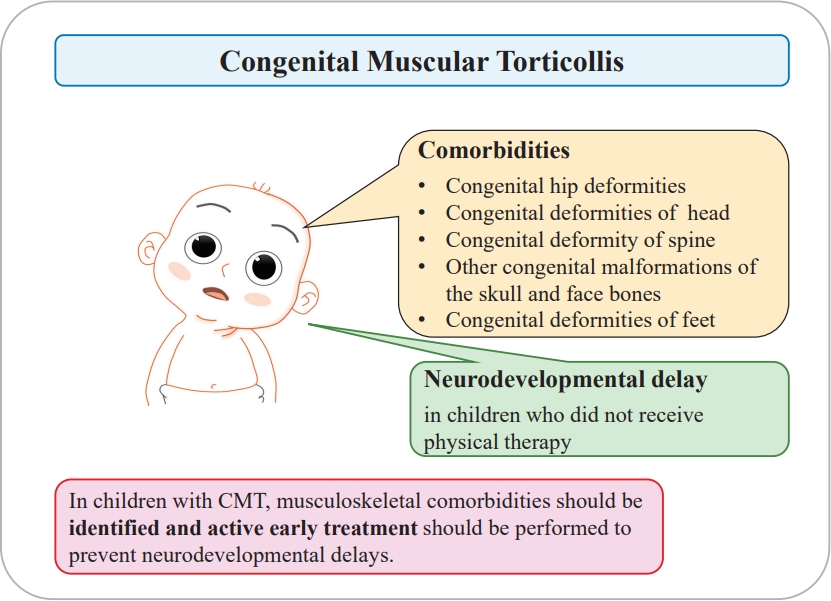
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Efficacies of different treatment strategies for infants hospitalized with acute bronchiolitis
-
Hyeri Jeong, Dawon Park, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Jeewon Shin, Hey-Sung Baek, Hyunsoo Hwang, Youn Ho Shin, Hye Mi Jee, Man Yong Han
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):608-618. Published online October 28, 2024
-

|
· This study analyzed 45 randomized controlled trials (5,061 participants, 13 interventions) of the comparative efficacies of treatments for acute bronchiolitis in infants.
· Inhalation therapy with epinephrine and hypertonic saline significantly reduced the length of hospital stay compared with normal saline.
· Hypertonic saline had the greatest ability to improve the clinical severity score of bronchiolitis in infants younger than 2 years of age. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Long COVID in children and adolescents: prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management strategies
-
Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Man Yong Han
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):465-474. Published online June 19, 2023
-

|
· Current definitions of long coronavirus disease (COVID) in children and adolescents vary in duration, ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
· The clinical spectrum of long COVID in children and adolescents comprises a wide range of symptoms and might be a multisystem disorder.
· Persistent health problems with a prevalence of 1%–66.5% were reported in children and adolescents after COVID-19, with a higher incidence of persistent single or multiple symptoms. |
-
-
- Allergy
- Cohort profile: National Investigation of Birth Cohort in Korea study 2008 (NICKs-2008)
-
Ju Hee Kim, Jung Eun Lee, So Min Shim, Eun Kyo Ha, Dong Keon Yon, Ok Hyang Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hyun Yong Koh, Kyu Young Chae, Seung Won Lee, Man Yong Han
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):480-488. Published online January 5, 2021
-
|
This national cohort study included all Korean children born in 2008 and 2009 observed over a period of more than 10 years. Our findings demonstrate that it is possible to analyze disease onset prior to hospitalization based on information such as lifestyle, eating habits, and risk factors by integrating National Health Insurance System data with national health screening data. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Prevalence, comorbidities, diagnosis, and treatment of nonallergic rhinitis: real-world comparison with allergic rhinitis
-
Hye Yung Yum, Eun Kyo Ha, Yoon Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):373-383. Published online August 10, 2020
-

|
Rhinitis is among the most common respiratory diseases in children. Nonallergic rhinitis, which involves nasal symptoms without evidence of systemic allergic inflammation or infection, is a heterogeneous entity with diverse manifestations and intensities. Nonallergic rhinitis accounts for 16%–89% of the chronic rhinitis cases, affecting 1%–50% (median 10%) of the total pediatric population. The clinical course of nonallergic rhinitis is generally... |
-
-
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Dietary habits and gastroesophageal reflux disease in preschool children
-
You Jin Choi, Eun Kyo Ha, Su Jin Jeong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):303-307. Published online July 31, 2016
-
|
|
Purpose To identify the relationship between dietary habits and childhood gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in preschool children. MethodsWe performed a questionnaire study to analyze the relationship between dietary habits and GERD in 85 preschool children with GERD and 117 healthy children of the same age. ResultsIrregular and picky eating were more p–revalent in the GERD group than in the control group (odds ratio... |
-
-
|