Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Influence of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic parameters in obese children and adolescents
- Ozlem Kara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):110-114. Published online March 6, 2020
-
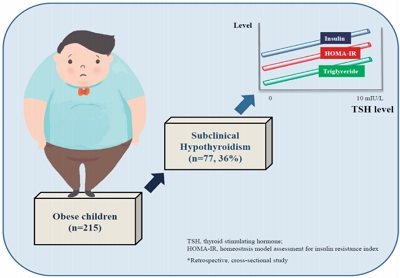
Question: Does subclinical hypothyroidism in obese children and adolescents affect metabolic parameters?
Finding: Insulin, HOMA-IR, and TG levels were higher and the HDL-C level was lower in patients with SH.
Meaning: A clear association is observed between SH, and insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in obese children. It can be said that the TSH may be evaluated as a metabolic risk factor in obese patients.
- Gastroenterology
- Thyroid disturbances in children treated with combined pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C
- Yasser K. Rashed, Fatma A. Khalaf, Sobhy E. Kotb
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):52-55. Published online September 27, 2019
-
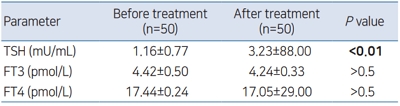
Background: Immunomodulatory properties of interferon (IFN) have been documented. It may induce autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroiditis with hypo- or hyperthyroidism. In addition, it may impair thyroid hormone synthesis through affecting iodide organification in thyroid gland.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to describe thyroid function tests disturbances in children with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) receiving pegylated interferon-alpha (PEG...
- Endocrinology
- Final height of Korean patients with early treated congenital hypothyroidism
- Jiyun Lee, Jeongho Lee, Dong Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):221-225. Published online July 15, 2018
-
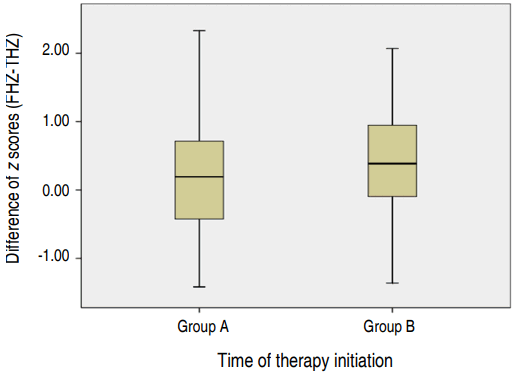
Purpose: Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is the most common endocrine disorder in children. Thyroid hormone deprivation results not only in mental retardation but also growth retardation. This study investigates the final height (FH) in Korean patients with CH detected by newborn screening and examines factors that may affect the FH. Methods: The medical records of Korean CH patients (n=45) were reviewed. The...
- Thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight preterm infants
- Ji Hoon Lee, Sung Woo Kim, Ga Won Jeon, Jong Beom Sin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):224-229. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose Thyroid dysfunction is common in preterm infants. Congenital hypothyroidism causes neurodevelopmental impairment, which is preventable if properly treated. This study was conducted to describe the characteristics of thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs), evaluate risk factors of hypothyroidism, and suggest the reassessment of thyroid function with an initially normal thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as part of a newborn...
- Characteristics of thyroid nodules in infant with congenital hypothyroidism
- Seo Young Youn, Jeong Ho Lee, Yun-Woo Chang, Dong Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(2):85-90. Published online February 24, 2014
-
Purpose This study aimed to assess the characteristics of thyroid nodules among infants diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism.
Methods A retrospective study of 660 infants (374 males, 286 females) diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism was carried out at the Pediatric Endocrine Clinic in Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Korea, between May 2003 and February 2013. The average age at diagnosis was 1.16±1.68 months.
Results Of the 28 patients (4.2%)...
- Case Report
- A family with Townes-Brocks syndrome with congenital hypothyroidism and a novel mutation of the
SALL1 gene - Won Ik Choi, Ji Hye Kim, Han Wook Yoo, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(12):1018-1021. Published online December 31, 2010
-
Townes-Brocks syndrome (TBS) is a rare autosomal dominant congenital disorder caused by mutations in the
SALL1 gene. Its signs and symptoms overlap with other genetic syndromes, including VACTERL association, Pendred syndrome, Baller-Gerold syndrome, and cat eye syndrome. Structural vertebral abnormalities, hypoplasia of the thumb, and radial bone abnormalities, which are not usually associated with TBS, help in the differential diagnosis...
- Original Article
- Asthma predictive index in children with recurrent wheezing
- Joo Young Jang, Hyo Bin Kim, So Yeon Lee, Ja Hyung Kim, Bong Seong Ki, Hee Jung Seo, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):298-304. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Purpose : We compared the asthma predictive index(API) and the modified asthma predictive index (mAPI) of the Tuscon Children's Respiratory Study Group in Korean children with recurrent wheezing. We investigated the atopic profiles and presence of allergen sensitization of each risk group, and ascertained the significant clinical risk factors. Methods : Two hundred and sixty two children, who visited for recurrent... -
- Endocrine dysfunction and growth in children with medulloblastoma
- In Suk Yoon, Ji Young Seo, Choong Ho Shin, Il Han Kim, Hee Young Shin, Sei Won Yang, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):292-297. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Purpose : In medulloblastoma, craniospinal radiation therapy combined with chemotherapy improves the prognosis of tumors but results in significant endocrine morbidities. We studied the endocrine morbidity, especially growth pattern changes. Methods : The medical records of 37 patients with medulloblastoma were reviewed retrospectively for evaluation of endocrine function and growth. We performed the growth hormone stimulation test in 16 patients whose... -
- Clinical Lecture
- Hypothyroidism
- Jong Duck Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):779-805. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Hypothyroidism is a deficiency in thyroid hormone secretion by the thyroid gland and a defect in thyroid hormonal receptor activity. It is categorized by the two major forms in children, the one is congenital hypothyroidism and the other is acquired hypothyroidism. Congenital hypothyroidism is one of the commonest treatable causes of mental retardation and occurs in 1 in 3,000-4,000 infants... -
- Original Article
- Reevaluation of the Neonatal Screening Test for Congenital Hypothyroidism
- So Young Kang, Young Pyo Chang, Jeesuk Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):387-394. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We performed this study to compare the TSH and free T4 levels according to gestational age and birth weight, and to reevaluate the cut-off values in the neonatal screening test for congenital hypothyroidism. Methods : Total 2,133 neonates(1,749 healthy newborns and 384 sick neonates) were screened in Dankook University Hospital from May 2000 to January 2003. Neonates with abnormal... -
- A Cost-benefit Analysis on Neonatal Screening of Phenylketonuria and Congenital Hypothyroidism in Korea
- Hoe Cheol Yoon, Nyeon Cheon Kim, Dong Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):369-375. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Many inborn errors of metabolism can be completely cured with early detection and early treatment. This is why neonatal screening on inborn errors of metabolism is implemented worldwide. In this study, a cost-benefit analysis was performed on the neonatal screening of phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism in Korea. Methods : This study included 2,908,231 neonates who took the neonatal screening... -
- Evaluation of Intellectual Development in Patients with Transient Congenital Hypothyroidism at Early School Age
- Pil Ju Jeong, Su Yung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(7):768-773. Published online July 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Thyroxine is the hormone indispensible to the growth and development of infants. We made this study to confirm the influence of temporary depression of serum thyroxine levels on the development of intelligence. Methods : I adopted as the study group 14 patients diagnosed with depression at the pediatrics department of Pusan National University Hospital from April of 1991 to... -
- Clinical Characteristic of Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Children
- Hye Rim Chung, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):76-80. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Although chronic autoimmune thyroiditis(AIT) is known to progress into overt hypothyroidism in adults, the outcomes of this disorder in pediatric patients are different from those in adults, so it is hard to predict its course. We reviewed clinical characteristics of chronic AIT in children. Methods : The medical records of 94 children, who were diagnosed as AIT, were analyzed,... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Thyroxine Binding Globulin Deficiency with Hypothyroidism
- Dong-Chul Lee, Sun-Hee Lee, Jae-Hong Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(6):796-799. Published online June 15, 2002
-
A child diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism after newborn screening and follow up thyroid function test at 1 month of life in another general hospital demonstrated euthyroid state with thyroxine(T4) supplementation until the age of 22 months of life, when he was transferred to our hospital, where he was diagnosed as thyroxine binding globulin(TBG) deficiency with low T4 and TBG. Withdrawal... -
- Original Article
- The Correlation Between the TSH Level in Neonatal Screening Test and the Prognosis of Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Hong Sun Park, Kye Shik Shim, Kyuchul Choeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(1):25-31. Published online January 15, 2001
-
Purpose : It is important to diagnose and treat newborn patients with congenital hypothyroidism as soon as possible because of neurodevelopmental outcome. If we can detect more severe forms of congenital hypothyroidism with neonatal screening test, the results of treatment will improve. Methods : Sixty-four term infants whose TSH levels in neonatal screening test had been higher than 20μIU were recalled.... -
- Characteristics of Transient Hypothyroidism Detected by Neonatal Screening Test
- Su-Yung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(11):1487-1495. Published online November 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To help differentiate transient hypothyroidism from congenital hypothyroidism, both of which might be confused initially, the clinical characteristics of transient hypothyroidism were compared to those of permanent ones. Methods : An analysis of the clinical data, including perinatal history, TFT(thyroid function test), and radionuclide scanning, was performed. The outcome of 18 patients of transient hypothyroidism was also compared to... -
- Follow up of Infants with Congenital Hypothyroidism Who were Detected by Newborn Screening Test
- Kyung Ah Kim, Eun Sil Lee, Son Moon Shin, Han Ku Moon, Yong Hoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(8):1141-1148. Published online August 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Developmental delay in congenital hypothyroidism can be prevented by early detection and treatment. We conducted a follow-up study to assess the growth and development of infants with congenital hypothyroidism who were detected by newborn screening test and received thyroid hormone therapy. Methods : Nineteen hypothyroid infants were detected by newborn screening test from April 1995 to May 1997. Measurements... -
- Comparison between Thyroid Function Test and Radiographic Size of Knee Epiphysis in Neonates with Congenital Hypothyroidism
- An Sung Koh, Jae Ock Park, Dong Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(8):1130-1135. Published online August 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Biochemical confirmation of congenital hypothyroidism takes about 10 days, which may result in a delay in diagnosis. The delay could be reduced if a faster method of investigation such as knee radiograph is used. The aim of this study is to assess the value of plain radiography of the knee in providing supportive evidence for the diagnosis of... -
- The Influence of the Use of Iodine during Perinatal Period on the Screening Test for Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Gyu Bum Cho, Dong Hwan Lee, Sang Jhoo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(2):195-206. Published online February 15, 1996
-
Purpose : This study was performed to detect the diseases of congenital hypothyroidism by the neonatal mass screening test early and to demonstrate the possible role of topical iodinated antiseptics(povidone-iodine, PVP-Ⅰ) on transient hyperthyrotropinemia in newborn infants. Methods : We performed neonatal screening tests for inborn errors of metabolism since 1985 by Guthrie test for PKU, maple syrup urine disease, histidinemia,... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Hypothyroidism with Echocardiograpnic Features Similar to Cardiomyopathy
- Suk Min Choi, Heung Dong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(10):1417-1421. Published online October 15, 1995
-
A case of congenital hypotyroidism with echocardiographic features similar to cardiomyopathy was presented. The patient was untreated and incidentally found. In 2-D echocadiography the ventricular septum was asymmetrically hypertrophied and chest X-ray showed cardiac enlargement. After treatment with thyroid hormone, the septal hypertrophy and cardiomegaly returned to normal. Therefore, we concluded that echocardiographic study was useful for diagnosis and for following up... -
-
- A Case of Hyperthyroidism Following Primary Hypotyroidism
- Han Sung Cho, Hwang Jae Yoo, Sang Ook Park, Jae Hong Park, Su Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(6):863-866. Published online June 15, 1995
-
A 9-year-old girl presented with primary hypothroidism have been followed by the development of hyperthyroidism. The diagnosis of primary hypothyroidism had been made by clinical manifestation, elavated serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level, antithyroglobulin antibody and antimicrosome antibody. Five and a quarter years later, the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism had been made by clinical maifestation such as enlargemetn of thyroid gland, tahcycardia, increased... -
- Original Article
- The Growth Hormone Response to Growth Hormone-Releasing Hexapeptide (GHRP-6) in the Sprague Dawley Rat with Hypothyroidism
- Sei Won Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(1):89-98. Published online January 15, 1994
-
We studied the effects of growth hormone to subthreshold, threshold, or suprathershold dose of growth hormone-releasing hexapeptide (GHRP-6) in conscious and unconscious (anesthesized with ketamine and phenobarbital) female Sprague Dawley rats with hypothyroidism, induced with methimazole and compared these results with those in conscious and unconscious rats with euthyroidism. The results were as below; 1) In conscious rats, the peak GH response... -
- Re-evaluation of TSH Screening TEST in Neonates
- Jin Young Song, Dong Woo Son, Beyong Il Kim, Sei Won Yang, Jung-Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yoon, Hyung Ro Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(11):1502-1506. Published online November 15, 1993
-
Five years ago, we made the cut-off value of TSH by dry filter paper method as 15μU/ml to screening congenital hypothyrodism. Since then, 1,210 term neonates, who had no perinatal problems, screening test with this cut-off point. Neonates had been recalled for measurement of serum T4/TSH to rule out congenital hypothyroidism if their TSH value by screening tests reveal more... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Goiter with Congenital Hypothyroidism due to Organification Defect
- Ik Hee Lee, Sung Yong Jung, Thi Hyung Park, Sa Jun Chung, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(7):1002-1008. Published online July 15, 1993
-
We experienced a case of congenital goiter with congenital hypothyroidism in 45 dayold male, who complained of respiratory difficulty and anterior neck mass. After admission, he was diagnosed congenital hypothyroidism by the clinical manifestations and laboratory tests including biochemistry, radioimmunoassay, radioisotope study, perchlorate discharge test, and bone radiography. We obtained positive finding at the perchlorate discharge test and found that his... -
- Original Article
- Growth Outcome in Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Mi Jung Park, Ho Seong Kim, Duk Hi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(5):713-720. Published online May 15, 1993
-
Congenital hypothyroidism is one of the most common endocrine disease in childhood and it causes not only mental retardation but also growth retardation. There were many papers about evaluation of developmental outcome in congenital hypothyroidism, The aim of this study was to evaluate growth outcome in congenital hypothyroidism. We evaluated 65 patients with congenital hypothyroidism diagnosed at yonsei University College... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Neonatal Hypothyroidism due to Maternal TSH-Binding Inhibitor Immunoglobulin
- Myung Lye Kim, Rhie Choi, Dong Hwan Lee, Sang Jhoo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(6):804-808. Published online June 15, 1992
-
Neonatal screening for congenital hypothroidism is important because of the possibility that mental retardation may be avoided if treatment started early. A 1 day old patient was admitted to our department of Pediatrics for congenital hypothyroidism screening. The mother was 33 years old and had been on thyroid replacement therapy since 32 years of age. During the pregnancy she was euthyroid... -
- Original Article
- The Incidence of Hypothyroidism in Children with Down Syndrome
- Seong Hyeon Jeon, Chun Ho Cho, Kyoung Sim Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(4):534-538. Published online April 15, 1992
-
A review of Thyroid function tests was performed on 32 children with Down syndrome confirmed by cytogenetic examination at the Dept. of Pediatrics, Kwangju Christian Hospital from Jan.1989 to Feb.1990. 1) Twenty among 32 children with Down syndrome were male, with the sex ratio being 1.7 : 1. Their ages ranged from 3 days to 5 years, with the mean age... -
- Two cases of ectopic sublingual thyroid with hypothyroidism to be appeared in fetal life.
- Dong Sik Kim, Mee Kyung Namgoong, Hae Yong Lee, Hwang Min Kim, Baek Keun Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(3):426-434. Published online March 31, 1991
-
Infants & children with hypothyrodism usually manifest variable skeletal abnormality. These features are the delay in longitudinal bone growth, the delay in epiphyseal maturation (=delay in bone age), the disturbances in bone mineralization and charateristic multiple stippled epiphysis (cretenoid epiphyseal dysgenesis). But many pediatrician have only concerned about the delay in epiphyseal maturation. Epiphyseal dysgenesis can be used a marker to find out the begining... -
- A case of IDDM associated with hypothyroidism.
- Kyung Min Lee, Kuk Sin Jang, Mi Kyung Jang, Chul Zoo Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(1):144-147. Published online January 31, 1991
-
The authors experienced a case of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with hypothyroidism. We recommend that all patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus be screened for thyroid mi- crosomal antibody and that those patients found to have thyroid microsomal antibody be followed annually for determination of free T4 and TSH values. We report this case with a review of related literatures. -
- Clinical Observation on isolated TRH deficient Congenital Hypothyroidism.
- Heon Seok Han, Hyung Ro Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(10):1388-1393. Published online October 31, 1990
-
Clinical features and endocrine function of 3 children with isolated TRH deficient congenital hypothyroidism followed at Seoul National University Children’s Hospital from Aug, 1986 to Aug. 1990 were reviewed. During above period 262 congenital hypothyroid patients were followed at endocrine clinic, number of congenital primary hypothyroidism was 218 cases (83.2%), and that of congenital secondary hypothyroidism was 44 cases (16.8%). Of the congenital primary hypothyroidism,... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











