Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 67(11); 2024 |
|
Abstract
Background
Purpose
Methods
Results
Footnotes
Table┬Ā1.
| Parameter | High-performance NICUs | Low-performance NICUs | Total | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of VLBWIs | 2,717 | 2,028 | 4,745 | |
| Gestational age (wk) | 28.6┬▒3.0 | 28.2┬▒3.1 | 28.4┬▒3.0 | <0.01 |
| Gestational age (wk) | ||||
| ŌĆāŌēż24 | 241 (8.9) | 254 (12.5) | 495 (10.4) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā25ŌĆō27 | 746 (27.5) | 569 (28.1) | 1,315 (27.7) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā>27 | 1,730 (63.7) | 1,205 (59.4) | 2,935 (61.9) | <0.01 |
| Birth weight (g) | 1,095┬▒282 | 1,060┬▒294 | 1,080┬▒287 | <0.01 |
| Birth weight (g) | ||||
| ŌĆā<750 | 395 (14.5) | 358 (17.7) | 753 (15.9) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā750ŌĆō999 | 556 (20.5) | 460 (22.7) | 1,016 (21.4) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā1,000ŌĆō1,499 | 1,766 (65.0) | 1,210(59.7) | 2,976 (62.7) | <0.01 |
| Small for gestational age | 737 (27.3) | 511 (25.3) | 1,248 (26.4) | 0.128 |
| Male sex | 1,361 (50.1) | 1,034 (51.0) | 2,395 (50.5) | 0.542 |
| Multiple gestation | 1,008 (37.1) | 715 (35.3) | 1,723 (36.3) | 0.191 |
| 1-min Apgar score Ōēż3 | 788 (29.2) | 599 (29.8) | 1,387 (29.4) | 0.676 |
| 5-min Apgar score Ōēż3 | 156 (5.8) | 153 (7.6) | 309 (6.6) | <0.05 |
| Cardiac compressions and epinephrine in the delivery room | 183 (5.7) | 98 (5.5) | 236 (5.6) | 0.773 |
| Initial BT, <36.5┬░C | 1,871 (70.0) | 1,452 (74.2) | 3,323 (71.8) | <0.01 |
| Initial pH, <7.25 | 944 (44.0) | 439 (32.5) | 1,383 (39.5) | <0.01 |
| Maternal age (yr) | 33.0┬▒4.2 | 33.0┬▒4.2 | 33.0┬▒4.2 | 0.970 |
| Maternal education (>12 yr) | 1,542 (76.1) | 1,136 (72.6) | 2,678 (74.6) | <0.05 |
| Pregnancy process, IVF | 691 (25.4) | 461 (22.7) | 1,152 (24.3) | <0.05 |
| Cesarean section | 2,166 (79.7) | 1,595 (78.7) | 3,761 (79.3) | 0.368 |
| Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios | 413 (16.7) | 268 (14.6) | 681 (15.8) | <0.05 |
| Chorioamnionitis | 825 (33.6) | 568 (37.9) | 1,398 (35.2) | <0.01 |
| PPROM | 943 (34.9) | 714 (35.7) | 1,657 (35.2) | 0.579 |
| DMa) | 24.2 (8.9) | 172 (8.5) | 414 (8.7) | 0.607 |
| HTNb) | 575 (21.2) | 416 (20.5) | 991 (20.9) | 0.586 |
| Antenatal steroid | 2,097 (78.3) | 1,618 (81.6) | 3,715 (79.7) | <0.01 |
| Out-of-hospital birth | 63 (2.3) | 64 (3.2) | 127 (2.7) | 0.077 |
Values are presented as mean┬▒standard deviation or number of cases (%).
After ranking the mortality rates of all neonatal intensive care units registered in the Korean Neonatal Network. High-performance, 1st and 2nd quartiles; lowperformance, 3rd and 4th quartiles.
VLBWI, very low birth weight infant; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; BT, body temperature; IVF, in vitro fertilization; PROM, preterm premature rupture of membrane; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension.
Table┬Ā2.
| Parameter | High-performance NICUs | Low-performance NICUs | Total | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDA treatmenta) | 926 (51.5) | 681 (51.6) | 1,607 (51.6) | 0.956 |
| Sepsis | 479 (17.7) | 481 (23.9) | 960 (20.3) | <0.01 |
| IVHŌēź3 | 194 (7.3) | 213 (11.2) | 407 (8.9) | <0.01 |
| PVL | 192 (7.2) | 118 (6.2) | 310 (6.8) | 0.178 |
| NEC, Ōēźstage 2 | 152 (5.6) | 166 (8.3) | 318 (6.8) | <0.01 |
| BPD, Ōēźmoderate | 718 (29.1) | 441 (27.7) | 1,159 (28.5) | 0.338 |
| ROP, Ōēźstage 3 or laser therapy | 309 (12.7) | 197 (12.6) | 506 (12.6) | 0.926 |
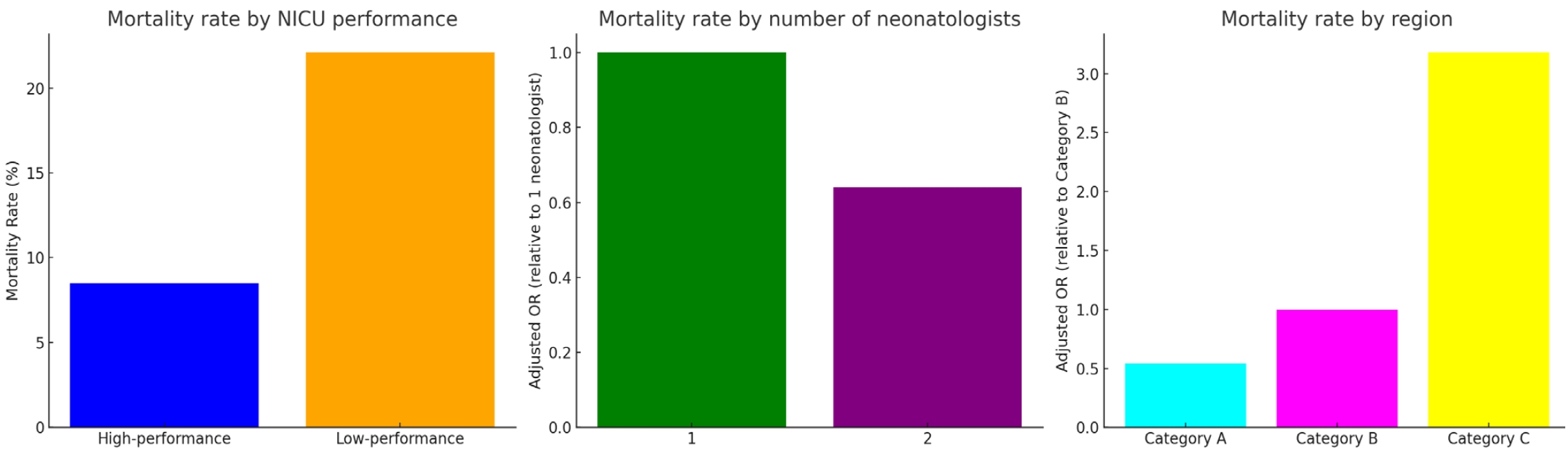
| Death | 230 (8.5) | 448 (22.1) | 678 (14.3) | <0.01 |
| Death by gestational age (wk) | ||||
| ŌĆāŌēż24 | 111 (46.1) | 180 (70.9) | 291 (58.8) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā25ŌĆō27 | 89 (11.9) | 194 (34.1) | 283 (21.5) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆā>27 | 30 (1.7) | 74 (6.1) | 104 (3.5) | <0.01 |
Values are presented as number of cases (%).
VLBWI, very low birth weight infant; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; PVL, periventricular leukomalacia; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity.
Table┬Ā3.
| Parameter | High-performance NICUs | Low-performance NICUs | Total | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit type | 0.389 | |||
| ŌĆāTertiary hospital | 2,133 (78.5) | 1,613 (79.5) | 3,746 (79.0) | |
| ŌĆāGeneral hospital | 584 (21.5) | 415 (20.5) | 999 (21.1) | |
| NICU capacity | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆāŌēż19 Beds | 341 (12.6) | 468 (23.1) | 809 (17.1) | |
| ŌĆā20ŌĆō39 Beds | 1,474 (54.3) | 1,312 (64.7) | 2,786 (58.7) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź40 Beds | 902 (33.2) | 248 (12.2) | 1,150 (24.2) | |
| Nurse staffing grade | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆāGrade 1 | 2,308 (85.0) | 1,595 (78.7) | 3,903 (82.3) | |
| ŌĆāGrade 2 | 365 (13.4) | 423 (20.9) | 788 (16.6) | |
| ŌĆāGrade 3 | 44 (1.6) | 10 (0.5) | 54 (1.1) | |
| No. of neonatologists | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆā1 | 447 (16.5) | 589 (29.0) | 1,036 (21.8) | |
| ŌĆā2 | 1,463 (53.9) | 963 (47.5) | 2,426 (51.1) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź3 | 807 (29.7) | 476 (23.5) | 1,283 (27.0) | |
| No. of pediatricians | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆā1 | 488 (18.0) | 500 (24.7) | 988 (20.8) | |
| ŌĆā2 | 1,320 (48.6) | 881 (43.4) | 2,201 (46.4) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź3 | 909 (33.5) | 647 (31.9) | 1,556 (32.8) | |
| NICU beds per pediatrician | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆāŌēż10 | 1,423 (52.4) | 963 (48.4) | 2,386 (50.7) | |
| ŌĆā11ŌĆō15 | 853 (31.4) | 629 (31.6) | 1,482 (31.5) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź16 | 441 (16.2) | 399 (20.0) | 840 (17.8) | |
| NICU therapy-level | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆāLevel II | 1,005 (37.0) | 1,148 (56.6) | 2,153 (45.4) | |
| ŌĆāLevel III | 832 (30.6) | 517 (25.5) | 1,349 (28.4) | |
| ŌĆāLevel IV | 880 (32.4) | 363 (17.9) | 1,243 (26.2) | |
| City or provincea) | <0.01 | |||
| ŌĆāCategory A | 1,353 (49.8) | 536 (26.4) | 1,889 (39.8) | |
| ŌĆāCategory B | 371 (13.7) | 95 (4.7) | 466 (9.8) | |
| ŌĆāCategory C | 993 (36.6) | 1,397 (68.9) | 2,390 (50.4) |
Table┬Ā4.
| Variable | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| No. of neonatologists | ||
| ŌĆā1 | Reference | |
| ŌĆā2 | 0.64 (0.54ŌĆō0.76) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāŌēź3 | 0.99 (0.78ŌĆō1.27) | 0.985 |
| NICU beds per pediatrician | ||
| ŌĆāŌēź16 | Reference | |
| ŌĆā11ŌĆō15 | 0.51 (0.41ŌĆō0.62) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāŌēż10 | 0.77 (0.63ŌĆō0.93) | <0.01 |
| NICU therapy-level | ||
| ŌĆāLevel IV | Reference | |
| ŌĆāLevel III | 1.56 (1.23ŌĆō1.97) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāLevel II | 2.85 (2.33ŌĆō3.47) | <0.01 |
| City or provincea) | ||
| ŌĆāCategory A | 0.54 (0.41ŌĆō0.73) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāCategory B | Reference | |
| ŌĆāCategory C | 3.18 (2.71ŌĆō3.72) | <0.01 |
| Nurse staffing grade | ||
| ŌĆāGrade 1 | Reference | |
| ŌĆāGrade 2 | 1.36 (1.14ŌĆō1.63) | <0.01 |
NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
The statistical methods involved multivariate logistic regression analysis with adjustment for covariables identified as significant through preliminary analyses and corroborated by prior research. Covariables included in the adjusted models were as follows: maternal age, maternal education, antenatal steroid, chorioamnionitis, gestational age, small for gestational age, child's sex, multiple gestation, sepsis, intraventricular hemorrhage grade III or IV, necrotizing enterocolitis, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Table┬Ā5.
| Variable | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of neonatologists | ||
| ŌĆā1 neonatologist | Reference | |
| ŌĆā2 neonatologists | 0.67 (0.50ŌĆō0.90) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāŌēź3 neonatologists | 1.43 (0.93ŌĆō2.21) | 0.107 |
| NICU beds per pediatrician | ||
| ŌĆāŌēź16 | Reference | |
| ŌĆā11ŌĆō15 | 0.44 (0.31ŌĆō0.63) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāŌēż10 | 0.68 (0.48ŌĆō0.96) | <0.01 |
| NICU therapy-level | ||
| ŌĆāLevel IV | Reference | |
| ŌĆāLevel III | 1.83 (1.23ŌĆō2.73) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāLevel II | 2.95 (2.09ŌĆō4.16) | <0.01 |
| City or provincea) | ||
| ŌĆāCategory A | 0.53(0.32ŌĆō0.89) | <0.01 |
| ŌĆāCategory B | Reference | |
| ŌĆāCategory C | 3.72 (2.84ŌĆō4.88) | <0.01 |
| Nurse staffing grade | ||
| ŌĆāGrade 1 | Reference | |
| ŌĆāGrade 2 | 1.03 (0.75ŌĆō1.41) | 0.873 |
CI, confidence interval; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; OR, odds ratio.
The statistical method involved multivariate logistic regression analysis with adjustment for covariables identified as significant through preliminary analyses and corroborated by prior research. Covariables included in the adjusted models were as follows: maternal age, maternal education, antenatal steroid, chorioamnionitis, gestational age, small for gestational age, child's sex, multiple gestation, sepsis, intraventricular hemorrhage grade III or IV, necrotizing enterocolitis, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation