- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
-
Gyu Hong Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):384-394. Published online December 28, 2022
-
|
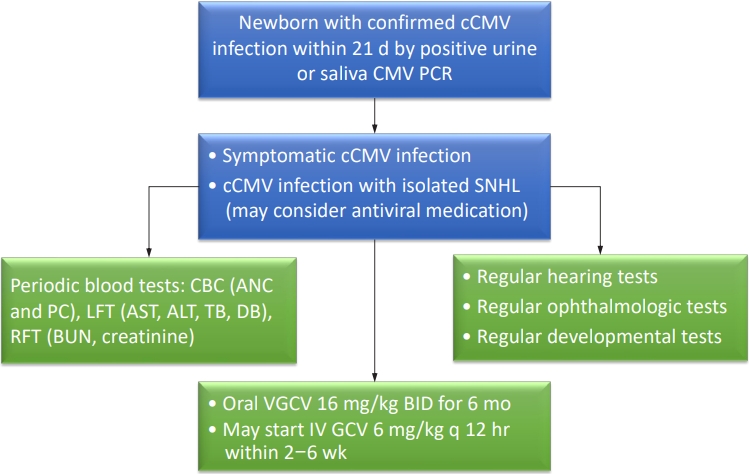
· Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is among the most common causes of nongenetic sensorineural hearing loss.
· Congenital CMV is initially treated with intravenous ganciclovir for 2–6 weeks and switched to oral valganciclovir, or with oral valganciclovir for the entire 6-month period.
· Infants with congenital CMV require periodic monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, platelet count, and blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function tests, audiological, ophthalmological, and developmental tests during antiviral medication. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Does cord blood cortisol have a mediating effect on maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight?
-
Gyu Hong Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):24-25. Published online November 30, 2022
-
|
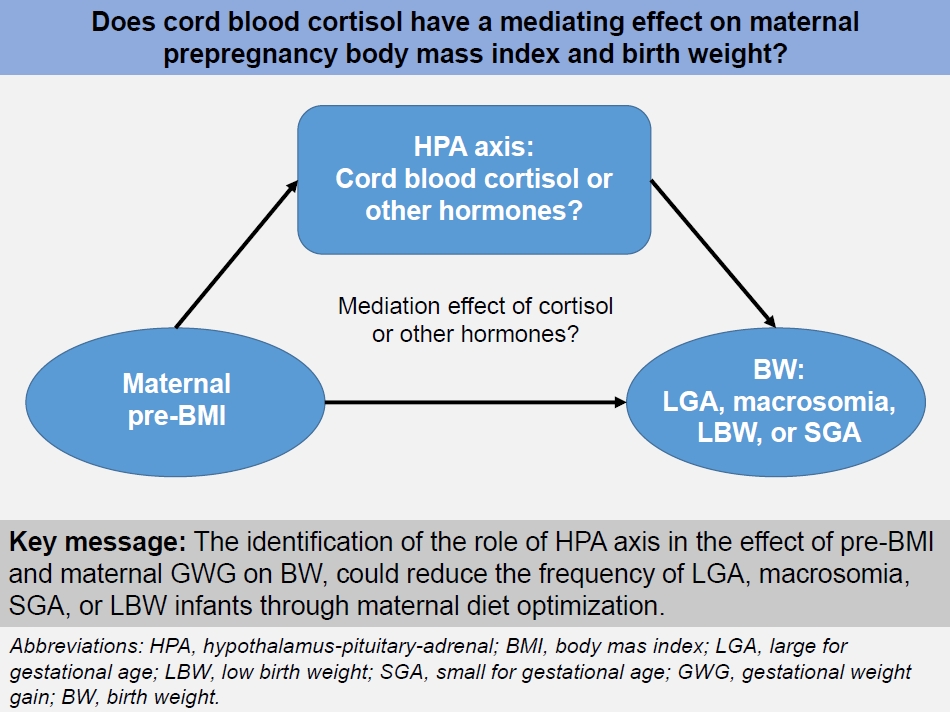
· A high prepregnancy body mass index (pre-BMI) is associated with large for gestational age (LGA) and macrosomia, whereas a low pre-BMI is associated with small for gestational age (SGA) and low birth weight (LBW).
· The identification of the role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in the effect of pre-BMI and maternal gestational weight gain on birth weight could reduce the frequency of LGA, macrosomia, SGA, or LBW through maternal diet optimization. |
-
-
- Which factors predict outcomes of neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy following therapeutic hypothermia?
-
Gyu Hong Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(4):169-171. Published online December 11, 2020
-
|
|
Determining the therapeutic hypothermia and predict long-term prognosis quickly and accurately in infants with moderate to severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy requires a thorough history taking, physical examination, amplitude-integrated elec�troencephalography, brain magnetic resonance imaging with diffusion-weighted imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, heart evaluation (cardiac enzymes, electrocardio�graphy, and echocardiography), and several other biomarkers. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Prognostic factors of neurological outcomes in late-preterm and term infants with perinatal asphyxia
-
Sun Young Seo, Gyu Hong Shim, Myoung Jae Chey, Su Jeong You
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(11):440-445. Published online November 18, 2016
-
|
|
Purpose This study aimed to identify prognostic factors of neurological outcomes, including developmental delay, cerebral palsy and epilepsy in late-preterm and term infants with perinatal asphyxia. MethodsAll late-preterm and term infants with perinatal asphyxia or hypoxic-ischemic insults who admitted the neonatal intensive care unit of Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital between 2006 and 2014 and were followed up for at least 2... |
-
-
- Short-term clinical outcomes of late preterm infants
-
Ji Youn Na, Narimi Park, Eun Sun Kim, Jin-A Lee, Gyu Hong Shim, Jin-A Lee, Chang Won Choi, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim, Beyong Il Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):303-309. Published online March 15, 2009
-
|
|
Purpose : To identify the short-term clinical outcomes of late preterm infants and to test the hypothesis that late preterm infants have more clinical problems during the early postnatal period than term infants.
Methods : One hundred late preterm infants [gestational age (GA) 34+0-36+6 weeks] and the same number of term infants (GA 37+0-41+6 weeks) were randomly selected from 289 late... |
-
-
- Study on the neurodevelopmental predictors for the results of the Bayley Scales of Infant Development II in high-risk neonates
-
Mi Kyeong Woo, Dong Wook Kim, Kyoung Huh, Gyu Hong Shim, Myoung Jae Chey
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1221-1227. Published online November 15, 2009
-
|
|
Purpose : To identify the risk factors for poor neurodevelopmental outcomes in high-risk neonates.
Methods : We studied 94 infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit at the Sanggye Paik Hospital between January 2002 and November 2005 and evaluated the follow-up data. The following events were considered as risk factors: ≤32 weeks of gestation, very low birth weight, Apgar scores... |
-
-
- Clinical characteristics of severe meconium aspiration syndrome
-
Chang Won Choi, Beyong Il Kim, Hyun Ju Lee, Kyoung Eun Joung, Gyu Hong Shim, In Suk Lim, Jin-A Lee, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):713-721. Published online July 15, 2008
-
|
|
Purpose : This study aims to describe the clinical characteristics of severe meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) which required mechanical ventilation over 48 h and to delineate the progress of respiratory failure and radiographic findings in severe MAS.
Methods : Twelve infants admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) of the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital diagnosed with severe MAS from... |
-
-
- Risk Factors of Nephrocalcinosis in Very Low Birth Weight(VLBW) Infants
-
Gyu Hong Shim, Jin A Lee, Yun Jung Shin, Ee Kyung Kim, June Dong Park, Beyong Il Kim, Jung Hwan Choi
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):275-281. Published online March 15, 2004
-
|
|
Purpose : Nephrocalcinosis in very low birth weight(VLBW) infants were known to be caused by a longer duration of furosemide use. However, etiologies, pathogenesis and risk factors remain unclear. Therefore, we examined the incidence and risk factors of nephrocalcinosis in VLBW infants retrospectively.
Methods : Inborn babies of birth weights less than 1,500 gm were examined retrospectively. Data were reviewed on... |
-
-
- Congenital Heart Disease in Jeju : Postnatal Incidence and Clinical Features
-
Jung Ha Lee, Gyu Hong Shim, Kyung Sue Shin, Jung Yun Hong, Yeoun Woo Kim, Seong Ho Kim, Chung Il Noh
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):294-303. Published online March 15, 2004
-
|
|
Purpose : This is a retrospective descriptive study to determine the incidence of congenital heart disease(CHD) in Jeju and to estimate the suitability of the Jeju population as the subject for a regional birth cohort study.
Methods : All patients with CHD diagnosed by two dimensional echocardiography in Cheju National University Hospital and Halla General Hospital from January 1999 to... |
-
-
|














