- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
-
Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
|
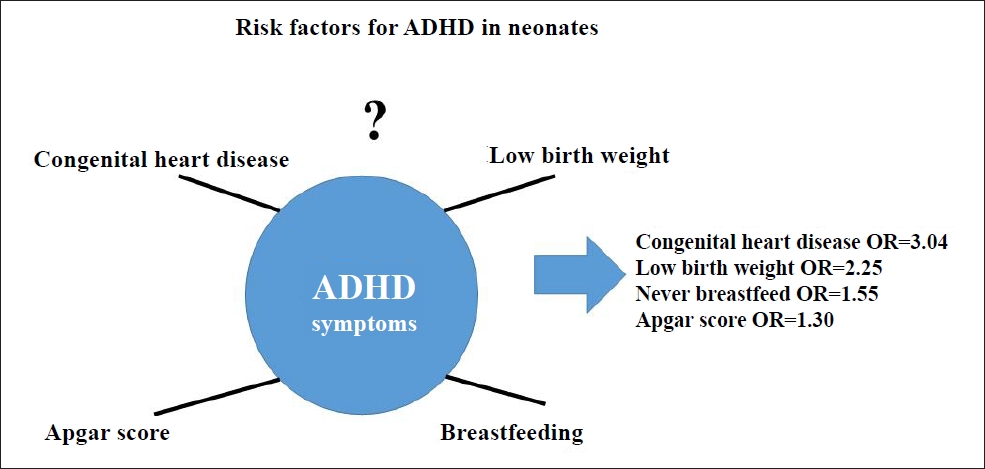
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD. |
-
-
- Other
- Association between pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl exposure during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder among children: a meta-analysis
-
Fereshteh Mehri, Saeid Bashirian, Salman khazaei, Ensiyeh Jenabi
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):286-292. Published online July 27, 2020
-

|
· This meta-analysis analyzed the association between pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) exposure during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) risk among children.
· A significant association was noted between PCB and pesticide exposure during pregnancy and ASD risk among children (odds ratio [OR], 1.80; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.26–2.34 and OR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.02–1.39), respectively.
· Pesticide and PCB exposure during pregnancy may affect ASD risk among children. |
-
-
|














