Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-
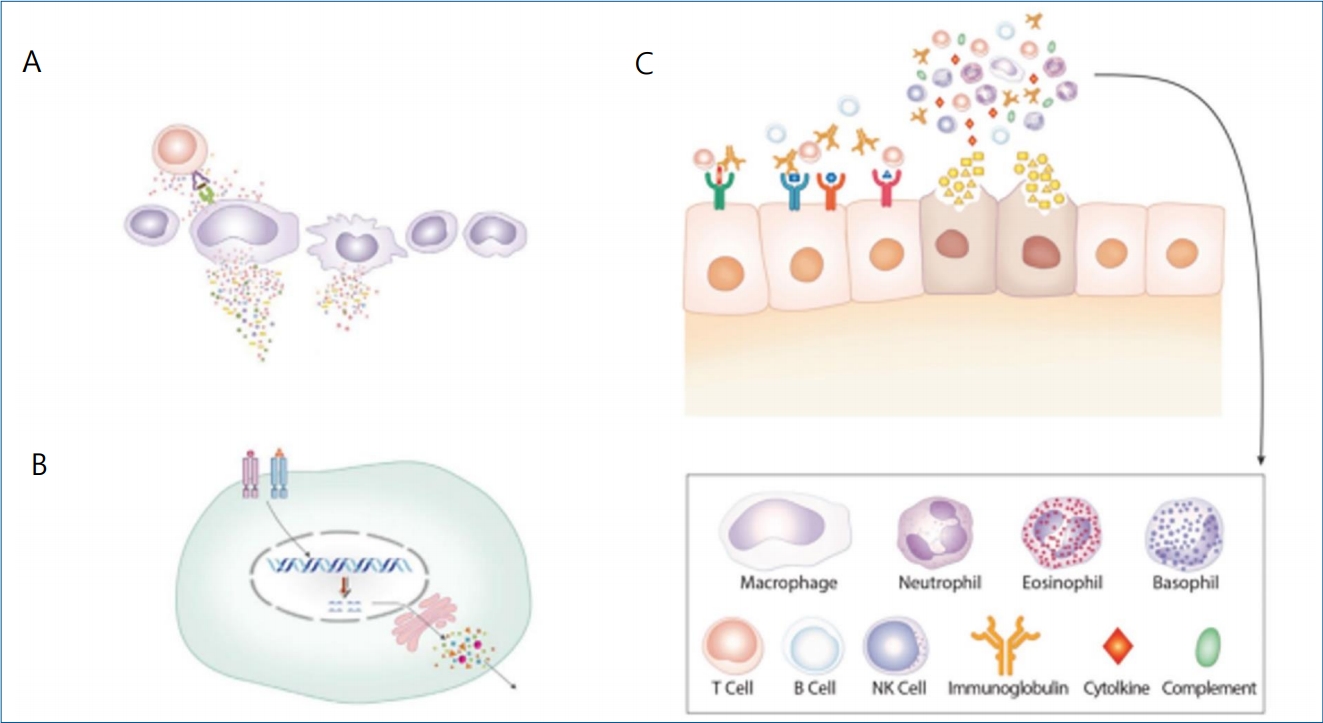
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Perspective
- Infection
- COVID-19 in children: reasons for uneventful clinical course
- Sweni Shah, Ramachandran Meenakshisundaram, Subramanian Senthilkumaran, Ponniah Thirumalaikolundusubramanian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):237-238. Published online June 18, 2020
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Should we regularly evaluate the neurodevelopmental status of moderate and late preterm infants?
- Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):217-218. Published online June 11, 2020
-

- Neurology
- Next-generation sequencing is a powerful method to enhance diagnostic yield in global developmental delay/intellectual disability
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):211-212. Published online June 11, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Other
- Review of epidemiological studies on air pollution and health effects in children
- Jong-Tae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):3-11. Published online June 10, 2020
-

This review summarized the accumulated epidemiologic evidence with emphasis on studies conducted in Korea and heterogeneity in the literature. Based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses, there is consistent evidence on the association between exposure to ambient air pollution and children’s health, especially respiratory health and adverse birth outcomes, and growing evidence on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
- Pulmonology
- Current perspectives on atypical pneumonia in children
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):469-476. Published online June 10, 2020
-
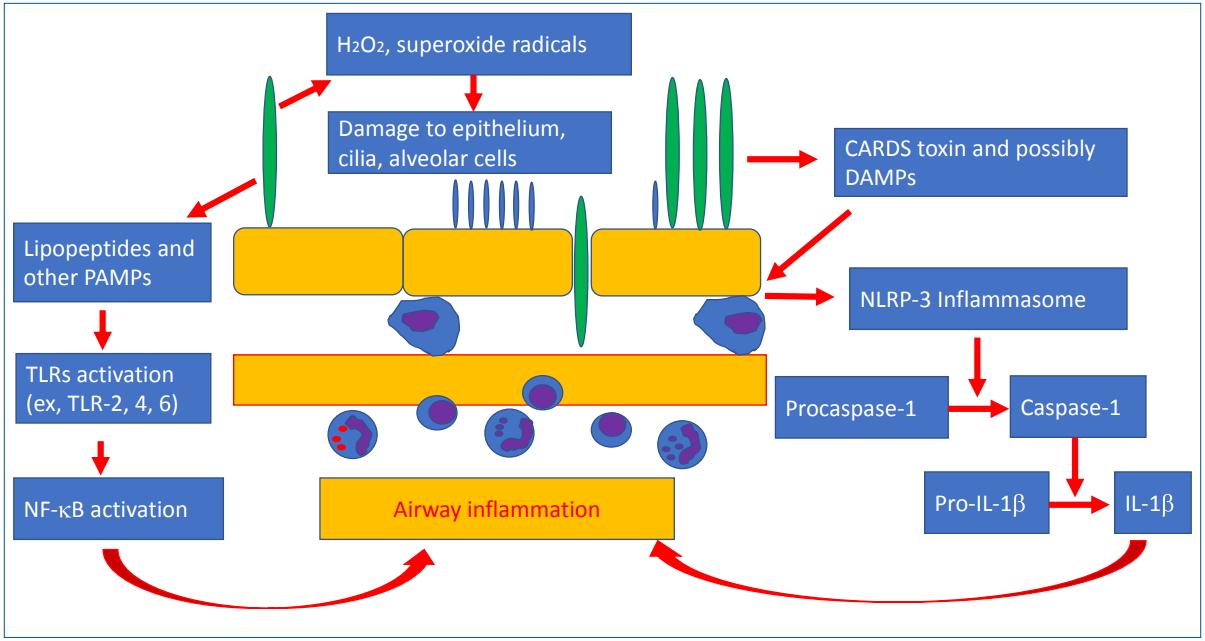
Macrolides are the first line treatment in atypical pneumonia caused by M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, and L. pneumophila. Macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumonia (MRMP) is emerging worldwide, especially in East Asia. Immune modulators such as corticosteroids or second line antibiotics are treatment options for MRMP. Pediatricians should be careful with empirical therapy of macrolides in children with mild to moderate community-acquired pneumonia not to increase the risk of MRMP.
- Original Article
- Other
- Evaluation of goodness of fit of semiparametric and parametric models in analysis of factors associated with length of stay in neonatal intensive care unit
- Fatemeh Kheiry, Sadegh Kargarian-Marvasti, Sima Afrashteh, Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi, Nima Daneshi, Salma Naderi, Seyed Hossein Saadat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):361-367. Published online June 10, 2020
-

Question: Hospitalization in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is associated with life-threatening hazards. What factors associated with neonatal length of stay (LOS) in the NICU?
Finding: Breastfeeding, phototherapy, acute renal failure (ARF), mechanical ventilation, and central venous catheter (CVC) access were identified as factors associated with NICU length of stay.
Meaning: Protective effects of breastfeeding and CVC access, whereas increase effects of phototherapy, ARF, and mechanical ventilation in LOS can be supporting evidence to establish effective interventions to reduce length of NICU stay.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Insights into pediatric pollen food allergy syndrome
- Jeong Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):483-484. Published online June 1, 2020
-
- Are you sure that it is a drug allergy?
- Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):213-214. Published online June 1, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Health effects of electromagnetic fields on children
- Jin-Hwa Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):422-428. Published online May 26, 2020
-
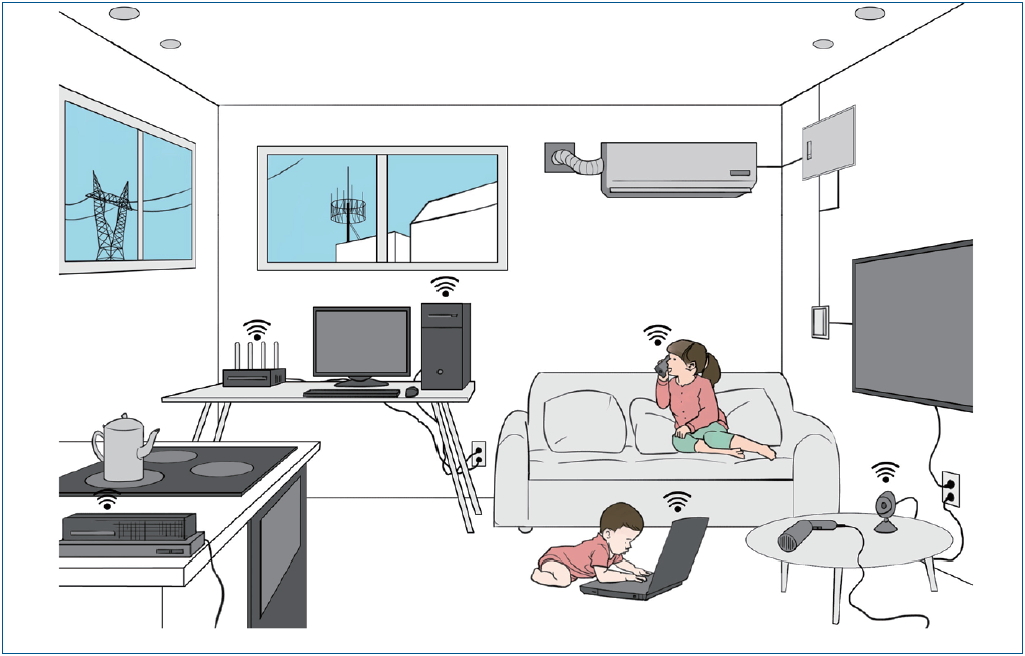
· The nervous systems of children are more vulnerable to the effects of electromagnetic waves than adults.
· The exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMFs) among children should be minimized.
· According to International Agency for Research on Cancer EMFs are possibly carcinogenic, it should not be overlooked or interpreted with bias.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Utility of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator in risk-based group B Streptococcus screening approach
- Myo-Jing Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):393-394. Published online May 22, 2020
-
· Evaluation of the risk factors for early-onset sepsis (EOS) is important to optimal prevention and treatment.
· The EOS calculator is still valid as part of the risk-based group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening approach.
· The risk factor assessment using the EOS calculator is worth use before the introduction of universal GBS screening.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Efficacy of conservative treatment of perianal abscesses in children and predictors for therapeutic failure
- Lars Boenicke, Johannes Doerner, Stefan Wirth, Hubert Zirngibl, Mike Ralf Langenbach
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):272-277. Published online May 15, 2020
-

Background: The optimal management of perianal abscess in children is controversial.
Purpose: To evaluate the efficiency of conservative treatment of perianal abscess in children and identify parameters that predict therapy failure. Methods: All cases of children younger than 14 years of age with perianal abscesses between 2001–2016 were evaluated. Results: Of the 113 enrolled patients, 64 underwent subsequent surgery for advanced disease (primary...
- Editorial
- Emergency Medicine
- Pediatric transport medicine: a yet unknown territory in Korea
- Jeong-Min Ryu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):182-183. Published online May 15, 2020
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Fluconazole prophylaxis against invasive candidiasis in very low and extremely low birth weight preterm neonates: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mahmoud Robati Anaraki, Masoud Nouri-Vaskeh, Shahram Abdoli Oskoei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(4):172-179. Published online May 14, 2020
-
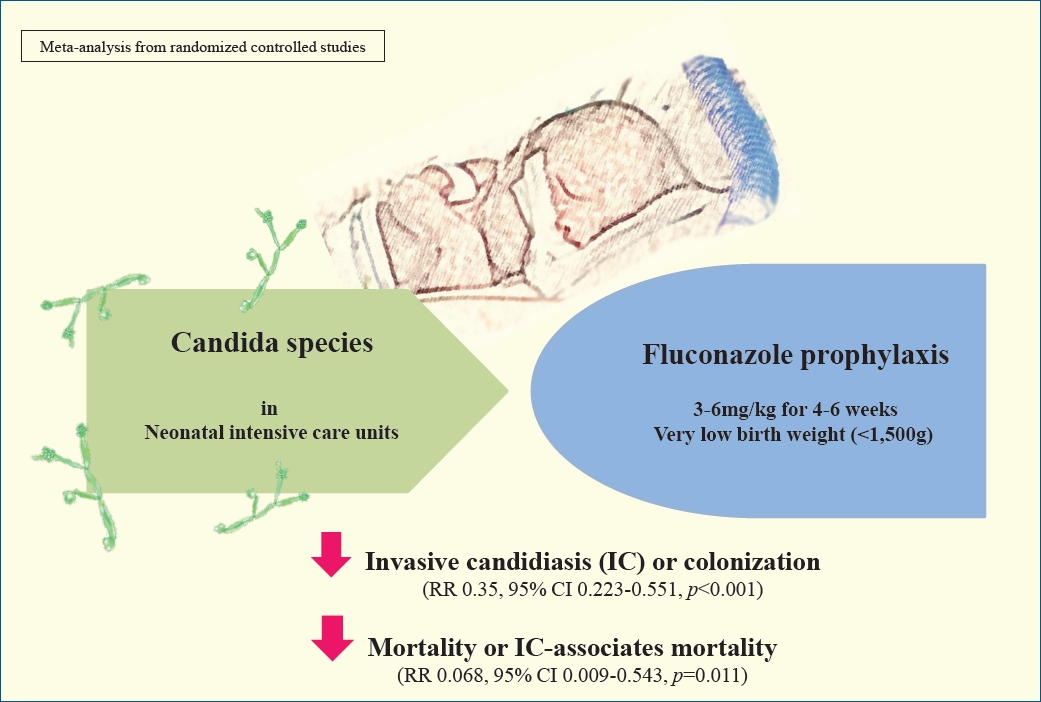
· Mortality is decreased significantly in meta-analysis of studies in different regimen of fluconazole prophylaxis.
· Significant decrease was seen in incidence of invasive candidiasis-associated mortality in extremely low birth weight infants in same schedules of prophylaxis.
· More studies required to relief the concerns.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disorders: clinical spectrum, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment options
- Yun-Jin Lee, Sang Ook Nam, Ara Ko, JuHyun Kong, Shin Yun Byun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(3):103-110. Published online May 14, 2020
-
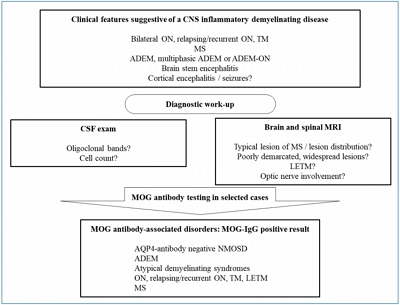
MOG antibody-associated disorder exhibits different pathophysiological and phenotypic findings than both aquaporin-4 antibody-associated neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and typical MS. MOG-antibody is of particular interest in pediatric patients with clinical or radiological non-MS typical findings. MOG-antibody was included in a diagnostic algorithm for children recommending for the first time a standardized use in clinical practice except in cases of typical MS.
- Endocrinology
- Early menarche and its consequence in Korean female: reducing fructose intake could be one solution
- Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):12-20. Published online May 14, 2020
-

In Korea, the average age of menarche has declined sharply. Early menarche is associated with psychosocial and behavioral problems and cardiometabolic disease. Excess fructose intake has been suggested as one cause of early menarche in recent studies, so reducing fructose intake may be one solution.
- Allergy
- Pollen-food allergy syndrome in children
- You Hoon Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):463-468. Published online May 14, 2020
-
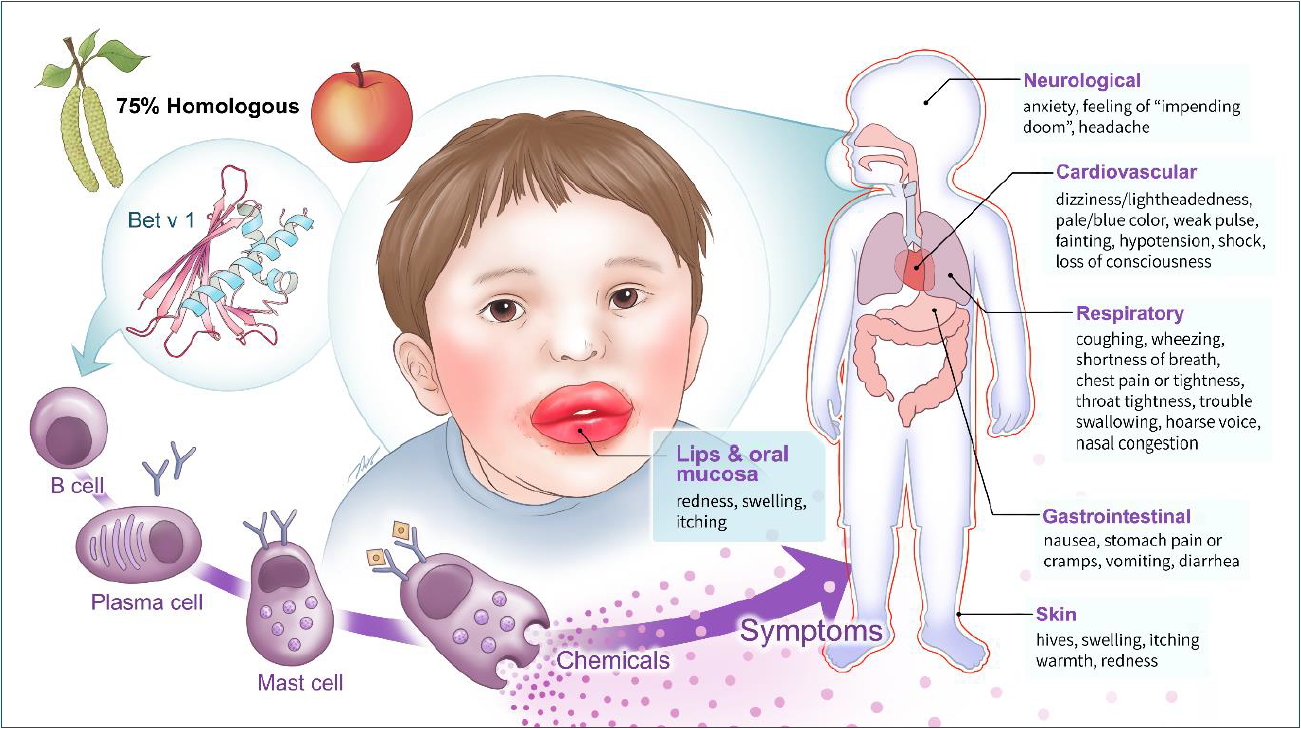
The prevalence of pollen-food allergy syndrome (PFAS) in Korean children with pollen allergy was recently reported to be 42.7%. PFAS can cause a wide range of symptoms from mild allergy to severe anaphylaxis depending on the nature of food allergens that share the epitopes with pollen. Cases of anaphylaxis caused by PFAS have recently increased. Treatments for PFAS should be individualized for patients according to the severity of symptoms.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Development of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST)
- Hee Jung Chung, Donghwa Yang, Gun-Ha Kim, Sung Koo Kim, Seoung Woo Kim, Young Key Kim, Young Ah Kim, Joon Sik Kim, Jin Kyung Kim, Cheongtag Kim, In-Kyung Sung, Son Moon Shin, Kyung Ja Oh, Hee-Jeong Yoo, Hee Joon Yu, Seoung-Joon Lim, Jeehun Lee, Hae-Ik Jeong, Jieun Choi, Jeong-Yi Kwon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):438-446. Published online May 14, 2020
-
Question: Can the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) be a useful screening tool for infants and children in Korea?
Finding: The K-DST has high reliability (internal consistency of 0.73–0.93, test-retest reliability of 0.77–0.88) and a high discriminatory ability with a sensitivity of 0.833 and specificity of 0.979.
Meaning: The K-DST is an effective and reliable screening tool for infants and children with neurodevelopmental disorders in Korea.
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Survival model application for analysis of neonatal length of stay
- Eun Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):357-358. Published online May 14, 2020
-
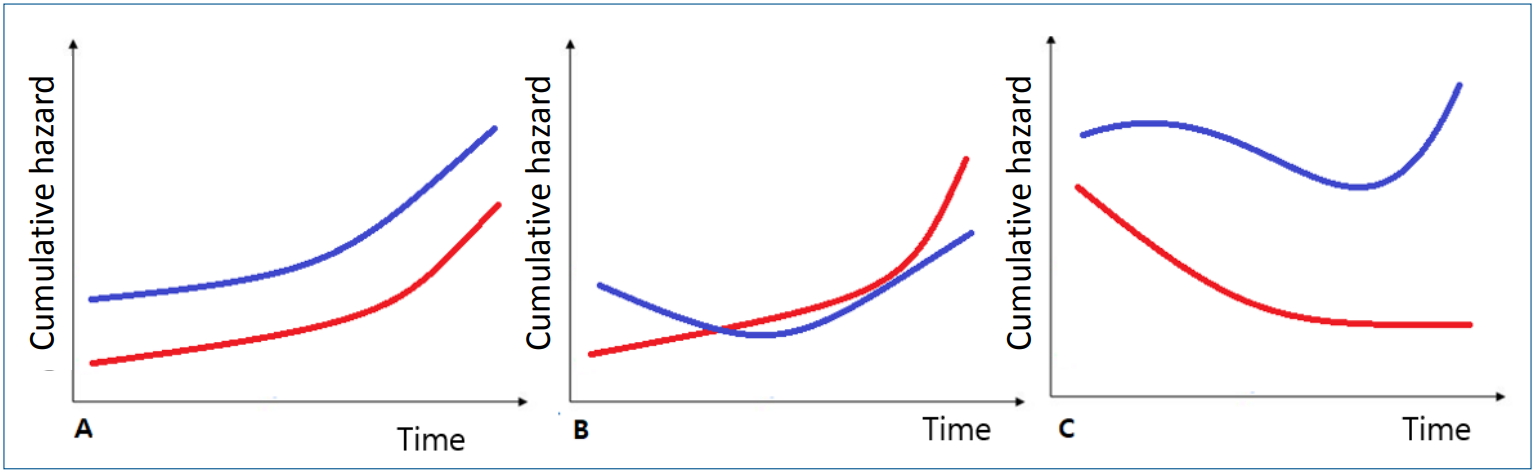
- Infection
- Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: choice of schedule and product development
- Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):259-260. Published online April 27, 2020
-

- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Risk-based maternal group B Streptococcus screening strategy is compatible with the implementation of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator
- Niek B. Achten, J. Wendelien Dorigo-Zetsma, Annemarie M.C. van Rossum, Rianne Oostenbrink, Frans B. Plötz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):406-410. Published online April 16, 2020
-
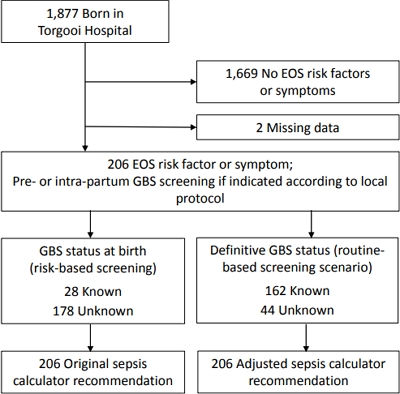
Question: To what extent does risk-based Group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening influence management recommendations by the early-onset sepsis (EOS) calculator?
Finding: In 97% of the newborn infants, the EOS calculator recommendation remained unchanged after the GBS status at birth was updated to the definitive GBS status.
Meaning: Risk-based GBS screening results are compatible with EOS calculator recommendations.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Role of neutrophil CD11b expression in diagnosis of earlyonset neonatal sepsis in full-term infant
- Safaa ELMeneza, Walaa Mohamed, Iman Elbagoury, Karima Bahagat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):44-45. Published online April 14, 2020
-
Question: Can CD11b detect sepsis in full-term infants with suspected sepsis?
Finding: The percentage of neutrophils expressing CD11b was significantly upregulated in the sepsis and suspected sepsis groups versus the control group.
Meaning: CD11b is a sensitive marker for sepsis and suspected sepsis in full-term neonates and it may be added to sepsis markers. This information would allow the neonatologist to confidently discontinue antibiotic use as long as the neonate is clinically stable.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Targeted temperature management and neuroprotective outcomes of pediatric patients after cardiac arrest
- Yun-Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):180-181. Published online April 14, 2020
-
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Dapsone: a steroid-sparing drug for refractory immunoglobulin A vasculitis?
- Jin-Soon Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):178-179. Published online April 14, 2020
-
- Allergy
- Trends in prevalence of allergic diseases in Korean children: how and why?
- Kyung Suk Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):263-264. Published online April 13, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Pediatric heart transplantation: how to manage problems affecting long-term outcomes?
- Young Hwue Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):49-59. Published online April 8, 2020
-

Since the initial International Society of Heart Lung Transplantation registry was published in 1982, the number of pediatric heart transplantations has increased markedly, reaching a steady state of 500–550 transplantation annually and occupying up to 10% of total heart transplantations. Heart transplantation is considered an established therapeutic option for patients with end-stage heart disease. The long-term outcomes of pediatric heart...
- Perspective
- Pulmonology
- Early preemptive immunomodulators (corticosteroids) for severe pneumonia patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):117-118. Published online April 8, 2020
-
- Clinical Note
- Allergy
- Recurrent urticaria caused by specific cat serum albumin IgE cross-reacting with pork serum albumin
- Cheon Kim, Sung Won Kim, Yoon Ha Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):451-453. Published online April 6, 2020
-
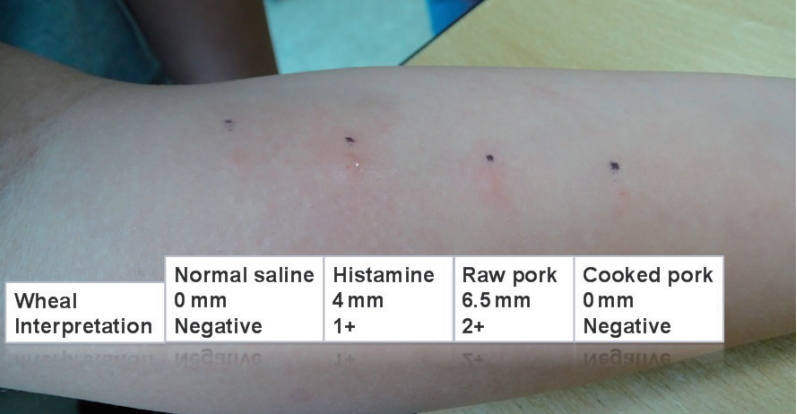
Question: What should be considered in children who complain of pork allergies?
Finding: History of raising a cat, the onset of symptoms after the ingestion of pork and specific IgE tests to pork, cat, milk, and Alpha-gal are needed.
Meaning: Pork cat syndrome could be the cause of pork allergies.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children
- Soo-Han Choi, Han Wool Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):125-132. Published online April 6, 2020
-

Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), which started in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 and declared a worldwide pandemic on March 11, 2020, is a novel infectious disease that causes respiratory illness and death. Pediatric COVID-19 accounts for a small percentage of patients and is often milder than that in adults; however, it can progress to severe disease in some cases. Even neonates...
- Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19)
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):119-124. Published online April 2, 2020
-
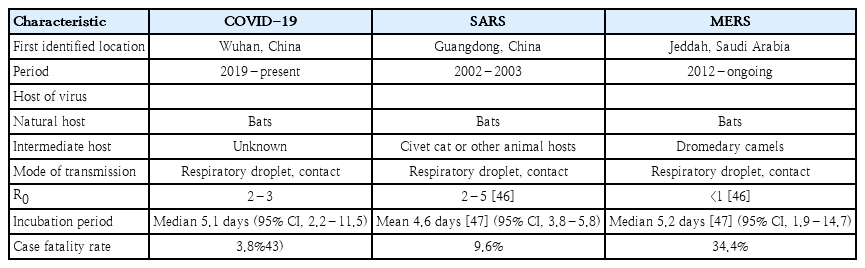
A cluster of severe pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan City, Hubei province in China emerged in December 2019. A novel coronavirus named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) was isolated from lower respiratory tract sample as the causative agent. The current outbreak of infections with SARS-CoV-2 is termed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) by the World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19...
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











