|
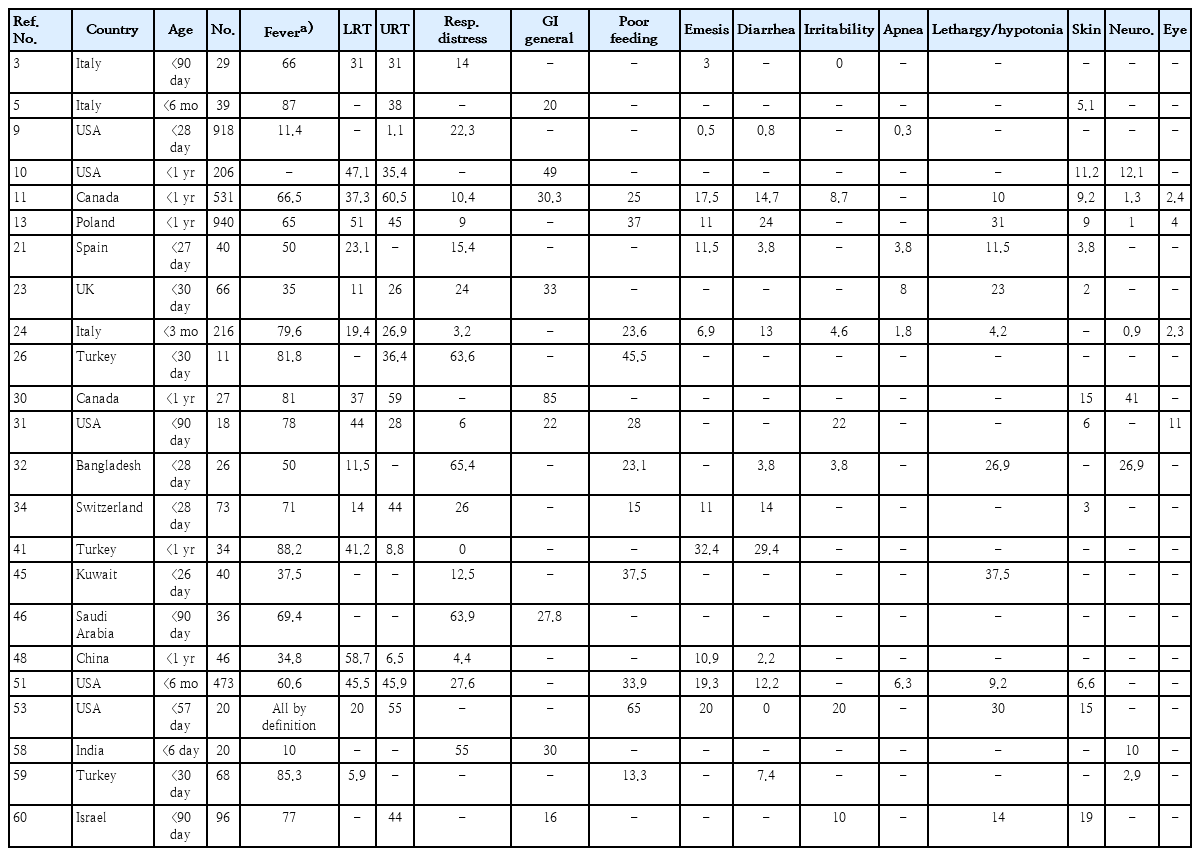
· Clinical studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in infants should be supported by rigorous laboratory diagnostic criteria.
· Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spreads to infants similarly to other viral respiratory infections.
· Among infants ≤1 year of age beyond the immediate postpartum period, COVID-19 is relatively mild, but even the low risk of severe disease requires prevention.
· Comorbidities increase infection vulnerability and complications in infants.
· Clinical and laboratory data do not sufficiently distinguish COVID-19 from other respiratory viral infections.
· Coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 is uncommon among infants.
· Unique infection sequelae, including multi-inflammatory syndrome in children and neonates and long COVID require further study and refinement of diagnostic criteria.
· Infection control standards applied to mother-infant dyads should be tempered by standard preventive strategies, maternal input, accommodation potential, and overall safety.
· Maternal vaccination prevents disease in early infancy. |






