Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Effect of face mask on pulmonary artery pressure during echocardiography in children and adolescents
- Alireza Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Sabri, Zohreh Sadat Navabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):161-167. Published online January 23, 2024
-
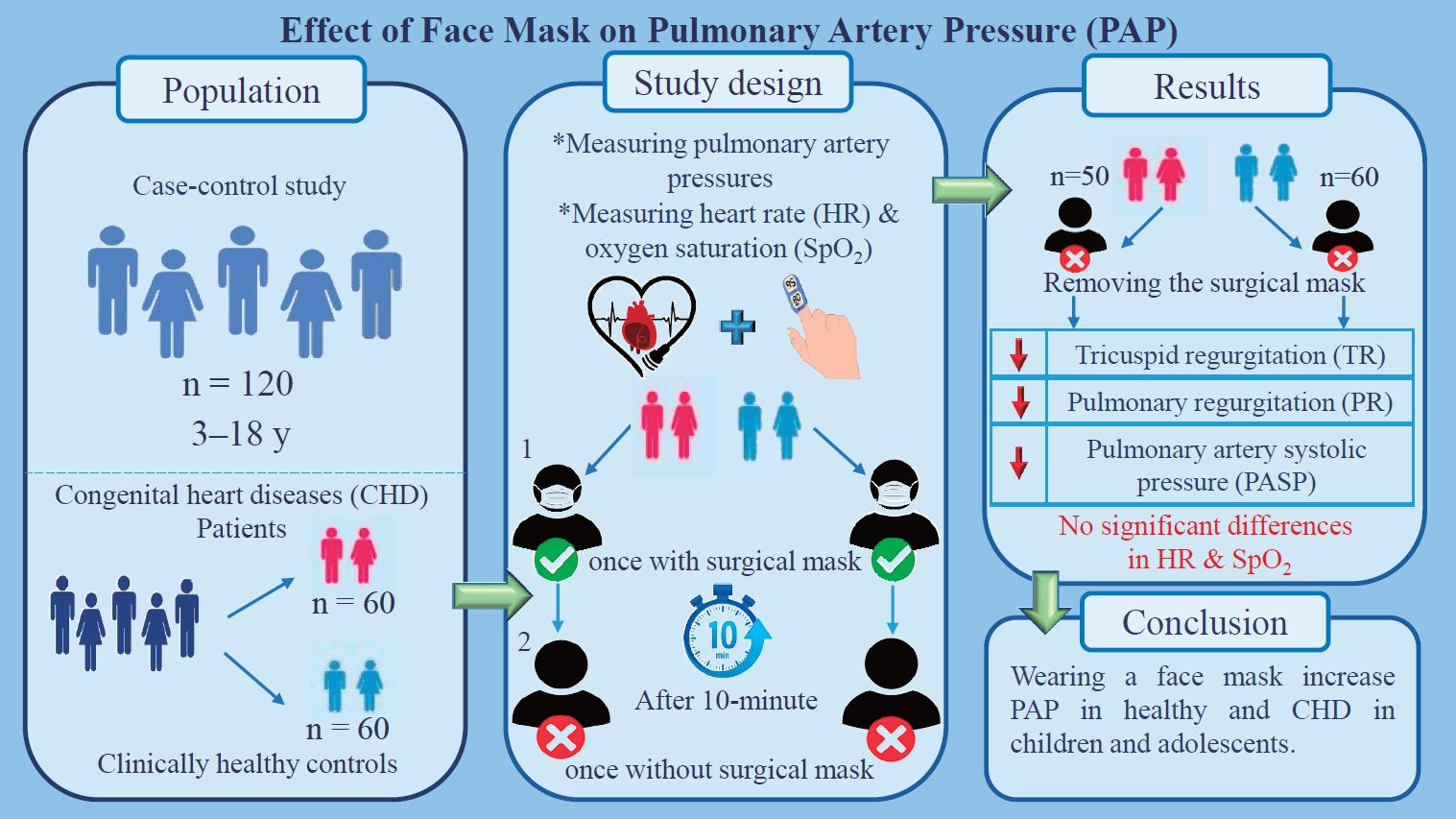
Question: Can face masks alter pulmonary pressure in children and adolescents with and without congenital heart disease?
Findings: Mask removal during echocardiography (ECHO) reduced pulmonary pressure.
Meaning: These findings suggest that face masks should be removed during ECHO in children and adolescents.
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-

Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Noninvasive markers for esophageal varices in children with cirrhosis
- Parisa Rahmani, Fatemeh Farahmand, Ghobad Heidari, Azadeh Sayarifard
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):31-36. Published online July 21, 2020
-
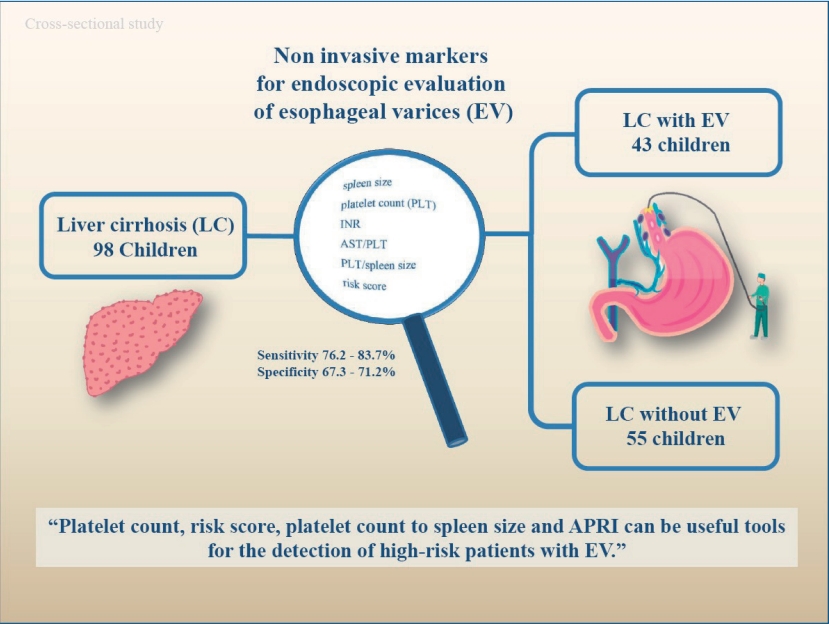
Question: Can noninvasive biomarkers identify esophageal varices among children with esophageal cirrhosis?
Finding: The spleen size, platelet count, international normalized ratio, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index, platelet count to spleen size ratio, and risk score differed significantly between the patients with and those without esophageal varices.
Meaning: These biological parameters can predict esophageal varices among pediatric patients and indicate the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Cardiology
- Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6–18 years, Iran
- Nastaran ahmadi, Seyedeh Mahdieh Namayandeh, Seyed Mahmood Sadr Bafghi, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Masoud Mirzaei, Mohammadtaghi Sarebanhassanabadi, Amir Houshang Mehrparvar, Reza Faraji, Neda Nilforoshan, Ahmad Karimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):321-328. Published online July 21, 2020
-

Question: What is the 90th, 95th, 99th percentile of blood pressure based on height as the cut point for diagnosis of hypertension in children of our province?
Finding: We used blood pressure of 456 males and 579 females in 6–18 years old in “Iranian Children and Adolescents' Psychiatric Disorders survey.
Meaning: The 90th, 95th, 99th percentiles of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in both sex based on age and 10-cm height intervals were developed in Yazd.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Placental histopathology in late preterm infants: clinical implications
- Kristina Ericksen, Joshua Fogel, Rita P. Verma
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):48-51. Published online August 19, 2019
-
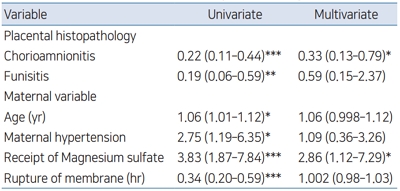
Question: Placental histopathology and its clinical implications in late preterm infants.
Finding: Placental vascular anomalies are more, and placental inflammation less common in late preterm infants compared to term. Higher maternal age, magnesium sulfate therapy and hypertension are clinical risk factors associated with late preterm delivery.
Meaning: Prevention and aggressive management of hypertension, and conception before 30 years of age might be effective in preventing late preterm births.
- Case Report
- Reninoma: a rare cause of curable hypertension
- Ji Hye Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Myung Hyun Cho, Eujin Park, Hye Sun Hyun, Yo Han Ahn, Hee Gyung Kang, Kyung Chul Moon, Il-Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):144-147. Published online October 29, 2018
-
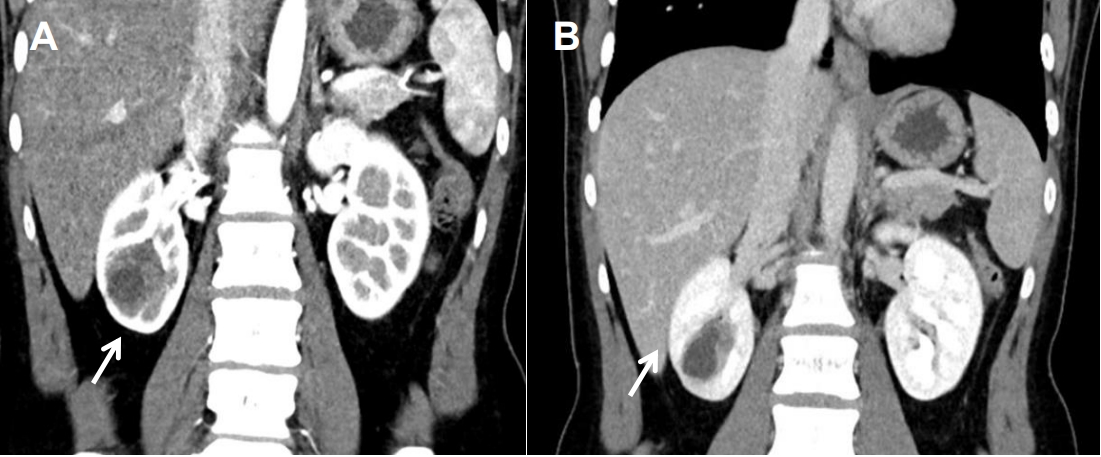
The most common type of refractory hypertension found in children is secondary hypertension, which is a potentially curable disease. Reninoma, a renin-secreting juxtaglomerular cell tumor, is a rare cause of severe hypertension that is usually diagnosed in adolescents and young adults. Surgical resection of the tumor completely cures the hypertension of patients with reninoma. The typical clinical presentation of reninoma...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Change of voltage-gated potassium channel 1.7 expressions in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):271-278. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: Abnormal potassium channels expression affects vessel function, including vascular tone and proliferation rate. Diverse potassium channels, including voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, are involved in pathological changes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Since the role of the Kv1.7 channel in PAH has not been previously studied, we investigated whether Kv1.7 channel expression changes in the lung tissue of a monocrotaline...
- Case Report
- Gastroenterology
- Intestinal duplication revealed by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- Yosra Kerkeni, Hela Louati, Mourad Hamzaoui
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(4):132-134. Published online April 23, 2018
-
We report a unique case of intestinal duplication detected on posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in a 13-year-old girl. She was admitted to the pediatric Emergency Department because of generalized seizures. Radiological assessment revealed a large, well-defined, thick-walled cystic lesion in the mid abdomen, suggestive of duplication cyst associated to a PRES. Exploration confirmed the diagnosis of ileal duplication cyst,...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Clinical characteristics of hypertensive encephalopathy in pediatric patients
- Chang Hoon Ahn, Seung-A Han, Young Hwa Kong, Sun Jun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):266-271. Published online August 14, 2017
-
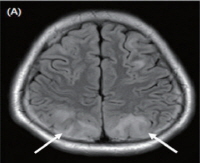
Purpose The aim of this study was to assess the clinical characteristics of hypertensive encephalopathy according to the underlying etiologies in children.
Methods We retrospectively evaluated 33 pediatric patients who were diagnosed as having hypertensive encephalopathy in Chonbuk National University Children's Hospital. Among the patients, 18 were excluded because of incomplete data or because brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was not performed. Finally,...
- Case Report
- Cardiology
- Idiopathic midaortic syndrome with malignant hypertension in 3-year-old boy
- Kyung Jin Ahn, Ja Kyoung Yoon, Gi Beom Kim, Bo Sang Kwon, Eun Jung Bae, Chung Il Noh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S84-S87. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Midaortic syndrome (MAS) is a rare vascular disease that commonly causes renovascular hypertension. The lumen of the abdominal aorta narrows and the ostia of the branches show stenosis. MAS is associated with diminished pulses in the lower extremities compared with the upper extremities, severe hypertension with higher blood pressure in the upper rather than lower extremities, and an abdominal bruit....
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- The effect of sildenafil on right ventricular remodeling in a rat model of monocrotaline-induced right ventricular failure
- Hyun Kyung Bae, Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):262-270. Published online June 30, 2016
-
Purpose Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) leads to right ventricular failure (RVF) as well as an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance. Our purpose was to study the effect of sildenafil on right ventricular remodeling in a rat model of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced RVF.
Methods The rats were distributed randomly into 3 groups. The control (C) group, the monocrotaline (M) group (MCT 60 mg/kg) and the...
- Correlation between the morning hypertension on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and the left ventricular mass in children
- Hyun Jung Kim, Kyung Hee Kim, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(9):403-409. Published online September 30, 2014
-
Purpose Although high morning blood pressure (BP) is known to be associated with the onset of cardiovascular events in adults, data on its effects in children with hypertension are limited. Our retrospective study aimed to define the clinical characteristics of children with morning hypertension (MH) and to determine its associated factors.
Methods We reviewed 31 consecutive patients with hypertension, confirmed by the ambulatory...
- An inhibitory effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist to gene expression in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertensive rats model
- Jung Hyun Kwon, Kwan Chang Kim, Min-Sun Cho, Hae Soon Kim, Sejung Sohn, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(3):116-124. Published online March 18, 2013
-
Purpose Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α is thought to contribute to pulmonary hypertension. We aimed to investigate the effect of infliximab (TNF-α antagonist) treatment on pathologic findings and gene expression in a monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension rat model.
Methods Six-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated to 3 groups: control (C), single subcutaneous injection of normal saline (0.1 mL/kg); monocrotaline (M), single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline...
- Effect of early postnatal neutropenia in very low birth weight infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension
- Yang Hee Park, Gyung Min Lee, Jung Min Yoon, Enn Jung Cheon, Kyung Ok Ko, Yung Hyuk Lee, Jae Woo Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):462-469. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose In this study, we aimed to investigate the perinatal clinical conditions of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) focusing on the effects of early postnatal neutropenia.
Methods We reviewed the medical records of 191 VLBW infants who were born at Konyang University Hospital, between March 2003 and May 2011. We retrospectively analyzed the clinical characteristics...
- Case Report
- Bronchial compression in an infant with isolated secundum atrial septal defect associated with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Sung-Hee Park, So Young Park, Nam Kyun Kim, Su-Jin Park, Han Ki Park, Young Hwan Park, Jae Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(8):297-300. Published online August 23, 2012
-
Symptomatic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in patients with isolated atrial septal defect (ASD) is rare during infancy. We report a case of isolated ASD with severe PAH in an infant who developed airway obstruction as cardiomegaly progressed. The patient presented with recurrent severe respiratory insufficiency and failure to thrive before the repair of the ASD. Echocardiography confirmed volume overload on...
- Pulmonary hypertension due to obstructive sleep apnea in a child with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
- Hyung Soon Choi, Jeong Jin Yu, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko, In-Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):212-214. Published online June 21, 2012
-
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS) is characterized by peculiar facies, mental retardation, broad thumbs, and great toes. Approximately one-third of the affected individuals have a variety of congenital heart diseases. They can also have upper airway obstruction during sleep, due to hypotonia and the anatomy of the oropharynx and airway, which make these patients susceptible to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In our...
- Review Article
- Pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Gi Beom Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(6):688-693. Published online June 23, 2010
-
An increase in the number of preterm infants and a decrease in the gestational age at birth have resulted in an increase in the number of patients with significant bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and secondary pulmonary hypertension (PH). PH contributes significantly to the high morbidity and mortality in the BPD patients. Therefore, regular monitoring for PH by using echocardiography and B-type...
- Original Article
- Surgical outcome of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension secondary to left-to-right shunt lesions
- Cha Gon Lee, Su In Jeong, June Huh, I-Seok Kang, Heung Jae Lee, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae Gook Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):195-202. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Despite recent advances in pulmonary hypertension management and surgery, appropriate guidelines remain to be developed for operability in congenital heart disease with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH). Our aim was to evaluate clinical outcomes of patients with severe PAH who underwent surgical closure of left-to-right shunt lesions (LRSL) on the basis of pulmonary reactivity. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed 21... -
- Case Report
- The effect of perioperative inhaled iloprost on congenital heart disease with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Su Nam Kim, Deok Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):93-96. Published online January 15, 2010
-
A 47-year-old male patient in whom atrial septal defect (ASD) had been diagnosed 15 years previously was admitted for cardiac catheterization. He had definite cyanotic lips and nail beds and severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). He had received medical treatment only for the last few years after being diagnosed with Eisenmenger syndrome. After cardiac catheterization, he received iloprost inhalation therapy... -
- Original Article
- Left ventricular dysfunction measured by tissue Doppler imaging and strain rate imaging in hypertensive adolescents
- Hye Mi Ahn, Sun Ok Jung, Jung Hyun Kwon, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):72-79. Published online January 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and impaired diastolic function may occur early in systemic hypertension. Diastolic dysfunction is associated with increased cardiovascular risk. Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)-derived tissue velocity and strain rate are new parameters for assessing diastolic dysfunction. The aim of this study is to determine whether TDI and strain rate imaging (SRI) would improve the ability to... -
- Review Article
- Neonatal respiratory distress: recent progress in understanding pathogenesis and treatment outcomes
- So Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):1-6. Published online January 15, 2010
-
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), and persistent pulmonary hypertension (PPHN) are the three most common disorders that cause respiratory distress after birth. An understanding of the pathophysiology of these disorders and the development of effective therapeutic strategies is required to control these conditions. Here, we review recent papers on the pathogenesis and treatment of neonatal... -
- Treatment of chronic kidney disease in children
- Joo Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1061-1068. Published online October 15, 2009
-
The treatment of pediatric patients with chronic renal disease comprises management of nutritional imbalance, fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disturbances, mineral bone disease, anemia, hypertension, and growth retardation. The treatment also includes administration of appropriate renal replacement therapy, if required. Adequate dietary intake of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins and caloric intake must be encouraged in such patients to ensure proper growth... -
- Hypertension in children and adolescents
- Jo Won Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(7):745-751. Published online July 15, 2009
-
Hypertension is a major risk factor for myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality in adults; its treatment reduces the risk of cardiovascular events. In recent times, attention is being paid to monitoring of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood. Childhood hypertension is associated with hypertension in later life, and early intervention is important. In the Korean socioeconomic background, a rapid... -
- Original Article
- Effect of endothelin receptor blockade on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
- Kyoung Ah Lim, Jung Yun Shim, Sang Ho Cho, Kwan Chang Kim, Jae Jin Han, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(6):689-695. Published online June 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To examine the effect of bosentan, a dual endothelin receptor (ER) antagonist, on the development of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats by especially focusing on the pulmonary vascular morphology changes. Methods : Sprague-Dawley rats were treated as follows: controls received a subcutaneous saline injection, MCT-treated rats received a subcutaneous MCT injection, and bosentan-treated rats received a MCT... -
- A study of the development of macrovascular complications and factors related to these complications in young adults with childhood/adolescence-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Min Jae Kang, Joo Hwa Kim, Hye Rim Chung, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang, You Yeh Kim, Seon Mi Jin, Chung Il Noh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(2):220-226. Published online February 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Macrovascular complications are the main cause of mortality in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). The purpose of this study was to clarify the presence of early vascular changes and to assess the risk factors of macrovascular complications in young adults with T1DM diagnosed in childhood and adolescence. Methods : Seventy-two patients (23.9¡¾2.4 years) with T1DM diagnosed before 18 years... -
- Serum level of the adiponectin and adiponectin I164T polymorphism in hypertensive adolescents
- Jung Ah Lee, Joo Hyun Gil, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(2):187-193. Published online February 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Adiponectin is a molecule that plays an important role in the metabolic syndrome. In addition, its concentration is known to be decreased in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and coronary artery disease. Although a relationship between hypertension and serum adiponectin concentrations has been reported by several authors, such findings continue to be debated. We investigated whether hypoadiponectinemia is related... -
- Angiotensinogen gene M235T polymorphism as a predictor of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive adolescents
- Joo Hyun Gil, Jung Ah Lee, Eun Young Park, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):36-43. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has been demonstrated to play a major role in regulating blood pressure. Therefore, components of the RAS are likely candidate genes that may predispose an individual to essential hypertension and cardiovascular complications. Among them, the M235T polymorphism of the angiotensinogen gene has been speculated to be associated with elevated circulating angiotensinogen concentrations and essential... -
- Prevalence of obesity, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia in Gunpo children of low economic status
- Kyung Hee Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1310-1314. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Purpose : This study aimed to assess the prevalence of obesity, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia in children from low-income families in Gunpo and to evaluate whether economic status affects the prevalence of obesity. Methods : Between October 2007 and March 2008, 341 children (167 girls and 174 boys; age, 6 to 13 years) were enrolled in this study. All these children came... -
- Normal blood pressure values and percentile curves measured by oscillometric method in children under 6 years of age
- Jin A Sohn, Hee Sook Lee, Kyoung Aha Lim, So Young Yoon, Jo Won Jung, Nam Su Kim, Chung Il Noh, Soon Young Lee, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(9):998-1006. Published online September 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Hypertension is defined as average systolic blood pressure and/or diastolic blood pressure that is ≥95th percentile for gender, age, and height on ≥three occasions. Knowing that blood pressure values increase in children as they grow older, the purposes of this study were to measure blood pressure by an oscillometric device and to determine normal values and percentile curves... -
- Evaluating and managing hypertension in children: a survey of Korean cardiologists and nephrologists
- Eun Hee Lee, Hyung Eun Yim, Gi Young Jang, Kee Hwan Yoo, Chang Sung Son, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(9):992-997. Published online September 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Hypertension (HTN) is no longer an exclusively adult disease; the prevalence of pediatric HTN is increasing. To understand the evaluation and treatment of childhood HTN in Korea, we investigated, via a questionnaire, how hypertensive children are currently assessed and managed by pediatric cardiologists (CA) and nephrologists (NE). Methods : We surveyed 82 pediatric CA and 77 NE, regarding... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94nd percentilePowered by







