Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six months.
- Clinical note
- General Pediatrics
- Diabetic ketoacidosis in children induced by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diabetic ketoacidosis post-COVID-19 in children (7 times)
- Neha Thakur, Narendra Rai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):209-210. Published online November 30, 2021
-
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems (7 times)
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
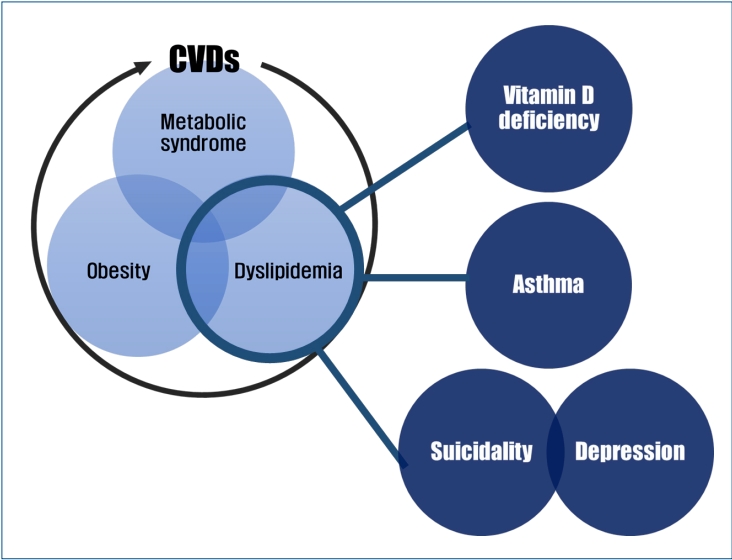
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Clinical and diagnostic importance of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (7 times)
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):129-130. Published online January 14, 2022
-
∙ Because childhood lipid concentrations continue into adulthood, early evaluation and treatment are needed, but dyslipidemia awareness is low.
∙ For the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in childhood and adolescence, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in adulthood, lifestyle modifications, appropriate exercise, and drug treatment are required.
∙ A large-scale study of the prevalence and therapeutic effects of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents in Korea is needed.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Changes in epidemiology of parainfluenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus infection during coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea (7 times)
- Kyung-Ran Kim, Hwanhee Park, Doo Ri Kim, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):320-321. Published online March 10, 2022
-

Question: How the epidemiology of other childhood respiratory viruses has changed during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea?
Finding: Parainfluenza virus (PIV) typically circulated in the spring, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) epidemic started in autumn in Korea before COVID-19 pandemic. PIV and RSV seasons disappeared in 2020 and came back in 2021 with atypical seasonality. PIV season was changed from spring to autumn, and the beginning of RSV season was slightly delayed from autumn to early winter in 2021.
Meaning: Circulation of PIV and RSV was changed to unusual seasons and patterns during COVID-19 pandemic period.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Coronavirus disease 2019 and mRNA vaccines: what’s next – miRNA? (7 times)
- Joon Kee Lee, Heon-Seok Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):302-303. Published online March 28, 2022
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small single-stranded noncoding RNA molecules that function in RNA silencing and the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. The potential role of miRNAs as biomarkers of myocarditis is promising, and miRNAs are expected to be utilized in various clinical fields in the future.
- Endocrinology
- Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children? (7 times)
- Minsun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):252-253. Published online March 29, 2022
-
· Evidence shows that patients with type 1 diabetes have been severely affected by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in various ways.
· Although there is no reliable evidence that COVID-19 worsens or induces diabetes, it can impair β-cell insulin secretion and glucose control by inducing inflammation and cytokine production.
· A study is needed of the short- and long-term relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 in the Korean pediatric population.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents (7 times)
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
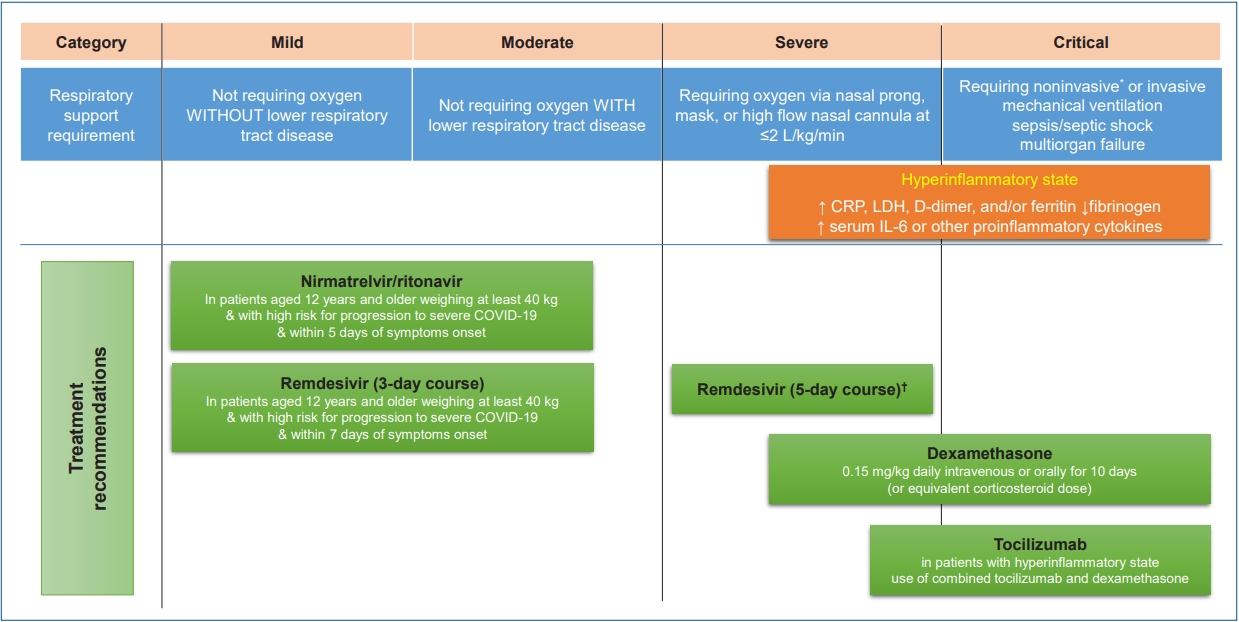
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Predicting COVID-19 transmission in a student population in Seoul, South Korea, 2020–2021 (7 times)
- Young Hwa Lee, Han Ho Kim, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):173-178. Published online December 22, 2022
-
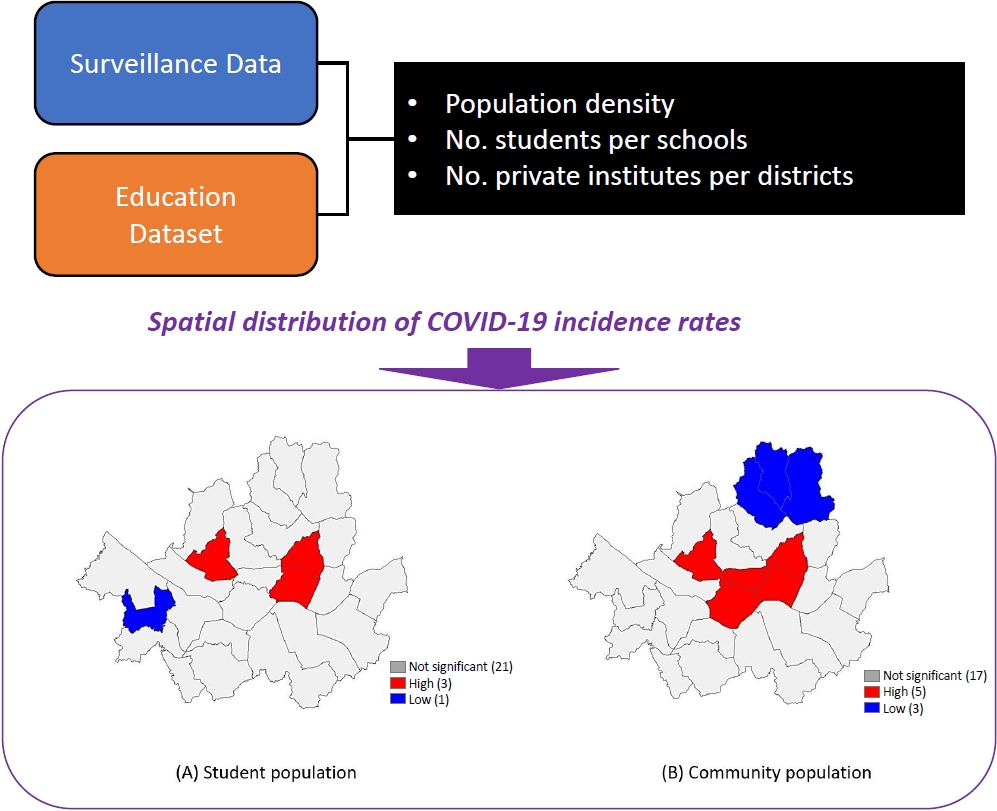
Question: What is the spatial distribution and determinants of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection among students in Korea?
Finding: The community population was closely associated with the risk of COVID-19, and the number of students per school class were inversely associated with COVID-19 rates in students.
Meaning: Our finding suggests that controlling the community-level burden of COVID-19 can help prevent sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in school-aged children.
- Hematology
- Changes and correlations of T-cell coinhibitory molecule programmed death-1 and interferon-γ in pediatric immune thrombocytopenia (7 times)
- Fady Mohamed El-Gendy, Amira M.F. Shehata, Esam Awad Abd El-Kawy, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):127-133. Published online February 24, 2023
-
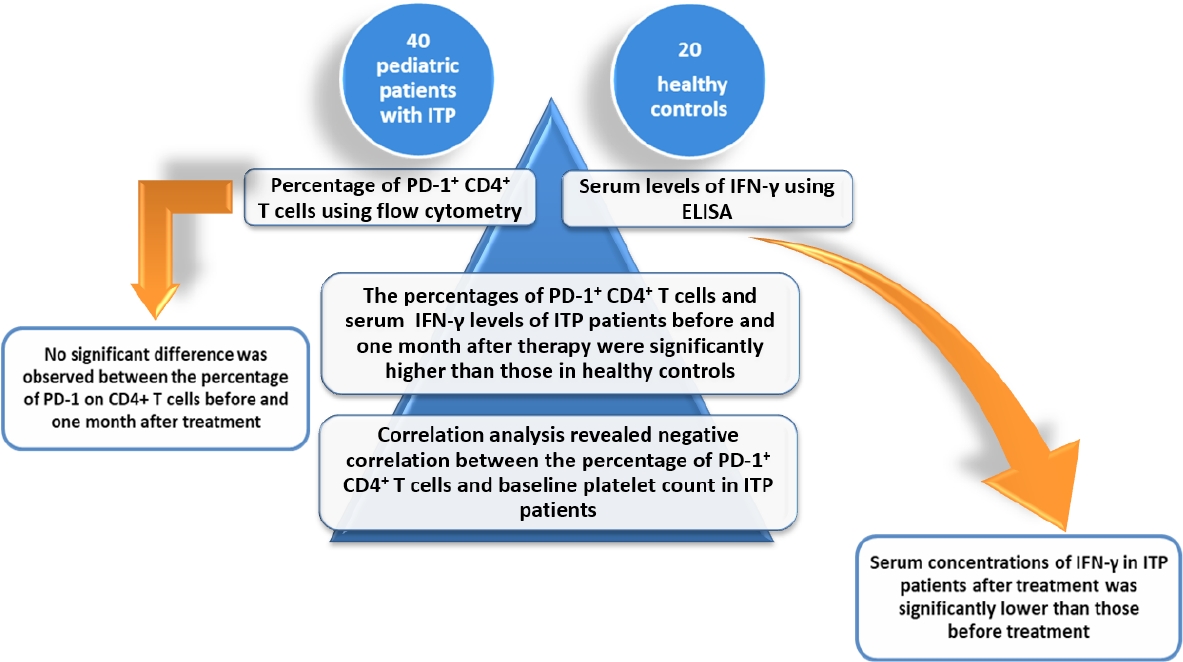
Question: What are the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and serum interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels of pediatric patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)?
Finding: Compared with healthy controls, the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in ITP patients before and 1 month after therapy.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that PD-1+ CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are involved in the pathophysiological process of ITP.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effectiveness of obesity interventions among South Korean children and adolescents and importance of the type of intervention component: a meta-analysis (6 times)
- Siyoung Choe, Jaesin Sa, Jean-Philippe Chaput, Deokjin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):98-107. Published online November 23, 2021
-
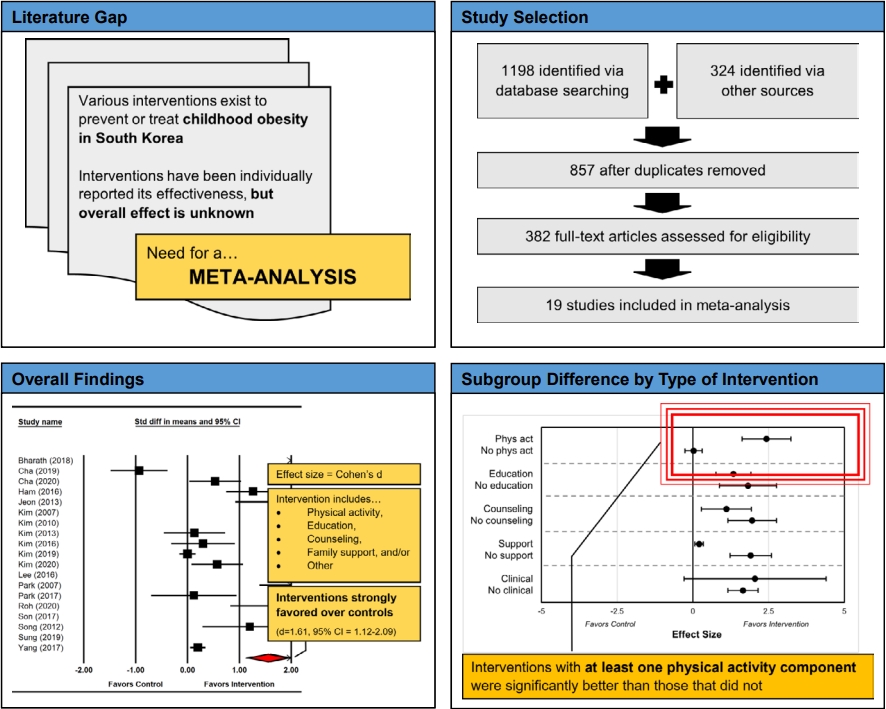
Question: What is the overall effect of obesity interventions among Korean children and what affects their effectiveness?
Finding: Interventions were strongly favored over controls. Interventions including at least one physical activity component were significantly better than those that did not. Sex, age, baseline weight category, intervention duration, and the number of intervention components were not significant.
Meaning: Future obesity interventions for Korean children must seek to include physical activity components.
- Letter to the Editor
- Oncology
- Retrospective review of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in children with acute leukemia from a tertiary care hospital in Northern India (6 times)
- Suhail Chhabra, Aditya Dabas, Richa Mittal, Neha Goel, Ritabrata Roy Chowdhary, Satyendra Batra, Amitabh Singh, Rani Gera
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):150-151. Published online November 26, 2021
-
- Editorial
- Infection
- Importance of maintaining a high childhood vaccination rate and surveillance program against Japanese encephalitis in Korea (6 times)
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):127-128. Published online February 16, 2022
-
∙ Recent epidemiologic changes of Japanese encephalitis (JE) in Korea are area (rural to urban or suburban) and age shift (children to adult).
∙ Although the main factors contributing to recent epidemiologic changes of JE are not well identified, maintaining high vaccination rates of JE appear to be important in preventing of JE in all age groups.
∙ Continuous surveillance for epidemiology and seroprevalence should be carried out.
- Correspondence and Reply
- Neurobehavior
- Association between polycystic ovary syndrome and risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring: a meta-analysis (6 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):152-152. Published online February 17, 2022
-
- Editorial
- Nutrition
- Human milk oligosaccharides as immunonutrition key in early life (6 times)
- Jung Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):344-345. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Human milk is a major source of immunonutrients for neonates and infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) act as prebiotics and promote the growth of commensal bacteria.
· HMOs inhibit microorganism adhesion to the gut mucosa through interactions with the commensal microbiome and improve gut barrier function by increasing short-chain fatty acid mediated by bifidobacteria and immunomodulation.
· Several randomized controlled trials recently reported on HMOs.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Role of lung ultrasound patterns in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children (6 times)
- Satyabrata Roychowdhoury, Subhajit Bhakta, Manas Kumar Mahapatra, Saptarshi Ghosh, Sayantika Saha, Mithun Chandra Konar, Mihir Sarkar, Mousumi Nandi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):358-366. Published online May 13, 2022
-
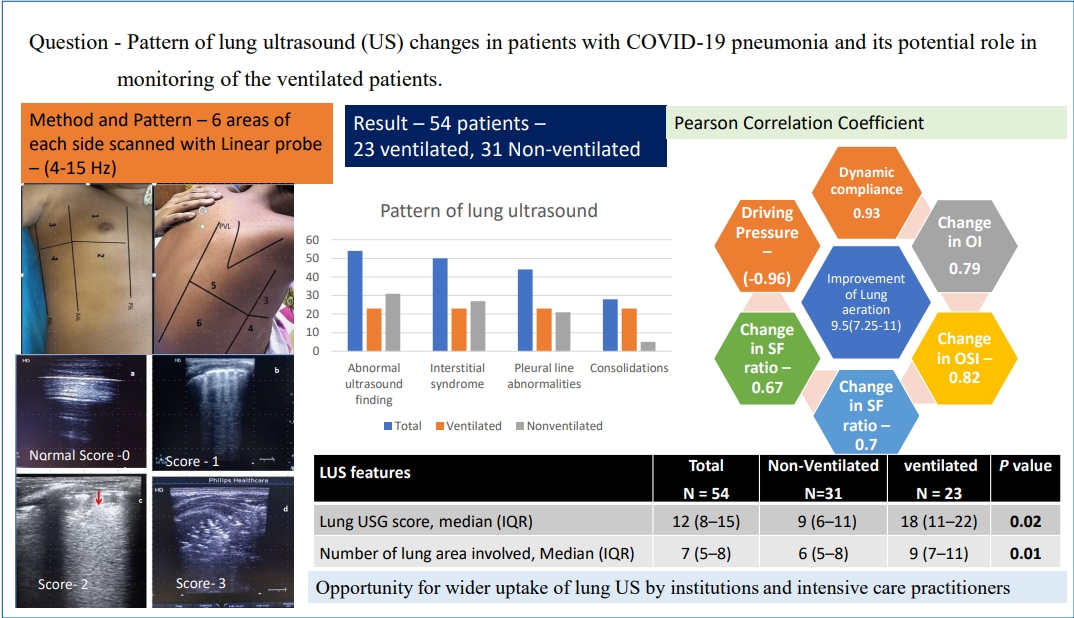
Question: Potential role of patterns of lung ultrasonography (US) in monitoring changes in mechanically ventilated patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.
Finding: Interstitial syndrome, an irregular pleural line, and peripheral microconsolidation were the most prevalent findings. Changes in lung aeration after mechanical ventilation corelated with improved oxygenation. A fall in lung ultrasound reaeration score ≤ 5 may predict successful weaning.
Meaning: Lung US is gaining wider utility for monitoring COVID-19 pneumonia.
- Retraction Notice
- Coronavirus disease 2019 in a 2-month-old male infant: a case report from Iran (6 times)
- Hosein Heydari, Seyed Kamal Eshagh Hossaini, Ahmad Hormati, Mahboubeh Afifian, Sajjad Ahmadpour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):417-417. Published online July 19, 2022
-
- Editorial
- Emergency Medicine
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children: teamwork approach (6 times)
- Ji-Hyun Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):66-67. Published online September 1, 2022
-
· The successful and safe enema reduction of intussusception depends primarily on the experience and preference of the radiologists and the availability of resources.
· The establishment of a standardized manual or protocol for reduction and pre-reduction treatment of intussusception, along with the collaboration of pediatricians, radiologists, and surgeons, is expected to improve the treatment success rate.
- Neurobehavior
- Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on children’s health (6 times)
- Joon Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):498-499. Published online September 16, 2022
-
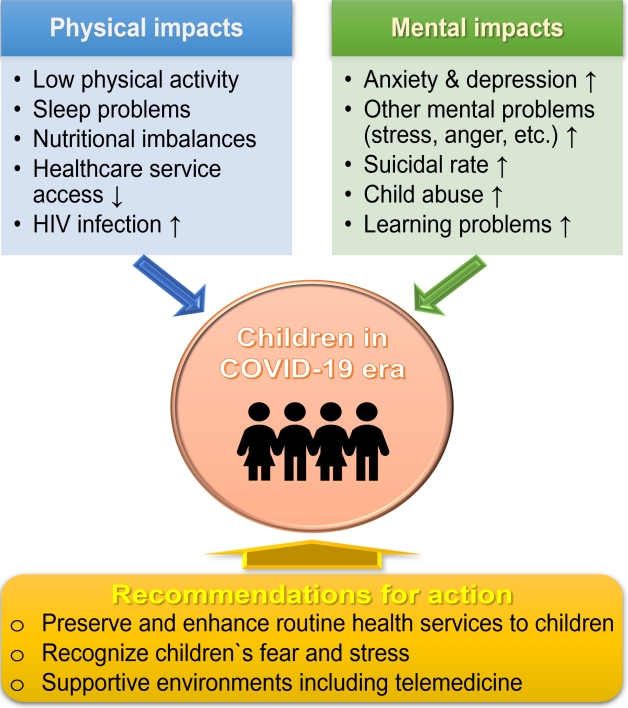
· Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has had an enormous impact on mental health and other aspects of children’s health.
· The prevalence of anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents have increased in the COVID-19 era.
· Cooperation among parents, guardians, academic societies, and the government is needed to maintain the mental health of children and adolescents.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Early myocardial functional abnormalities in primary dyslipidemia: clinical and echocardiographic observations in young children from a highly consanguineous population (5 times)
- Nehal M. El-koofy, Aya M. Fattouh, Areef Ramadan, Mohamed A. Elmonem, Dina H. Hamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):410-416. Published online December 8, 2021
-
In children with primary dyslipidemia, functional myocardial abnormalities can occur at young age, including diastolic functional impairment of both ventricles and narrowing of the aortic valve and the sinus of Valsalva. Echocardiographic evaluations of high-risk children may be as important as biochemical evaluations.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Recent research trends in Kawasaki disease-related infection (5 times)
- Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):538-539. Published online July 22, 2022
-
The incidence of Kawasaki disease has reportedly decreased since the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) quarantine. However, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children has reportedly occurred more frequently in areas where COVID-19 was prevalent than in previous years. Research into the etiology of childhood and adolescent systemic vasculitis in infection-related immune responses during the COVID-19 pandemic has increased accordingly.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of polymicrobial probiotic and mono-strain probiotic to reduce functional abdominal pain in children: a randomized clinical trial (5 times)
- Seyed Sajad Jafari, Seyed Mojtaba Hashemi, Bahman Sadeghi, Amir Almasi-Hashiani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):589-594. Published online October 31, 2022
-

· This study compared the ability of 2 probiotics to reduce and improve functional abdominal pain (FAP) in children.
· In the polymicrobial probiotic (PMP) group, 10.34% of children reported no pain; in the mono-strain probiotic (MSP) group, all patients reported low-degree pain. The mean pain score decreased significantly over time in both groups.
· The use of both PMP and MSP is recommended to reduce pain in patients with FAP.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of allergic diseases in COVID-19 era (5 times)
- Sungsu Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):587-588. Published online November 29, 2022
-
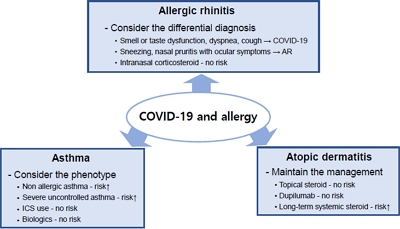
The risk of sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes is not elevated in patients with the type 2 phenotype and well-controlled asthma. Inhaled corticosteroids, intranasal corticosteroids, and topical steroids can be safely used in COVID-19 patients. Biologics can be safely used by patients with allergic diseases without concern about antibody responses.
- Perspective
- Other
- New public-centered child protection system in Korea (5 times)
- We Sun Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):179-181. Published online April 18, 2023
-
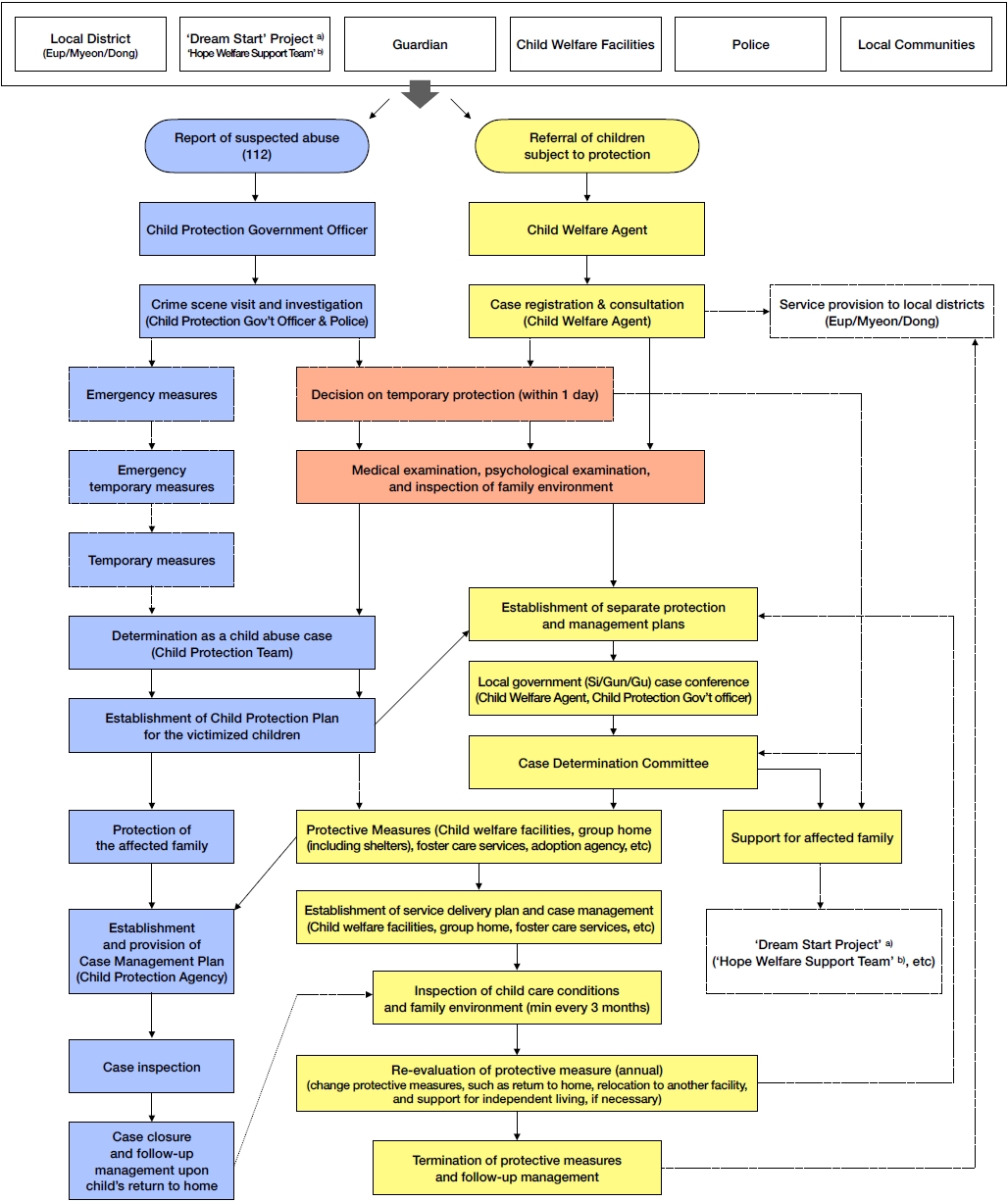
Korea’s child abuse response system was transformed under policy change in April 2020, from what was previously operated on a private-centered basis to a focus on the public sector with expanded role of local governments. Promising outcomes are expected with new system as greater governmental intervention will effectively protect at-risk children with acceleration in institutional collaboration and expertise in information management and administration.
- Letter to the Editor
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of rolling over pattern and caregiver perception on plagiocephaly in Korean infants (5 times)
- Jin A Yoon, Soo-Yeon Kim, Yong Beom Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):272-273. Published online May 24, 2023
-
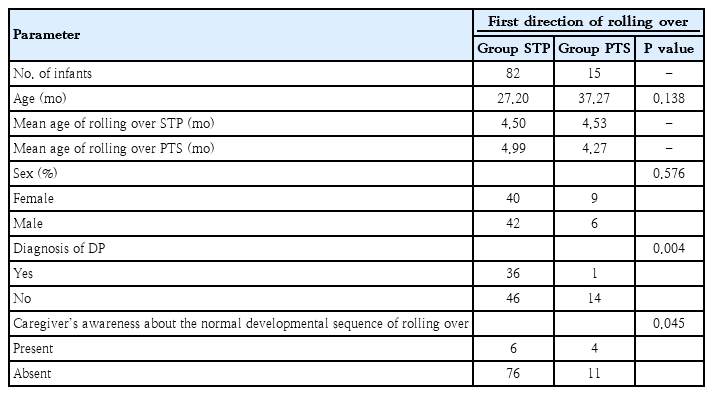
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Is it time to add point-of-care ultrasound education to pediatric residency curriculum? (4 times)
- Shin Ae Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):33-34. Published online October 12, 2021
-
Growing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) use in pediatric patients has led to the need for POCUS education for pediatric residents. Recent experimental studies have suggested that POCUS education improves self-rated POCUS confidence and comfort in pediatric resident training. Considering the effective and sustainable POCUS education curriculum in pediatric resident training, simulation-based education would be a solution.
- Neurology
- Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in various pediatric neurologic diseases (4 times)
- Jeongho Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):81-82. Published online January 6, 2022
-

Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has many important biomarkers that are commonly analyzed in pediatric neurologic diseases, including central nervous system infection and inflammation. Neurologic disease in pediatrics is difficult to diagnosis, there are challenges in developing CSF profiles. Some biomarkers are expected to help differential diagnosis.
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
- Changes in air pollution and childhood respiratory viral infections in Korea post-COVID-19 outbreak (4 times)
- Hyung Kyu Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):211-213. Published online February 17, 2022
-
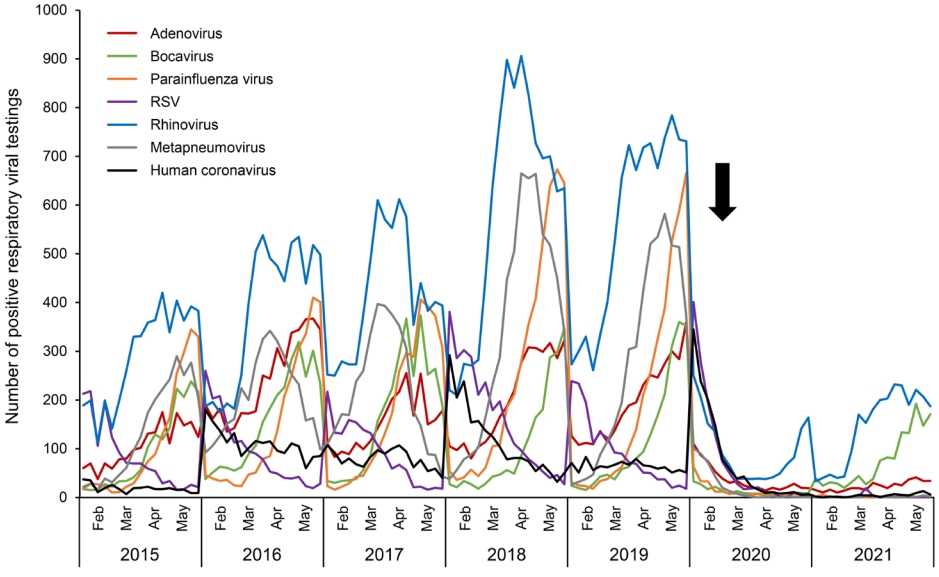
- Editorial
- Pulmonology
- Influence of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on respiratory health in children (4 times)
- Hyo-Bin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):348-349. Published online May 3, 2022
-
· Practicing hand hygiene, wearing a mask, maintaining social distancing, and other lockdown measures were implemented to reduce the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a worldwide disaster that started in 2019.
· The advent of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic resulted in positive secondary effects, such as reduced respiratory viral infections in children and decreased degrees of air pollution.
- Review Article
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (4 times)
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-

∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Clinical Note
- Endocrinology
- Graves’ disease: an uncommon cause of late sequelae following DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) (4 times)
- Therdpong Tempark, Amatanun Tangthanapalakul, Tawatchai Deekajorndech, Susheera Chatproedprai, Vichit Supornsilchai, Siriwan Wananukul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):602-604. Published online June 22, 2022
-
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







