Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2023 during the last six months.
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota’s impact on obesity
(9 times)
-
Sujin Jeong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):294-295. Published online June 14, 2023
-

|
· An imbalance of the gut microbiota with a relative increase in Firmicutes versus Bacteroidetes is associated with the pathogenesis of obesity.
· Dysbiosis is associated with microbial genes associated with short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production and increased colonic SCFA levels. SCFAs have also been shown to regulate appetite and satiety hormones, which can affect food intake and energy balance.
· A dietary high-fat intake is reportedly associated with increased plasma lipopolysaccharide. Altered Toll-like receptor-4 signaling leads to propagating the cascade of further inflammation and promoting insulin resistance. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Kidney complications associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and adolescents: a brief review
(9 times)
-
Hee Sun Baek, Min Hyun Cho
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):424-431. Published online June 28, 2023
-
|
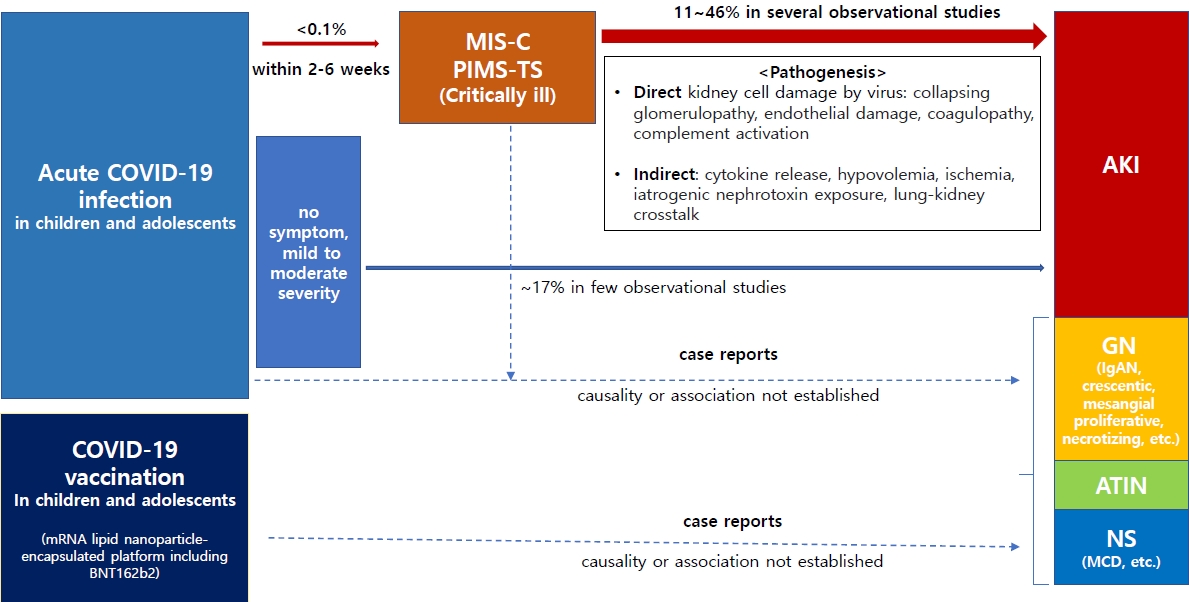
Several observational studies have shown that acute kidney injury affects up to 46% of children and adolescents who develop severe postinflammatory responses, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood, due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although causality has not been established, some cases of glomerulopathy or nephrotic syndrome occurring after COVID-19 infection or vaccination have been reported. Therefore, kidney complications associated with these conditions in children and adolescents warrant attention. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of kidney complications in children after COVID-19 infection or vaccination
(9 times)
-
Jiwon Jung, Joo Hoon Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):35-36. Published online November 17, 2023
-
|
|
· The proper monitoring for and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill children, are recommended.
· Glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 or its vaccination has been reported, and the overall clinical course is similar to that of non-COVID-19-associated diseases.
· Additional COVID-19 vaccinations are recommended; however, careful and individualized decisions should be made in patients with COVID-19- or vaccination-associated glomerulopathy. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Lumbar puncture or not: when does febrile seizure require a neurodiagnostic evaluation?
(8 times)
-
Seung Soo Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):68-69. Published online December 9, 2022
-
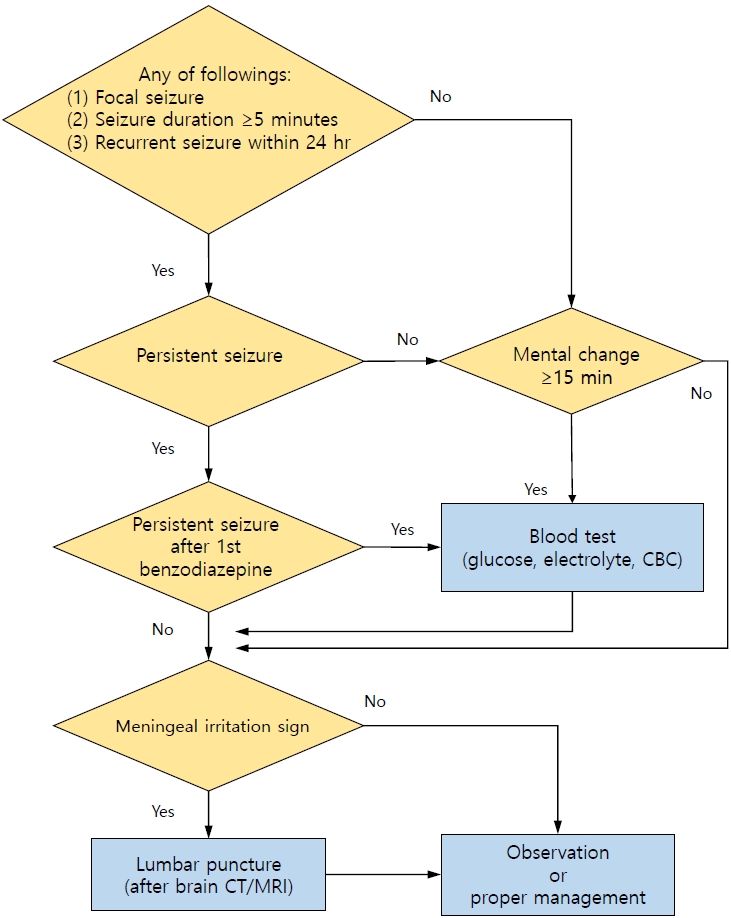
|
· A neurodiagnostic evaluation (lumbar puncture, blood tests, electroencephalography, and neuroimaging) is not indicated in most patients with simple febrile seizures.
· A lumbar puncture is indicated when a central nervous system infection is suspected in any patient with febrile seizures.
· Blood tests (glucose, electrolytes, and complete blood count) are indicated in patients with persistent seizure after benzodiazepine treatment, prolonged loss of consciousness, poor general condition, or signs of dehydration. |
-
-
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
(8 times)
-
Ji-Eun Ban
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
|
|
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C. |
-
-
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between feeding intolerance and intestinal dysbiosis in very premature infants
(8 times)
-
Putri Maharani Tristanita Marsubrin, Agus Firmansyah, Rinawati Rohsiswatmo, Zakiudin Munasir, Saptawati Bardosono, Safarina G. Malik, Yuditiya Purwosunu, Ina S. Timan, Tetty Yuniati, Maya Yulindhini
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):501-503. Published online October 24, 2023
-
-
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Recent advances in food allergen immunotherapy
(8 times)
-
You Hoon Jeon, Edwin H. Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):386-394. Published online December 7, 2023
-

|
· To enhance the safety of food allergen immunotherapy, alternative approaches such as sublingual immunotherapy, epicutaneous immunotherapy, low-dose oral immunotherapy (OIT), and omalizumab with OIT are being explored.
· Factors such as causative allergen type, natural outgrowth, symptom severity, and patient age should be considered.
· Individualized food allergen immunotherapy plans should be established to determine the most beneficial treatment for each patient. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
(8 times)
-
Hyeon-Soo Lee, Young-Joon Ryu, Min-Jae Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):540-549. Published online September 27, 2024
-

|
Lung injury is generated from the early stage of hyperoxia through the biologic effects of cell death and inflammatory response, which eventually leads to evolution of bronchopul-monary dysplasia. Therefore, a protective measure against hyperoxia-induced lung injury is needed. The present study observed that anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 had protective effects on newborn rat lungs from injury induced at the early stage of hyperoxia, by preventing cell death and down-regulating inflammatory response. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Infection
- Impact and role of vitamins as immunonutrition in children during COVID-19 pandemic
(7 times)
-
Yoo Min Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):212-214. Published online April 18, 2023
-
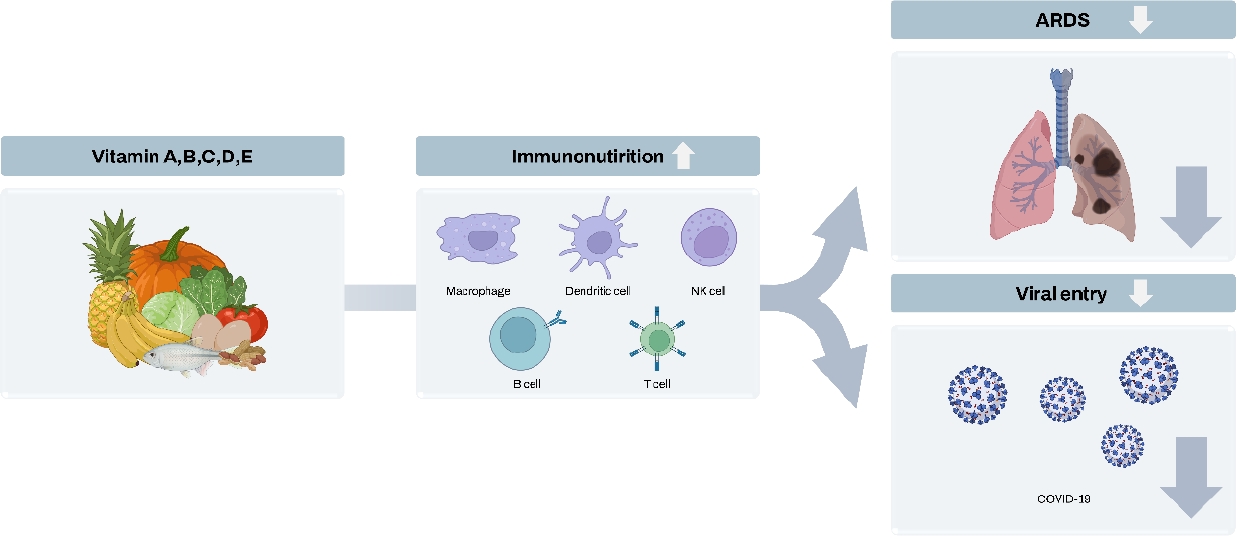
|
· Vitamins have effector mechanisms in the innate and adaptive immune systems and potential roles in preventing and reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
· Vitamins may be immunonutrients in the treatment of COVID-19 infections and prevention of patient deterioration due to critical illness, thus demonstrating the significance of a nutritious, well-balanced diet. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age
(6 times)
-
Jeewon Shin, Yoowon Kwon, Ju Hee Kim, Su Jin Jeong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):76-81. Published online November 30, 2022
-

|
Question: What are the risk factors of newborn birth weight? Does gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index affect childhood weight?
Finding: Excess maternal weight gain increases the risk of overweight/obesity, newborn birth weight, and child body mass index at 4–6 years.
Meaning: Maternal weight control before and during pregnancy should be well controlled. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Critical Care Medicine
- Is it possible to provide palliative care to pediatric patients with neurological diseases?
(6 times)
-
Young-Hoon Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):403-404. Published online February 15, 2024
-
|
|
· Patients with neurological diseases often require external mechanical support to maintain mechanical ventilation or supply.
· Little has been done to help the families of affected children make difficult decisions that carry significant physical and psychological consequences.
· The establishment of a department that provides pediatric palliative care for neurological patients should be considered. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Impacts of maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy on neonatal health and epidemiology
(5 times)
-
Jae Woo Lim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):149-151. Published online December 28, 2023
-

|
Newborns born to mothers infected with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be closely monitored for respiratory disorders, such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, regardless of their COVID-19 test results. Further research is required of the development of infants born to mothers with COVID-19. The trends in Korea's birth rate and infant mortality rates have not been significantly affected by COVID-19. |
-
-
- Gastroenterology
- Recent advances in epigenetic mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of pediatric gastrointestinal allergic disorders
(4 times)
-
Eell Ryoo
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):250-251. Published online May 19, 2023
-
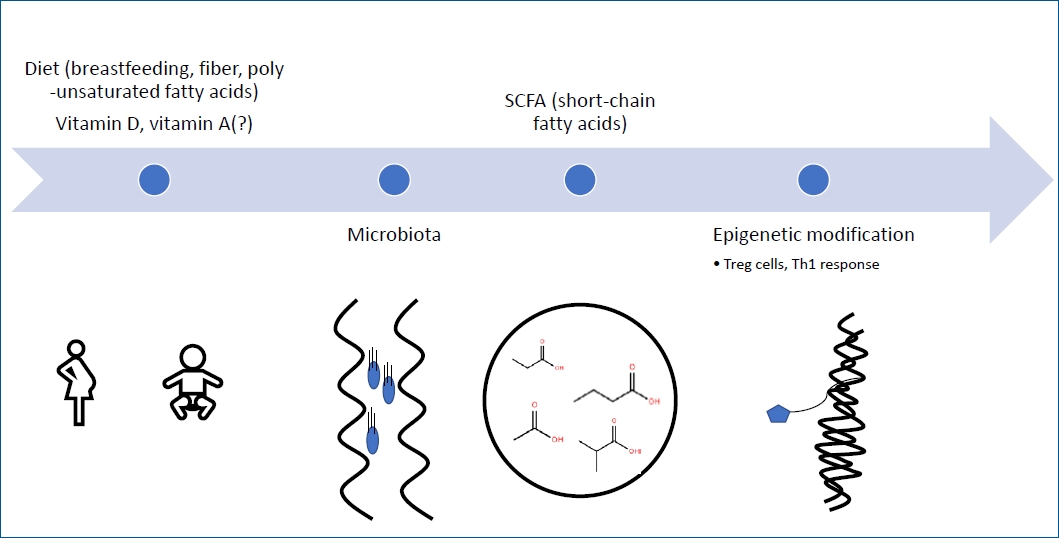
|
· Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in rapidly increasing food allergy.
· There is still no definitive way to diagnose food allergy.
· Early introduction of peanuts, eggs, and cow’s milk reduces food allergy incidence.
· Administration of probiotics such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium bifidum can partially reduce the occurrence of allergic symptoms. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Is there a link between social media usage and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children?
(3 times)
-
Hae Jeong Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):169-170. Published online March 23, 2023
-
|
|
Social media use has potential benefits and risks, including links to adverse health problems in children such as functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). Screen time control, emotional support, and parental guidance can help children navigate social media safely and reduce the risk of developing FGIDs. |
-
-