Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
- Hyeon-Soo Lee, Young-Joon Ryu, Min-Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):540-549. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Lung injury is generated from the early stage of hyperoxia through the biologic effects of cell death and inflammatory response, which eventually leads to evolution of bronchopul-monary dysplasia. Therefore, a protective measure against hyperoxia-induced lung injury is needed. The present study observed that anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 had protective effects on newborn rat lungs from injury induced at the early stage of hyperoxia, by preventing cell death and down-regulating inflammatory response.
- Infection
- Role of lung ultrasound patterns in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children
- Satyabrata Roychowdhoury, Subhajit Bhakta, Manas Kumar Mahapatra, Saptarshi Ghosh, Sayantika Saha, Mithun Chandra Konar, Mihir Sarkar, Mousumi Nandi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):358-366. Published online May 13, 2022
-
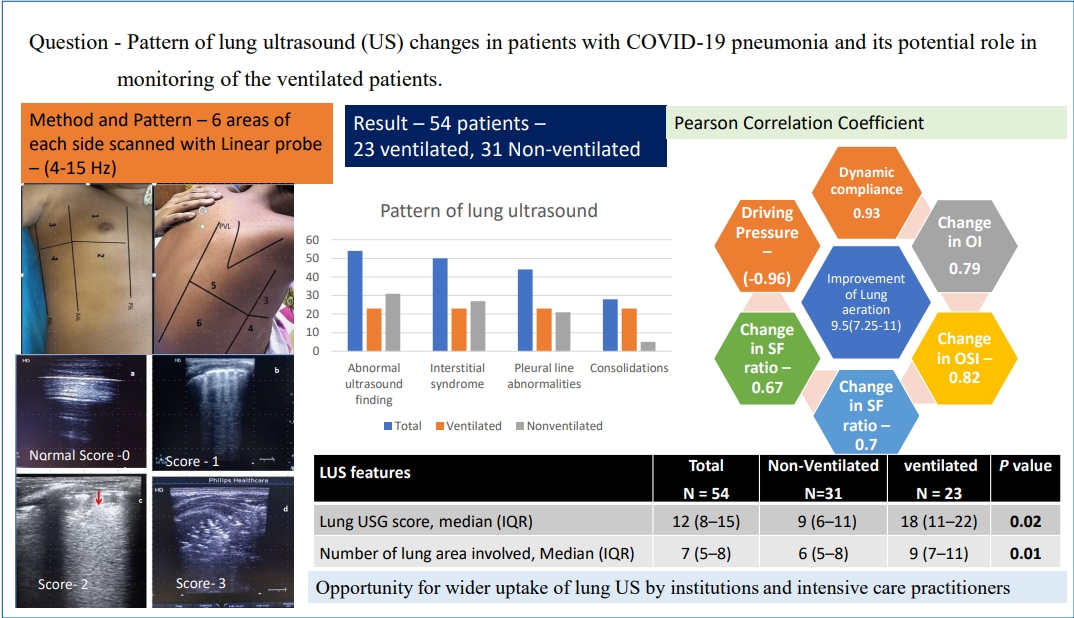
Question: Potential role of patterns of lung ultrasonography (US) in monitoring changes in mechanically ventilated patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.
Finding: Interstitial syndrome, an irregular pleural line, and peripheral microconsolidation were the most prevalent findings. Changes in lung aeration after mechanical ventilation corelated with improved oxygenation. A fall in lung ultrasound reaeration score ≤ 5 may predict successful weaning.
Meaning: Lung US is gaining wider utility for monitoring COVID-19 pneumonia.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- The past, present, and future of humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases in children
- Eun Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):251-258. Published online December 9, 2019
-
Exposure to environmental factors can cause interstitial lung diseases (ILDs); however, such types of ILDs are rare. From 2007 to 2011, an ILD epidemic occurred in South Korea owing to inhalational exposure to toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants (HDs). HD-associated ILDs (HD-ILDs) are characterized by rapidly progressing respiratory failure with pulmonary fibrosis and a high mortality rate of 43.8%−58.0%. Although...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?
- Tae-Jung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):367-373. Published online May 17, 2019
-

Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease of preterm infants with multiple factors affected from prenatal to postnatal periods. Despite significant advances in neonatal care over almost 50 years, BPD rates have not decreased; in fact, they may have even increased. Since more preterm infants, even at periviable gestational age, survive today, different stages of lung development affect the...
- Case Report
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Case of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung associated with congenital pulmonary airway malformation in a neonate
- Juneyoug Koh, Euiseok Jung, Se Jin Jang, Dong Kwan Kim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):30-34. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM), previously known as congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation, is a rare developmental lung abnormality associated with rhabdomyosarcoma, pleuropulmonary blastoma, and mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. We report an unusual case of a 10-day-old male newborn with a left lower lobe pulmonary cyst who underwent lobectomy, which revealed type II CPAM complicated by multifocal mucinous adenocarcinoma. KRAS...
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics of lung abscess in children: 15-year experience at two university hospitals
- Mi Suk Choi, Ji Hye Chun, Kyung Suk Lee, Yeong Ho Rha, Sun Hee Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):478-483. Published online December 22, 2015
-
Purpose Information on the clinical features of lung abscess, which is uncommon in children, at hospitalizationis helpful to anticipate the disease course and management. There is no report concerning lung abscess in Korean children. We aimed to identify the clinical characteristics of pediatric lung abscess and compare the difference between primary and secondary abscess groups.
Methods The medical records of 11 lung abscess...
- Review Article
- Association of wheezing phenotypes with fractional exhaled nitric oxide in children
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(5):211-216. Published online May 31, 2014
-
Asthma comprises a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by airway inflammation, airway obstruction, and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR). Airway inflammation, which induces AHR and recurrence of asthma, is the main pathophysiology of asthma. The fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) level is a noninvasive, reproducible measurement of eosinophilic airway inflammation that is easy to perform in young children. As airway inflammation precedes...
- Case Report
- Lung torsion after tracheoesophageal fistula repair in an infant
- Eun Mi Yang, Eun Song Song, Hae in Jang, In Seok Jeong, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(4):186-190. Published online April 22, 2013
-
Lung torsion is a very rare event that has been reported in only 9 cases in the pediatric literature but has not yet been reported in Korean infants. We present a case of lung torsion after tracheoesophageal fistula repair in an infant. Bloody secretion from the endotracheal tube and chest radiographs and computed tomographic scan results indicated lung torsion. Emergency...
- Review Article
- Lung interstitial cells during alveolarization
- Chang Won Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(12):979-984. Published online December 31, 2010
-
Recent progress in neonatal medicine has enabled survival of many extremely low-birth-weight infants. Prenatal steroids, surfactants, and non-invasive ventilation have helped reduce the incidence of the classical form of bronchopulmonary dysplasia characterized by marked fibrosis and emphysema. However, a new form of bronchopulmonary dysplasia marked by arrest of alveolarization remains a complication in the postnatal course of extremely low-birth-weight infants....
- Original Article
- Analysis of reports on orphan lung diseases in Korean children
- Sun Jung Jang, Hyun Kyung Seo, Sung Jae Yi, Kyong Min Kim, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(6):711-717. Published online June 23, 2010
-
Purpose Orphan lung diseases are defined as lung diseases with a prevalence of 1 or less in 2,000 individuals. Despite an increase in the numbers of patients with such diseases, few studies on Korean children have appeared. To obtain epidemiologic and demographic data on these diseases, we systematically reviewed reports on pediatric orphan lung diseases in Korea over the last 50...
- Review Article
- Environmental tobacco smoke and childhood asthma
- Dae Jin Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):121-128. Published online February 15, 2010
-
In recent years, environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) has become an important worldwide public health issue. Children are particularly vulnerable to ETS because they are still developing. ETS exposure causes a wide range of adverse health effects on childhood asthma. There is convincing evidence that ETS exposure is causally associated with an increased prevalence of asthma, increased severity of asthma and... -
- Original Article
- The outcomes of retinopathy of prematurity in relation to duration of low dose oxygen therapy
- Pil Sang Lee, Jae Won Choi, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):50-55. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : This study aimed to determine the influence of low-dose oxygen (FiO2 <25%) therapy through nasal cannulae on the progress and prognosis of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) as well as methods of preventing ROP. Methods : Our subjects comprised premature infants (gestation period <37 weeks; birth weight <1,750 g) born in Daegu Fatima Hospital between February 1, 2001 and... -
- Case Report
- Congenital hernia of the lung through the azygoesophageal recess
- Young Seok Choi, Young Jun Son, Si Young Bae, Kyung Sun Min, Young Kuk Cho, Woo Yeon Choi, Young Youn Choi, Jae Sook Ma, Tai Ju Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(10):1123-1126. Published online October 15, 2008
-
A lung hernia, defined as the protrusion of pulmonary tissue and pleural membranes through a defect in the thoracic wall, is a rare event. It can be congenital or acquired, and cervical, thoracic, or diaphragmatic in location. We report the rare occurrence of a congenital atraumatic lung herniation through the azygoesophageal recess. An 8-month-old male infant, who was born... -
- Original Article
- Transforming growth factor-β promoted vascular endothelial growth factor release by human lung fibroblasts
- Sang Uk Park, Joo Hwa Shin, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Hye Lim Jung, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(8):879-885. Published online August 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The human lung fibroblast may act as an immunomodulatory cell by providing pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which are important in airway remodeling. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces mucosal edema and angiogenesis. Thymus and activation regulated chemokine (TARC) induces selective migration of T helper 2 cells. We investigated whether human lung fibroblasts produced VEGF and TARC, and the... -
- Is routine screening examination necessary for detecting thromboembolism in childhood nephrotic syndrome?
- Mun Sub Kim, Ja Wook Koo, Soung Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):736-741. Published online July 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The incidence of thromboembolic episodes in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) is low; however, these episodes are often severe. Moreover, both pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and renal vein thrombosis (RVT) rarely show clinical symptoms. This study was performed to determine the benefits of routine screening in the detection of thrombosis in childhood NS. Methods : Among 62 children with... -
- Reference values for respiratory system impedance using impulse oscillometry in school-aged children in Korea
- Young Sun Wee, Hyoung Yun Kim, Da Wun Jung, Hye Won Park, Yoon Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):862-867. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The impulse oscillometry (IOS) is applicable to young children because it requires minimal cooperation and a non-invasive method to measure the mechanics of respiratory system. This study aimed to develop the reference values in school-aged children in Korea, using IOS which is a modification of forced oscillation technique (FOT). Methods : Measurements were performed in 92 previously untrained healthy... -
- Antithrombin-III as an early prognostic factor in children with acute lung injury
- Young Seung Lee, Seonguk Kim, Eun Kyeong Kang, June Dong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(5):443-448. Published online May 15, 2007
-
Purpose : To evaluate the potential prognostic value of the antithrombin-III (AT-III) level in the children with acute lung injury (ALI), we analyzed several early predictive factors of death including AT-III level at the onset of ALI and compared the relative risk of them for mortality. Methods : Over a 18-month period, a total of 198 children were admitted to our... -
- Review Article
- Lung function tests in preschool children
- Yong-Mean Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(5):422-429. Published online May 15, 2007
-
Measurement of lung function is an integral component of respiratory physiology and of clinical assessment of lung diseases in school age children and adults. Pulmonary function test of infants and children under the age of 2 years have now been standardised and are being used both in research and as an adjunct to clinical management. By contrast, until recegntly, children... -
- Case Report
- A case of lung abscess caused by Burkholderia cepacia in healthy child
- Jung Hwa Lee, So Hee Lee, Seong Jin Hong, Young Chil Choi, Eun Gu Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(1):89-94. Published online January 15, 2007
-
Burkholderia cepacia is a Gram-negative aerobic bacillus known to cause opportunistic infections in the immune-compromised hosts. This microorganism is strongly virulent and causes a necrotising invasive infection that may lead to death. As B. cepacia is highly resistant to various antimicrobials, combination antimicrobial therapy must be used instead of monotherapy. We report a successful treatment of lung abscess that was... -
- A Case of Basaloid Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma in an 11-year-old Boy
- Nyeon Cheon Kim, Seung Soo Kim, Won Suk Seo, Kyeong Bae Park, Joon Soo Park, Sang Mann Shin, Hyun Deuk Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(2):208-211. Published online February 15, 2005
-
Primary lung cancer is unusual in children; the squamous cell variant is extremely rare. Lung cancer is classified by histologic types into small-cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung caner, carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma. Furthermore, non-small cell lung cancer is subclassified into adenocarcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The incidence of lung cancer is influenced by smoking,... -
- Medical Lecture Course
- Factors Involved in Lung Development and Alveolarization
- Min Soo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(10):1031-1035. Published online October 15, 2004
-
Lung development is a sum of processes that involve harmonized orchestration of expressions of various factors in time and space. The mastermind governing these phenomena is not known, but cumulative efforts so far have helped us gain some insights as to what are involved in and how complex the developmental process is. Beginning as primitive foregut, lungs undergo processes called... -
- Original Article
- Prevention of Chronic Lung Disease with Early Dexamethasone Treatment in less than 32 Weeks Premature : Randomized Controlled Study
- So Yun Shim, Su Jin Cho, Eun Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):521-526. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Purpose : The optimal timing and the consequences of dexamethasone therapy in chronic lung disease remain unknown. The purpose of this study was to determine whether early dexamethasone therapy would reduce the incidence of chronic lung disease and to determine the adverse effects and complications of prematurity associated with such therapy. Methods : Twenty neonates with hyaline membrane disease(dexamethasone n=10, placebo... -
- The Effect of Post-natal Weight Changes on the Development of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Hye One Jhon, Young Min Kim, Hee Joo Hong, Chong Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):269-274. Published online March 15, 2004
-
Purpose : The subjects were compared and measured for differences in the aspects of weight changes between the groups that developed bronchopulmonary dysplasia(BPD) after treatment and those that did not, to analyze the relations between the patterns of early weight change after birth and the development of BPD. Methods : Retrospective analysis of medical records were performed for birth weight and... -
- The Effect of Histologic Chorioamnionitis on the Development of Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Chronic Lung Disease in Preterm Infants
- Heui seung Jo, Beyong Il Kim, Chang Won Choi, Jun Dong Park, Chong Jai Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(2):150-156. Published online February 15, 2004
-
Purpose: Histologic chorioamnionitis may play a role in the development of respiratory distress syndrome(RDS) and chronic lung disease(CLD) independently or through its association with preterm birth. We investigated the relationship between histologic chorioamnionitis and clinical complications including, RDS and CLD, of preterm infants. Methods: Clinical data were collected retrospectively from 478 preterm infants(gestational period≤34 weeks) who were admitted to the neonatal... -
- The Utilities of Lung Biopsy in Pediatric Lung Disease
- Jae Hee Lee, So Yeon Lee, Ja Hyung Kim, Bong Sung Kim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(12):1230-1234. Published online December 15, 2003
-
Purpose : The aim of this study is to evaluate the value of lung biopsies for the management of children with lung disease. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed 19 lung biopsies done at Asan Medical Center, Seoul between 1993 and 2001. Data gathered included demographic information, underlying conditions, diagnosis before biopsy, final diagnosis, change in therapy, morbidity and mortality. Results : Nineteen... -
- Serotypes and Penicillin Susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Specimens and Healthy Carriers of Korean Children
- Jin-A Lee, Nam-Hee Kim, Dong-Ho Kim, Ki-Won Park, Yun-Kyung Kim, Kyoung-Hyo Kim, Jin-Young Park, Eun-Hwa Choi, Hoan-Jong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(9):846-853. Published online September 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Pneumoccocus is one of the most important causes of invasive infection through the childhood period and the prevelance of antibiotics resistance of pneumococcus is increasing worldwide. A 7-valent conjugate vaccine has been developed. It is important to know the prevalence of each serotype of pneumococci in the countries where the vaccine is used to estimate the coverage rate... -
- Effect of Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Hemodynamics, Gas Exchange and Pulmonary Inflammation in Newborn Piglets with Escherichia coli Induced Septic Lungs
- Yun Sil Chang, Sun Young Ko, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(8):777-783. Published online August 15, 2003
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of inhaled nitric oxide(iNO) on gas exchange, hemodynamics and pulmonary inflammation in newborn piglets with E. coli induced septic lung. Methods : Twenty three instrumented and ventilated piglets were randomized into three groups : CON(n=6), PCON(n=9), and PNO(n=8). In the piglets of the PCON and PNO groups, E. coli... -
- Case Report
- Stenosis of Individual Pulmonary Veins
- Mira Lee, Kil Soon Choi, Nam Su Kim, Myung Kul Yum, Yong Joo Kim, In Jun Sul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(6):610-614. Published online June 15, 2003
-
Pulmonary hypertension may be associated with variable conditions such as the hyperkinetic state or pulmonary vascular obstruction. In these, stenosis of the individual pulmonary veins without any cardiac or vascular malformation is very rare. We experienced stenosis of individual pulmonary veins in a 10 months old boy who was admitted with recurrent dyspnea and cyanosis and then underwent angiogram and... -
- Original Article
- Clinical Spectrum and Lung Pathology in Children with Interstitial Lung Disease
- Ji-Hyun Chung, Seung-Ju Ha, Bong-Seong Kim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(1):79-87. Published online January 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Interstitial lung disease(ILD) is a rare and poorly characterized disorder in children with poor prognosis. To understand the ILD in children, we reviewed our experience with 21 patients who were diagnosed interstitial lung disease during 9-year period at Asan Medical Center retrospectively. Methods : Severity-of-illness score was measured by the Denver protocol. We evaluated underlying diseases, clinical manifestations, high resolution computed tomography findings,... -
- Classification and Risk Factors for Chronic Lung Disease(CLD) of Prematurity : Classical CLD Versus Atypical CLD
- Chang Won Choi, Beyong Il Kim, Heui Seung Jo, Jun Dong Park, Chong Jae Kim, Bo Hyun Yoon, Jung-Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(11):1222-1232. Published online November 15, 2001
-
Purpose : We tried to classify the different type of CLD and assess the risk factors for classical CLD and atypical CLD. Methods : Retrospective cohort analysis was done in 120 preterm infants with birth weights less than 1,500 g who were admitted to NICU in Seoul National University Children's Hospital between Jan. 1993 and Dec. 1998 and survived more... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











