Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Knowledge and perceptions of kangaroo mother care among health providers: a qualitative study
- Hadi Pratomo, Tiara Amelia, Fatmawati Nurlin, Asri C. Adisasmita
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):433-437. Published online July 21, 2020
-
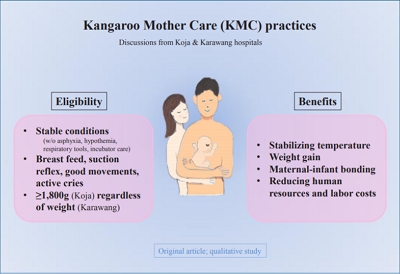
Question: What are health providers’ knowledge and perceptions of Kangaroo mother care (KMC)?
Finding: Health providers’ knowledge of KMC was sufficient; however, some of their perceptions about it could create barriers to the successful implementation of hospital KMC programs.
Meaning: Health providers’ perceptions about KMC should be considered to ensure successful KMC implementation. Locally designed on-site training programs could overcome the challenges.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- How can neurological outcomes be predicted in comatose pediatric patients after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest?
- Hyo Jeong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):164-170. Published online October 10, 2019
-

The prognosis of patients who are comatose after resuscitation remains uncertain. The accurate prediction of neurological outcome is important for management decisions and counseling. A neurological examination is an important factor for prognostication, but widely used sedatives alter the neurological examination and delay the response recovery. Additional studies including electroencephalography, somatosensory-evoked potentials, brain imaging, and blood biomarkers are useful for...
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Assessment of interhospital transport care for pediatric patients
- Krittiya Chaichotjinda, Marut Chantra, Uthen Pandee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):184-188. Published online August 29, 2019
-

Background: Many critically ill patients require transfer to a higher-level hospital for complex medical care. Despite the publication of the American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines for pediatric interhospital transportation services and the establishment of many pediatric transport programs, adverse events during pediatric transport still occur.
Purpose: To determine the incidence of adverse events occurring during pediatric transport and explore their complications...
- Emergency Medicine
- A nationwide study of children and adolescents with pneumonia who visited Emergency Department in South Korea in 2012
- Chang Hyu Lee, Youn Kyoung Won, Eui-Jung Roh, Dong In Suh, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):132-138. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose Acute respiratory infection, particularly pneumonia, is the most common cause of hospitalization and death among children in developing nations. This study aimed to investigate the characteristics of children and adolescents with pneumonia who visited Emergency Department (ED) in South Korea in 2012.
Methods We analyzed National Emergency Department Information System (NEDIS) records from 146 EDs in South Korea for all pediatric patients...
- Parental satisfaction with pediatric emergency care: a nationwide, cross-sectional survey in Korea
- Hye Young Jang, Young Ho Kwak, Ju Ok Park, Do Kyun Kim, Jin Hee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):466-471. Published online December 22, 2015
-
Purpose This study attempted to examine parental satisfaction with pediatric emergency care (PEC) in Korea and investigate the features influencing overall satisfaction.
Methods A nationwide, cross-sectional survey was conducted among parents who had taken their children to an Emergency Department (ED) in the three years prior to the study. A 21-item, structured questionnaire was administered to the parents through a web-based system. Participants'...
- Review Article
- Regionalization of pediatric emergency care in Korea
- Do Kyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(12):477-480. Published online December 31, 2011
-
In order to care for an ill or injured child, it is crucial that every emergency department (ED) has a minimum set of personnel and resources because the majority of children are brought to the geographically nearest ED. In addition to adequate preparation for basic pediatric emergency care, a comprehensive, specialized healthcare system should be in place for a critically-ill...
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and outcomes among pediatric patients hospitalized with pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 infection
- Eun Lee, Ju-Hee Seo, Hyung-Young Kim, Shin Na, Sung-Han Kim, Ji-Won Kwon, Byoung-Ju Kim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):329-334. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Purpose The purpose of this article is to describe the clinical and epidemiologic features and outcomes among children hospitalized with pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 infection.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the charts of hospitalized pediatric patients (<18 years) diagnosed with pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 infection by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction at a tertiary hospital in Seoul, Korea, between September 2009 and February 2010.
Results A total...
- Clinical analysis of febrile infants and children presenting to the pediatric emergency department
- Byeong Gon Kwak, Hyun Oh Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(8):839-844. Published online August 15, 2006
-
Purpose : We studied clinical patterns of the febrile infants and children presenting to the Pediatric Emergency Department(ED) in the general pediatric population. Method : We analyzed 1,764 infants and children who had a history of measured body temperature of 38.3℃ or higher, before or after arrival at Pediatric ED of Ilsan Paik Hospital from September 2004 to August 2005.... -
- Incidence and Risk Factors of Rehospitalization with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Premature Infants
- Eun Ah Lee, Jea Heon Jeong, Seung Taek Yu, Chang Woo Lee, Hyang Suk Yoon, Do Sim Park, Yeon Kyun Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):510-514. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We performed this study to evaluate the risk of rehospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus(RSV) infection among premature infants discharged from a neonatal intensive care unit(NICU). Methods : We performed a retrospective study for rehospitalization for RSV infection and risk factors among premature infants who were admitted to NICU and discharged between May 2001 and April 2003 in Wonkwang... -
- Comparison of Rehospitalization during the First Year of Life in Normal and Low Birth Weight Infants Discharged from NICU
- Sae Ah Min, Myung Won Jeon, Sun Hee Yu, Oh Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(12):1503-1511. Published online December 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Although the short- and long-term outcomes of low birth weight(LBW) neonatal intensive care unit(NICU) survivors have been extensively studied, much less information is available for normal birth weight(NBW) infants(greater than 2,500 gm) who require NICU care. Methods : We retrospectively examined the neonatal hospitalizations and one year health status of 302 NBW and 131 LBW admissions to our... -
- Rehospitalization of Low-birth-weight Infants Who Were Discharged from NICU
- Kyung Dan Choi, Young Suk Chae, Oh Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(4):484-490. Published online April 15, 1999
-
Purpose : We tried to compare normal term infants with low-birth-weight infants discharged from NICU by evaluating morbidity. So we studied rates of rehospitalization, reasons for rehospitalization and neonatal risk factors that affect rehospitalization of normal term infants and low-birth-weight infants discharged from NICU. Methods : This study was performed on 217 low-birth-weight infants discharged from NICU and 126 normal term... -
- Comparison of Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Nosocomial and Community-Acquired Pathogens in Children of Medium-Sized Hospital
- Kil Soo Joung, Jae Kook Cha, Kon Hee Lee, Hye Sun Yoon, Wonkeun Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(11):1537-1543. Published online November 15, 1997
-
Purpose : We evaluated the identification and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens in children of the medium-sized hospital. Methods : The 357 bacterial strains isolated from Pediatric department of Dongsan Sacred Heart Hospital were examined the species identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test during the period of March to October 1996. Results : Fifty three strains(15%) of 357 strains were nosocomial pathogens. A... -
- Assessment by Question-Naire of Disease Status of the Pupils in Two Primary Schools in Seoul
- Jae Kyung Choi, Nam Soo Kim, Soo Jee Moon, Hahng Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(7):994-1001. Published online July 15, 1993
-
We studied the disease status by question-naire in Seoul of the pupils in two primary schools on May, 1991 and carried out statistical analysis of their results. The following results were observed: 1) Total number of answered pupil was 2330;1103 were male and 1227 were female and the ratio of male to female was 1:1.1. Average age was 9.27 years. 2) Number of... -
- Statistical Analysis of Patients in Seoul National University Children's Hospital (1985~1988).
- Kyung Mo Kim, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(6):744-753. Published online June 30, 1990
-
Statistical analysis of outpatients and inpatients from 1985 to 1988 was assessed with aims to have an overal grasp of patterns and trends of childhood diseases at Seoul National University Children, s Hospital. 1) Number of outpatient visits were totally 458,390 with annual number of visits of 144,754 and average daily number of 461, including 241 visits in Department of Pediatrics. 2) Number of patients at Eemergency... -
- Studies in Anemia of Infancy and Children During Hospitalization.
- Tae Kyu Hame, Jeong Sam Jeon, Kyu Chul Choi, Yong Mook Choi, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(10):1338-1345. Published online October 31, 1988
-
This investigational work-ups were studied in 303 cases of anemia including 45 cases of severe degree anemia retrospectively among total inpatients of 3387 in the Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University Hospital for recent two years form Mar. 1985 to Feb. 1987. The results were obtained as follows; 1) The orerall incidence of anemia among total inpatients(3387) was 8.9%(303 case). The incidence of severe anemia was... -
- Clinical Observation of Tricuspid Atresia.
- Myung Hyun Lee, Yong Soo Yoon, Chang Yee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(8):751-759. Published online August 31, 1983
-
Twenty one cases of triciispid atresia which were diagnosed at the department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital during past twelve years and eleven months were reviewed and analysed. The results were as follows. 1) There were 8 males and 13 females. According to anatomical classification, 15 cases were in type 1, 4 cases in type 표 and 2 cases in type... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







