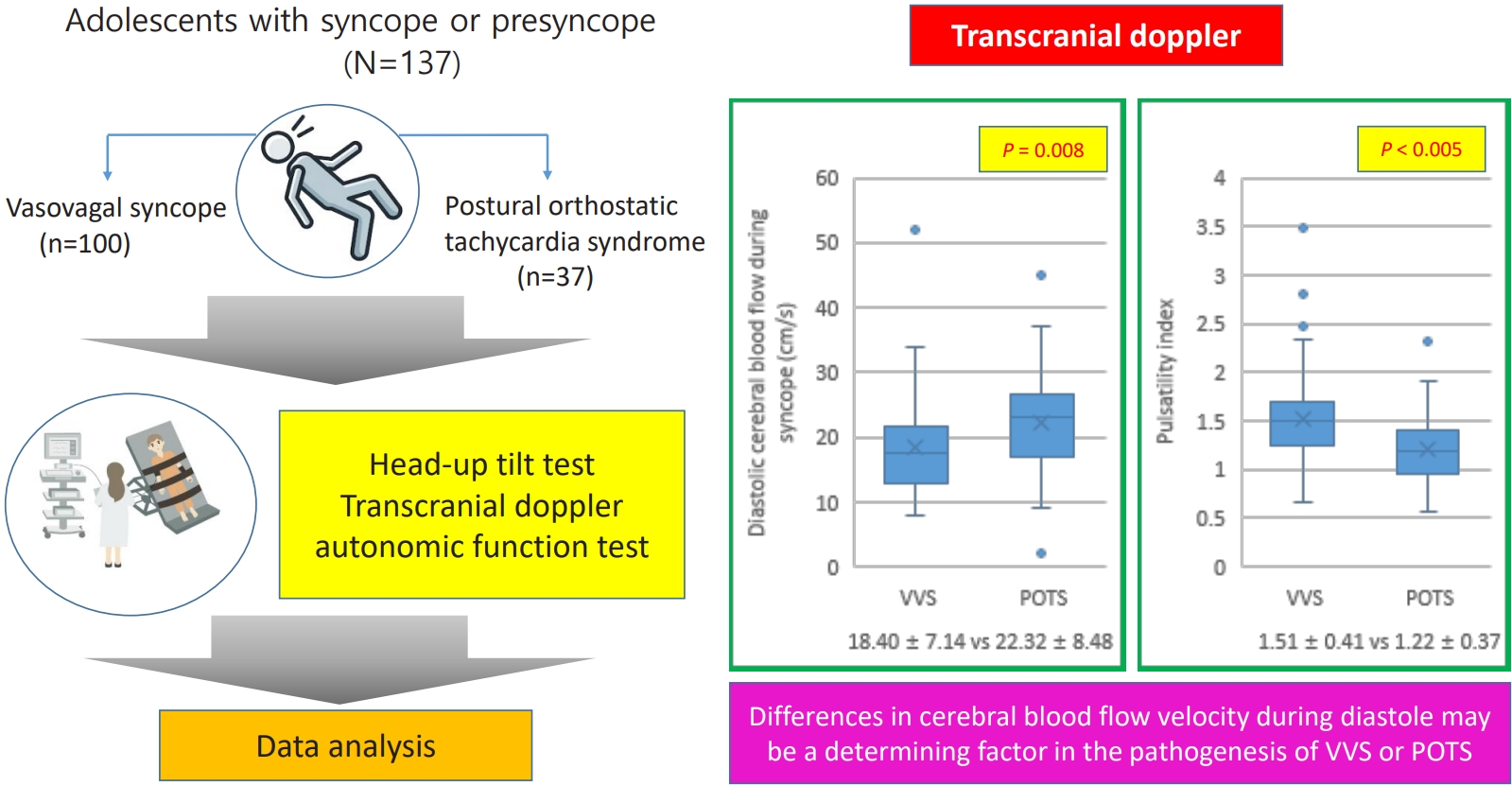
Question: Vasovagal syncope (VVS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) are representative forms of neurally mediated syncope. What influences the occurrence of each?
Finding: Autonomic function test results did not differ, but cerebral blood flow during diastole on transcranial doppler differed between VVS and POTS.
Meaning: Differences in diastolic cerebral blood flow velocity play an important role in VVS and POTS.
- Correspondence
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Authors' reply: a commentary on “COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children with systemic lupus erythematosus”
- Karnchanit Sausukpaiboon, Nuanpan Penboon, Pornpimol Rianthavorn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):626-627. Published online July 18, 2025
-
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Liposomal SunActive versus conventional iron for treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in children aged 2–12 years: a prospective randomized controlled trial
- Wael A. Bahbah, Yasmin A.H.S. Younis, Hanan Salama Elbelouny, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):608-615. Published online July 18, 2025
-
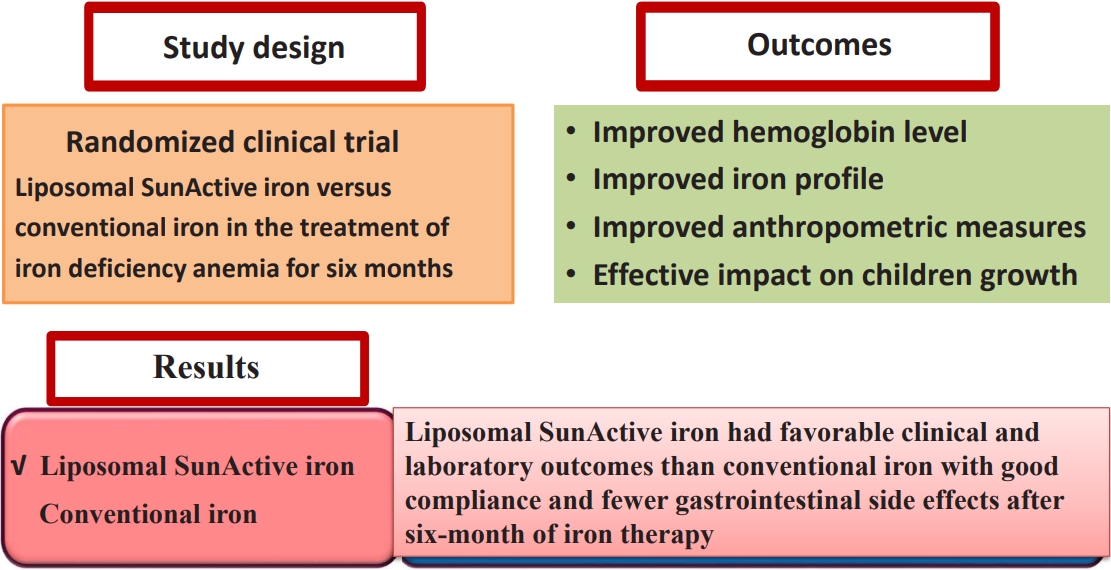
Background: Liposomal iron, a novel oral formulation of ferric pyrophosphate that demonstrates improved gastrointestinal absorption and bioavailability with fewer side effects than conventional iron, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).
Purpose: To conduct an in-depth comparative study of liposomal SunActive and conventional iron supplements (iron polymaltose complex) for treating IDA in children aged 2–12 years Methods: This...
- Editorial
- Other
- Beyond the eye: a multidisciplinary perspective on managing pediatric myopia
- Eoi Jong Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):566-568. Published online July 18, 2025
-
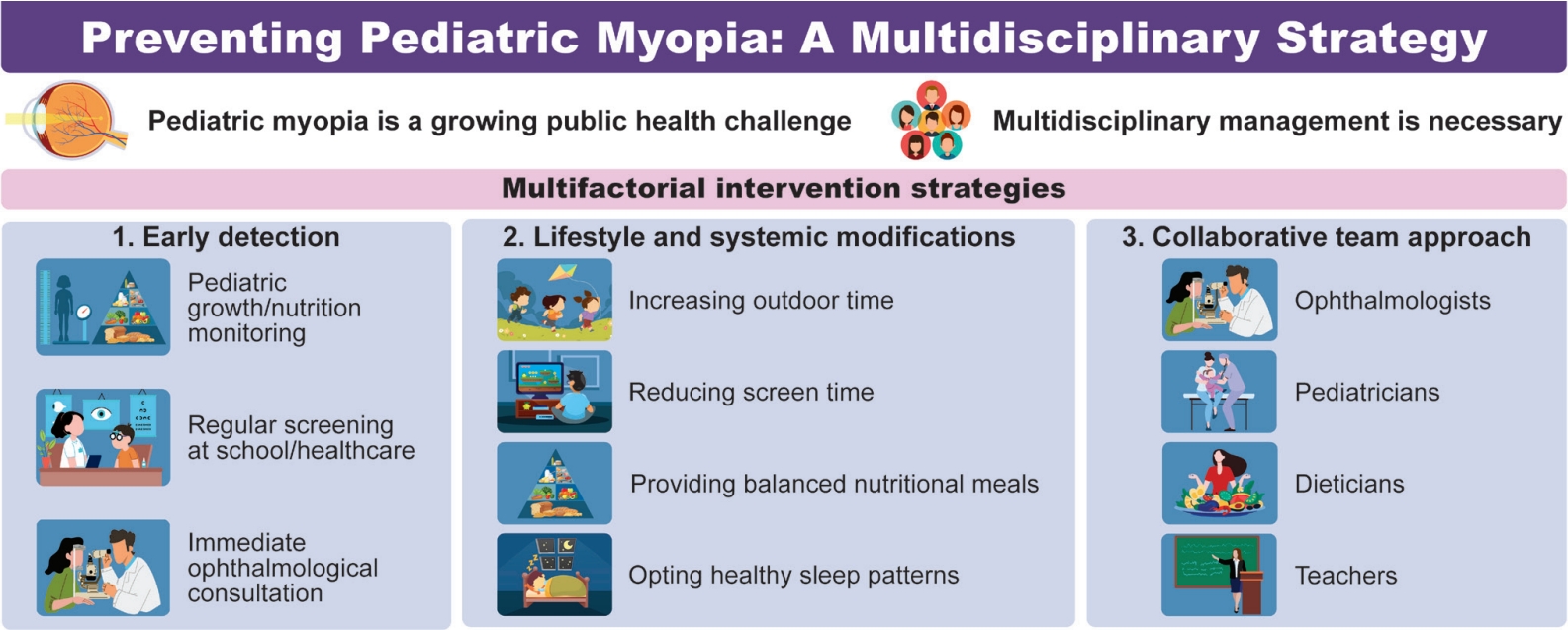
Myopia is a growing global public health concern because of its association with irreversible vision loss such as myopic traction maculopathy, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and glaucoma. The effective prevention of myopia in childhood requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates ophthalmologic care with lifestyle, nutrition, and sleep interventions. Early detection through regular visual screening in schools and primary care settings and timely ophthalmology referrals are critical to preventing high myopia.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia: links to vitamin cofactor deficiencies and oxidative stress
- Arzu Dadashova, Gunay Aliyeva, Rana Rahimova, Gulnara Azizova, Khayala Mammadova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):819-830. Published online July 8, 2025
-

Question: What are the biochemical and clinical correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia, and how does it relate to vitamin status, oxidative stress, and splenectomy?
Finding: Most pediatric β-thalassemia patients exhibited severe hyperhomocysteinemia, which was strongly associated with folate and B12 deficiencies and influenced oxidative stress patterns, particularly in splenectomized individuals.
Meaning: These findings suggest that routine monitoring and correction of B-vitamin deficiencies may mitigate hyperhomocysteinemia-related risks in pediatric thalassemia.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Respiratory severity score-guided postnatal systemic corticosteroid therapy for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants
- Gyeong Eun Yeom, Ju Sun Heo, Baek Sup Shin, Seh Hyun Kim, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):656-665. Published online July 8, 2025
-
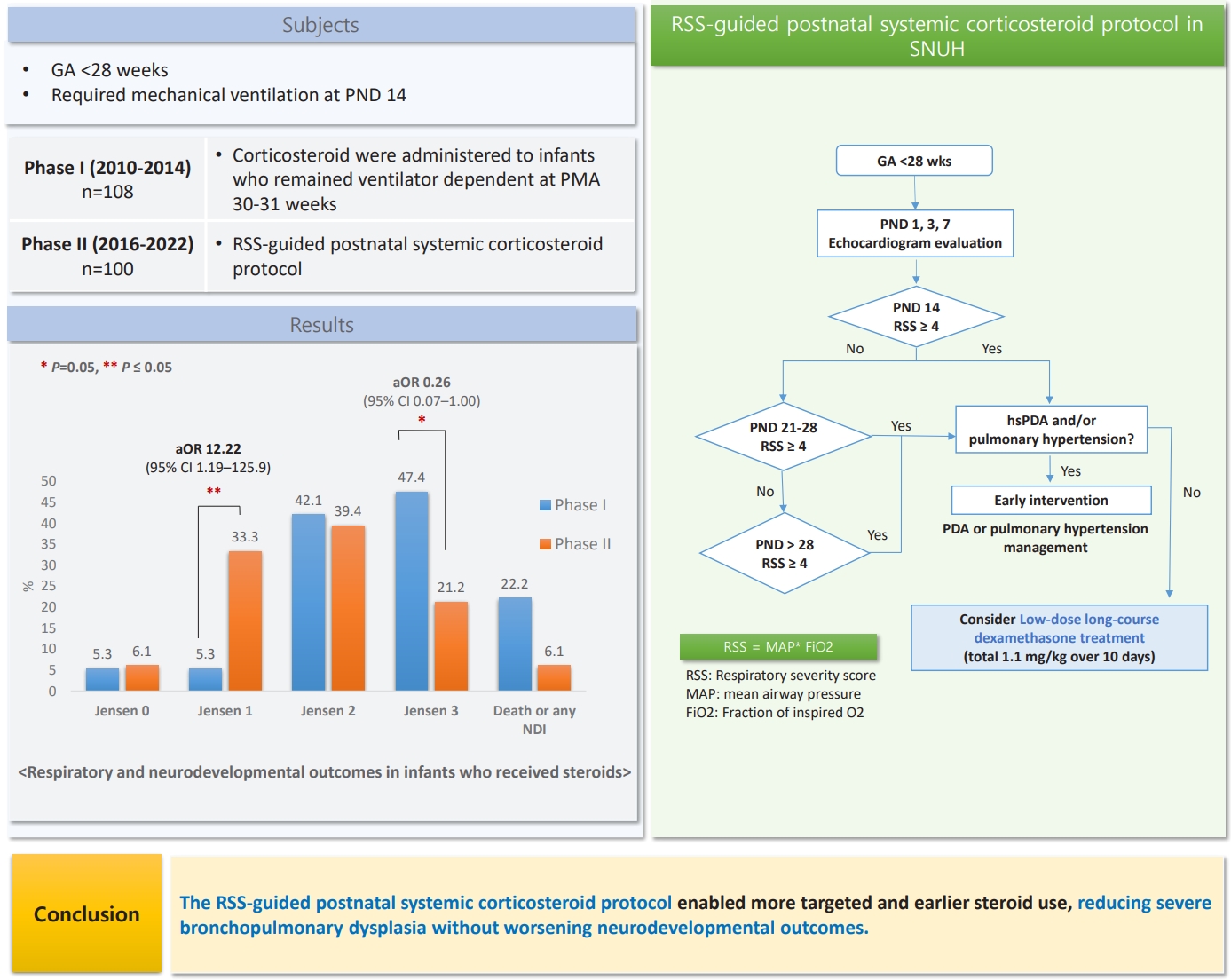
Question: Does a respiratory severity score (RSS)-guided postnatal corticosteroid protocol improve respiratory outcomes of extremely preterm (EP) infants without worsening neurodevelopmental outcomes?
Finding: The protocol enabled targeted and early steroid use, thereby reducing severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia without affecting mortality or causing neurodevelopmental impairments.
Meaning: The RSS-guided protocol may offer a more precise and individualized postnatal corticosteroid therapy for EP infants.
- General Pediatrics
- Trends and determinants in breastfeeding among Korean infants (2007–2021): a nationwide study using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children
- Minwoong Kang, Eui Kyung Choi, Jeung Min Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Son Moon Shin; Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):772-780. Published online July 4, 2025
-

Question: What are the recent trends and determinants of breastfeeding in South Korea?
Finding: Breastfeeding rates in South Korea declined significantly from 2007 to 2021, with lower rates observed in preterm, low-birthweight, and multiple-birth infants as well as rural or lower-income households.
Meaning: Targeted interventions, including prenatal education, postnatal support, and community-based programs, are required to address disparities and improve breastfeeding rates.
- Oncology
- Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for treatment of relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancy in children and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ghea Mangkuliguna, Edi Setiawan Tehuteru, Reganedgary Jonlean, Nicholas Adrianto, Stella Kallista
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):712-721. Published online July 4, 2025
-
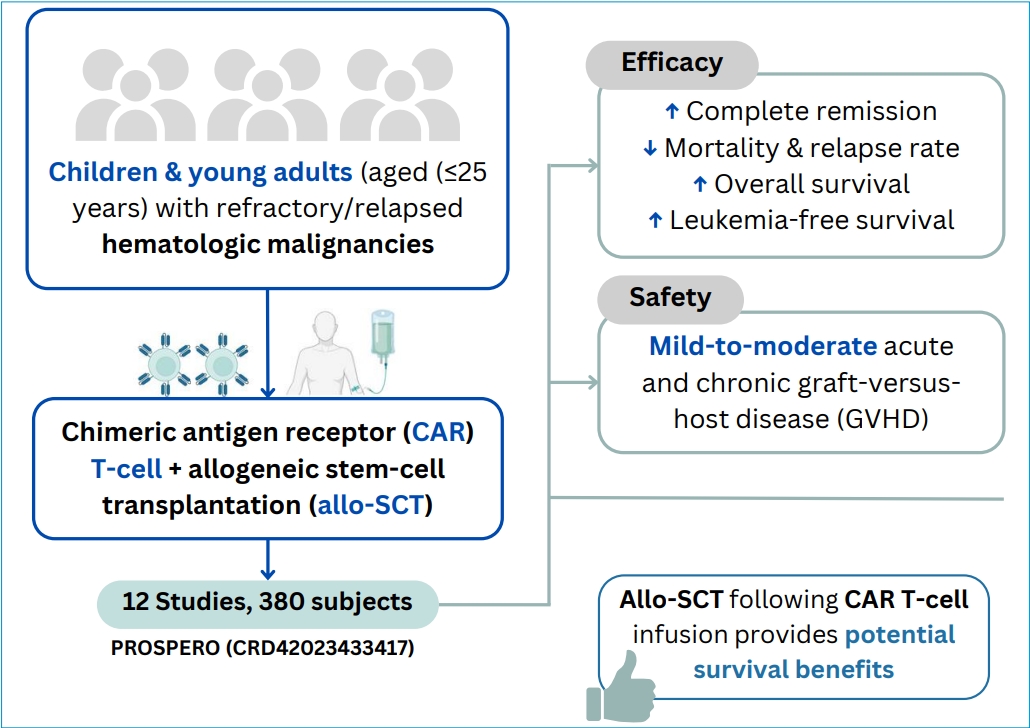
Question: Does consolidative allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy improve outcomes of children and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies?
Finding: The meta-analysis showed reduced relapse rates and favorable survival trends with allo-SCT despite low evidence quality.
Meaning: Consolidative allo-SCT after CAR T-cell therapy may enhance survival; however, further clinical studies are needed.
- Review Article
- Other
- Artificial intelligence in pediatric healthcare: current applications, potential, and implementation considerations
- Taejin Park, In-Hee Lee, Seung Wook Lee, Sek Won Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):641-651. Published online June 25, 2025
-
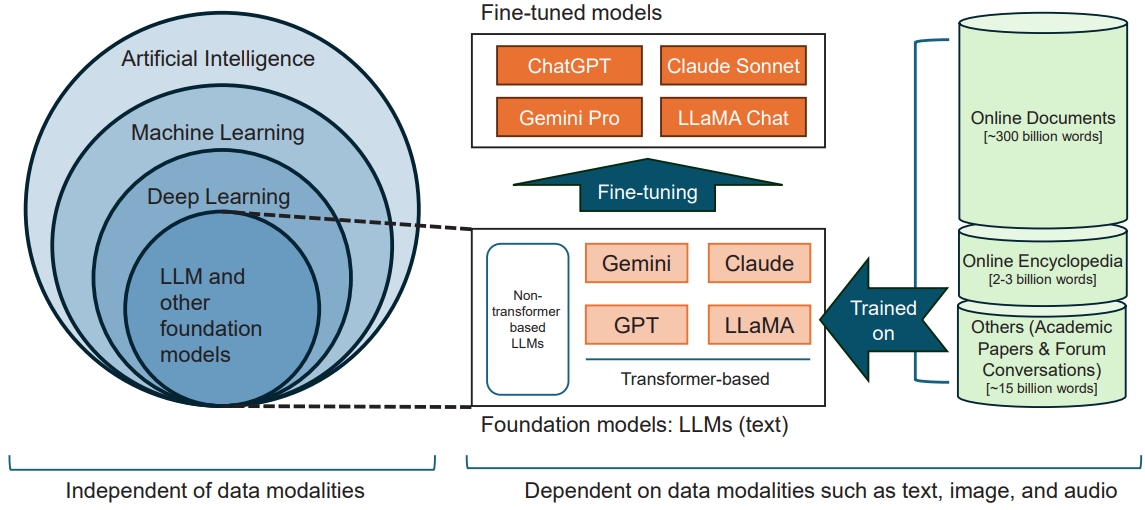
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential benefits in pediatric care, but its real-world adoption requires clinician literacy, ethical and legal safeguards, and cautious implementation. Large language models are emerging across healthcare, but their use in pediatric clinical practice remains premature. Thus, the cautious and accountable implementation of AI is crucial to preventing unintended harm and realizing its potential.
- Original Article
- Other
- Role of neutrophil elastase in predicting infection among children with chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia
- Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Doaa M. Elian, Mai El-Sayad Abd El-Hamid, Esraa T. Allam, Mariam S. Kandeel, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):801-807. Published online June 10, 2025
-

Question: Can neutrophil elastase (NE) levels predict infection— the primary cause of mortality—among children with hematological malignancies and febrile neutropenia (FN)?
Finding: Elevated levels of NE were found in children with chemotherapy-induced FN and a bacterial infection.
Meaning: Increased NE levels and prolonged FN are important factors associated with mortality risk.
- Gastroenterology
- Treatment targeting pediatric inflammatory bowel disease-associated anemia: experience from a single tertiary center
- Ana S.C. Fernandes, Sara Azevedo, Ana Rita Martins, Ana Isabel Lopes
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):722-731. Published online June 10, 2025
-
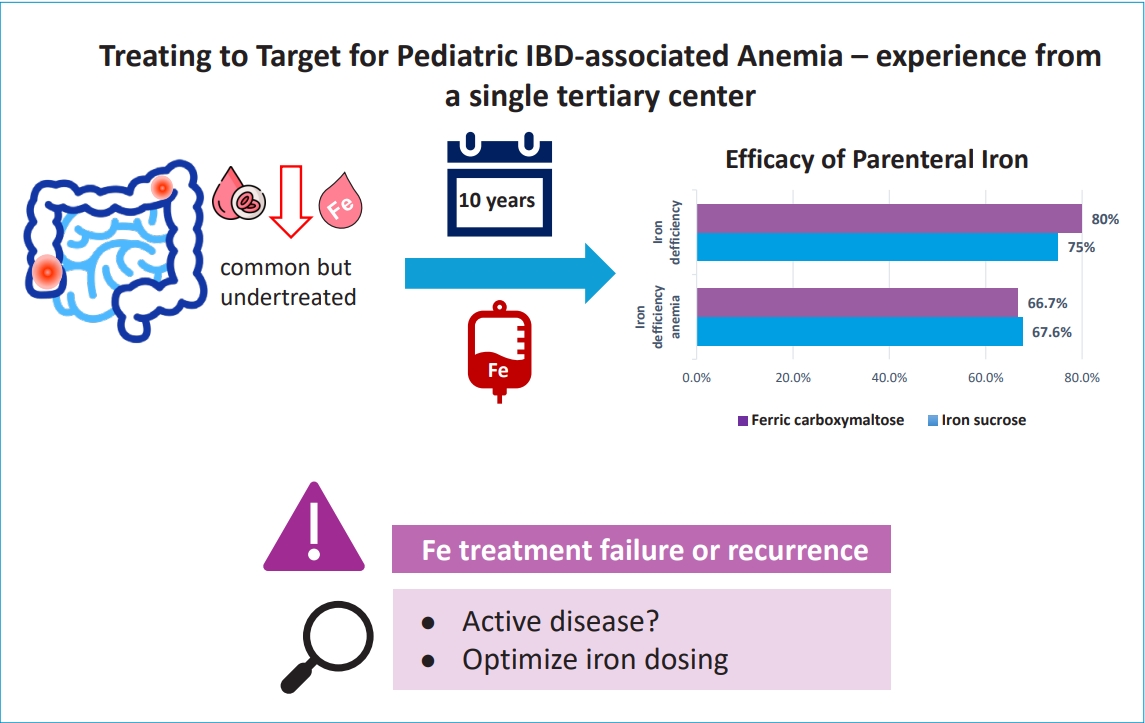
Question: Does treating iron deficiency (ID) using intravenous iron in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) feature long-term safety and efficacy?
Finding: Intravenous iron supplementation was safe and effective. However, the ID recurrence rate was higher than expected.
Meaning: Proactive screening and treatment of ID in pediatric IBD are essential. The Ganzoni formula likely underestimates the iron requirements of pediatric patients. Prospective trials are needed to optimize iron treatment dosing.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











