Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2023 during the last six months.
- Original Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Long-term follow-up of neurocognitive function in patients with citrin deficiency and cholestasis (65 times)
- Meng-Ju Melody Tsai, Jung-Chi Chang, Heng-Yu Lu, Susan Shur-Fen Gau, Yin-Hsiu Chien, Wuh-Liang Hwu, Yen-Hsuan Ni, Huey-Ling Chen, Ni-Chung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):257-265. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Question: Do transient metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency have lasting effects on neurocognitive function?
Finding: Children with citrin deficiency have a higher prevalence of ADHD compared to the general population, with elevated ammonia levels in infancy associated with increased hyperactivity-impulsivity risk.
Meaning: Metabolic disturbances in early childhood due to citrin deficiency may contribute to long-term neurocognitive impacts, particularly ADHD, while IQ and life outcomes generally remain normal.
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
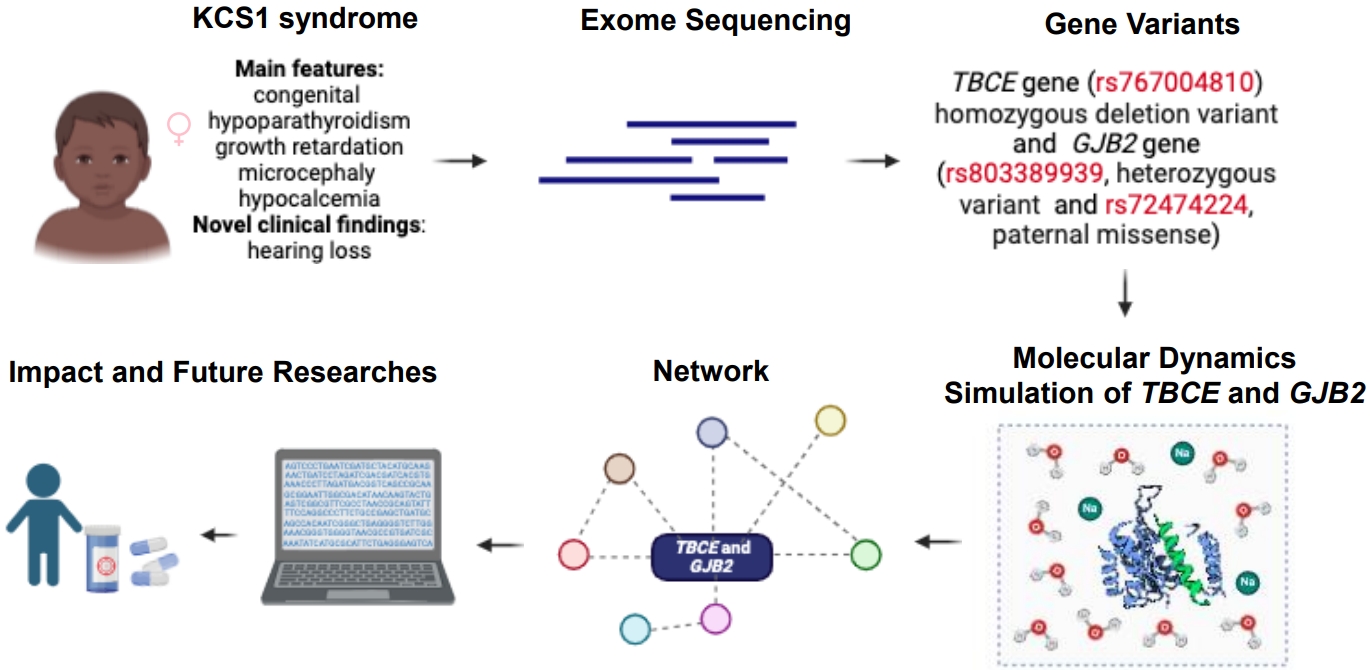
- Expanding genotype-phenotype correlation of Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1 (64 times)
- Manuela Lo Bianco, Federica Sipala, Xena Giada Pappalardo, Gaia Fusto, Roberta Rizzo, Federico Favata, Carla Cimino, Silvia Marino, Martino Ruggieri, Agnese Suppiej, Simone Ronsisvalle, Raffaele Falsaperla
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):616-619. Published online May 12, 2025
-
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Efficacy of leuprolide acetate versus triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for treatment of central precocious puberty (63 times)
- Thanaporn Thaneetrakool, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Vichit Supornsilchai, Suttipong Wacharasindhu, Khomsak Srilanchakon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):91-96. Published online November 6, 2024
-

Question: What are the differences in efficacy between leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate administered every 3 months for the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP)?
Finding: There were no significant intergroup differences in luteinizing hormone suppression or predicted adult height at the end of treatment in girls with CPP.
Meaning: Leuprolide acetate and triptorelin pamoate have comparable efficacy for treating CPP.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The predetermined future: tackling South Korea’s total fertility rate crisis (63 times)
- Jin Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):225-227. Published online November 6, 2024
-

· South Korea faces a severe demographic crisis with the lowest global fertility rate. Despite significant investments, the total fertility rate continues to decline.
· It is necessary to fully mobilize national capabilities and execute comprehensive strategies that focus on both intangible and tangible values.
· Immediate and decisive action is essential to addressing these challenges effectively.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions (62 times)
- Ja Hyang Cho, Hae Woon Jung, Kye Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559. Published online October 28, 2024
-

Height gains result from longitudinal bone growth. Upon adequate growth, growth plate closure limits longitudinal bone growth. To date, gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs, aromatase inhibitors, C-type natriuretic peptide analogs, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 inhibitors have been studied or used as therapeutic interventions to delay growth plate closure and increase human height. The development of more effective therapeutic modalities for short stature, precocious puberty, and skeletal dysplasia is anticipated.
- Letter to the Editor
- General Pediatrics
- Debate around and impact of digital screen time and media parenting on children’s development (62 times)
- Gowda Parameshwara Prashanth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):551-553. Published online March 11, 2025
-

- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Nonlinear association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and asthma in children and adolescents in the United States: a cross-sectional study (61 times)
- Chuhan Cheng, Liyan Zhang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):489-496. Published online March 11, 2025
-

Question: Is there a nonlinear relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and asthma in children and adolescents?
Finding: NLR showed a nonlinear association with asthma, with an NLR threshold of 2.23 identifying individuals at higher risk.
Meaning: An NLR<2.23 may serve as a potential biomarker for asthma risk assessment and management in pediatric populations, thereby offering a simple tool for the early identification of at-risk individuals.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review (60 times)
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
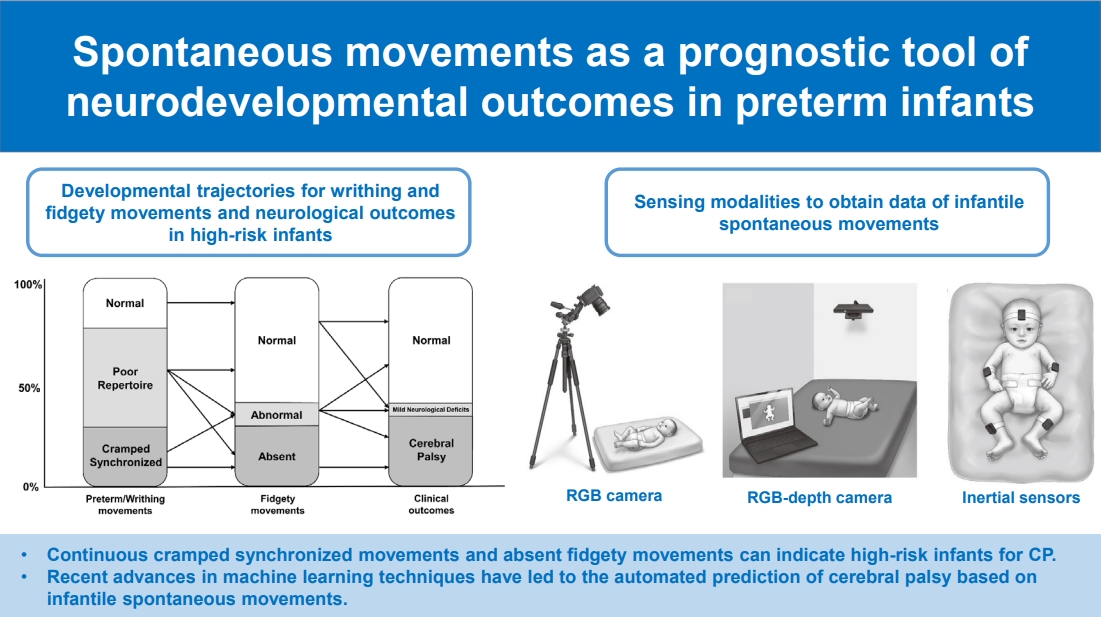
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models (60 times)
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
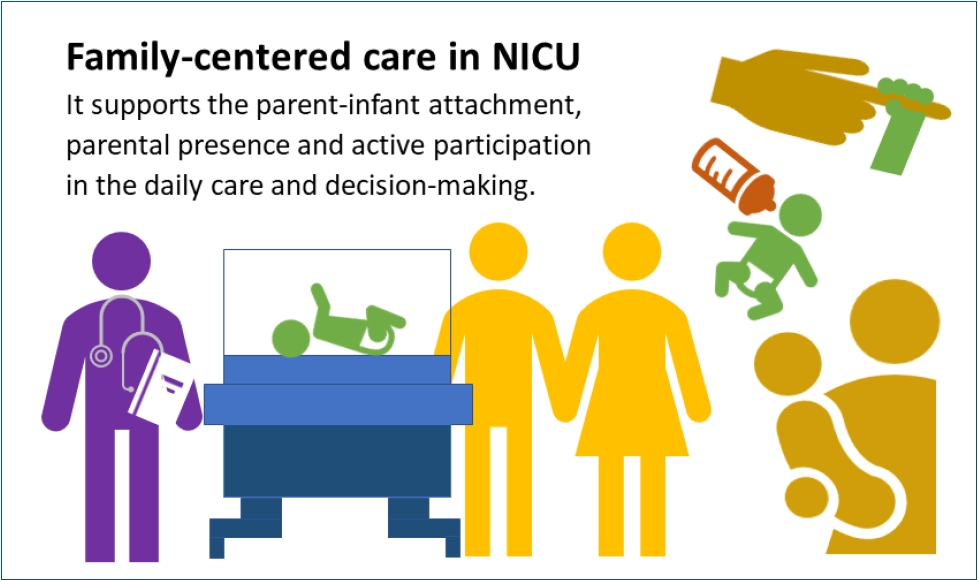
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis (60 times)
- Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age.
- Nutrition
- Differential effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on adiposity of children with obesity (60 times)
- Anekchoke Tangtongsoong, Chonnikant Visuthranukul, Yuda Chongpison, Sirinuch Chomtho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(5):370-378. Published online February 3, 2025
-

Question: How do dietary intake and physical activity affect body mass index (BMI) z scores and adiposity among children with obesity?
Finding: Higher dietary protein and fiber intakes were significantly associated with a decrease in BMI z scores and adiposity among children with obesity.
Meaning: Optimizing dietary interventions by focusing on protein and fiber intakes could be an effective strategy for managing childhood obesity.
- Perspective
- Gastroenterology
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children: a practical update based on Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ISPGHAN) 2024 guidelines (59 times)
- Ankit Agrawal, Arghya Samanta
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):546-550. Published online May 12, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Allergy
- Natural course of IgE-mediated food allergy in children (58 times)
- Kyunguk Jeong, Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):504-511. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Dendritic, regulatory T, and regulatory B cells significantly contribute to the natural course of food allergy.
· Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergies tend to resolve in earlier childhood but recent studies show that 50% of patients still persist into school age.
· The potential factors affecting the natural course of food allergy are age at diagnosis, symptom severity, sensitization status and its change rate, and external factors such as diet and interventions.
· There is a considerable possibility of food allergy outgrow if specific IgE levels are 2–5 kUA/L or less, but other factors such as age and recent symptoms should be considered together.
· With a clear understanding of the natural course of food allergy, pediatricians can provide appropriate assessment and interventions to our patients, and consequently can help patients overcome their food allergy and improve the social safety net.
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases (58 times)
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-

· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Endocrinology
- Two- versus one-bag fluid delivery in pediatric and adolescent diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis (58 times)
- Maya L. Nasser, Joseph Nasr, Reem B. Zalloum, Nathanael Q.E. Yap, Natalie E. Bourdakos, Shahid Miangul, Tara A. Betts, Hayato Nakanishi, Christian A. Than, Serge Jabbour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):486-497. Published online June 27, 2024
-

· The safety and efficacy of the two-bag versus one-bag system for treating patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) < 21 years remains unestablished.
· Our meta-analysis demonstrated similar safety outcomes but sooner DKA resolution and shorter mean response time for intravenous fluid changes for the two-bag system.
· This preliminary evidence suggests that the two-bag system has some advantages in efficacy, but further studies are needed to evaluate their extent.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Screen time and neurodevelopment in preschoolers: addressing a growing concern in pediatric practice (58 times)
- Soongang Park, Hyewon Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):434-436. Published online January 13, 2025
-
· Excessive screen time in preschoolers is associated with neurodevelopmental delays, particularly during the early years of life.
· Parental supervision and national guidelines are critical in mitigating the negative impacts of excessive screen time and fostering healthy media habits in preschoolers.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis (58 times)
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Wafaa M. Abo El Fotoh, Mona S. Habib, Salem E. Deraz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):578-586. Published online February 26, 2025
-
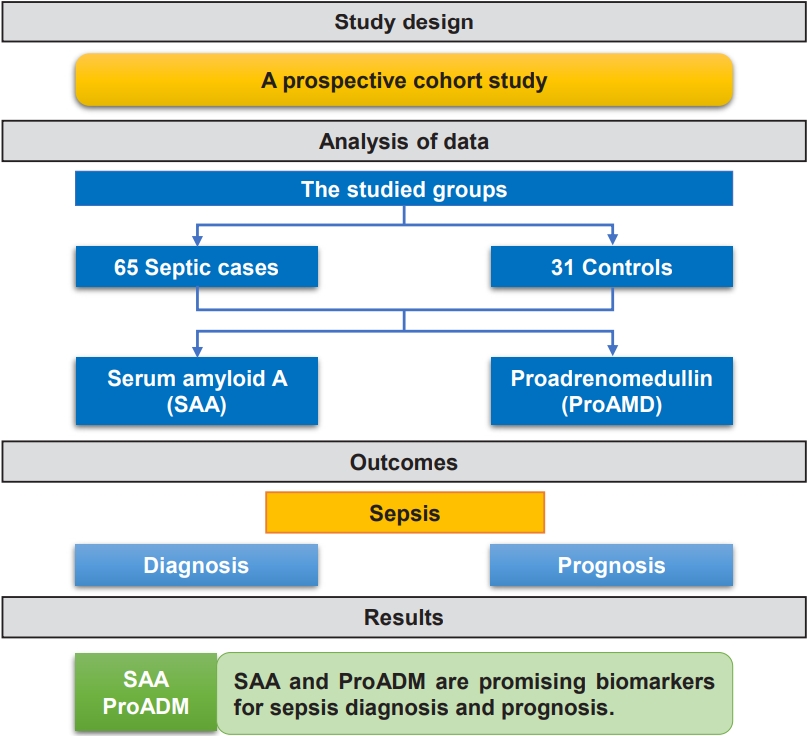
Question: Are serum amyloid A (SAA) and proadrenomedullin (proADM) levels early markers in critically ill children with sepsis?
Finding: This prospective case-control study included 65 critically ill children with sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and 31 controls. SAA and proADM levels were significantly higher in patients versus controls.
Meaning: SAA and proADM are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in pediatric sepsis.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Incidence of neural tube defects in tertiary care university hospital in Bangladesh (58 times)
- Ismat Jahan, Arif Hossain, Shah Nizam Uddin Shaon, Sadeka Choudhury Moni, Mohammad Kamrul Hassan Shabuj, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):530-538. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: What is the burden of neural tube defects (NTDs) in a tertiary care neonatal intensive care unit in Bangladesh?
Finding: The overall incidence of NTD was 6.4 (range, 4.59–11.2) per 1,000 live births, and the meningomyelocele complex was the most frequent location.
Meaning: The high incidence of NTD found in a leading tertiary care multidisciplinary referral hospital in Bangladesh may not reflect that of the wider population.
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Promising role of voxelotor in managing sickle cell disease in children: a narrative review (57 times)
- Amit Agrawal, Gaurav Jadon, Japna Singh, Dalwinder Janjua
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):106-114. Published online November 13, 2024
-

Voxelotor has promising ability to increase hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis markers in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Several preclinical and phase II/III trials have demonstrated its efficacy, dose-dependent responses, and tolerability in children. Ongoing trials are assessing its safety and effectiveness in various populations, including children younger than 12 years. These findings suggest its potential as a disease-modifying drug, warranting further exploration of its role in SCD management.
- Endocrinology
- Impact of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on growth outcomes in mucopolysaccharidosis: a systematic review (57 times)
- Farzaneh Abbasi, Asal Khalili Dehkordi, Reihaneh Mohsenipour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):417-427. Published online March 11, 2025
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) enhances the growth outcomes of pediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis, with early intervention leading to improved height, weight, and body mass index. However, achieving a standard adult height remains uncommon among these patients, even in cases of early HSCT. Growth hormone therapy provides short-term benefits but does not address long-term height deficits. Pubertal development is generally normal; however, precocious puberty and pubertal arrest may occur.
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy (56 times)
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
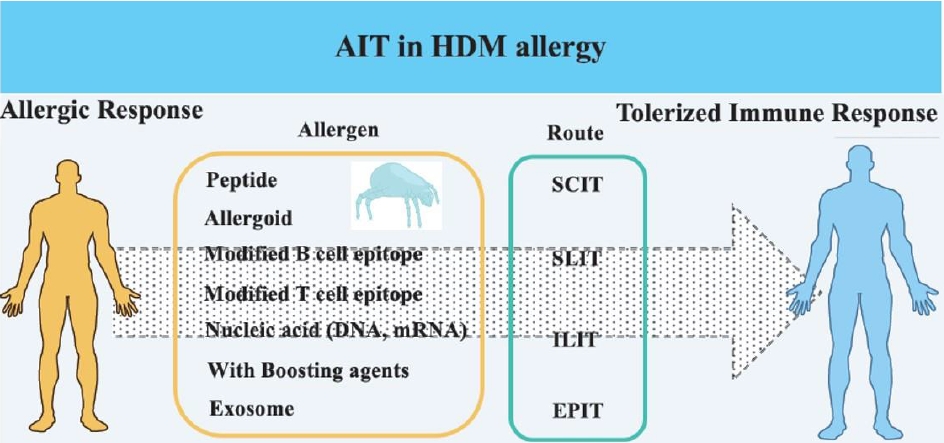
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Action-plan and as-needed therapy in allergic rhinitis (56 times)
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):267-273. Published online May 21, 2024
-

· The guidelines may not work in the real world.
· An action-plan reflecting patient’s severity and variable of symptoms, values and preferences as well as the benefits and harms of treatment, may be a useful alternative.
· The action plan and as-needed therapy must include the following elements: when, what, how, and why.
· Action plan and as-needed therapy can help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
- Clinical Note
- Oncology
- Right ventricular mass in a 10-year-old girl with osteosarcoma: an unusual case of asymptomatic cardiac metastasis (56 times)
- Jun Ah Lee, Hyun-Ju Lim, Jong Woong Park, Sang-Hoon Shin, Mi Hyang Kwak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):725-727. Published online November 26, 2024
-

- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Hidden link between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pediatric obesity (55 times)
- Min Won Shin, Shin-Hye Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(3):199-222. Published online November 28, 2024
-

Studies indicate potential connections between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and childhood obesity. Variations in the impact of EDCs in epidemiological studies may result from differences in exposure concentrations and timing, measurement methods, and interactive effects of multiple EDCs. Longitudinal studies on exposure to multiple EDCs are crucial to elucidating their contribution to pediatric obesity and minimize the adverse health consequences of EDC exposure.
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases (55 times)
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):569-577. Published online April 1, 2025
-
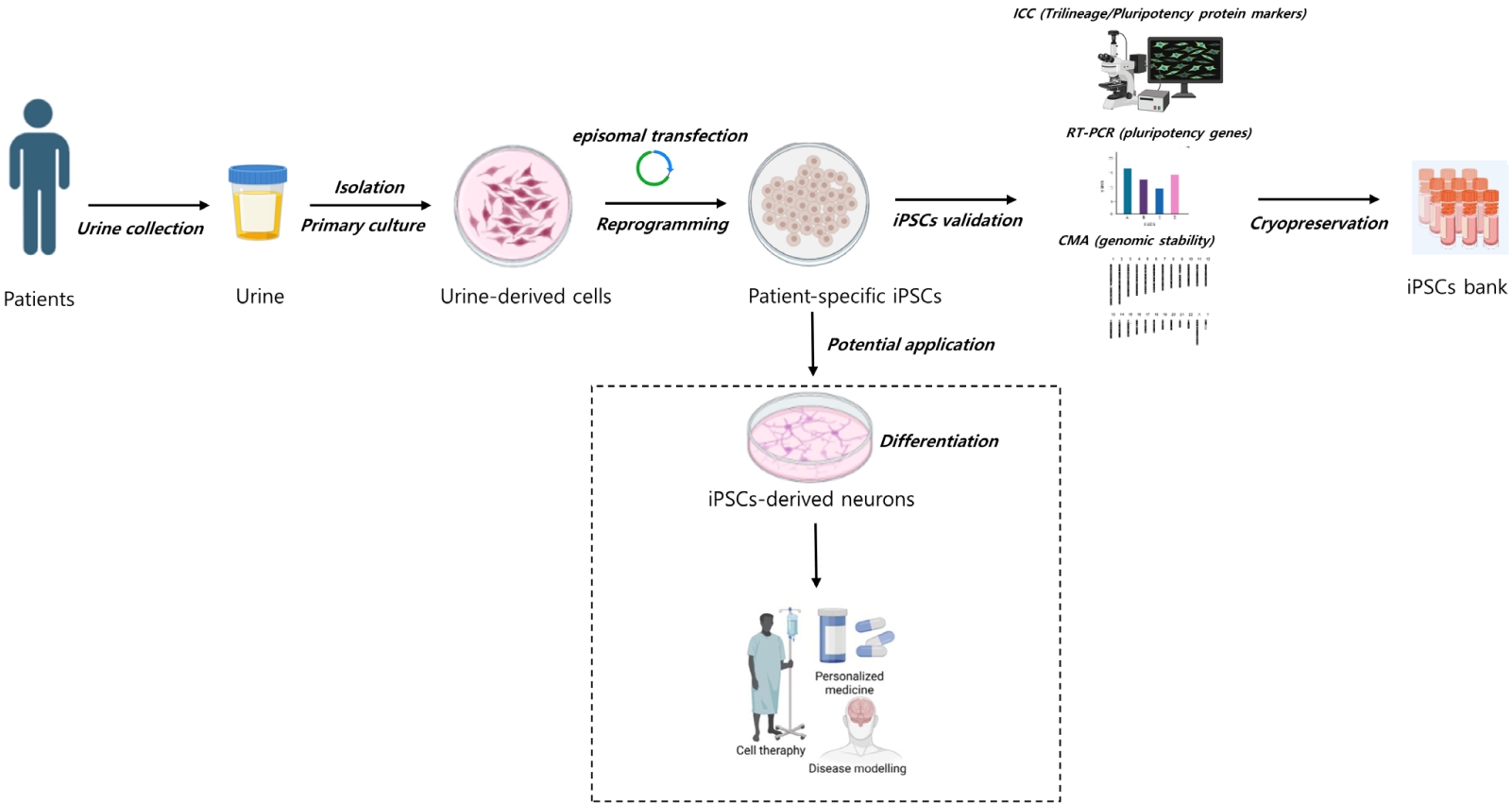
Question: What can be used to create a reliable supply of somatic cells for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generation and standardize procedures for building an iPSC bank for researching pediatric neurogenetic disorders?
Findings: Noninvasively acquired urine cells are a desirable cell source for iPSC reprogramming.
Meaning: An iPSC bank can be created from diverse patient cell sources and offer a useful resource for translating research results into clinical therapy for pediatric neurogenetic disorders.
- Clinical Note
- General Pediatrics
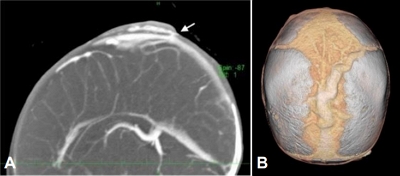
- Aplasia cutis congenita with unique vascular malformation and cranial hypoplasia: a case in a preterm infant (54 times)
- Yasufumi Sakata, Natsumi Fujii, Sadahiro Nomura, Yoshihiro Azuma, Hiroki Hamano, Hidenobu Kaneyasu, Seigo Okada, Kazumasa Takahashi, Shunji Hasegawa
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):472-474. Published online March 11, 2025
-
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Electroencephalography source localization (53 times)
- Tae-Hoon Eom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):201-209. Published online December 29, 2022
-

· Electroencephalography (EEG) directly images the electrical activity of neurons at a higher temporal resolution than other neuroimaging techniques.
· EEG is still widely used in brain function research due to its advantages.
· Forward and inverse problems of EEG analyses require solutions.
· Methods such as the dipole and distributed source models have been introduced.
· Applications of EEG are expanding with the integration of other technologies and large-scale data.
- Allergy
- Skin and oral intervention for food allergy prevention based on dual allergen exposure hypothesis (53 times)
- Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Yukihiro Ohya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):477-485. Published online June 14, 2023
-

To prevent food allergy in infants, based on the dual allergen exposure hypothesis, we recommend a personalized approach consisting of both skin intervention (eczema treatment to achieve early remission and well-controlled skin without eczema to prevent percutaneous immunoglobulin E sensitization) and oral intervention (early allergenic food introduction).
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum in preterm neonates: a double-blind placebocontrolled randomized trial (53 times)
- Ameneh Lamsehchi, Maryam Shokouhi Solgi, Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Elahe Talebi Ghane, Kiana Kimiaei Asadi, Sina Azadnajafabad
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):73-79. Published online October 31, 2024
-

Question: What are the short-term outcomes of oropharyngeal administration of colostrum (OAC) in preterm neonates?
Finding: This study demonstrated the significantly lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis, clinically suspected sepsis, shorter hospital stay, period to full enteral feeding, and antibiotic therapy period in the OAC group.
Meaning: This trial may further expand the clinical application of OAC in premature infants to reduce their length of hospital stay and complications.
- Gastroenterology
- Efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide versus room-air insufflation in pediatric colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial (52 times)
- Ajay Aravind, Ujjal Poddar, Anshu Srivastava, Moinak Sen Sarma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):594-600. Published online March 11, 2025
-
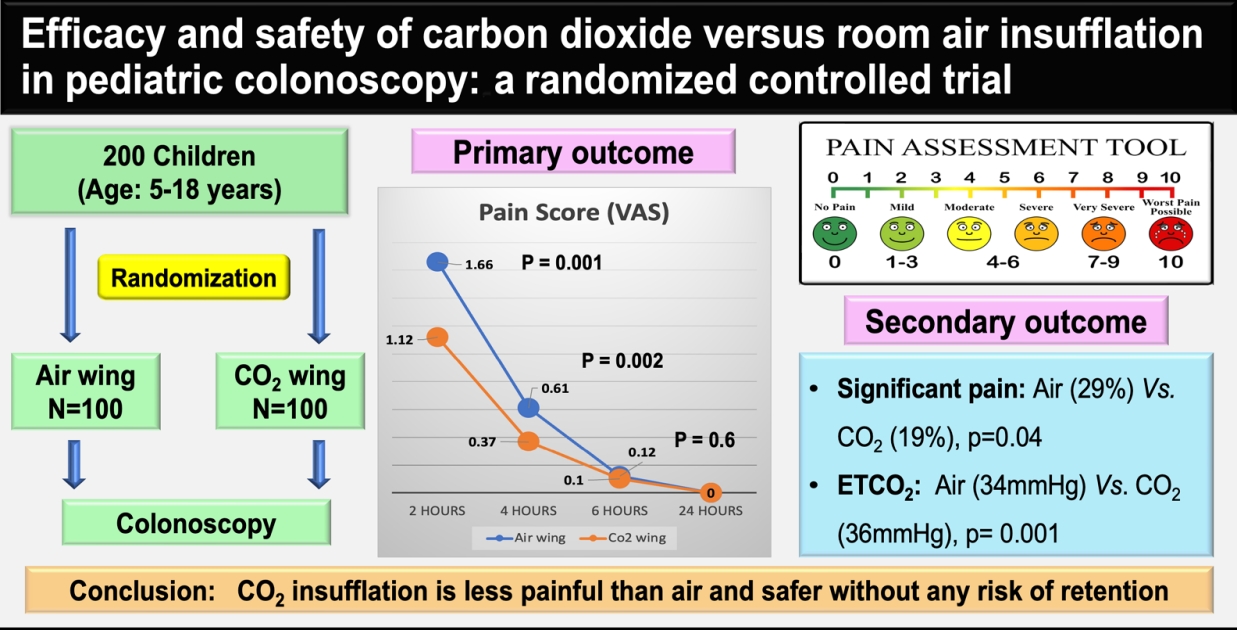
CO2 insufflation has been used instead of air insufflation to reduce postprocedure pain and discomfort in adults; however, adequately powered studies in children are scarce. This randomized controlled trial of 200 children showed that CO2 insufflation reduces postprocedure pain and discomfort during pediatric colonoscopy with no signs of CO2 retention. CO2 insufflation is safe and causes less pain in children.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











