- Review Article
- Neurology
- Neonatal seizures: diagnostic updates based on new definition and classification
-
Eun-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Shin, Byoung Kook Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):387-397. Published online April 4, 2022
-
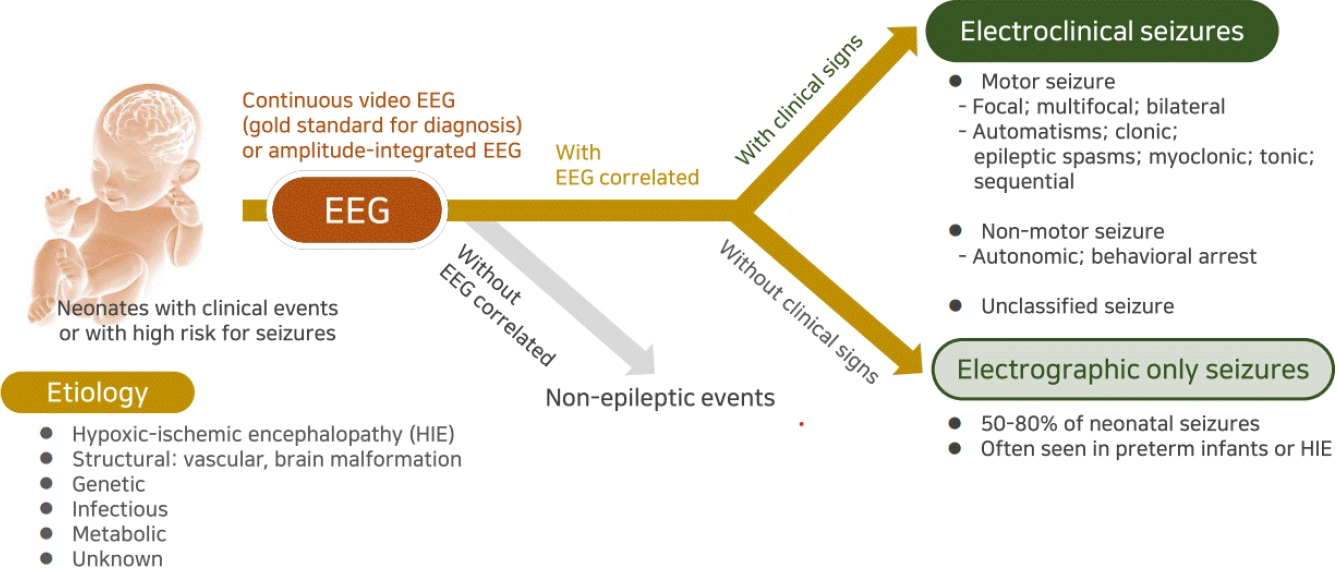
|
· Neonatal seizures are often electrographic-only seizures without clinical signs; therefore, the identification of electrical seizure activity on electroencephalography is the gold standard for diagnosis.
· Clinical signs of neonatal seizures are divided into motor or nonmotor seizures, and motor seizures are mostly focal or multifocal.
· Most neonatal seizures are caused by acute symptomatic etiologies, but in cases of intractable seizures, structural, genetic, or metabolic etiologies should be investigated. |
-
-
- Case Report
- Neurology
- A rare case of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor combined with encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis and intractable seizures
-
Jee-Yeon Han, Mi-Sun Yum, Eun-Hee Kim, Seokho Hong, Tae-Sung Ko
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S139-S144. Published online November 30, 2016
-
|
|
Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (ECCL) is a rare neurocutaneous syndrome that affects ectomesodermal tissues (skin, eyes, adipose tissue, and brain). The neurologic manifestations associated with ECCL are various including seizures. However, ECCL patients very rarely develop brain tumors that originate from the neuroepithelium. This is the first described case of ECCL in combination with dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET) that presented with intractable... |
-
-
- A young child of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis presenting with epilepsia partialis continua: the first pediatric case in Korea
-
Eun-Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Kim, Tae-Sung Ko, Mi-Sun Yum, Jun Hwa Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S133-S138. Published online November 30, 2016
-
|
|
Anti-N-methyl D-aspartate receptor (anti-NMDAR) encephalitis, recently recognized as a form of paraneoplastic encephalitis, is characterized by a prodromal phase of unspecific illness with fever that resembles a viral disease. The prodromal phase is followed by seizures, disturbed consciousness, psychiatric features, prominent abnormal movements, and autonomic imbalance. Here, we report a case of anti-NMDAR encephalitis with initial symptoms of epilepsia partialis... |
-
-
- Two cases of familial cerebral cavernous malformation caused by mutations in the CCM1 gene
-
Im-Yong Yang, Mi-Sun Yum, Eun-Hee Kim, Hae-Won Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Tae-Sung Ko
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):280-284. Published online June 30, 2016
-
|
|
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a vascular malformation characterized by abnormally enlarged capillary cavities without any intervening neural tissue. We report 2 cases of familial CCMs diagnosed with the CCM1 mutation by using a genetic assay. A 5-year-old boy presented with headache, vomiting, and seizure-like movements. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed multiple CCM lesions in the cerebral hemispheres. Subsequent... |
-
-
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Cognitive impairment in childhood onset epilepsy: up-to-date information about its causes
-
Eun-Hee Kim, Tae-Sung Ko
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):155-164. Published online April 30, 2016
-
|
|
Cognitive impairment associated with childhood-onset epilepsy is an important consequence in the developing brain owing to its negative effects on neurodevelopmental and social outcomes. While the cause of cognitive impairment in epilepsy appears to be multifactorial, epilepsy-related factors such as type of epilepsy and underlying etiology, age at onset, frequency of seizures, duration of epilepsy, and its treatment are considered... |
-
-
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Intravenous levetiracetam versus phenobarbital in children with status epilepticus or acute repetitive seizures
-
Yun-Jeong Lee, Mi-Sun Yum, Eun-Hee Kim, Tae-Sung Ko
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(1):35-39. Published online January 22, 2016
-
|
|
Purpose This study compared the efficacy and tolerability of intravenous (i.v.) phenobarbital (PHB) and i.v. levetiracetam (LEV) in children with status epilepticus (SE) or acute repetitive seizure (ARS). MethodsThe medical records of children (age range, 1 month to 15 years) treated with i.v. PHB or LEV for SE or ARS at our single tertiary center were retrospectively reviewed. Seizure termination was defined... |
-
-
|













