- Original Article
- Neurology
- Instability of revised Korean Developmental Screening Test classification in first year of life
-
Ji Eun Jeong, You Min Kim, Na Won Lee, Gyeong Nam Kim, Jisuk Bae, Jin Kyung Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(1):97-103. Published online November 11, 2024
-

|
Question: How stable are the revised Korean Developmental Screening Test score classifications in early infancy?
Finding: A significant number of infants improved into the peer and high-level group (≥-1 standard deviations), especially in the gross motor area.
Meaning: The early detection of developmental delay requires a comprehensive medical history, physical and neurological examinations, and repeated developmental screenings. |
-
-
- Pulmonology
- Increased procalcitonin level is a risk factor for prolonged fever in children with Mycoplasma pneumonia
-
Ji Eun Jeong, Ji Eun Soh, Ji Hee Kwak, Hye Lim Jung, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):258-263. Published online August 15, 2018
-
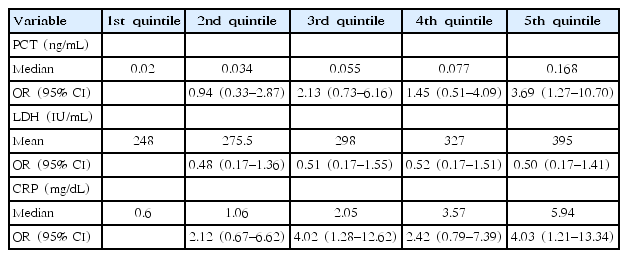
|
Purpose: Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is characterized by prolonged fever and radiological progression despite macrolide treatment. Few studies have examined serum procalcitonin (PCT) level in children with MPP. We aimed to investigate the association of acute inflammation markers including PCT with clinical parameters in children with MPP. Methods: A total of 147 children were recruited. The diagnosis of MPP... |
-
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Augmentation of respiratory muscle activities in preterm infants with feeding desaturation
-
Dong Rak Kwon, Gi Young Park, Ji Eun Jeong, Woo Taek Kim, Eun Joo Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):78-83. Published online March 19, 2018
-
|
|
Purpose Frequent desaturation due to immature incoordination of suck-swallow-breathing in preterm infants can influence multiple organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain, which can then affect growth and development. Most notably in preterm infants, feeding desaturation may even affect pulmonary function during gavage feeding. Because respiratory muscle activities may reflect the work required during respiration, we evaluated the differences in... |
-
-
- Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin against hypoxic injury via modulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and apoptosis
-
Ji Eun Jeong, Jae Hyun Park, Chun Soo Kim, Sang Lak Lee, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim, Eun Joo Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):181-188. Published online June 22, 2017
-
|
|
Purpose Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is a significant cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. Erythropoietin (EPO) is emerging as a therapeutic candidate for neuroprotection. Therefore, this study was designed to determine the neuroprotective role of recombinant human EPO (rHuEPO) and the possible mechanisms by which mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), JNK, and p38 MAPK is modulated in... |
-
-
- Original Article
- Taurine exerts neuroprotective effects via anti-apoptosis in
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
-
Ji Eun Jeong, Tae Yeol Kim, Hye Jin Park, Kye Hyang Lee, Kyung Hoon Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Jin Kyung Kim, Hai Lee Chung, Eok Su Seo, Woo Taek Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(12):1337-1347. Published online December 15, 2009
-
|
|
Purpose : Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a simple sulfur-containing amino acid. It is abundantly present in tissues such as brain, retina, heart, and skeletal muscles. Current studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of taurine, but limited data are available for such effects during neonatal period. The aim of this study was to determine whether taurine could reduce hypoxic-ischemic (HI) cerebral... |
-
-
|














