Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old
- Dedy Rahmat, Agus Firmansyah, Ina S. Timan, Saptawati Bardosono, Joedo Prihartono, Pramita Gayatri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):538-544. Published online November 16, 2023
-
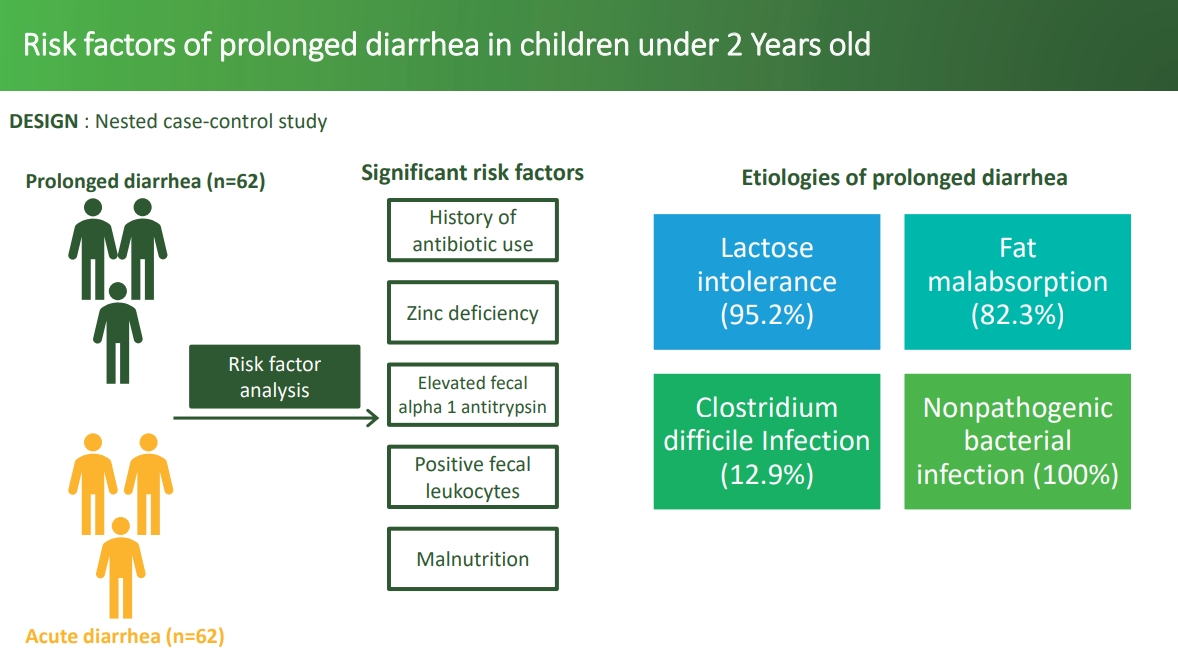
Question: What are the risk factors for prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old?
Finding: History of antibiotic use, zinc deficiency, and elevated fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels were the main risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Rational antibiotic usage is necessary as well as thorough testing of serum zinc level and fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
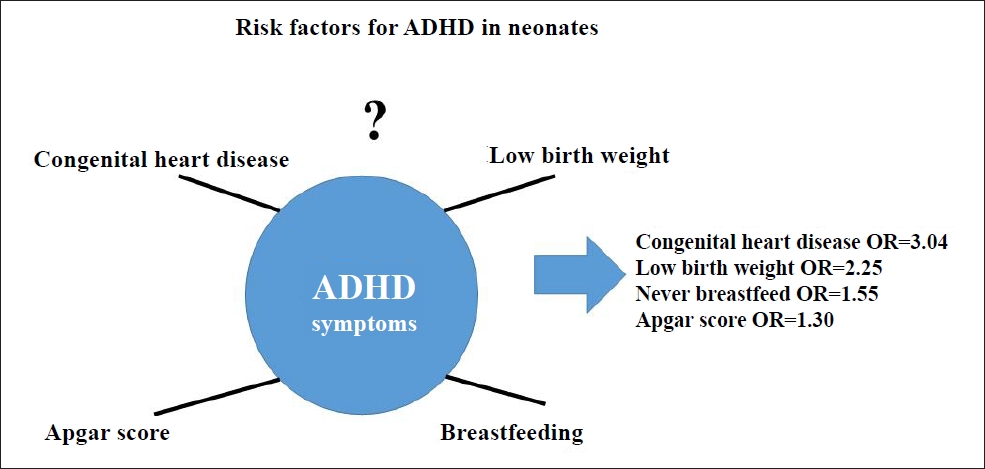
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-

Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-

Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Original Article
- Emergency Medicine
- Nonfatal injuries in Korean children and adolescents, 2007–2018
- Gyu Min Yeon, Yoo Rha Hong, Seom Gim Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):194-200. Published online September 9, 2021
-

Question: How many children and adolescents have experienced nonfatal injuries in the previous year?
Finding: Among Korean children and adolescents, 8.1% experienced at least one injury per year. We found no significant change in the incidence of injuries over the previous 12 years.
Meaning: The incidence of injuries is higher than this estimation; therefore, more attention and effort are needed to prevent injuries among children and adolescents.
- Endocrinology
- Prevalence and associates of obesity and overweight among school-age children in a rural community of Thailand
- Teechaya Nonboonyawat, Wuttipat Pusanasuwannasri, Nattanon Chanrat, Natta Wongthanavimok, Danutanut Tubngern, Piengkwan Panutrakul, Mathirut Mungthin, Thirapa Nivesvivat, Panadda Hatthachote, Ram Rangsin, Phunlerd Piyaraj
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):179-186. Published online February 8, 2019
-
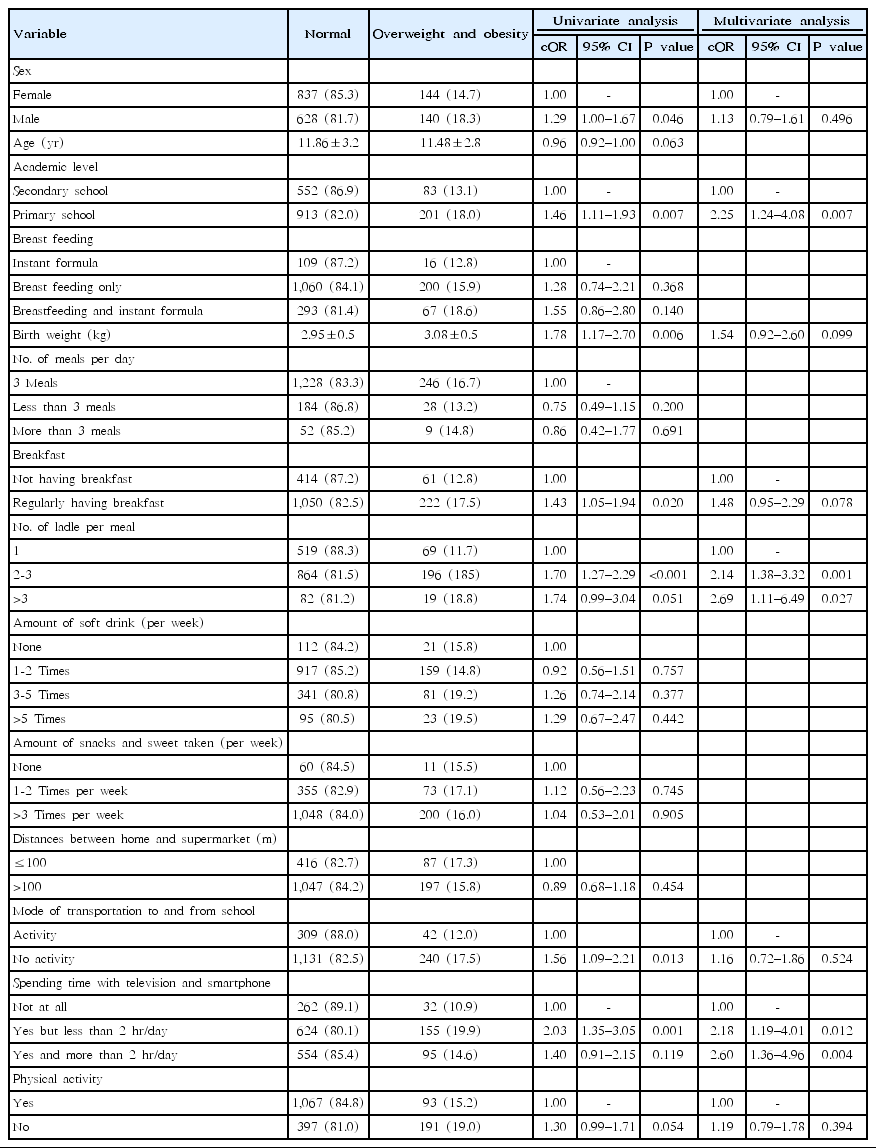
Purpose: Information about overweight and obesity among students in rural areas of Thailand is limited. Therefore, we aimed to determine overweight and obesity prevalences and associated factors among school-aged children in a rural community of Thailand. Methods: We selected 9 public schools through cluster sampling in 2 provinces located in central Thailand in 2016. Anthropometric measurements were measured using standard techniques,...
- General Pediatrics
- The correlation of depression with Internet use and body image in Korean adolescents
- Chang Hoon Lim, Eun Ji Kim, Jong Hyun Kim, Jue Seong Lee, Yoon Lee, Sang Hee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(1):17-23. Published online January 24, 2017
-
Purpose To examine the correlation of depression with Internet use and body image perception, and to analyze the risk factors of depression in a total of 920 students in Seoul, Korea.
Methods Students were recruited by contacting school principals and teachers and were encouraged to fill out a self-report questionnaire designed specifically for this study in July of 2008.
Results Female participants had an increased...
- Gastroenterology
- Risk factors of delayed diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children: for early detection of acute appendicitis
- Jea Yeon Choi, Eell Ryoo, Jeong Hyun Jo, Tchah Hann, Seong Min Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(9):368-373. Published online September 21, 2016
-
Purpose This study examined the risk factors of a delayed diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children undergoing an appendectomy.
Methods This retrospective study involved children aged below 18 years, who underwent an appendectomy. After dividing them into a delayed diagnosis group and nondelayed diagnosis group according to the time interval between the initial hospital visit and final diagnosis, the risk factors of delayed...
- Clinical risk factors associated with the development of wheezing in children less than 2 years of age who required hospitalization for viral lower respiratory tract infections
- Joon Hwan Kim, Ji-Yeon Choi, Na Yeon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hye Sung Baek, Jung Won Yoon, Hye Mi Jee, Sun Hee Choi, Hyeung Yoon Kim, Ki Eun Kim, Youn Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(7):245-250. Published online July 22, 2015
-
Purpose Wheezing following viral lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in children <2 years of age is an important risk factor for the development of asthma later in life; however, not all children with viral LRTIs develop wheezing. This study investigated risk factors for the development of wheezing during viral LRTIs requiring hospitalization.
Methods The study included 142 children <2 years of age hospitalized...
- Postnatal weight gain in the first two weeks as a predicting factor of severe retinopathy of prematurity requiring treatment
- Jongmoon Kim, Jang Yong Jin, Sung Shin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(2):52-59. Published online February 28, 2015
-
Purpose This study aimed to investigate the relative weight gain at 2-week intervals up to 6 weeks after birth to predict retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) requiring treatment among very low birth weight infants.
Methods A total of 211 preterm infants with birth weights <1,500 g and gestational age <32 weeks were retrospectively reviewed. The main outcome was the development of ROP requiring treatment....
- Review Article
- Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns: update in pathophysiology and newly emerging therapeutic strategies
- Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):505-513. Published online December 31, 2014
-
While the survival of extremely premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome has increased due to advanced respiratory care in recent years, necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains the leading cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. NEC is more prevalent in lower gestational age and lower birth weight groups. It is characterized by various degrees of mucosal or transmural necrosis of the intestine....
- Original Article
- Cardiovascular risk factors of early atherosclerosis in school-aged children after Kawasaki disease
- Hyun Jeong Cho, Soo In Yang, Kyung Hee Kim, Jee Na Kim, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(5):217-221. Published online May 31, 2014
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to determine whether school-aged children with Kawasaki disease (KD) have an increased risk for early atherosclerosis.
Methods The study included 98 children. The children were divided into the following groups: group A (n=19), KD with coronary arterial lesions that persisted or regressed; group B (n=49), KD without coronary arterial lesions; and group C (n=30), healthy children....
- Vitamin D deficiency in infants aged 1 to 6 months
- You Jin Choi, Moon Kyu Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(5):205-210. Published online May 28, 2013
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to recognize the state of vitamin D among healthy infants aged 1 to 6 months in South Korea, and also to identify the risk factors affecting the level of vitamin D.
Methods A total of 117 infants were enrolled in this study for 12 months, from March 1, 2011 to February 29, 2012. Serum levels of...
- Review Article
- Bone mineral density deficits in childhood cancer survivors: Pathophysiology, prevalence, screening, and management
- Min Jae Kang, Jung Sub Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):60-67. Published online February 25, 2013
-
As chemotherapy and other sophisticated treatment strategies evolve and the number of survivors of long-term childhood cancer grows, the long-term complications of treatment and the cancer itself are becoming ever more important. One of the most important but often neglected complications is osteoporosis and increased risk of fracture during and after cancer treatment. Acquisition of optimal peak bone mass and...
- Original Article
- Risk factors of ocular involvement in children with mitochondrial respiratory chain complex defect
- Jung Hyun Chae, Jung Hun Lee, Kyo Ryung Kim, Suk Ho Byeon, Young Mock Lee, Hoon Chul Kang, Joon Soo Lee, Heung Dong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(12):994-999. Published online December 31, 2010
-
Purpose Mitochondrial dysfunction can present with various symptoms depending on the organ it has affected. This research tried to analyze the ophthalmologic symptoms and ophthalmologic examination (OE) results in patients with mitochondrial disease (MD).
Methods Seventy-four patients diagnosed with mitochondrial respiratory chain complex defect with biochemical enzyme assay were included in the study. They were divided into 2 groups based on the OE...
- Review Article
- Practical stepwise approach to rhythm disturbances in congenital heart diseases
- June Huh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(6):680-687. Published online June 23, 2010
-
Patients with congenital heart diseases (CHD) are confronted with early- and late-onset complications, such as conduction disorders, arrhythmias, myocardial dysfunction, altered coronary flow, and ischemia, throughout their lifetime despite successful hemodynamic and/or anatomical correction. Rhythm disturbance is a well-known and increasingly frequent cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with CHD. Predisposing factors to rhythm disturbances include underlying cardiac defects,...
- Original Article
- The risk factors and prognosis associated with neonatal pulmonary hemorrhage
- Su Jin Park, Ki Tae Yun, Won Duck Kim, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):503-509. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Although neonatal pulmonary hemorrhage is rare, it is associated with high mortality. We aimed to evaluate the risk factors associated with pulmonary hemorrhage in preterm infants and to describe the clinical course, including neonatal morbidity, of infants who developed pulmonary hemorrhage. Methods : We performed a retrospective case-control study of 117 newborn infants aged less than 37 gestational weeks admitted... -
- Predictable risk factors and clinical courses for prolonged transient tachypnea of the newborn
- Ji Young Chang, Chang Ryul Kim, Ellen A Kim, Ki Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):349-357. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is usually benign and improves within 72 hours. However, it can also progress to prolonged tachypnea over 72 hours, profound hypoxemia, respiratory failure, and even death. The aim of this study is to find predictable risk factors and describe the clinical courses and outcomes of prolonged TTN (PTTN). Methods : The medical records... -
- Risk factors associated with complicated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in neonates
- Young Jin Lee, Hyen Jin Kim, Shin Yun Byun, Su Eun Park, Hee Ju Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):173-177. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an important pathogen that causes nosocomial infection in NICU. It contributes to neonatal morbidity and mortality with variable complications. This study was conducted to identify the risk factors associated with complicated MRSA bacteremia in neonates. Methods : We reviewed the medical records of 44 neonates with positive blood culture for MRSA who were admitted... -
- Clinical characteristics and courses of congenital muscular torticollis
- Kyong Eun Choi, Hee Chul Lee, So Young Youn, Jung Mi Chun, Son Moon Shin, Byung Hee Han, Yong Taek Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1273-1278. Published online November 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Congenital muscular torticollis (CMT), a common musculoskeletal disorder in infants, is characterized by the rotation and flexion deformity of the neck caused by sternocleidomastoid muscle shortening. We investigated the clinical courses and perinatal risk factors of CMT. Methods : Less than 6-month-old patients (98; M:F = 60:38) diagnosed with CMT between February 2007 and August 2008 were classified... -
- The outcomes of retinopathy of prematurity in relation to duration of low dose oxygen therapy
- Pil Sang Lee, Jae Won Choi, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):50-55. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : This study aimed to determine the influence of low-dose oxygen (FiO2 <25%) therapy through nasal cannulae on the progress and prognosis of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) as well as methods of preventing ROP. Methods : Our subjects comprised premature infants (gestation period <37 weeks; birth weight <1,750 g) born in Daegu Fatima Hospital between February 1, 2001 and... -
- Infantile risk factors for obesity in preschool children
- Sun Ju Park, Jae Won Moon, Hyun Ji Kim, Min Jung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(8):804-811. Published online August 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Childhood obesity is a problem that places a child at great risk for becoming an obese adult. To prevent obesity, it is important to focus on early life risk factors that may contribute to childhood obesity. The aim of this study is to find obesity-causing infantile risk factors in preschool children. Methods : A total of 223 children aged... -
- Long term prognosis of patients who had a Fontan operation
- Hyun-Jung Kim, Eun-Jung Bae, Jung-Il Noh, Jung-Yun Choi, Yong-Su Yun, Wong-Hwan Kim, Jung-Yeul Lee, Yong-Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(1):40-46. Published online January 15, 2007
-
Purpose : This study assessed the long term survival rate and long term complications of patients who had a modified Fontan operation for functionally univentricular cardiac anomaly. Methods : Between June 1986 and December 2000, 302 patients with a functional single ventricle underwent surgical interventions and were followed up until February 2006. The mean follow-up period was 8.3?.3 years (range 3.5-18... -
- Review Article
- Regionalization of neonatal care and neonatal transport system
- Jong Beom Sin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(1):1-6. Published online January 15, 2007
-
In the United States, The concept of designation for hospital facilities that care for newborn infants according to the level of complexity of care provided was first proposed in 1976. The extent of perinatal health care regionalization varies widely from one area to the other. facilities that provide hospital care for newborn are classified into three categories on the basis... -
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and risk factors for staphylococcal infections in neonatal intensive care unit
- Min Kook Chung, Jeong Ho Choi, Jin Keun Chang, Sung Hoon Chung, Chong Woo Bae, Sung Ho Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(12):1287-1295. Published online December 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The importance of staphylococcal infections in NICU has been emphasized in terms of increased resistant strains and increased incidence of morbidity and mortality. In this study, we inrestignted the clinical characteristics and risk factors for staphylococcal infections, and looked into sensitivity trends of antibiotics in the era of a high rate of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in our... -
- Changes of neurodevelopmental outcomes and risk factors of very low birth weight infants below 1,500 g, in the last 10 years
- Se Kyu Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1050-1055. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : As a result of advances in neonatal intensive care and perinatal care, neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infant(VLBWIS) is expected to lead to improvement. The aim of this study was to report neurodevelopmental outcomes and risk factors of neurologic impairment of very low birth weight infants during the past 10 years. Method : We performed a retrospective... -
- Review Article
- Early recognition of high risk factors of acute abdominal pain in children
- Jin-Bok Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(2):117-128. Published online February 15, 2006
-
Non-traumatic acute abdominal pain in children presents a diagnostic dilemma. Numerous disorders can cause abdominal pain. Although many etiologies are benign, some require a rapid diagnosis and treatment in order to minimize morbidity. This review concentrates on the clinical office evaluation of acute abdominal pain in infants and children and details the clinical guideline for the diagnostic approach to imaging... -
- Original Article
- N-terminal Pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide as a Predictive Risk Factor in Fontan Operation
- Gi Young Jang, Jae Young Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Woo Sup Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(12):1362-1369. Published online December 15, 2005
-
Purpose : This study aimed to investigate the correlation between the plasma level of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide(pro-BNP) and several known risk factors influencing outcomes after Fontan operations, and to assess whether pro-BNP levels can be used as predictive risk factors in Fontan operations. Methods : Plasma pro-BNP concentrations were measured in 35 patients with complex cardiac anomalies before catheterization.... -
- Risk Factors for the Early Recognition of Cow's Milk Protein-induced Enterocolitis
- Sung Hyuk Lee, Seon Yun Choi, Byung Cheol Lee, Won Joung Choi, Byung Kyu Choe, Yeo Hyang Kim, Una Kang, Sin Kam, Jin-Bok Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):991-997. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Cow's milk protein-induced enterocolitis(CMPIE) is a symptom complex of vomiting and/ or diarrhea caused by delayed hypersensitivity and may result in serious complications. This study was undertaken to identify high risk factors to facilitate the early recognition of CMPIE. Methods : We reviewed the data of 101 patients, aged 15 to 45 days, admitted due to vomiting and/... -
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE) Colonization in Neonates
- Hwa Yun Lee, Gi Hwan Kim, Jin Su Choi, Sun Hee Kim, Young Youn Choi, Tai Ju Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):946-952. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Vancomycin-resistant enterococci(VRE) are now nosocomial pathogens in Korea. But little is known about the prevalence of stool colonization with VRE in neonates in Korea. So we studied the prevalence and risk factors of VRE colonization in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit(NICU). Methods : From January 2000 to December 2004, the medical records of 294 neonates(127 cases of VRE group... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







