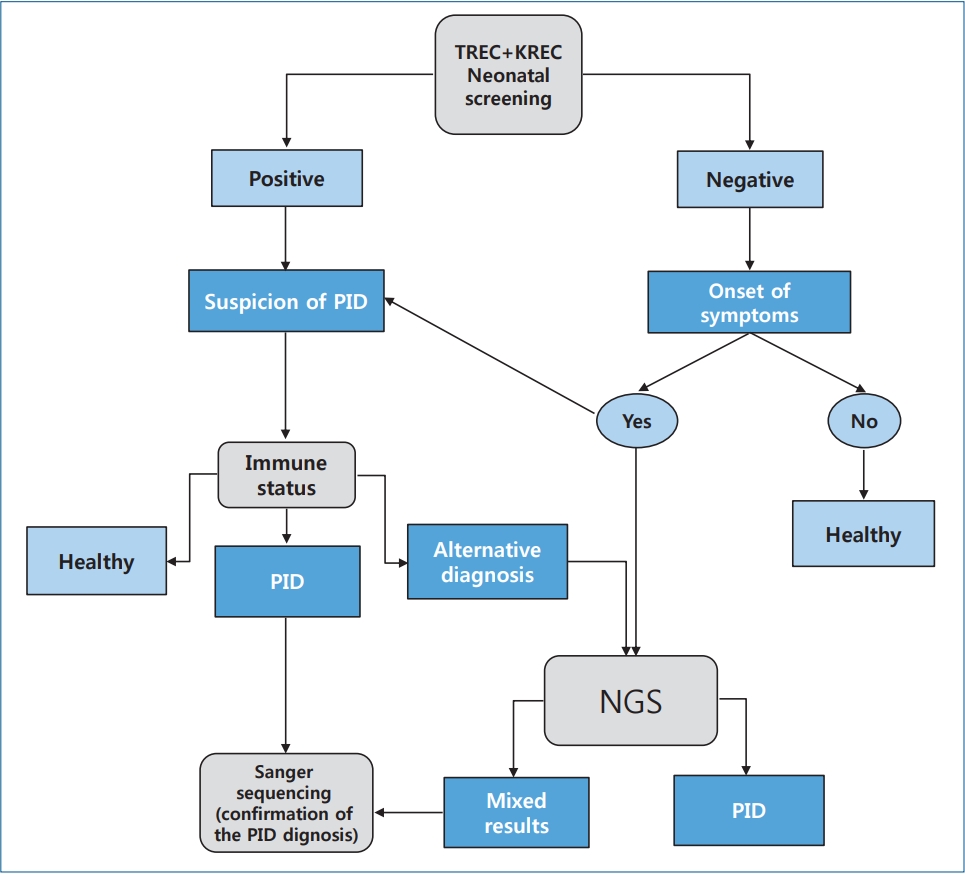
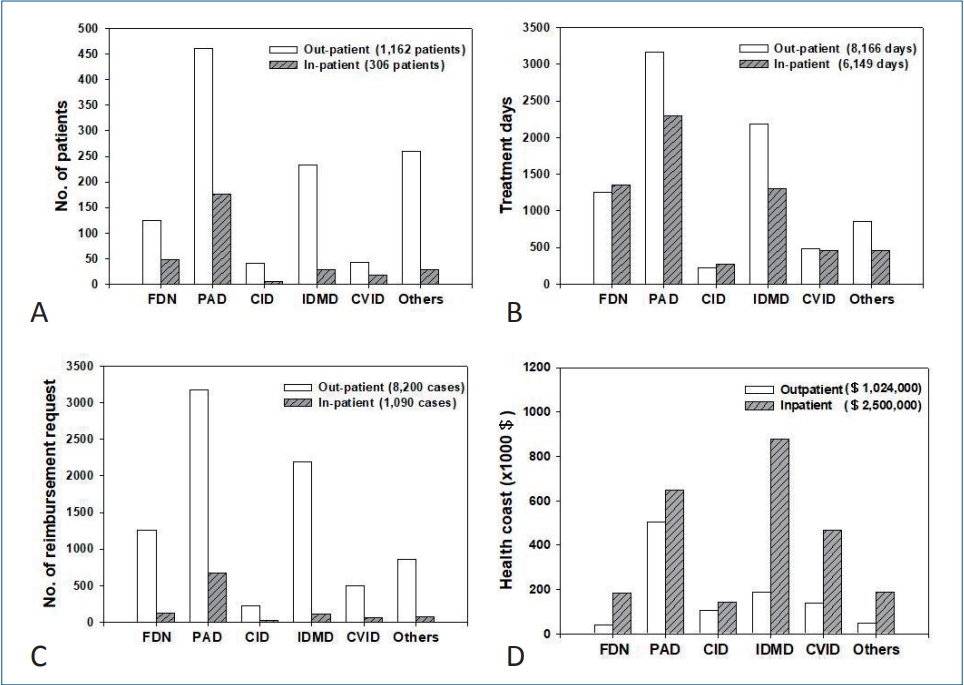
|
|
Nezelof's syndrome(combined immunodeficiency with immunoglobulin) is a hereditary primary
immunodeficiency characterized by recurrent chronic pulmonary infections, oral and cutaneous
candidiasis, failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea, skin infection, urinary tract infection,
gram-negative sepsis, severe progressive varicella infection, lymphopenia, diminished lymphoid
tissue, abnormal structure of the thymus, and presence of normal or increased levels of one or
more of the major immunoglobulin classes, but with impaired antibody... |