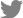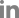Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 64(12); 2021 |
|
Abstract
Background
Infantile colic (IC) is excessive crying in otherwise healthy children. Despite vast research efforts, its etiology remains unknown.
Purpose
Most treatments for IC carry various side effects. The collection of evidence may inform researchers of new strategies for the management and treatment of IC as well as new clues for understanding its pathogenesis. This review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and possible mechanisms of probiotics for mananaging IC.
Methods
Ten papers met the study inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the meta-analysis was conducted using Review Manager (RevMan) software and a random-effects model.
Graphical abstract
Infantile colic (IC) is a common problem in infancy that induces excessive crying in infants during the first few months of life [1,2]. IC is characterized by excessive crying at least 3 hours a day on at least 3 days a week for the duration of about 3 weeks leading to parental exhaustion, stress, anxiety, and depression [3,4]. The symptoms of IC peak at 6 weeks and disappears in the 12 weeks of age [5].
Previously studies have indicated IC follows a circadian rhythm of pain starting in the evening [6] also the prevalence of colic follow an equal pattern between male and female infants [7]. The pathogenesis of IC is not well understood. This condition is described as a multifactorial syndrome [8]. There are some options included in the aetiology of IC such as food allergies to milk proteins, an excessive amount of gas in the intestinal tract and intestinal hormones abnormalities. Recently some studies have declared the role of dysbiosis of microbiota, maternal smoking, and hormone alterations as well as gastrointestinal inflammation (GII) for the development of colic [9-11]. Some studies also indicated a correlation between parental issues and IC such as postpartum depression, parental anxiety, stressful pregnancies, dissatisfaction with the sexual relationship, negative experiences during childbirth, poor parental skills, and dysregulation of gut-brain axis [7]. the global incidence of IC is about 20% [12]. This condition makes one in 6 families to consult a healthcare system about the problem of excessive crying [13]. Still, there is not any kind of approved medications to fix this problem for instance simethicone failed to show superior characteristics over placebo [14,15]. Other studies also have shown promising effects of Dicyclomine hydrochloride in the treatment of IC but the incidence of side effects caused it to be contraindicated in infants [16].
Very low-quality shreds of evidence describe some other options for the treatment of this condition such as Cimetropium bromide, or Herbal agents But due to the lake of powerful evidence their administration for IC is not approved comprehensively [17]. Another option for the treatment of IC may be probiotic supplementation. Probiotics are nonpathogenic live strains of bacteria that when administrated in adequate amounts exert beneficial effects on the host. Prebiotics are substances that promote the growth of probiotic bacteria playing a vital role in the modulation of the gut microbiome a synbiotic is a combination of synergistically acting probiotics and prebiotics [18,19]. probiotics consist mostly strains of the genera Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, additionally, strains of Bacillus, Pediococcus and some yeasts can be introduced as suitable candidates. These strains together play an important role in the protection of the host against pathogen microorganisms and also host's immune system strengthens additionally in the maintenance of the intestinal microbial balance as well as anti-inflammatory responses [20,21].
Studies also revealed that low-grade systemic inflammation may be another important etiological factor for IC which is covered by other factors leading to being neglected [11].
Previous studies declared about increased levels of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) as well as interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the blood of patients experiencing functional gastrointestinal disorders when compared to control group [22,23].
Darkoh et al. [24] in a study showed significantly higher levels of inflammatory cytokines such as Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), IL-1β, and TNF-α in the people experiencing gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome moreover the concentration of chemokines such as monocytes chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β), and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 was significantly higher in the patients experiencing gastrointestinal disorders. They also revealed that anti-inflammatory cytokines found to be lower in the patients experiencing gastrointestinal disorders all of them in comparison to control group.
Calprotectin a marker of colonic inflammation is increased in infants experiencing colic [25]. Another study revealed that forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) a member of the forkhead transcription factor family is decreased in colicky infants that are another indicator of inflammation [26,27].
Based on the role of inflammation in functional gastrointestinal disorders especially colic it may be hypnotized that reducing inflammation would be a treatment strategy for IC. The present study aims to evaluate the role of probiotics as a treatment option for IC with a brief description of anti-inflammatory roles.
The studies were included if they were qualified based on the following criteria: (1) expressed a randomized controlled trial (RCT), (2) consisted of a control group and a clinical cohort and the clinical cohort was based on the consumption of probiotics, (3) the scales were described as mean±standard deviation (SD), (4) the time course for the report of crying time was minute/day, (5) accessibility to the full text, and (6) published in a scientific journal.
The studies were excluded if they: (1) did not qualify based on our inclusion criteria; (2) the report of crying time was not in minute/day; (3) the full text of paper was not accessible or the paper was not published in a scientific journal; (4) results were not expressed as means±SDs.
This review includes data about the effectiveness of probiotics for the management of IC as well as the role of inflammation in IC and probiotics with anti-inflammatory properties as a therapeutic option for treatment and control of IC until June 10, 2020.
Scientific databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, Science Direct, Scopus, and Google Scholar were used.
Keywords such as infantile colic, probiotic strains, anti-inflammation, inflammation, cytokines, gastrointestinal inflammation, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-8, dysbiosis, gut microbiome, fecal calprotectin (FC), breast-fed infants, formula-fed infants, colic symptoms, and daily crying as well as their combinations were used. Finally, about 167 articles from 1954–2020 were found that after qualification based on the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria 10 papers were included in our meta-analysis. the data for meta-analysis were extracted using a form collection of the dose regimen outcome and the other relative data (Table 1). The articles whose language was not English and the full text was not accessible were excluded.
The analysis was performed using the Review Manager (RevMan) Version 5.4. (The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Nordic Cochrane Center, Copenhagen, Denmark). the study outcome variables were described as standard mean differences (SMD) and a random effect based on the heterogeneity between the studies was chosen. we also used I2 for evaluation of heterogeneity between the studies If the I2 was ≥50%, the result was considered to exhibit a significant heterogeneity, and the specific model for evaluation of parameters was the random effect model. The risk of bias for each of the RCTs was evaluated using the Cochrane “risk of risk” assessment tool based on the author's judgments.
A PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram shows the process in which the studies were included for our meta-analysis a total of 126 studies were screened and after qualification based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 10 papers (including 367 intervention cases and 345 controls, Table 1) were entered the meta-analysis (Fig. 1).
The risk of bias among the studies in the meta-analysis using the Cochrane “risk of risk” assessment tool was evaluated based on the author's judgment and the results are presented in Fig. 2. As it is obvious the risk of bias among the studies was relatively low. all the studies used probiotic as an intervention and placebo as the control group. In one of the studies, the intervention was not blinded. All other studies were randomized and the intervention was blinded properly.
As it is shown in Fig. 3, the meta-analysis revealed that probiotics effectively reduce the main symptom of IC that is excessive crying (SMD=-1.98; 95% confidence interval [CI], -2.74 to -1.22).
In the present study, we investigated the efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of IC our results showed that probiotics can effectively reduce excessive crying in colicky infants the results of our meta-analysis showed a significant effect of probiotics for the treatment and management of IC (SMD=-1.98; 95% CI, -2.74 to -1.22).
Evaluation of the risk of bias between the studies showed quite a low risk of bias between the included studies. A random model was chosen for the assessment that’s why the included studies were different in some factors such as age, duration of treatment, and the dose of intervention. It would be more reliable to use a random effect in such a situation [36].
Skonieczna-Żydecka et al. [37] in a meta-analysis showed the efficacy of probiotics for the management of IC (MD=-2.012; 95% CI, -2.763 to -1.261).
Another study conducted to evaluate the efficacy of probiotics for reduction of crying time showed that after 4 weeks of treatment probiotics significantly reduced the crying time (weighted mean difference [WMD]=-56.32; 95% CI, -89.49 to -23.16; P=0.001) [38]. Sung et al. [39] in a study based on the meta-analysis declared that probiotics effectively reduce the crying time in colicky infants (MD=-67.72; 95% CI, -99.79 to -35.64).
A meta-analysis composed of 32 RCTs and 2,242 patients showed a superior effect for probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 when compared to other treatments (WMD, -51.3; 95% CI, -72.2 to -30.5]; P=0.0001) [40]. The results of these studies are in concordance with our studies.
Inflammation is a physiologic response protecting cells from various injuries or infections that terminates automatically using endogenous or exogenous anti-inflammatory agents leading to hemostasis in various tissues and organs but when this regulation disrupts the result is uncontrolled inflammation is associated with pathologic conditions especially in the gastrointestinal tract [41,42]. Inflammation remarked by increased FC is associated with IC meanwhile decreased crying is observed in infants with lower levels of FC [25,43,44]. But some studies also failed to show a statistically significant correlation between fussing, crying, and FC [4,45].
Researches declared that FC may be influenced through the various source of infantile feedings such as formula or breastfeeding. Formula-fed infants usually indicate lower levels of FC but FC is increased in breast-fed infants, after all, some studies indicated that regardless of the source of feeding increased FC is associated with IC [25,26,46]. FC is increased in various inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases and can be used for assessment of the inflammatory situation in these patients also some other studies expressed that FC is an indication of granulocyte migration through the gut wall [47-49]. Increased intestinal permeability is found in various inflammatory situations in the gastrointestinal tract and the studies have observed a significant correlation between Calprotectin and intestinal permeability as a consequence of transepithelial granulocytes migration and inflammation [50]. There are some studies about absorption of macromolecules during IC indicating increased intestinal permeability during this situation these may reflect inflammatory situations during colic [51-54].
IC also induces alterations in other components of immune system profile such as MIP-1β, MCP-1/CCL2, and IL-8 that were significantly higher in the serum of infants experiencing colic additionally the serum concentration of TNF-α looks to be higher in the colicky infants notably indicating a systemic inflammation involved in it [11,55-57].
As we all know immune system composed of 2 major components including innate and adaptive immune systems that probiotics can exert various effects in both of them, this may inform about the role of probiotics in inflammation that is shown in previous studies too [58-61].
Probiotics are well known for their role in inflammation partly due to their effect to reduce the FC and/or fecal lactoferrin indicated by different studies [26,62,63].
Santas et al. [64] showed that treatment with probiotics Pediococcus pentosaceus CECT 8330 and Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7894 is associated with increased IL-10 production along with the significant reduction of crying time in infants with excessive crying. As it is obvious we all know the anti-inflammatory roles of IL-10 in the pathogenesis of various diseases [65].
Administration of L. reuteri DSM 17938 significantly increased the values of Foxp3+ T cells in the ileum besides this probiotic decreased the percentage of these cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes in a rat model of Necrotizing enterocolitis [66].
Additionally, this probiotic strain also reduced the ratio of retinoid-related orphan receptor-γ/Foxp3 messenger RNA levels due to significant increment of Foxp3 mRNA levels leading to the significant reduction of crying time in colicky infants as a result of modulation of T cells functions [26].
Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are known to be associated with maintenance of gut homeostasis, control of inflammation, inducing tolerance and also anti-inflammatory properties [67,68]. These pieces of evidence also highlight the immunomodulatory/anti-inflammatory roles of probiotics, especially in IC.
L. reuteri DSM17938 administration at a dose of 108 colony-forming unit in 28 days significantly increased the CC-chemokine receptor 7 in infants whose crying time was reduced. CC-chemokine receptor 7 is a homeostatic chemokine receptor that modulates leukocyte trafficking, induces and also silences inflammation between the peripheral tissues and the lymphoid tissue [30,69].
The efficacy of probiotics for management of IC is also summarized in the Table 2.
Administration of probiotics also have shown anti-inflammatory effects in other models of inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders for instance: Liu et al. [66] performed a study on probiotics all of which revealed anti-inflammatory effects through various approaches for instance: L. reuteri strains (ATCC PTA 4659, 5289, and 6475) significantly reduce Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) induced IL-8 production in IPEC-J2 (intestinal porcine enterocytes) cell line (obtained from the jejunal epithelium of a neonatal piglet). Incubation of rat intestinal epithelial cell line iec-6 (intestinal epithelioid cell) (obtained from the rat crypt) with LPS significantly increased cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1) (equivalent to IL-8) but L. reuteri strain 4659 significantly reduced CINC-1 as a marker of anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics [70]. Probiotics also exert anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. Keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC)/growth-regulated oncogene (GRO) (Cxcl1 or CINC-1) (an inflammatory indicator with similar function to human IL-8) in ileal tissues lysates were significantly increased after LPS administration in newborn rat pups but L. reuteri strains ATCC PTA4659, DSM17938, ATCC PTA 6475, and ATCC PTA 5289 significantly reduced this ratio [70]. The ratio of KC/GRO also expresses an activated Nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway which promotes the production of inflammatory cytokines. So reduced KC/GRO is proof for anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics [71]. Further investigations on the anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics result in revealing the role of probiotics on the expression of type 1 and 2 T helper (Th1 and Th2) cytokines in the rat intestine. Cytokines associated with Th1 include: IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-1β meanwhile Th2-type cytokines include IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in the rat intestine. L. reuteri strains (ATCC PTA4659, DSM17938, ATCC PTA 6475, and ATCC PTA 5289) significantly reduced the LPS-induced mRNA overexpression of IFN-γ. The levels of TNF-α or IL-1β were significantly decreased by various strains of probiotics. L. reuteri ATCC PTA 4659 and 5289 significantly decreased LPS-induced TNF-α production additionally L. reuteri DSM 17938 and ATCC PTA 6475 induce significant decrement of IL-1β. It was also observed that L. reuteri strain DSM 17938 or ATCC PTA 4659 significantly downregulates the mRNA level of IL-13 in the intestine when compared to the group treated with LPS. Inhibition of IL-4 and IL-5 overproduction due to LPS treatment was observed by L. reuteri strain DSM 17938. All of these cytokines are involved in the pathogenesis of various GIIs [70,72-74]. The results suggested above is indications of in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics too.
Increased TNF-α is associated with IC as described previously [11] meanwhile administration of specific L. reuteri strains such as ATCC PTA 6475 and ATCC PTA 5289 can decrease TNF-α production in the monocytoid THP-1 cells [61]. Lin et al. [21] in their study showed that L. reuteri strain ATCC PTA 6475 potentially decrease the LPS-induced increment of TNF-α in Monocytes and primary monocyte-derived macrophages isolated from children experiencing Crohn disease. The chemokine MCP-1/CCL2 was also reduced in macrophages of children received this strain of probiotic who were experiencing alleviation.
Scully et al. [75] in a study showed that Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 possess the ability to significantly reduce Peyer’s patch macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α) and MIP-1β secretion induced by salmonella infection that is partly due to increased Peyer’s patch CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.
Another study showed that the supplementation of ageing mice with L. acidophilus DDS-1 modulated the gut microbiome community and significantly reduced the serum levels of MIP-1β when compared to the control group [76]. As described previously increased MIP-1β in serum is associated with IC.
Two strains of probiotics L. reuteri DSM 17938 and ATCC PTA 4659 were investigated for their immunomodulatory effects in LPS-induced ileitis in rats, the results of this study showed anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics evidenced by significant downregulation of TNF-α, IL-6, toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4), and NF-κB as well as significant up-regulation of IL-10. As described previously TNF-α, IL-6, TLR-4, and NF-κB are markers of the inflammatory situation and IL-10 is a potent anti-inflammatory cytokine which all of them announce probiotics as anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agents [77]. Probiotics especially L. reuteri has shown the potency against proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α production in mice experiencing colitis [78] leading to reduced IL-8 production [79].
Another study showed that IL-10 deficient mice exhibited lower levels of colonic L. sp. And normalizing the levels of this probiotic reduce colonic mucosal adherent leading to alleviation of statues in colitis [80].
The gut microbiome is one important factor for protecting the gastrointestinal tract from various pathogenic conditions, the imbalanced gut microbiome is associated with various pathogenic situations especially colic [81,82].
Some studies also declared that dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is associated with inflammation which is observed in IC too [11,25]. The gut microbiome is known to produce some products such as short-chain fatty acids that perform anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Microbiome community in the gut also exert immunomodulatory functions not only in the gastrointestinal tract but also in wider aspects such as systemic immune disorders [83-85]. So balanced gut microbiome is an important issue in the pathogenesis of IC which should be specially taken into consideration.
There is a lot of studies about protecting the roles of probiotics against gut microbiome dysbiosis [86-88]. This also highlights the anti-inflammatory roles of probiotics in the gastrointestinal tract.
In conclusion, some specific strains of probiotics exert desirable efficacy for treatment of IC through multiple therapeutic ways including anti-inflammatory roles. Preservation of gut microbiome homeostasis is another therapeutic role accomplished by probiotics. The complicated base of IC with limitations in the treatment and diagnosis may introduce specific strains of probiotics as a new therapeutic strategy for the management of this burden.
Acknowledgments
Hereby, it would give us great pleasure to thank all researches whose articles were used in this study!
Fig. 2.
(A) Risk of bias for each randomized controlled trial included in our study: low risk of bias (+), high risk of bias (‐), unclear risk of bias (?). (B) Bar chart expressing the percent risk of bias for each included study.
Fig. 3.
Evaluation of probiotic efficacy in the treatment of infantile colic. SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom.

Table 1.
Clinical trials included in the meta-analysis
| Study | Type of study | Probiotic strain (dose) | Duration of treatment | Population and type of feeding | Age | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kianifar et al. [28] | A randomized controlled trial | Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium infantis, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and fructooligosaccharide (108 CFU/day) | 30 Days | BF infants | 15–120 Days | Significant improvement of colic symptoms in the probiotics group |
| Pärtty et al. [4] | Doubleblind placebo-controlled intervention trial | LGG (4.5 × 109 CFU/day) | 28 Days | 30 BF and FF infants | 34.8–38 Days | The parents declared about the protective role of probiotics in infantile colic but the results of the evaluation of crying time were not significantly different between placebo and probiotics group |
| Mi et al. [29] | A placebo-controlled observational randomized study | Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 (108 CFU) | 21 Days | 42 BF infants | Less than 4 months | 100% Treatment success in the probiotic group, significant reduction of mean crying time, maternal depression and significant increment of maternal satisfaction. |
| Savino et al. [30] | Randomized clinical trial | Lactobacillus reuteri DSM17938 (1×108 CFU/day) | 28 Days | 50 BF infants | <50 Days | Probiotics treatment significantly reduced crying time partly due to the increased expression of CC-chemokine receptor Meanwhile, there was no significant difference in the experimental groups in term of IL-10. |
| Gerasimov et al. [31] | Phase II randomized parallel group prospective controlled multi-center dietary study. | Lactobacillus rhamnosus 19070- 2 and Lactobacillus reuteri 12246 (125×106 CFU/day), vitamin D3 (200 IU/day), fructooligosaccharides (3.33 mg/day) | 28 Days | 168 BF infants | 4–12 Weeks | Significant reduction of crying and fussing after 28 days of probiotic administration. |
| Sung et al. [32] | Double-blind, placebocontrolled randomized trial. | Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 (1×108 CFU/day) | 30 Days | 167 BF or FF infants | <3 Months | There was not a significant difference in crying time, fecal calprotectin levels, or Escherichia coli load probiotic group cried 49 minutes more than the placebo group |
| Savino et al. [26] | A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial | Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 (1 × 108 CFU/day) | 30 Days | 87 BF infants | <12 Weeks | Significantly shorter crying time in the infants received probiotics. |
| Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) significantly increased with probiotic consumption. | ||||||
| Increased Lactobacillus and reduced fecal calprotectin were observed in the probiotic group. | ||||||
| Ashraf et al. [33] | A nonblinded randomized controlled trial | Lactobacillus reuteri (108 CFU/day) | 7 Days | 90 BF infants | 21–90 Days | Improvement of colic symptoms was associated with the probiotic consumption |
| Giglione et al. [34] | A pilot, controlled, randomized, and doubleblind study | Bifidobacterium breve B632 and BR03 (5 cc/108) | 90 Days | 60 FF and BF infants | | Significant reduction of the mean crying time in the probiotic group was observed after treatment for 3 months. |
| Baldassarre et al. [35] | A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial | Lactobacillus paracasei DSM 24733, Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 24730, Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 24735, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, Bifidobacterium longum DSM 24736, Bifidobacterium breve DSM 24732, Bifidobacterium infantis DSM 24737, and Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 24731 (5×109 CFU/day) | 21 days | 62 BF Infants | 30–90 Days | Significant reduction of crying time in comparison with the placebo as well as higher responders to treatment was observed in the probiotic group. |
| No significant difference were observed regarding bowel movements, microbiota composition or stool consistency. |
Table 2.
Anti-inflammatory properties of probiotics with efficacy proven in clinical trials
| Single strain | Anti-inflammatory marker | Dose (duration) | Probiotic combination | Anti-inflammatory marker | Dose (duration) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938* | Increased CC-chemokine receptor 7 [30], increased FOXP3 mRNA levels [26] and reduced fecal calprotectin89) | 108 CFU/day (21 and 28 days) | Lactobacillus rhamnosus 19070-2 and Lactobacillus reuteri 12246* | Reduced intestinal permeability [90] | (125×106 CFU/day) (28 days) |
| Lactobacillus reuteri (American Type Culture Collection (AT CC) str ain 55730) | - | 108 CFU/day (28 days) | Bifidobacterium lactis Bb 12 and Streptococcus thermophilus* | Reduced fecal calprotectin as well as increased fecal IgA due to Bifidobacterium lactis Bb 1291) and also maintenance of mocusal barrier and reduced intestinal permeability by Streptococcus thermophilus [92] | 107 and 106 CFU/g 240 mL of solution per day (mean±SD, 210±127) |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus HA122 | - | 1×109 twice a day (28 days) | Bifidobacterium breve B632 and BR03* | reduced TNF-α levels [93] | 5 mL/108 (90 days) |
| - | - | - | Pediococcus. pentosaceus CECT 8330 and Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7894* | Increased IL-10 production [64] | 109 CFU per day (14 days) |
| - | - | - | Lactobacillus paracasei DSM 24733, Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 24730, Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 24735, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, Bifidobacterium longum DSM 24736, Bifidobacterium breve DSM 24732, Bifidobacterium infantis DSM 24737, and Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 24731* | Normalization of intestinal integrity along with the reduced mucosal secretion of TNF-alpha and IFNgamma in the animal models of Crohn's disease [94,95] | 5×109 CFU/day (21 days) |
| - | - | - | Lactobacillus rhamnosus LCS-742 and Bifidobacterium infantis M63 | - | 107 CFU (30 days) |
| - | - | - | Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Streptococcus thermophilusm, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium infantis, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, and fructooligosaccharide* | Reduced TNF-α [96] | 108 CFU/day (30 days) |
References
3. Wessel MA, Cobb JC, Jackson EB, Harris GS, Detwiler AC. Paroxysmal fussing in infancy, sometimes called "colic". Pediatrics 1954;14:421–35.



4. Pärtty A, Lehtonen L, Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG therapy and microbiological programming in infantile colic: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatr Res 2015;78:470.


8. Romanello S, Spiri D, Marcuzzi E, Zanin A, Boizeau P, Riviere S, et al. Association between childhood migraine and history of infantile colic. JAMA 2013;309:1607–12.


10. Savino F, Clara Grassino E, Guidi C, Oggero R, Silvestro L, Miniero R. Ghrelin and motilin concentration in colicky infants. Acta Paediatr 2006;95:738–41.


11. Pärtty A, Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Infantile colic is associated with low-grade systemic inflammation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2017;64:691–5.


14. Danielsson B, Hwang CP. Treatment of infantile colic with surface active substance (simethicone). Acta Paediatr Scand 1985;74:446–50.


15. Metcalf TJ, Irons TG, Sher LD, Young PC. Simethicone in the treatment of infant colic:a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Pediatrics 1994;94:29–34.



16. Goldman MH. Dicycloverine for persistent crying in babies: dicycloverine is contraindicated in infants. BMJ 2004;328:956–7.

17. Biagioli E, Tarasco V, Lingua C, Moja L, Savino F. Pain-relieving agents for infantile colic. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;9:CD009999.


18. FAO/WHO Working Group. Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotic in food [Internet]. Ontario (Canada): FAO/WHO Working Group; 2002 [cited 2020 Feb 25]. Available from: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/en/probiotic_guidelines.pdf.
19. Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr 1995;125:1401–2.


20. Soccol CR, Vandenberghe LPdS, Spier MR, Medeiros ABP, Yamaguishi CT, Lindner JDD, et al. The potential of probiotics: a review. Food Technol Biotech 2010;48:413–34.
21. Lin YP, Thibodeaux CH, Peña JA, Ferry GD, Versalovic J. Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri suppress proinflammatory cytokines via c-Jun. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2008;14:1068–83.


22. Bashashati M, Rezaei N, Shafieyoun A, McKernan DP, Chang L, Öhman L, et al. Cytokine imbalance in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2014;26:1036–48.


23. Pike BL, Paden KA, Alcala AN, Jaep KM, Gormley RP, Maue AC, et al. Immunological biomarkers in postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. J Travel Med 2015;22:242–50.


24. Darkoh C, Comer L, Zewdie G, Harold S, Snyder N, Dupont HL. Chemotactic chemokines are important in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS One 2014;9:e93144.



25. Rhoads JM, Fatheree NY, Norori J, Liu Y, Lucke JF, Tyson JE, et al. Altered fecal microflora and increased fecal calprotectin in infants with colic. J Pediatr 2009;155:823–8.e821.


26. Savino F, Garro M, Montanari P, Galliano I, Bergallo M. Crying time and RORγ/FOXP3 expression in Lactobacillus reuteri DSM17938-treated infants with colic: a randomized trial. J Pediatr 2018;192:171–7.e171.


28. Kianifar H, Ahanchian H, Grover Z, Jafari S, Noorbakhsh Z, Khakshour A, et al. Synbiotic in the management of infantile colic: a randomised controlled trial. J Paediatr Child Health 2014;50:801–5.


29. Mi GL, Zhao L, Qiao DD, Kang WQ, Tang MQ, Xu JK. Effectiveness of Lactobacillus reuteri in infantile colic and colicky induced maternal depression: a prospective single blind randomized trial. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015;107:1547–53.


30. Savino F, Galliano I, Savino A, Daprà V, Montanari P, Calvi C, et al. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 probiotics may increase CC-chemokine receptor 7 expression in infants treated with for colic. Front Pediatr 2019;7:1–7.



31. Gerasimov S, Gantzel J, Dementieva N, Schevchenko O, Tsitsura O, Guta N, et al. Role of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (FloraActive™) 19070-2 and Lactobacillus reuteri (FloraActive™) 12246 in infant colic: a randomized dietary study. Nutrients 2018;10:1975.



32. Sung V, Hiscock H, Tang ML, Mensah FK, Nation ML, Satzke C, et al. Treating infant colic with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri: double blind, placebo controlled randomised trial. BMJ 2014;348:g2107.



33. Ashraf MW, Ayaz SB, Ashraf MN, Matee S, Shoaib M. Probiotics are effective in alleviating infantile colic; results of a randomized controlled trial held at Benazir Bhutto hospital, Rawalpindi, Pakistan. RMJ 2015;40:277–80.
34. Giglione E, Prodam F, Bellone S, Monticone S, Beux S, Marolda A, et al. The association of Bifidobacterium breve BR03 and B632 is effective to prevent colics in bottle-fed infants: a pilot, controlled, randomized, and double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2016;50:S164–7.

35. Baldassarre ME, Di Mauro A, Tafuri S, Rizzo V, Gallone MS, Mastromarino P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of a probiotic-mixture for the treatment of infantile colic: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with fecal real-time PCR and NMR-based metabolomics analysis. Nutrients 2018;10:195. 1-13.



36. Shen JM, Feng L, Feng C. Role of mtDNA haplogroups in the prevalence of osteoarthritis in different geographic populations: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2014;9:e108896.



37. Skonieczna-Żydecka K, Janda K, Kaczmarczyk M, Marlicz W, Łoniewski I, Łoniewska B. The effect of probiotics on symptoms, gut microbiota and inflammatory markers in infantile colic: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med 2020;9:1–21.

38. Xu M, Wang J, Wang N, Sun F, Wang L, Liu XH. The efficacy and safety of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for infantile colic: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One 2015;10:e0141445.



39. Sung V, Collett S, de Gooyer T, Hiscock H, Tang M, Wake M. Probiotics to prevent or treat excessive infant crying: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatrics 2013;167:1150–7.

40. Gutiérrez-Castrellón P, Indrio F, Bolio-Galvis A, Jiménez-Gutiérrez C, Jimenez-Escobar I, López-Velázquez G. Efficacy of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for infantile colic: systematic review with network meta-analysis. Medicine 2017;96:e9375–5.


41. Rahimi VB, Askari VR, Shirazinia R, Soheili-Far S, Askari N, RahmanianDevin P, et al. Protective effects of hydro-ethanolic extract of Terminalia chebula on primary microglia cells and their polarization (M1/M2 balance). Mult Scler Relat Disord 2018;25:5–13.


42. Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, et al. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017;9:7204–18.



43. Fatheree NY, Liu Y, Ferris M, Van Arsdall M, McMurtry V, Zozaya M, et al. Hypoallergenic formula with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for babies with colic: a pilot study of recruitment, retention, and fecal biomarkers. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016;7:160–70.



44. Rhoads JM, Collins J, Fatheree NY, Hashmi SS, Taylor CM, Luo M, et al. Infant colic represents gut inflammation and dysbiosis. J Pediatr 2018;203:55–61.e53.



45. Olafsdottir E, Aksnes L, Fluge G, Berstad A. Faecal calprotectin levels in infants with infantile colic, healthy infants, children with inflammatory bowel disease, children with recurrent abdominal pain and healthy children. Acta Paediatrica 2002;91:45–50.


46. Sung V, Cabana MD. Probiotics for colic—is the gut responsible for infant crying after all? J Pediatr 2017;191:6–8.


47. Røseth A, Fagerhol M, Aadland E, Schjønsby H. Assessment of the neutrophil dominating protein calprotectin in feces: a methodologic study. Scand J Gastroenterol 1992;27:793–8.


48. Røseth AG, Aadland E, Jahnsen J, Raknerud N. Assessment of disease activity in ulcerative colitis by faecal calprotectin, a novel granulocyte marker protein. Digestion 1997;58:176–80.


49. Røseth AG, Schmidt PN, Fagerhol MK. Correlation between faecal excretion of indium-111-labelled granulocytes and calprotectin, a granulocyte marker protein, in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999;34:50–4.


50. Berstad A, Arslan G, Folvik G. Relationship between intestinal permeability and calprotectin concentration in gut lavage fluid. Scand J Gastroenterol 2000;35:64–9.


51. Lothe L, Lindberg T, Jakobsson I. Macromolecular absorption in infants with infantile colic. Acta Pædiatrica 1990;79:417–21.

52. Michielan A, D’Incà R. Intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease:pathogenesis, clinical evaluation, and therapy of leaky gut. Mediators Inflamm 2015;2015:1–11.


53. Fukui H. Increased intestinal permeability and decreased barrier function: does it really influence the risk of inflammation? Inflamm Intest Dis 2016;1:135–45.



54. Hietbrink F, Besselink MGH, Renooij W, de Smet MBM, Draisma A, van der Hoeven H, et al. Systemic inflammation increases intestinal permeability during experimental human endotoxemia. Shock 2009;32:374–8.


55. Carr MW, Roth SJ, Luther E, Rose SS, Springer TA. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994;91:3652–6.



56. Xu LL, Warren MK, Rose WL, Gong W, Wang JM. Human recombinant monocyte chemotactic protein and other C-C chemokines bind and induce directional migration of dendritic cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol 1996;60:365–71.


57. Maurer M, von Stebut E. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004;36:1882–6.


58. Wu HJ, Wu E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012;3:4–14.



60. Geremia A, Biancheri P, Allan P, Corazza GR, Di Sabatino A. Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13:3–10.


61. Jones SE, Versalovic J. Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteribiofilms produce antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory factors. BMC Microbiol 2009;9:35. 1-9.



62. Fallahi G, Motamed F, Yousefi A, Shafieyoun A, Najafi M, Khodadad A, et al. The effect of probiotics on fecal calprotectin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Turk J Pediatr 2013;55:475–8.

63. Lai HH, Chiu CH, Kong MS, Chang CJ, Chen CC. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei: effective for managing childhood diarrhea by altering gut microbiota and attenuating fecal inflammatory markers. Nutrients 2019;11:1150.



64. Santas J, Fuentes MC, Tormo R, Guayta-Escolies R, Lázaro E, Cuñé J. Pediococcus pentosaceus CECT 8330 and Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7894 show a trend towards lowering infantile excessive crying syndrome in a pilot clinical trial. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2015;6:458–66.
65. Couper KN, Blount DG, Riley EM. IL-10: the master regulator of immunity to infection. J Immunol 2008;180:5771.


66. Liu Y, Fatheree NY, Dingle BM, Tran DQ, Rhoads JM. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 changes the frequency of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the intestine and mesenteric lymph node in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS One 2013;8:e56547.



67. Tran DQ, Ramsey H, Shevach EM. Induction of FOXP3 expression in naive human CD4+FOXP3 T cells by T-cell receptor stimulation is transforming growth factor-beta dependent but does not confer a regulatory phenotype. Blood 2007;110:2983–90.


68. Meyer zu Hörste G, Cordes S, Mausberg AK, Zozulya AL, Wessig C, Sparwasser T, et al. FoxP3+ regulatory T cells determine disease severity in rodent models of inflammatory neuropathies. PLoS One 2014;9:e108756.



69. Noor S, Wilson EH. Role of C-C chemokine receptor type 7 and its ligands during neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 2012;9:77.



70. Liu Y, Fatheree NY, Mangalat N, Rhoads JM. Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri strains differentially reduce intestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010;299:G1087–96.



71. Rahimi VB, Shirazinia R, Fereydouni N, Zamani P, Darroudi S, Sahebkar AH, et al. Comparison of honey and dextrose solution on post-operative peritoneal adhesion in rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 2017;92:849–55.

72. Mannon P, Reinisch W. Interleukin 13 and its role in gut defence and inflammation. Gut 2012;61:1765–73.


73. Van Kampen C, Gauldie J, Collins S. Proinflammatory properties of IL-4 in the intestinal microenvironment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005;288:G111–7.


74. Nemeth ZH, Bogdanovski DA, Barratt-Stopper P, Paglinco SR, Antonioli L, Rolandelli RH. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis show unique cytokine profiles. Cureus 2017;9:e1177.



75. Scully P, MacSharry J, O’Mahony D, Lyons A, O’Brien F, Murphy S, et al. Bifidobacterium infantis suppression of Peyer’s patch MIP-1α and MIP-1β secretion during Salmonella infection correlates with increased local CD4+CD25+ T cell numbers. Cell Immunol 2013;281:134–40.


76. Vemuri R, Gundamaraju R, Shinde T, Perera AP, Basheer W, Southam B, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 modulates intestinal-specific microbiota, short-chain fatty acid and immunological profiles in aging mice. Nutrients 2019;11:1–23.

77. Liu Y, Fatheree NY, Mangalat N, Rhoads JM. Lactobacillus reuteri strains reduce incidence and severity of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis via modulation of TLR4 and NF-κB signaling in the intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;302:G608–17.


78. Peña JA, Li SY, Wilson PH, Thibodeau SA, Szary AJ, Versalovic J. Genotypic and phenotypic studies of murine intestinal lactobacilli: species differences in mice with and without colitis. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004;70:558–68.

79. Ma D, Forsythe P, Bienenstock J. Live Lactobacillus rhamnosus [corrected] is essential for the inhibitory effect on tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin-8 expression. Infect Immun 2004;72:5308–14.



80. Madsen KL, Doyle JS, Jewell LD, Tavernini MM, Fedorak RN. Lactobacillus species prevents colitis in interleukin 10 gene-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 1999;116:1107–14.


81. Bull MJ, Plummer NT. Part 1: the human gut microbiome in health and disease. Integr Med (Encinitas) 2014;13:17–22.


82. Dubois NE, Gregory KE. Characterizing the intestinal microbiome in infantile colic: findings based on an integrative review of the literature. Biol Res Nurs 2015;18:307–15.

83. Liu Y, Alookaran JJ, Rhoads JM. Probiotics in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. Nutrients 2018;10:1537.



84. Wu X, He B, Liu J, Feng H, Ma Y, Li D, et al. Molecular insight into gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2016;17:431.



85. Lee N, Kim WU. Microbiota in T-cell homeostasis and inflammatory diseases. Exp Mol Med 2017;49:e340.



86. Dutta SK, Verma S, Jain V, Surapaneni BK, Vinayek R, Phillips L, et al. Parkinson's disease: the emerging role of gut dysbiosis, antibiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019;25:363–76.



87. Gagliardi A, Totino V, Cacciotti F, Iebba V, Neroni B, Bonfiglio G, et al. Rebuilding the gut microbiota ecosystem. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018;15:1–24.

88. Kumar R, Sood U, Gupta V, Singh M, Scaria J, Lal R. Recent advancements in the development of modern probiotics for restoring human gut microbiome dysbiosis. Indian J Microbiol 2020;60:12–25.


89. Savino F, De Marco A, Ceratto S, Mostert M. Fecal calprotectin during treatment of severe infantile colic with Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 2015;135(Supplement 1): S5–6.

90. Mu Q, Tavella VJ, Luo XM. Role of Lactobacillus reuteri in human health and diseases. Front Microbiol 2018;9:757.



91. Mohan R, Koebnick C, Schildt J, Mueller M, Radke M, Blaut M. Effects of Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 supplementation on body weight, fecal pH, acetate, lactate, calprotectin, and IgA in preterm infants. Pediatr Res 2008;64:418–22.


92. Bailey JR, Vince V, Williams NA, Cogan TA. Streptococcus thermophilus NCIMB 41856 ameliorates signs of colitis in an animal model of inflammatory bowel disease. Benef Microbes 2017;8:605–14.


93. Klemenak M, Dolinšek J, Langerholc T, Di Gioia D, Mičetić-Turk D. Administration of Bifidobacterium breve Decreases the Production of TNF-α in Children with Celiac Disease. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:3386–92.


94. Kumar M, Hemalatha R, Nagpal R, Singh B, Parasannanavar D, Verma V, et al. Probiotic approaches for targeting inflammatory bowel disease: an update on advances and opportunities in managing the disease. Int J Probiotics Prebiotics 2016;11:99–116.








 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation