- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study
-
Phakwan Laohathai, Rathaporn Sumboonnanonda, Puthita Saengpanit, Chodchanok Vijarnsorn, Chatchawan Srisawat, Kwanjai Chotipanang, Sarawut Junnu, Supawan Kunnangja, Hathaichanok Rukprayoon, Phakkanan Phuangphan, Sompong Liammongkolkul, Arthima Phaokong, Narumon Densupsoontorn
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):666-672. Published online April 16, 2025
-
|
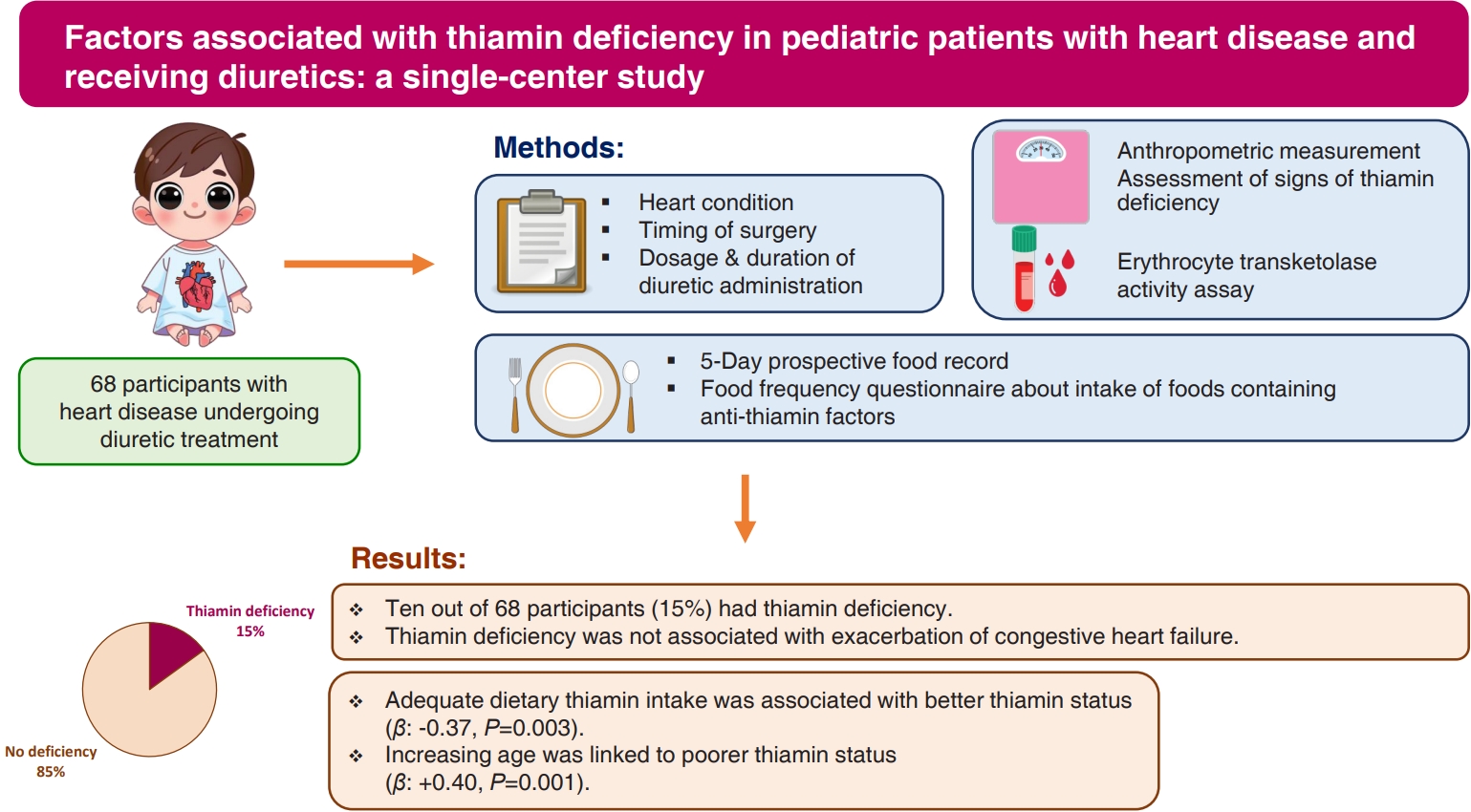
Question: Are pediatric patients with heart disease who are receiving diuretics at risk of thiamin deficiency (TD)?
Finding: Fifteen percent of the patients had TD. TD was associated with inadequate dietary thiamin intake and increasing age.
Meaning: The thiamin pyrophosphate effect should be assessed in those with high risk of TD. Dietary counseling should be emphasized to ensure adequate dietary thiamin intake. |
-
-
- Success rates of conservative treatment and optimal surgical timing for pediatric chylothorax
-
Pakwan Kaewchusen, Narumon Densupsoontorn, Supaluck Kanjanauthai, Puthita Saengpanit
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):871-878. Published online August 6, 2025
-

|
Question: What is the success rate of conservative treatment for pediatric chylothorax, and when should surgical intervention be employed?
Finding: Overall success rate of conservative treatment was 83.3%. Surgically related etiologies and lower peak pleural fluid drainage rates were significantly associated with successful conservative management of pediatric chylothorax.
Meaning: If chylous drainage persists at ≥10 mL/kg/day beyond 2 weeks of optimal conservative treatment, surgical intervention should be considered. |
-
-
|














