Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 68(6); 2025 |
|
Abstract
Background
Purpose
Methods
Results
Supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 3.
Footnotes
Funding
Commercial ELISA kits, other reagents and disposable consumables for carrying out this research were funded by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), process number 2021/04280-4, and this funding was granted to the to the Prof. Dr. Thelma Suely Okay - senior investigator. The first author (EHS) has been receiving a PhD scholarship from CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), finance Code 001, Brazilian government, process number 88887.648600/2021-00. The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis and interpretation of data; preparation, review or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
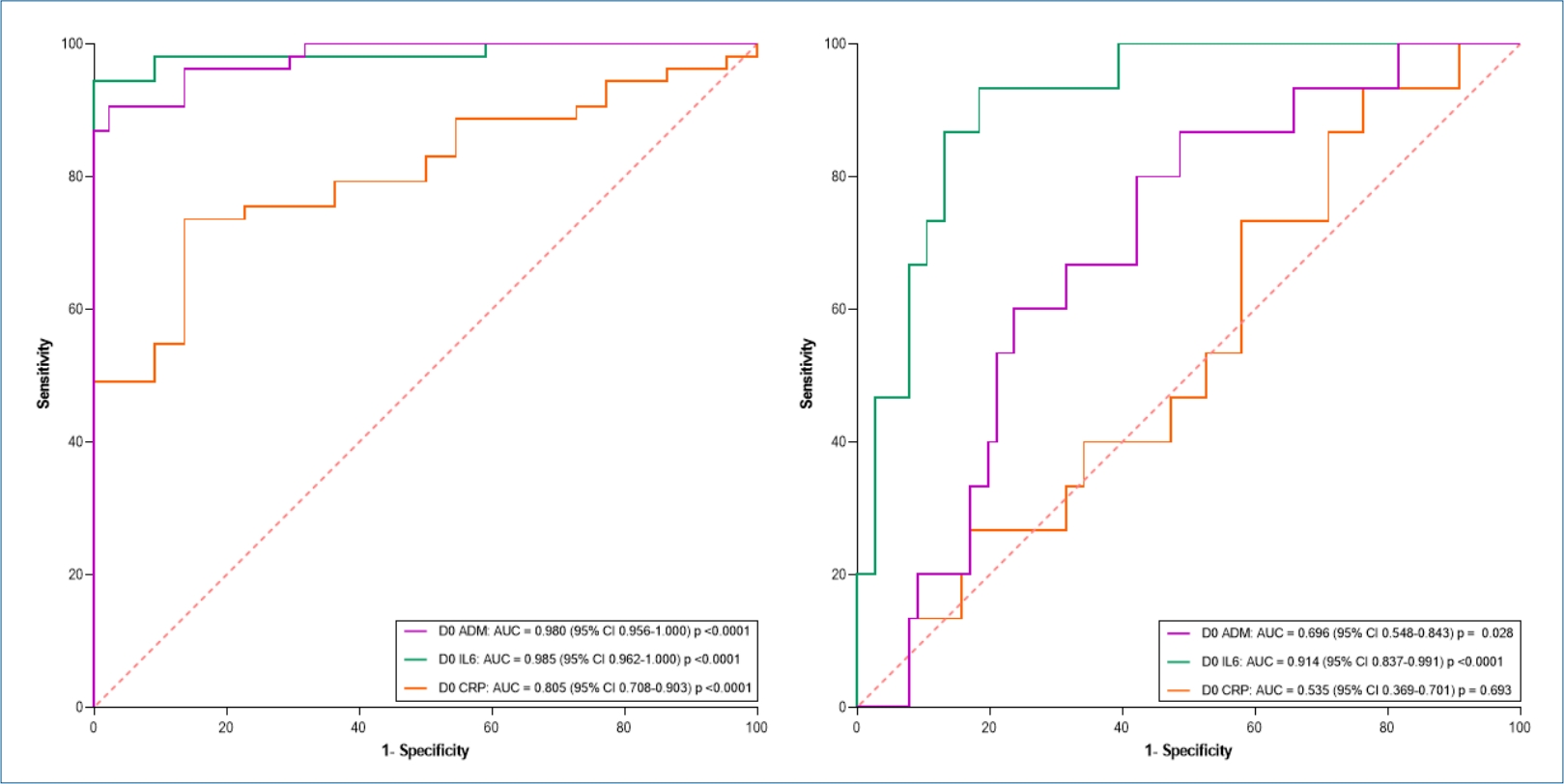
Fig. 1.
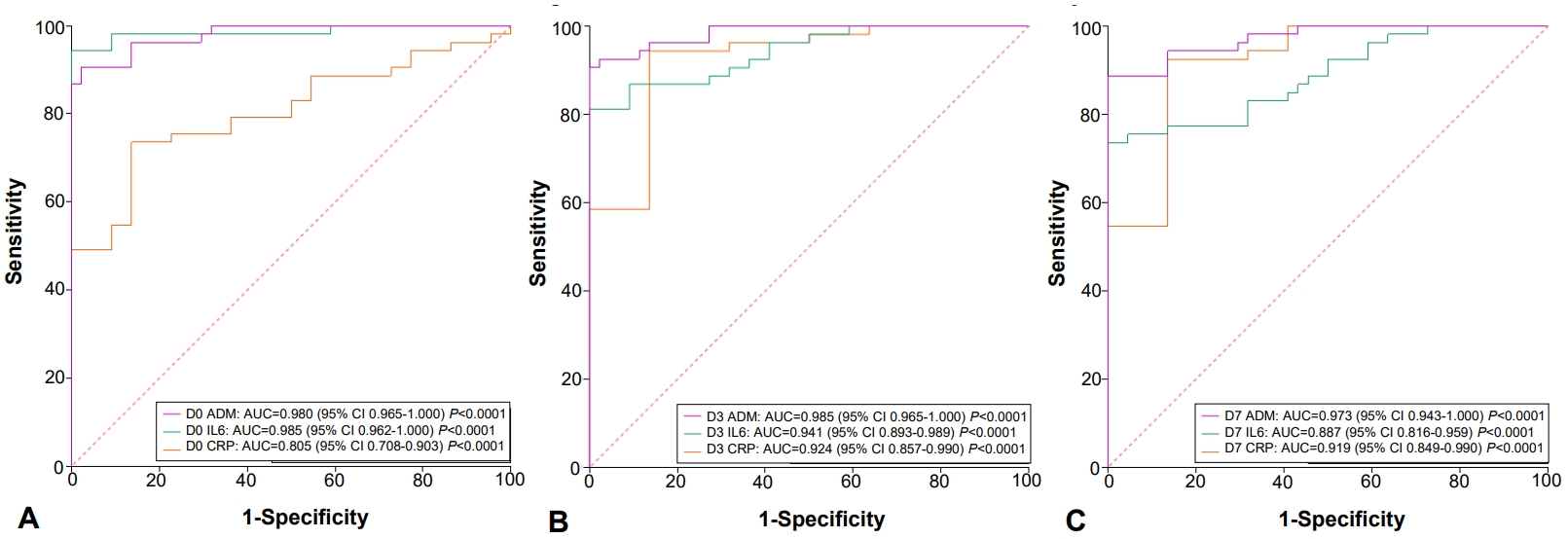
Fig. 2.
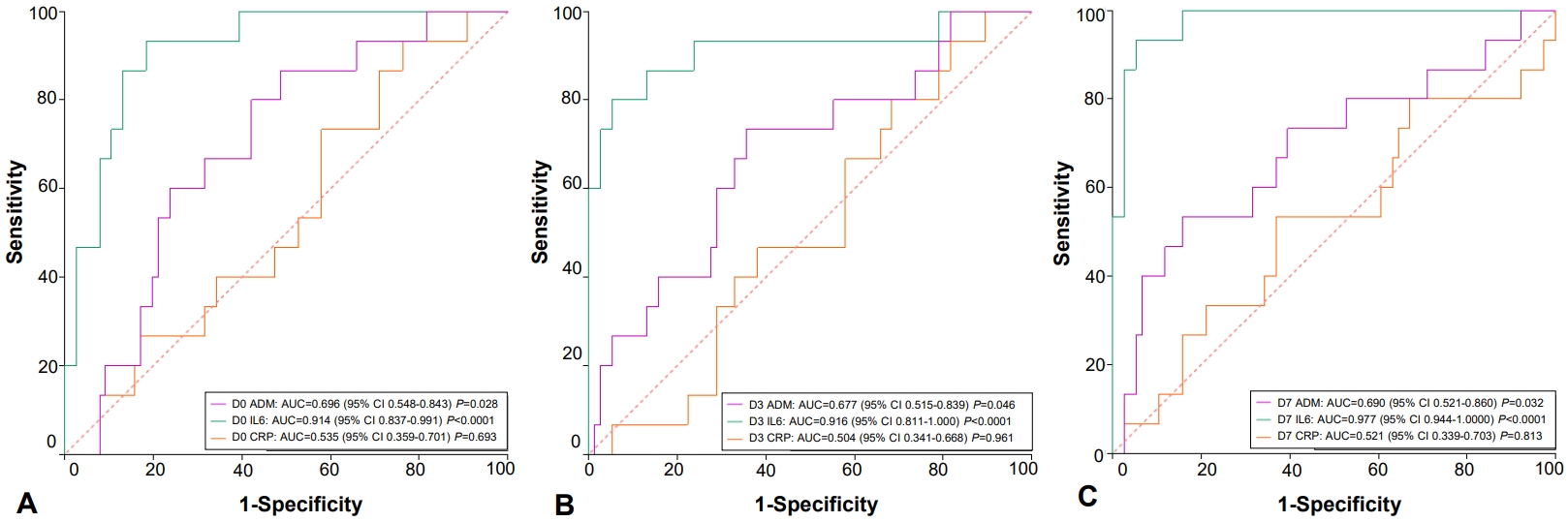
Table 1.
Table 2.
ADM, adrenomedullin; IL-6, interleukin 6; CRP, C-reactive potein; D0, neonatal intensive care unit admission; D3 and D7, days 3 and 7 after hospitalization and prescription of antibiotics; SE, sensitivity; SP, specificity; NPV, negative predictive value; PPV, positive predictive value.
The best cutoff value for each biomarker at the 3 collection points is highlighted in bold.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation