Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 65(9); 2022 |
|
Abstract
During early life, the gut microbial composition rapidly changes by maternal microbiota composition, delivery mode, infant feeding mode, antibiotic usage, and various environmental factors, such as the presence of pets and siblings. An integrative study on the diet, the microbiota, and genomic activity at the transcriptomic level may give an insight into the role of diet in shaping the human/microbiome relationship. Disruption in the gut microbiota (i.e., gut dysbiosis) has been linked to necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy, as well as some chronic diseases in later, including obesity, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, allergies, and asthma. Therefore, understanding the impact of maternal-to-infant transfer of dysbiotic microbes and then modifying infant early colonization or correcting early-life gut dysbiosis might be a potential strategy to overcome chronic health conditions.
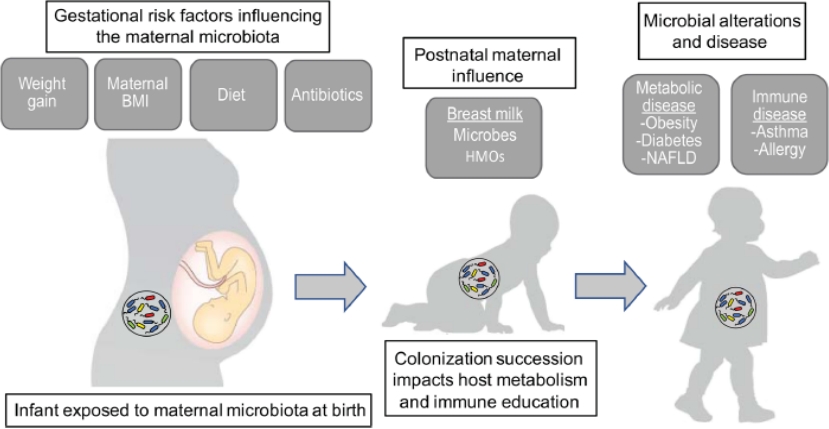
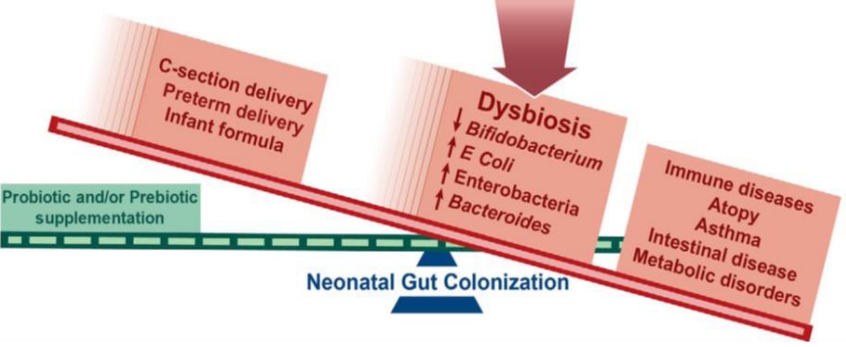
The collection of bacteria, archaea, and eukarya colonizingthe gastrointestinal tract is termed the "gut microbiota." [1] The microbiota offers many benefits to the host through a range of physiological functions such as strengthening gut integrity or shaping the intestinal epithelium [2], harvesting energy [3], protecting against pathogens [4], and regulating host immunity [5]. The newborn infant microbiota is highly dynamic and undergoes rapid changes in composition through the first years of life toward a stable adult-like structure with distinct microbial communities of unique composition and functions at specific body sites [6-9]. Markedly, multiple mother-infant studies have indicated the vertical transmission of microbes from motherto-infant that can contribute to microbiota colonization [10,11]. During early life, the gut microbial composition rapidly changes by maternal microbiota composition, delivery mode, infant feeding mode, antibiotic usage, and various environmental factors such as the presence of pets and siblings [12]. Disruption in the gut microbiota (i.e., gut dysbiosis) has been linked to necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy as well as some chronic diseases in later life, including obesity, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, allergies, asthma [13], and neurological diseases associated with the gut-brain axis [14]. This review focuses on the process of early colonization to elucidatethe factors influencing microbial colonization of the infant gut.
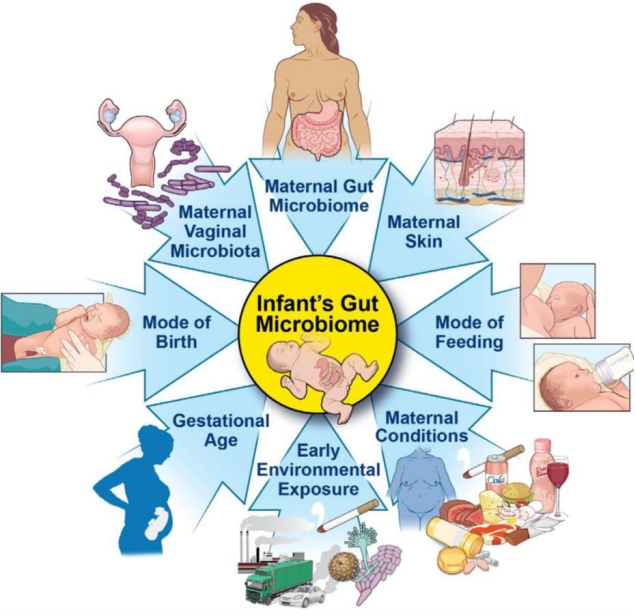
The uterus and fetus are considered sterile environment unless clinical infection occurs, such as in chorioamnionitis; however, a growing body of evidence indicates that the intrauterine environment is not sterile but that maternal-fetal transmission of microbiota occurs during pregnancy. Nonpathogenic bacteria are detected in the placenta, umbilical cord [15,16], and the meconium of healthy newborns independent of delivery mode [17], and its composition is associated with gestational age. Interestingly, in a healthy pregnancy, intrauterine bacteria appear to be similar to those of the mother's oral cavity [18]. Animal experiments revealed the maternal provision of the same bacteria in the oral cavity and the placenta [19]. These data demonstrate mother-to-fetus transmission of bacteria during gestation. Potential mechanisms of maternal-fetal microbiome interactions and delivery outcomes remain to be elucidated.
Obesity is characterized by an imbalance in the Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio in the gut [20]. Birth cohort studies disclose that infants born to overweight or obese mothers were profusely colonized with bacterial genera belonging to the phyla Firmicutes, mainly of the Lachnospiraceae family, and three times more likely to be overweight by 1 year of age, a rate that increases to 5 times in infants born by cesarean section (C-section) [21]. Weight gain during pregnancy is a normal physiological response; however, excessive gestational weight gain (defined as 16 kg or above for women with a body mass index [BMI] of 19.8–25 kg/m2 or 11.5 kg/m2 or above for women with a BMI >25 kg/m2) has been shown to result in the increased relative expansion of Bacteroides [22], Enterobacteriaceae, and Escherichia coli and a reduction in Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia muciniphila [23]. Moreover, a metagenomics analysis reported that gestational weight gain impacts infant microbiome function [24] by significantly reducing the community of bacteria involved in metabolic signaling and energy regulation, including Enterococcus, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, and Hydrogenophilus. Infant gut dysbiosis associated with maternal obesity increases gut permeability and directly initiates pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [25]. Infants delivered by C-section to overweight mothers are at higher risk of becoming overweight later in life than those born vaginally to overweight or obese mothers [26].
Maternal weight status might also affect maternal milk composition [27,28]. Cabrera-Rubio et al. [29] observed higher total bacterial counts, the expansion of Staphylococcus and Lactobacillus, and reduced levels of Bifidobacterium in the milk of obese versus normal weight women during the first 6 months of lactation. This suggests an additional mechanism explaining the intensified obesity risk in infants born to obese and overweight mothers.
Longitudinal cohort data showed that a maternal high-fat diet altered early bacterial colonization independent of maternal obesity. In association with a maternal high-fat diet, the neonatal meconium microbiome varied with a significant immediate relative depletion in Bacteroides that persisted until 6 weeks of age [30]. A maternal high-fat diet rather than just maternal obesity profoundly shapes the gut microbiota early in life [31]. A combination of a high-fat/high-sugar diet led to gut dysbiosis in mice [32] and the dietary intake of refined sugars modulates the gut microbial composition to that of an inflammatory-type microbiota [33]. Since the maternal milk microbiota is hypothesized to originate from the maternal gut microbiota, gut dysbiosis associated with the maternal diet might be transferred to the maternal milk and further exacerbate dysbiosis seen in the early gut microbiome in breastfed infants. However, research is lacking of the long-term impact of maternal lifestyle and health status during gestation and lactation on the infant's gut microbiota.
Antibiotic exposure during gestation has an extensive effect on the microbiome by reducing microbial load and altering composition as well as long-term influences on the developing infant gut microbiome [34]. Because microbial colonization in early life coincides with key neurodevelopmental periods, antibiotic-induced perturbation in the infant gut microbiota might be linked to disruption of the gut-brain axis and potentially related to neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism [35]. Antibiotic treatment can also affect the breast milk microbiome. Higher Bifidobacterium counts were found in the breast milk of mothers who did not receive antibiotics versus those who did [36]. Antibiotics during lactation reduced the microbial community of breast milk, including lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, and is associated with lower bacterial diversity in breast milk [37,38].
Maternal allergies may affect the microbiome of the breast milk. Depleted levels of Bifidobacterium in breast milk have been reported in mothers with allergies [39].
Low to moderate levels of ethanol exposure in combination with artificial sweeteners reduced Clostridium and Bacillus and increased Eubacterium levels in the gut microbiota of pregnant versus control mice [40].
Early life exposure to maternal and environmental smoke increased the levels of Ruminococcus, and Akkermansia in the infant gut microbiota was associated with a higher risk of overweight and obesity at 1–3 years of age [41].
Air pollution is hypothesized as a potential factor of neonatal gut dysbiosis, particularly the depletion of the Firmicutes phylum [42].
Jašarević et al. [43] showed that maternal stress in the first week of pregnancy caused lasting disruption in fecal microbial diversity, community composition, and composition of the vaginal microbiota during gestation and after birth.
Gestational diabetes mellitus-related dysbiosis can be vertically transmitted to the offspring. Increases in Corynebacterium, Bacteroides, and Bevundimonas were seen in the stool of infants of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus in one study [44], but the longer term effects of this finding are not fully understood.
Several studies have shown relatively favorable effects of probiotic administration during the perinatal period [45-47]. Maternal supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG; 2×109 CFU/day) during late pregnancy (30–36 weeks) showed colonization with LGG in the infant's gut that was stable for up to 24 months in some cases [48]. In contrast, LGG administration (1.8×1010 CFU/day) from 36 weeks of gestation until delivery enhanced the intestinal colonization of Bifidobacterium species but not LGG in breastfed infants [49]. Interestingly, the mother-toinfant transfer of LGG reportedly establishes more diversity in Bifidobacterium in the infant gut [50]. Some studies examined the safety of probiotic administration during pregnancy. However, they did not show a significant adverse effect. Investigations revealed that probiotic supplementation during pregnancy is both safe and effective in protection against preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, vaginal infections, maternal and infant weight gain, and later childhood diseases [46]. Maternal probiotic supplementation only during gestation resulted in the appearance of bacteria in the fecal samples of their breastfed neonates, even in those born by C-section and thereby lacking exposure to the vaginal microbiome [51]. This emphasizes the important role of breast milk in the transfer of microbes to infants.
The mode of delivery is generally accepted as a major factor determining initial colonization [52]. Infants born by C-section can have altered immune development and are at higher risk of numerous noncommunicable diseases such as obesity, allergy, asthma, and atopy [53]. Infants delivered vaginally are colonized with bacteria present in the maternal vagina [52], whereas those delivered by C-section are colonized with bacteria similar to those of the maternal skin and oral cavity [54,55]. Although most vaginal and skin bacteria do not seem to take hold in the infant gut, their presence may differentially affect the colonization abilities of other bacteria. Longer-period studies that have followed microbiota composition in infants during the first 2 years of life have confirmed an association of C-section with delayed colonization of the Bacteroidetes phylum, and with lower total microbial diversity up to 2 years of age [56]. Additionally, differences between the microbiotas of C-section and vaginally born infants were detected in analyses performed at 7 years of age [57]. The C-section delivery mode impacts the microbiota through several means: (1) lack of exposure to the mother's vaginal and fecal microbes will alter microbial type and diversity that colonize the gut at birth; and (2) the different starting points in terms of microbial exposure and immune environment will mark the course of microbiota [58]. The microbial origin in C-section-born infants is distinct between infants born by elective or emergency C-section. The source of the gut microbiota in infants born by emergency C-section is reportedly the skin and vagina, whereas the skin is thought to be the predominant microbial origin of the gut microbiota in infants born by elective C-section [59]. These differences may be due to fetal membrane rupture, which commonly occurs before emergency C-section, leading to infiltration by vaginal microbes.
Gestational age at delivery impacts the bacterial microbiota [60]. Preterm infants are precociously exposed to extensive use of antibiotics and often long-term hospitalization; they require mechanical ventilation and usually receive parenteral nutrition. Each one of these conditions may produce irreversible changes in the natural gut microbiota colonization and development processes [61]. The analysis of the knowledge about a preterm infant's microbiota and its relationship with clinical outcomes (sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, but it may also impact growth rates, immune function, and the risk for various chronic diseases and conditions) showed that facultative anaerobes dominated the preterm infant gut, including Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus [62].
Microbial colonization of the infant gut occurs rapidly after birth and is influenced by delivery mode, feeding, and many other factors, such as environmental factors (including geographic location) and household exposure (e.g., siblings and furry pets). The infant microbiota composition changes rapidly in the first weeks following birth and then stabilizes until the infant is weaned off an exclusive milk diet and started on solid foods.
Recent studies reported that human milk is not sterile and is a primary and main factor that drives the acquisition and evolution of the gut microbiota in early life [63,64]. Motherto- child transmission studies support that mother-to-infant bacterial transfer occurs via the breast milk [65-67]. Breast milk contributes significantly to the metabolism, development of gut integrity, and maturation of the immune and neuroendocrine systems [68,69]. Breastfeeding confers protection against respiratory and gastrointestinal infections and decreases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome and certain inflammatory diseases such as dermatitis, asthma, obesity, and types 1 and 2 diabetes [70,71]. Breast milk itself is also a source of commensal bacteria that are naturally present in this secretory fluid. Breastfed infants reportedly ingest between 1×104 and 1×106 bacteria daily [72] (Table 1) [73]. Streptococci (mitis and salivarius groups) and coagulase-negative staphylococci are potentially able to compete with the establishment of undesired pathogens (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus) in the infant gut. Propionibacterium acnes can prevent the growth of S. aureus [74]. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus spp. in breast milk are known to activate immunoglobulin A-producing plasma cells in the neonatal gut. An association was shown between low levels of intestinal Bifidobacterium microbiota during infancy and an increased risk of atopy later in life [75-77]. As with the composition of breast milk itself, its associated microbiome changes during the lactation period. Different factors are thought to be responsible for its composition and diversity, such as gestational age, lactation stage, environmental exposures, geographical location [78-80], daily breastfeeding practices, infant sex, and maternal factors (BMI, parity, and delivery mode) [81]. As previously discussed, obesity influences the maternal gut microbiota, but it also affects the milk microbiota [82,83]. Breast milk microbial alterations might be attributed to the physiological stress and/or hormonal changes that occur with labor or an emergency C-section [78]. Indeed, breast milk dysbiosis was only observed in mothers who underwent an elective C-section. Vaginal delivery might induce intestinal permeability and enhance bacterial translocation from the gut to the mammary gland and breast milk [84]. Human milk contains human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), a type of prebiotic. HMOs promote the growth of specific bifidobacteria, supporting an early Bifidobacteria-dominated gut microbiome [85]. Over 200 different oligosaccharides have been identified in human milk [86].
Antibiotic administration is another major factor that interferes with the composition of the gastrointestinal microbiome. In particular, antibiotic exposure within 1 month of birth alters the balanced development of the microbiome momentarily and persistently [87]. Resistance of some gut microbes to antibiotic agents may also occur, and these resistant genes can possibly be transferred to pathogens. Immune homeostasis will be challenged, disrupting the T-reg/Th balance [88]. Therefore, antibiotic administration increases the risk of developing immunemediated diseases, such as cow milk protein allergy, diabetes, and asthma [88]. The younger the patient, the more frequently this occurs, and the larger the spectrum of antibiotic agents administered, the stronger the association with overweight status [89].
The impact of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and other acid-blocking medications in young infants is gaining more attention, as disturbances in the microbiome have been reported. PPI usage for 8 weeks resulted in a decrease in Lactobacilli and Stenotrophomonas and an increase in Haemophilus. Additionally, the relative abundances of the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria changed significantly [90]. The specific adverse effects associated with PPIs include necrotizing enterocolitis, lateonset sepsis in premature infants, Clostridium difficile infection, asthma, obesity, and small intestine bacterial overgrowth in young children [91]. PPI use is associated with hypergastrinemia and hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like cells. PPIs also induce hypochlorhydria, which interferes with gastric bactericidal function, and their long-term use can predispose patients to enteric infections. The exact mechanism of PPI-induced C. difficile infection is not well known, but a hypothesis suggests that C. difficile spores are acid-resistant. Vegetative forms that are susceptible to acidity and, therefore, buffering the acidity with PPIs may allow C. difficile to proliferate.
Intervention with probiotics as a means of maintaining a healthy gut ecosystem in early life has become popular. In attempts to mimic the composition of human milk, the design of some infant formulas includes the addition of probiotics. It is important to note that not all probiotics are equally safe, and the effects demonstrated from one strain cannot be extrapolated to another strain, even if they belong to the same species [92].
Supplementation with bifidobacteria strains to infant formula from birth does not seem to compensate for the differences in gut microbiota composition observed between breastfeeding and formula feeding in early life in full-term infants [93]. However, other data in preterm infants showed that, compared with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis supplementation, Bifidobacterium infantis significantly increased the fecal bifidobacteria levels in formula-fed preterm infants [94]. This might be because, among bifidobacterial strains, B. infantis is the only one that has the ability to consume HMOs because of its specific genome sequence [95].
Adding LGG to an extensively hydrolyzed casein-based commercially available formula designed for infants at high risk for allergic manifestations associated with immunoglobulin E-mediated cow's milk allergy reduced the incidence of other allergy manifestations and improved the development of oral tolerance to cow's milk [96]. The beneficial effect of LGG might be attributed to the alterations in the strain level bacterial community structure expanding butyrate-producing bacterial strains in food allergic infants [97].
A recent review of clinical trials and case studies that evaluated several probiotics (e.g., Bacillus, Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Saccharomyces, and probiotic mixtures) in premature infants with low or very low birth weight found that a probiotic mixture with Bifidobacterium reduced the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis [98]. Moreover, probiotic supplementation in premature infants reportedly improved the intestinal barrier, enhanced the production of immunoglobulin A and anti-inflammatory cytokines, increased the diversity and functionality of the gut microbiota, and reduced pathological bacterial translocation [99].
Although human milk is rich in prebiotics (HMOs), bovine milk also contains oligosaccharides, some of which are structurally similar to HMOs. Attempts are being made to stimulate the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the infant gut to levels detected in breastfed infants by the addition of various kinds of prebiotics (e.g., fructo-oligosaccharides and galacto-oligosaccharides) to infant formula [100]. By inducing a fecal microbiota that closely resembles the microbiota of breastfed infants [101], prebiotic supplementation in infants may improve the gut mucosal barrier and prevent enteric pathogen infection and bacterial translocation [102,103].
The impact of breastfeeding on the microbiome after weaning from milk to solid food is correlated with the duration of exclusive breastfeeding rather than the age at which weaning occurs [104,105]. Early (vs. later) introduction to solid foods in infancy is associated with altered gut microbiota composition and BMI in early childhood; however, these associations differ by duration of breastfeeding [106]. The effects of breastfeeding on the postweaning microbiota decrease with time; Bifidobacterium spp. are replaced as the dominant species with a concurrent increased relative abundance of members of the phyla Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes such as Bacteroides, Bilophilia, Roseburia, Ruminococcus, and Clostridium [104,105]. The types of complementary food also affect the microbiota composition and diversity [104]. Increased intake of protein and fiber in foods such as meat, cheese, and rye bread is associated with an increase in alpha diversity.
Maternal and infant factors can influence the composition and development of the infant gut microbiota. Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth, but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial. Maternal factors during pregnancy that can affect the infant microbiota include maternal diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage; however, their overall impact is low compared to that of birth mode, infant diet, and antibiotic treatment. Microbes are passed from the mother to the infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, and intrapartum and early life antibiotic treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism. Emerging data demonstrating the importance of early life gut microbiome development as a protective factor against gut dysbiosis-related diseases later in life support the rationale for targeted therapies to restore the early life gut microbiome.
Therefore, understanding the impact of maternal-to-infant transfer of dysbiotic microbes and then modifying infant early colonization or correcting early life gut dysbiosis is a potential strategy to overcome chronic health conditions.
References
1. Arrieta MC, Stiemsma LT, Amenyogbe N, Brown EM, Finlay B. The intestinal microbiome in early life: health and disease. Front Immunol 2014;5:427.



2. Natividad JMM, Verdu EF. Modulation of intestinal barrier by intestinal microbiota: Pathological and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Res 2013;69:42–51.


3. Besten GD, Eunen KV, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud DJ, Bakker BM. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res 2013;54:2325–40.



4. Bäumler AJ, Sperandio V. Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut. Nature 2016;535:85–93.




5. Gensollen T, Iyer SS, Kasper DL, Blumberg RS. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016;352:539–44.



6. Backhed F, Roswall J, Peng Y, Feng Q, Jia H, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, et al. Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe 2015;17:690–703.


7. Costello EK, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Fierer N, Gordon JI, Knight R. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009;326:1694–7.



8. Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012;486:207–14.




9. Koenig JE. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2011;108:4578–85.



10. Ferretti P, Pasolli E, Tett A, Asnicar F, Gorfer V, Fendi S, et al. Mother-to-infant microbial transmission from different body sites shapes the developing infant gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2018;24:133–45.



11. Elizabeth KC, Keaton S, Dethlefsen L, Bohannan BM, Relman DA. The application of ecological theory toward an understanding of the human microbiome. Science 2012;336:1255–62.



12. O'Neill IJ, Sanchez Gallardo R, Saldova R, Murphy EF, Cotter PD, McAuliffe FM, et al. Maternal and infant factors that shape neonatal gut colonization by bacteria. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;14:651–64.


13. Young VB. The intestinal microbiota in health and disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2012;28:63–9.



14. Ma Q, Xing C, Long W, Wang HY, Liu Q, Wang RF. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: the gut-brain axis. J Neuroinflammation 2019;16:53.




15. Lauder AP, Roche AM, Sherrill-Mix S, Bailey A, Laughlin AL, Bittinger K, et al. Comparison of placenta samples with contamination controls does not provide evidence for a distinct placenta microbiota. Microbiome 2016;4:29.




16. de Goffau MC, Lager S, Sovio U, Gaccioli F, Cook E, Peacock SJ, et al. Human placenta has no microbiome but can contain potential pathogens. Nature 2019;572:329–34.




17. Jiménez E, Marín ML, Martín R, Odriozola JM, Olivares M, Xaus J, et al. Is meconium from healthy newborns actually sterile? Res Microbiol 2008;159:187–93.


18. Aagaard K, Ma J, Antony KM, Ganu R, Petrosino J, Versalovic J. The placenta harbors a unique microbiome. Sci Transl Med 2014;6:237. ra65.



19. Rautava S, Kainonen E, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Maternal probiotic supplementation during pregnancy and breast-feeding reduces the risk of eczema in the infant. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:1355–60.


20. Kumari M, Kozyrskyj AL. Gut microbial metabolism defines host metabolism: an emerging perspective in obesity and allergic inflammation. Obes Rev 2017;18:18–31.



21. Tun HM, Bridgman SL, Chari R, Field CJ, Guttman DS, Becker AB, et al. Roles of birth mode and infant gut microbiota in intergenerational transmission of overweight and obesity from mother to offspring. JAMA Pediatr 2018;172:368–77.



22. Collado MC, Isolauri E, Laitinen K, Salminen S. Distinct composition of gut microbiota during pregnancy in overweight and normalweight women. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;88:894–9.


23. Santacruz A, Collado MC, García-Valdés L, Segura MT, Martín-Lagos JA, Anjos T, et al. Gut microbiota composition is associated with body weight, weight gain and biochemical parameters in pregnant women. Br J Nutr 2010;104:83–92.


24. Baumann-Dudenhoeffer AM, D’Souza AW, Tarr PI, Warner BB, Dantas G. Infant diet and maternal gestational weight gain predict early metabolic maturation of gut microbiomes. Nat Med 2018;24:1822–9.




25. Soderborg TK, Clark SE, Mulligan CE, Janssen RC, Babcock L, Ir D, et al. The gut microbiota in infants of obese mothers increases inflammation and susceptibility to NAFLD. Nat Commun 2018;9:4462.




26. Singh SB, Madan J, Coker M, Hoen A, Baker ER, Karagas MR, et al. Does birth mode modify associations of maternal pre-pregnancy BMI and gestational weight gain with the infant gut microbiome? Int J Obes (Lond) 2020;44:23–32.




27. Fields DA, George B, Williams M, Whitaker K, Allison DB, Teague A, et al. Associations between human breast milk hormones and adipocytokines and infant growth and body composition in the first 6 months of life. Pediatr Obes 2017;12:78–85.




28. Whitaker KM, Marino RC, Haapala JL, Foster L, Smith KD, Teague AM, et al. Associations of maternal weight status before, during, and after pregnancy with inflammatory markers in breast milk. Obesity 2017;25:2092–9.




29. Cabrera-Rubio R, Collado MC, Laitinen K, Salminen S, Isolauri E, Mira A. The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;96:544–51.


30. Chu DM, Antony KM, Ma J, Prince AL, Showalter L, Moller M, et al. The early infant gut microbiome varies in association with a maternal high-fat diet. Genome Med 2016;8:77.




31. Ma J, Prince AL, Bader D, Hu M, Ganu R, Baquero K, et al. Highfat maternal diet during pregnancy persistently alters the offspring microbiome in a primate model. Nat Commun 2014;5:3889.




32. Martinez-Medina M, Denizot J, Dreux N, Robin F, Billard E, Bonnet R, et al. Western diet induces dysbiosis with increased E. coli in CEABAC10 mice, alters host barrier function favouring AIEC colonisation. Gut 2014;63:116–24.


33. Spreadbury I. Comparison with ancestral diets suggests dense acellular carbohydrates promote an inflammatory microbiota, and may be the primary dietary cause of leptin resistance and obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2012;5:175–89.



34. Suez J, Zmora N, Zilberman-Schapira G, Mor U, Dori-Bachash M, Bashiardes S, et al. Post-antibiotic gut mucosal microbiome reconstitution is impaired by probiotics and improved by autologous FMT. Cell 2018;174:1406–23.


35. Mezzelani A, Landini M, Facchiano F, Elisabetta Raggi M, Villa L, Molteni M, et al. Environment, dysbiosis, immunity and sex-specific susceptibility: a translational hypothesis for regressive autism pathogenesis. Nutr Neurosci 2015;18:145–61.



36. Hermansson H, Kumar H, Collado MC, Salminen S, Isolauri E, Rautava S. Breast milk microbiota is shaped by mode of delivery and intrapartum antibiotic exposure. Front Nutr 2019;6:4.



37. Jiménez E, de Andrés J, Manrique M, Pareja-Tobes P, Raquel Tobes, Martínez-Blancht JF, et al. Metagenomic analysis of milk of healthy and mastitis-suffering women. J Hum Lact 2015;31:406–15.



38. Patel SH, Vaidya YH, Patel RJ, Pandit RJ, Joshi CG, Kunjadiya AP. Culture independent assessment of human milk microbial community in lactational mastitis. Sci Rep 2017;7:7804.




39. Grönlund MM, Gueimonde M, Laitinen K, Kociubinski G, Grönroos T, Salminen S, et al. Maternal breastmilk and intestinal bifidobacteria guide the compositional development of the Bifidobacterium microbiota in infants at risk of allergic disease. Clin Exp Allergy 2007;37:1764–72.


40. Labrecque MT, Malone D, Caldwell KE, Allan AM. Impact of ethanol and saccharin on fecal microbiome in pregnant and nonpregnant mice. J Preg Child Health 2015;2:1000193.



41. McLean C, Jun S, Kozyrskyj A. Impact of maternal smoking on the infant gut microbiota and its association with child overweight: a scoping review. World J Pediatr 2019;15:341–9.



42. Vallès Y, Francino MP. Air pollution, early life microbiome, and development. Curr Envir Health Rpt 2018;5:512–21.




43. Jašarević E, Howard CD, Misic AM, Beiting DP, Bale TL. Stress during pregnancy alters temporal and spatial dynamics of the maternal and offspring microbiome in a sex-specific manner. Sci Rep 2017;7:44182.




44. Wang J, Zheng J, Shi W, Du N, Xu X, Zhang Y, et al. Dysbiosis of maternal and neonatal microbiota associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Gut 2018;67:1614–25.



45. Baldassarre M, Di Mauro A, Mastromarino P, Fanelli M, Martinelli D, Urbano F, et al. Administration of a multi-strain probiotic product to women in the perinatal period differentially affects the breast milk cytokine profile and may have beneficial effects on neonatal gastrointestinal functional symptoms. A randomized clinical trial. Nutrients 2006;8:677.



46. Sohn K, Underwood MA. Prenatal and postnatal administration of prebiotics and probiotics. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2017;22:284–9.



47. Luoto R, Laitinen K, Nermes M, Isolauri E. Impact of maternal probiotic-supplemented dietary counselling on pregnancy outcome and prenatal and postnatal growth: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Nutr 2010;3:1792–9.

48. Lahtinen SJ, Boyle RJ, Kivivuori S, Oppedisano F, Smith KR, Browne RR, et al. Prenatal probiotic administration can influence Bifidobacterium microbiota development in infants at high risk of allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;123:499–501.e8.


49. Gueimonde M, Sakata S, Kalliomäki M, Isolauri E, Benno Y, Salminen S. Effect of maternal consumption of Lactobacillus GG on transfer and establishment of fecal Bifidobacterial microbiota in neonates. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006;42:166–70.


50. Arroyo R, Martín V, Maldonado A, Jiménez E, Fernández L, Rodríguez JM. Treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation: antibiotics versus oral administration of Lactobacilli isolated from breast milk. Clin Infect Dis 2010;50:1551–8.


51. Schultz M, Göttl C, Young RJ, Iwen P, Vanderhoof JA. Administration of oral probiotic bacteria to pregnant women causes temporary infantile colonization. J Pediat Gastroenterol Nutr 2004;38:293–7.

52. Dominguez-Bello MG, Costello EK, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Fierer N, et al. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2010;107:11971–5.



53. Sandall J, Tribe RM, Avery L, Mola G, Visser GH, Homer CS, et al. Short-term and long-term effects of caesarean section on the health of women and children. Lancet 2018;392:1349–57.


54. Bäckhed F, Roswall J, Peng Y, Feng Q, Jia H, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, et al. Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe 2015;17:852.


55. MacIntyre DA, Chandiramani M, Lee YS, Kindinger L, Smith A, Angelopoulos N, et al. The vaginal microbiome during pregnancy and the postpartum period in a European population. Sci Rep 2015;5:8988.




56. Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, Henderson N, Jay M, Li H, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med 2016;8:34.



57. Penders J, Gerhold K, Thijs C, Zimmermann K, Wahn U, Lau S, et al. New insights into the hygiene hypothesis in allergic diseases: mediation of sibling and birth mode effects by the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014;5:239–44.



58. Francino MP. Birth mode-related differences in gut microbiota colonization and immune system development. Ann Nutr Metab 2018;73:12–6.



59. Kim G, Bae J, Kim MJ, Kwon HJ, Park GC, Kim SJ, et al. Delayed establishment of gut microbiota in infants delivered by cesarean section. Front Microbiol 2020;11:2099.



60. Ardissone AN, de la Cruz DM, Davis-Richardson AG, Rechcigl KT, Li N, Drew JC, et al. Meconium microbiome analysis identifies bacteria correlated with premature birth. PLoS One 2014;9:e90784.



61. Milani C, Duranti S, Bottacini F, Casey E, Turroni F, Mahony J, et al. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2017;81:e00036–117.




62. Tirone C, Pezza L, Paladini A, Tana M, Aurilia C, Lio A, et al. Gut and lung microbiota in preterm infants: immunological modulation and implication in neonatal outcomes. Front Immunol 2019;10:2910.



63. Kumar H, du Toit E, Kulkarni A, Aakko J, Linderborg KM, Zhang Y, et al. Distinct patterns in human milk microbiota and fatty acid profiles across specific geographic locations. Front Microbiol 2016;7:1619.



64. Pannaraj PS, Li F, Cerini C, Bender JM, Yang S, Rollie A, et al. Association between breast milk bacterial communities and establishment and development of the infant gut microbiome. JAMA Pediatr 2017;171:647.



65. Asnicar F, Manara S, Zolfo M, Tin Truong D, Scholz M, Armanini F, et al. Studying vertical microbiome transmission from mothers to infants by strain-level metagenomics profiling. mSystems 2017;2:e00164–216.


66. Duranti S, Lugli GA, Mancabelli L, Armanini F, Turroni F, Jamnes K, et al. Maternal inheritance of bifidobacterial communities and bifidophages in infants through vertical transmission. Microbiome 2017;5:66.




67. Murphy K, Curley D, O’Callaghan TF, O’Shea CA, Dempsey EM, O’Toolee PW, et al. The composition of human milk and infant faecal microbiota over the first three months of life: a pilot study. Sci Rep 2017;7:40597.




68. Fernández L, Langa S, Martín V, Maldonado A, Jiménez E, Martín R, et al. The human milk microbiota: origin and potential roles in health and disease. Pharmacol Res 2013;69:1–10.


69. Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger C, Chassard C. Impact of human milk bacteria and oligosaccharides on neonatal gut microbiota establishment and gut health. Nutr Rev 2015;73:426–37.


70. Fitzstevens JL, Smith KC, Hagadorn JI, Caimano MJ, Matson AP, Brownell EA. Systematic review of the human milk microbiota. Nutr Clin Pract 2017;32:354–64.



72. Heikkilä MP, Saris PEJ. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk. J Appl Microbiol 2003;95:471–8.


73. Kapourchali FR, Cresci GAM. Early-life gut microbiome—the importance of maternal and infant factors in its establishment. Nutr Clin Practice 2020;35:386–405.


74. Shu M, Wang Y, Yu J, Kuo S, Coda A, Jiang Y, et al. Fermentation of propionibacterium acnes, a commensal bacterium in the human skin microbiome, as skin probiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One 2013;8:e55380.



75. Stsepetova J, Sepp E, Julge K, Vaughan E, Mikelsaar M, de Vos WM. Molecularly assessed shifts of Bifidobacterium ssp. and less diverse microbial communities are characteristic of 5-year-old allergic children. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007;51:260–9.


76. Kalliomäki M, Kirjavainen P, Eerola E, Kero P, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:129–34.


77. Suzuki S, Shimojo N, Tajiri Y, Kumemura M, Kohno Y. Differences in the composition of intestinal Bifidobacterium species and the development of allergic diseases in infants in rural Japan. Clin Exp Allergy 2007;37:506–11.


78. Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger CP, Rochat F, Chassard C. Vertical motherneonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ Microbiol 2014;16:2891–904.


79. Fujita M, Roth E, Lo YJ, Hurst C, Vollner J, Kendell A. In poor families, mothers’ milk is richer for daughters than sons: a test of Trivers-Willard hypothesis in agropastoral settlements in northern Kenya. Am J Phys Anthropol 2012;149:52–9.


80. Michaelsen KF, Skafte L, Badsberg JH, Jørgensen M. Variation in macronutrients in human bank milk. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1990;11:229–39.


81. Moossavi S, Sepehri S, Robertson B, Bode L, Goruk S, Field CJ, et al. Composition and variation of the human milk microbiota are influenced by maternal and early-life factors. Cell Host Microbe 2019;25:324–35.


82. Gohir W, Ratcliffe EM, Sloboda DM. Of the bugs that shape us: maternal obesity, the gut microbiome, and long-term disease risk. Pediatr Res 2015;77:196–204.



83. Goldsmith F, O'Sullivan A, Smilowitz JT, Freeman SL. Lactation and intestinal microbiota: how early diet shapes the infant gut.Cell Host Microbe. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2015;20:149–58.



84. Davis EC, Wang M, Donovan SM. First 1000 days and beyond after birth: gut microbiota and necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Front Microbiol 2022;21:905380.
85. Vandenplas Y, Berger B, Carnielli VP, Ksiazyk J, Lagström H, Sanchez Luna M, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides: 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL) and lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) in infant formula. Nutrients 2018;10:1161.



86. Urashima T, Taufik E, Fukuda K, Asakuma S. Recent advances in studies on milk oligosaccharides of cows and other domestic farm animals. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2013;77:455–66.


87. Zeissig S, Blumberg RS. Life at the beginning: perturbation of the microbiota by antibiotics in early life and its role in health and disease. Nat Immunol 2014;15:307–10.



88. Francino MP. Antibiotics and the human gut microbiome: dysbioses and accumulation of resistances. Front Microbiol 2016;6:1543.



89. Miller SA, Wu RKS, Oremus M. The association between antibiotic use in infancy and childhood overweight or obesity: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Obes Rev 2018;19:1463–75.



90. Castellani C, Singer G, Kashofer K, Huber-Zeyringer A, Flucher C, Kaise M, et al. The influence of proton pump inhibitors on the fecal microbiome of infants with gastroesophageal reflux- a prospective longitudinal interventional study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:444.



91. Levy EI, Hoang DM, Vandenplas Y. The effects of proton pump inhibitors on the microbiome in young children. Acta Paediatr 2020;109:1531–8.



92. McFarland LV, Evans CT, Goldstein EJC. Strain-specificity and disease-specificity of probiotic efficacy: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Front Med 2018;5:124.



93. Bazanella M, Maier TV, Clavel T, Lagkouvardos I, Lucio M, Maldonado-Gòmez MX, et al. Randomized controlled trial on the impact of early-life intervention with bifidobacteria on the healthy infant fecal microbiota and metabolome. Am J Clin Nutr 2017;106:1274–86.


94. Underwood MA, Kalanetra KM, Bokulich NA, Lewis ZT, Mirmiran M, Tancredi DJ, et al. A comparison of two probiotic strains of Bifidobacteria in premature infants. J Pediatr 2013;163:1585–91.e9.



95. Smilowitz JT, Moya J, Breck MA, Cook C, Fineberg A, Angkustsiri K, et al. Safety and tolerability of Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis EVC001 supplementation in healthy term breastfed infants: a phase I clinical trial. BMC Pediatr 2017;17:133.




96. Berni Canani R, Di Costanzo M, Bedogni G, Amoroso A, Cosenza L, Di Scala C, et al. Extensively hydrolyzed casein formula containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reduces the occurrence of other allergic manifestations in children with cow’s milk allergy: 3-year randomized controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017;139:1906–13.e4.


97. Berni Canani R, Sangwan N, Stefka AT, Nocerino R, Paparo L, Aitoro R, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-supplemented formula expands butyrate-producing bacterial strains in food allergic infants. ISME J 2016;10:742–50.




98. Bi L, Yan B, Yang Q, Cui H. Which is the best probiotic treatment strategy to prevent the necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. Medicine 2019;98:e17521.



99. Wang Q, Dong J, Zhu Y. Probiotic supplement reduces risk of necrotizing enterocolitis and mortality in preterm very low-birth-weight infants: an updatedmeta-analysis of 20 randomized, controlled trials. J Pediatr Surg 2012;47:241–8.


100. Underwood MA, Salzman NH, Bennett SH, Mills DA, Marcobal A, Tancredi DJ, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled comparison of 2 prebiotic/probiotic combinations in preterm infants: impact on weight gain, intestinal microbiota, and fecal short-chain fatty acids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;48:216–25.



101. Haarman M, Knol J. Quantitative real-time PCR assays to identify and quantify fecal Bifidobacterium species in infants receiving a prebiotic infant formula. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005;71:2318–24.




102. Cherbut C, Michel C, Raison V, Kravtchenko T, Severine M. Acacia gum is a Bifidogenic dietary fibre with high digestive tolerance in healthy humans. Microb Ecol Health Dis 2003;15:43–50.

103. Guarner F. Studies with inulin-type fructans on intestinal infections, permeability, and inflammation. J Nutr 2007;137:2568S–2571S.


104. Laursen MF, Andersen LB, Michaelsen KF, Mølgaard C, Trolle E, Bahl MI, et al. Infant gut microbiota development is driven by transition to family foods independent of maternal obesity. mSphere 2016;1:e00069–15.










 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation