Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six months.
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Hypertension in adulthood is programmed during the perinatal period
(4 times)
-
Min Hyun Cho
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):494-495. Published online August 12, 2022
-
|
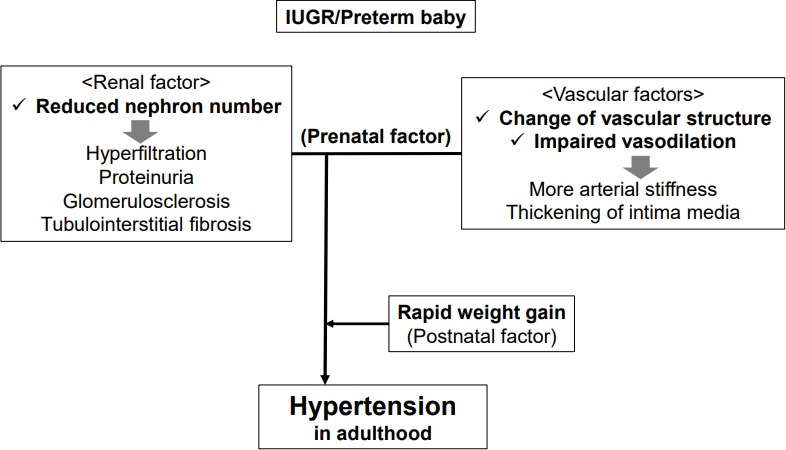
∙ Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and preterm birth can be significant risk factors for the development of adult hypertension.
∙ Several perinatal factors of hypertension are related to IUGR, including renal, vascular, and rapid catch-up growth. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Management of patients with allergic diseases in the era of COVID-19
(4 times)
-
Eun Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):529-535. Published online September 23, 2022
-
|
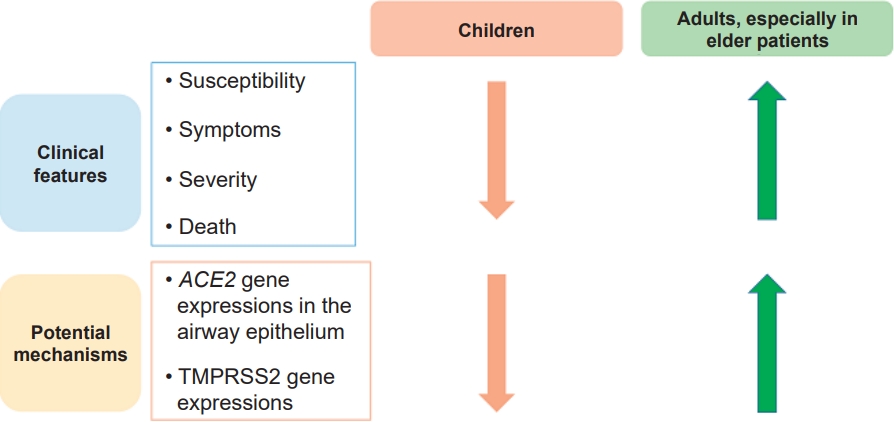
In the early days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, allergic diseases, especially asthma, were considered to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These concerns stemmed from the idea that individuals with allergic diseases are generally more susceptible to respiratory virus infections, which are major causes of exacerbation of allergic diseases. However, epidemiologic data with... |
-
-
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Ability of probiotics to reduce functional abdominal pain in children
(4 times)
-
Ji Sook Park
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):585-586. Published online October 6, 2022
-
|
|
· The ability of probiotics to relieve pain caused by functional abdominal pain disorders (FAPD) in children is unclear.
· Lactobacillus reuteri may effectively reduce pain caused by childhood FAPD.
· Since the routine use of probiotics cannot be recommended due to a lack of clinical evidence, research into probiotic mixtures or symbiotics remains necessary. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Early echocardiographic screening for subclinical myocardial dysfunction in children and adolescents with dyslipidemia: why and when?
(3 times)
-
Hyun Gyung Lee, Hwa Jin Cho
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):398-400. Published online March 7, 2022
-
|
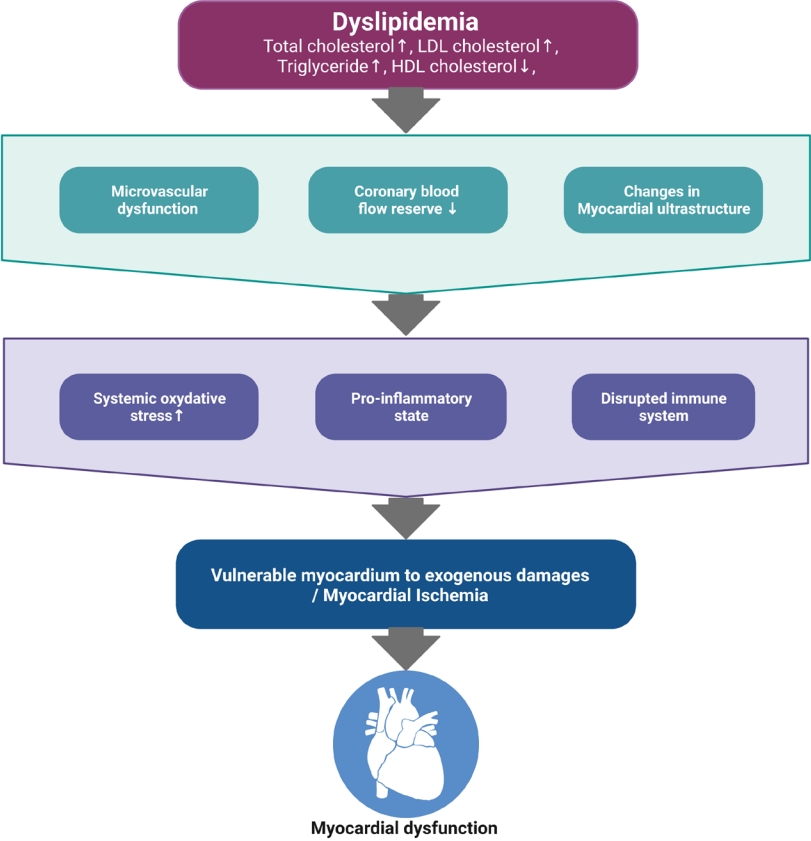
Dyslipidemia contributes to early atherosclerosis, premature cardiovascular disease, and subclinical ventricular dysfunction in children. This paper highlights the need for echocardiographic evaluation for impaired diastolic function of both ventricles and narrowing of the aortic valve and sinus of Valsalva. Therefore, early echocardiographic screening of children with primary hyperlipidemia should be considered. |
-
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Ideal timing for aggressive screening to detect developmental dysplasia of the hip in term and preterm infants
(3 times)
-
Won-Ho Hahn
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):346-347. Published online March 14, 2022
-
|
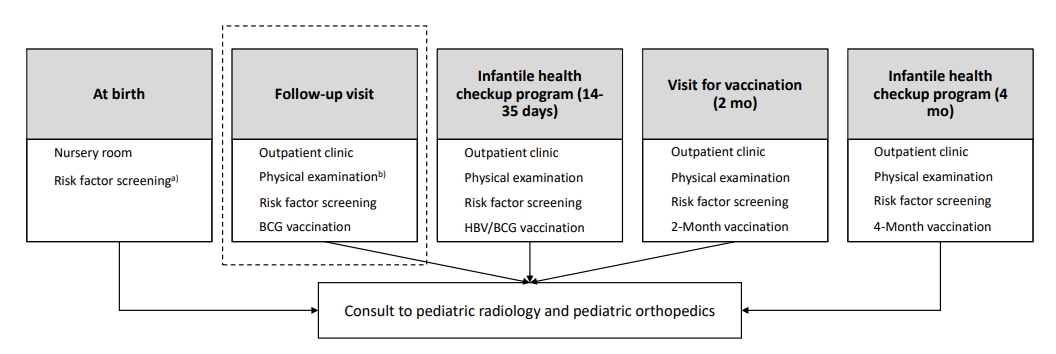
The risk factors and pathogenesis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) are unclear. Moreover, no universal screening method can entirely eliminate the risk of DDH. However, its incidence is significant and its early detection is critical for improving patient prognosis. Although the ideal evaluation time and risk factors, especially for premature infants, are unclear, the necessity for DDH screening programs for term and preterm infants is emerging. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Pediatricians must consider familial environment when diagnosing and managing childhood obesity
(2 times)
-
Young Suk Shim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):31-32. Published online April 19, 2021
-
|
|
•The prevalence of childhood obesity is increasing worldwide, including in the Republic of Korea, creating a major public healthissue.
•Accumulated evidence indicates a strong relationship between parentalandchildobesity.
•A family-based approach is indicated to prevent and manage childhoodandadultobesity. |
-
-
- Other
- Three-dimensional printing technolgy in orthopedic oncology
(2 times)
-
Yongsung Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):496-497. Published online May 11, 2022
-
|
|
Orthopedic oncology is one of the most active fields in applying 3-dimensional printing technology from preoperative planning to intraoperative procedures such as accurate resection of tumors and reconstruction of huge bone defects. |
-
-
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
- Evaluation of simulation-based ultrasound course for pediatricians: a starting point for future training curriculum
(1 time)
-
Chon In Kuok, Avis Siu Ha Leung, Jonan Chun Yin Lee, Winnie Kwai Yu Chan
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):53-55. Published online July 28, 2021
-
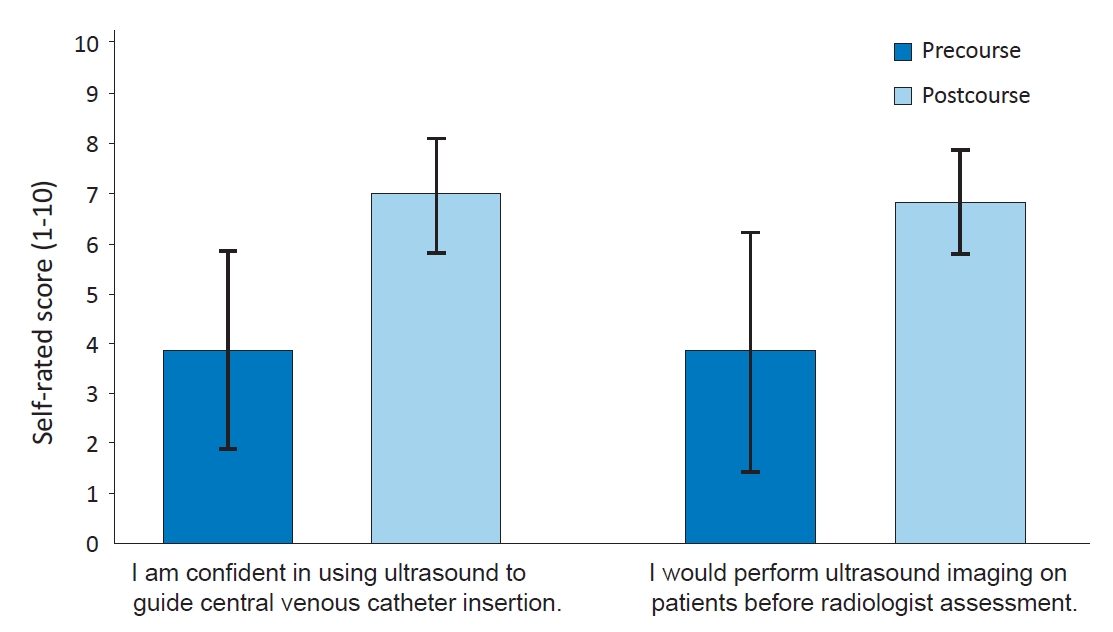
|
Question: Simulation-based ultrasound training is becoming more popular. Is there a role for pediatricians in such training programs?
Finding: Our program received promising feedback from its participants. Self-rated confidence in image interpretation and ultrasound-guided catheter insertion improved after the simulation. Participants reported a higher preference for performing ultrasound scans before radiologist assessment.
Meaning: Ultrasound training can be considered as part of the pediatric training curriculum in the future. |
-
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Telemedicine as progressive treatment approach for neonatal jaundice due to the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
(1 time)
-
Sukanya Sudhir Joshi, Bithiah Roy Benroy, Isabell Nelson Lawrence, Thanuja Jayasri Suresh
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):269-271. Published online February 7, 2022
-
|
|
Question: How can the management of neonatal jaundice (NJ) be enhanced through telemedicine?
Finding: Teleconsultations, drive-through testing, and the use of an application to assess neonatal jaundice at home are being successfully used, but they must be further researched before being implemented on a larger scale.
Meaning: Recent technology allows for the treatment of NJ at home with an application that helps reduce hospital burden. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Infection
- Effects of nonpharmaceutical interventions for coronavirus disease 2019
(1 time)
-
Jae Hong Choi
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):250-251. Published online March 22, 2022
-
|
|
∙ Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have decreased the incidence of various infectious diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
∙ During the 2-year COVID-19 pandemic, NPIs changed patients’ daily lives, and the impact on mental health was notable.
∙ The effects of NPIs were evaluated in detail, considering both infections and mental health. |
-
-















