Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" Articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last six month.
- Original Article
- Other
- Virtual, augmented, and mixed reality: potential clinical and training applications in pediatrics (1,360 times)
- Suyoung Yoo, Meong Hi Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):92-103. Published online May 24, 2023
-
· Review of articles that investigated the applications of virtual, augmented, or mixed reality in pediatric clinical settings and in the training of pediatric medical professionals was conducted.
· A total of 89 studies were retrieved, with 36 randomized controlled trials.
· In most studies, intervention using the novel technology was at least as effective or more effective than the traditional method.
· Use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality has potential in pediatrics.
- Review Article
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases (1,354 times)
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-
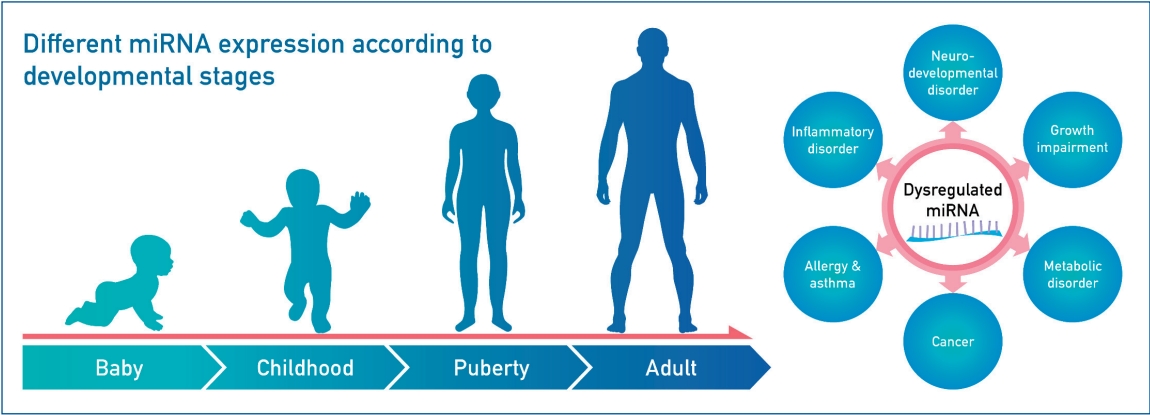
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Clinical Note
- Rheumatology
- Haploinsufficiency A20 misdiagnosed as PFAPA (periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and cervical adenitis) syndrome with Kikuchi disease (1,353 times)
- Kyo Jin Jo, Su Eun Park, Chong Kun Cheon, Seung Hwan Oh, Seong Heon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):82-84. Published online June 22, 2022
-
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmia and COVID-19 in children (1,335 times)
- Mi Kyoung Song, Bryan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):190-200. Published online April 18, 2023
-
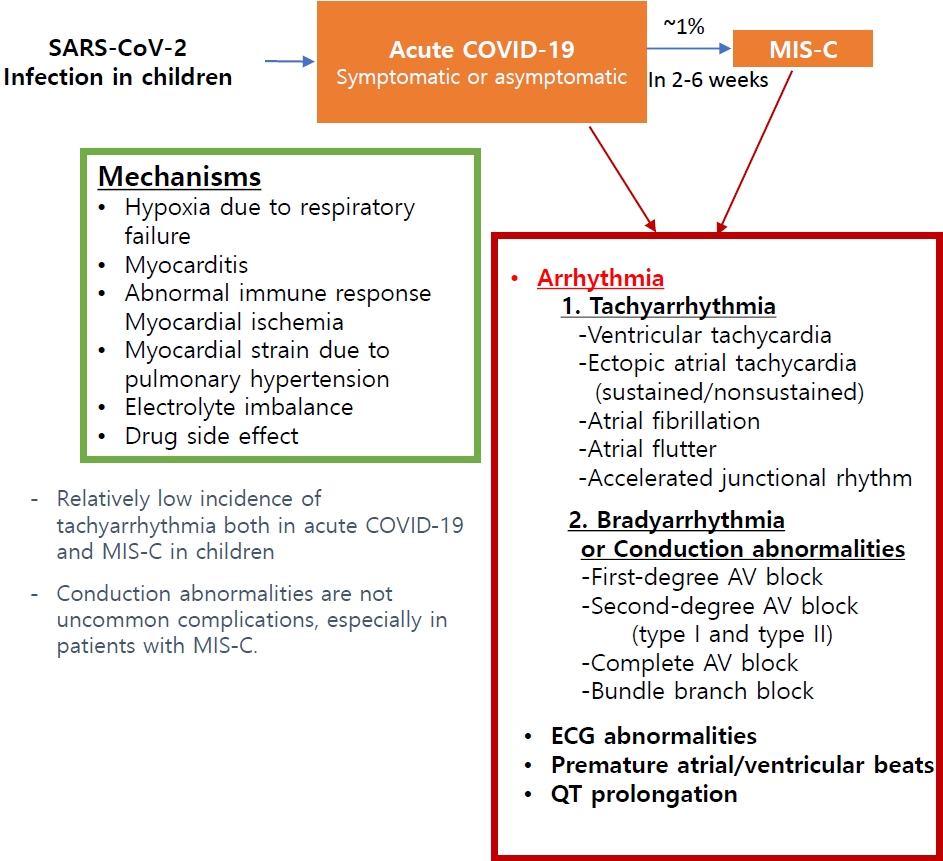
· Pediatric patients have a relatively low incidence of tachyarrhythmia both in acute coronavirus disease 2019 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), but it was associated with an increased risk of poor outcomes.
· Conduction abnormalities were not uncommon, especially in those with MIS-C. Most patients recovered to normal sinus rhythm; however, some progressed to advanced atrioventricular block and rarely required permanent pacemaker implantation.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Impact of short and intensive art-based intervention on symptomatology and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (1,331 times)
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Bayar Mohammed Omar Abdulla, Pranee Liamputtong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):447-454. Published online September 14, 2023
-

Question: Does a short and intensive art-based intervention affect symptoms and social interactions among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Finding: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not affect symptoms in children with ASD level 2 or 3, including social awareness, social cognition, social communication, social motivation, and autistic mannerisms.
Meaning: The short and intensive art-based intervention did not improve the symptoms of patients with ASD.
- Editorial
- Endocrinology
- Clinical and diagnostic importance of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic (1,312 times)
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):129-130. Published online January 14, 2022
-
∙ Because childhood lipid concentrations continue into adulthood, early evaluation and treatment are needed, but dyslipidemia awareness is low.
∙ For the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in childhood and adolescence, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease in adulthood, lifestyle modifications, appropriate exercise, and drug treatment are required.
∙ A large-scale study of the prevalence and therapeutic effects of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents in Korea is needed.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pathophysiology, classification, and complications of common asymptomatic thrombocytosis in newborn infants (1,305 times)
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):182-187. Published online October 18, 2021
-
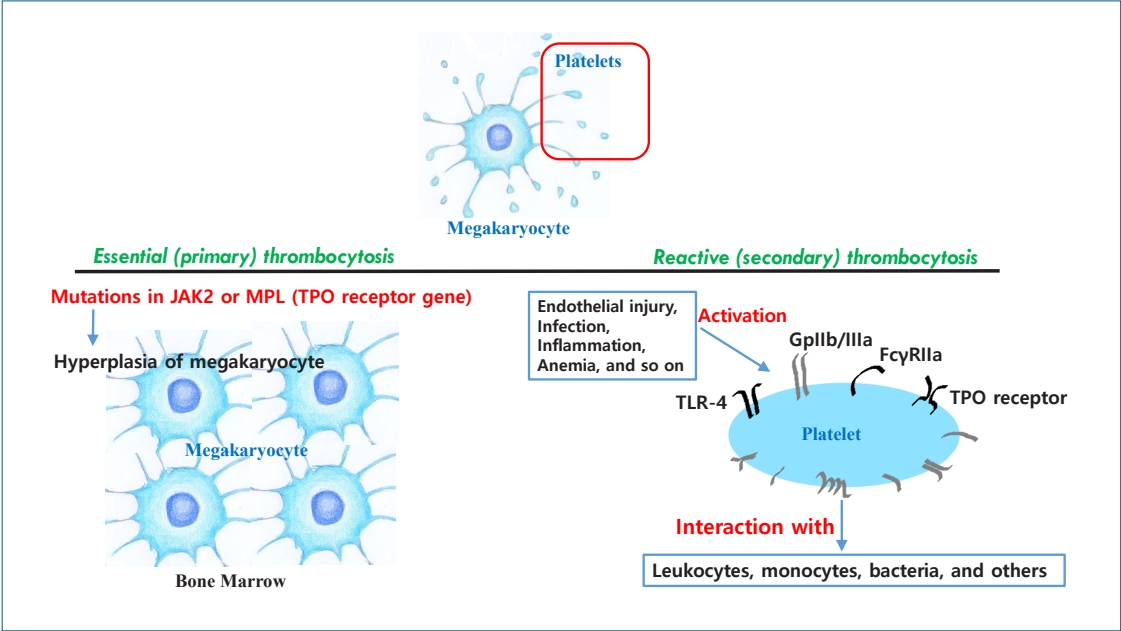
· Thrombocytosis, common in newborns and infants (<2 years) (3%–13%), is caused by elevated thrombopoietin (TPO) concentrations.
· Serum TPO levels are significantly higher immediately to 1 month postnatal and decrease with age.
· Platelet counts are positively correlated with gestational age at birth and postnatal age.
· Thrombocytosis is more common in preterm than in term infants.
· Thrombocytosis in newborns is reactive and resolves spontaneously without complications.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review (1,294 times)
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
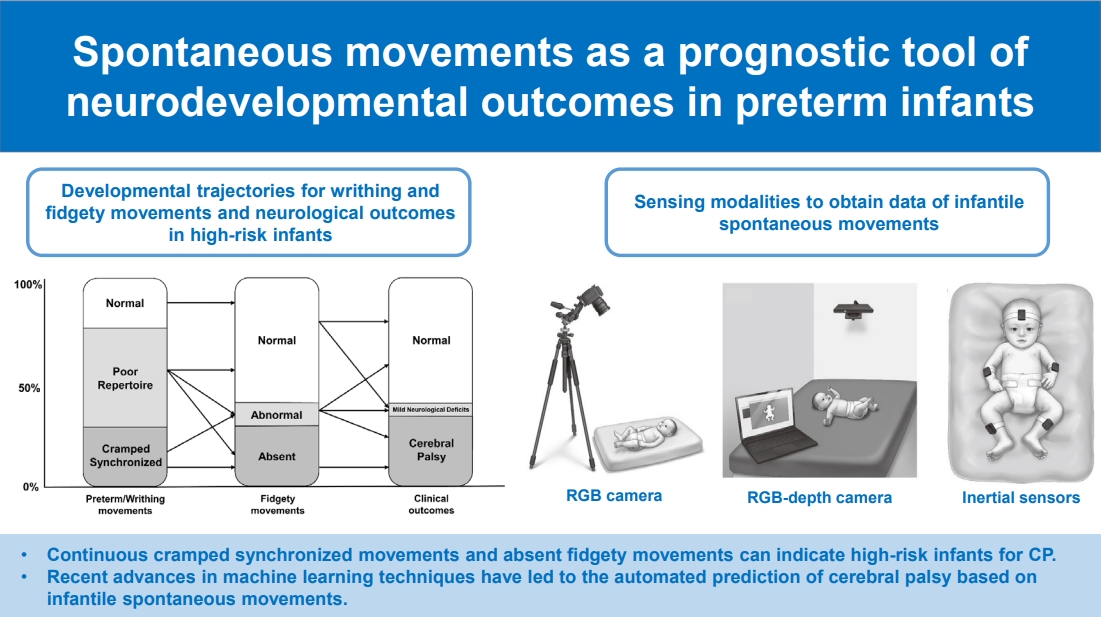
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Other
- Knowledge-guided artificial intelligence technologies for decoding complex multiomics interactions in cells (1,264 times)
- Dohoon Lee, Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):239-249. Published online November 26, 2021
-

· The need for data-driven modeling of multiomics interactions was recently highlighted.
· Many artificial intelligence-driven models have been developed, but only a few have incorporated biological domain knowledge within model architectures or training procedures.
· Here we provide a comprehensive review of deep learning models to decipher complex multiomics interactions regarding the biological guidance imposed upon them to facilitate further development of biological knowledge-guided deep learning models.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations (1,252 times)
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings.
- Pulmonology
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines (1,236 times)
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
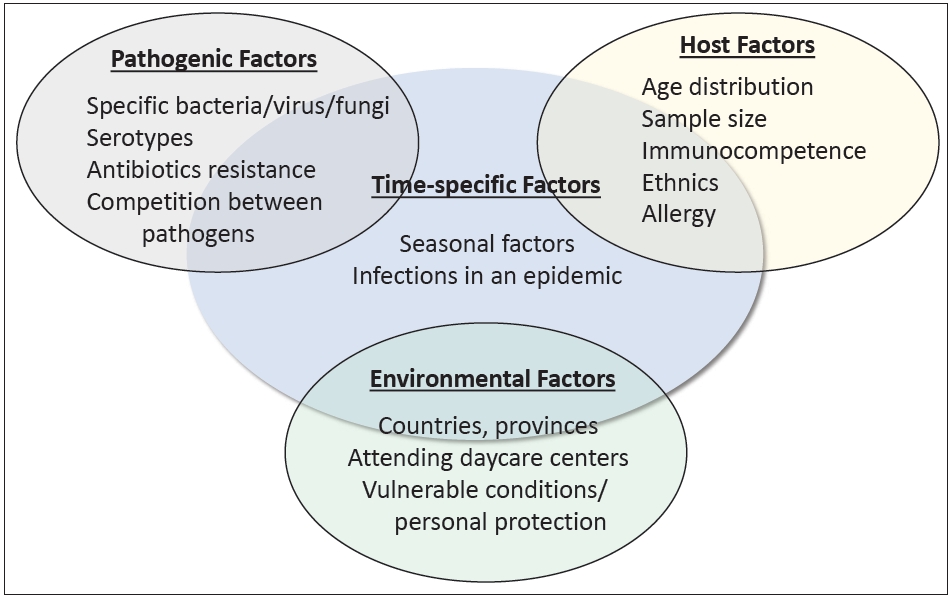
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic (1,224 times)
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Increasing our understanding of rotavirus-induced central nervous system manifestations (1,210 times)
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):536-537. Published online May 6, 2022
-
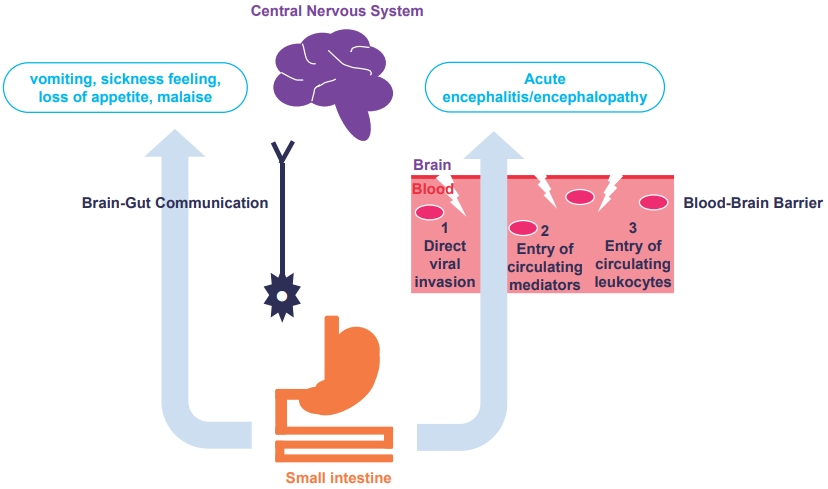
· Diverse clinicoradiological features of central nervous system (CNS) complications in rotavirus infection can be identified with the rapid and wide use of various brain magnetic resonance imaging protocols.
· An increased understanding of the various pathophysiological mechanisms of rotavirus-induced CNS manifestations will enable precise management in the future.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Research trends on causes of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 era: focus on viral infections (1,208 times)
- Young Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):1-11. Published online June 22, 2022
-
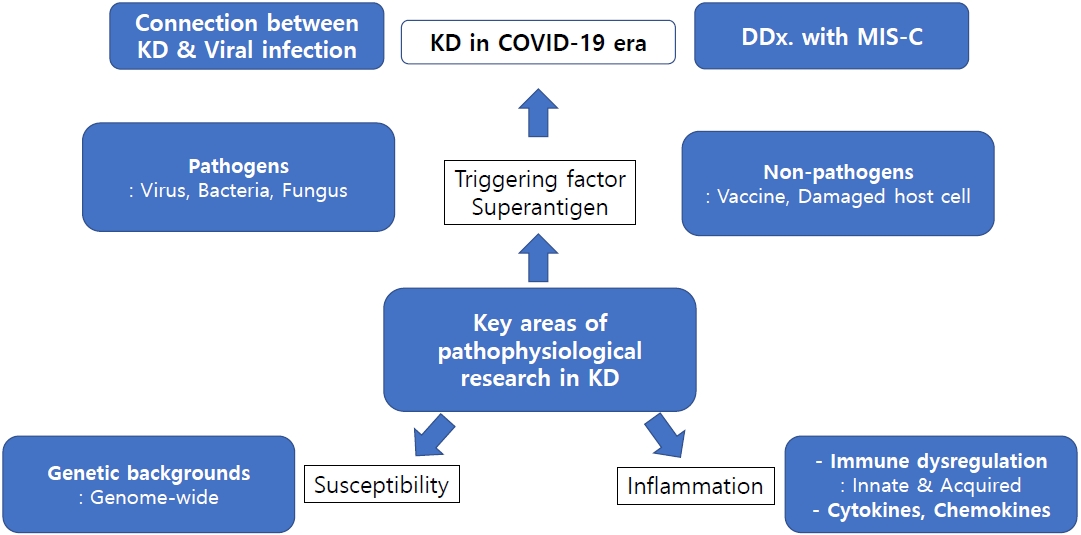
· The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unclear, but its clinical, epidemiological, and pathophysiological characteristics are strongly associated with infectious diseases.
· In the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic era, viruses are attracting the most attention. Sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection causes various hyperinflammation in children that require differentiation from KD.
· Immune responses in patients with KD may be induced by host cell damage. To effectively prevent and treat KD, the genetic background and immune responses of KD patients and triggering pathogens require identification.
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical considerations and practical issues of kidney complications in children after COVID-19 infection or vaccination (1,185 times)
- Jiwon Jung, Joo Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):35-36. Published online November 17, 2023
-
· The proper monitoring for and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill children, are recommended.
· Glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 or its vaccination has been reported, and the overall clinical course is similar to that of non-COVID-19-associated diseases.
· Additional COVID-19 vaccinations are recommended; however, careful and individualized decisions should be made in patients with COVID-19- or vaccination-associated glomerulopathy.
- Clinical Note
- Neurology
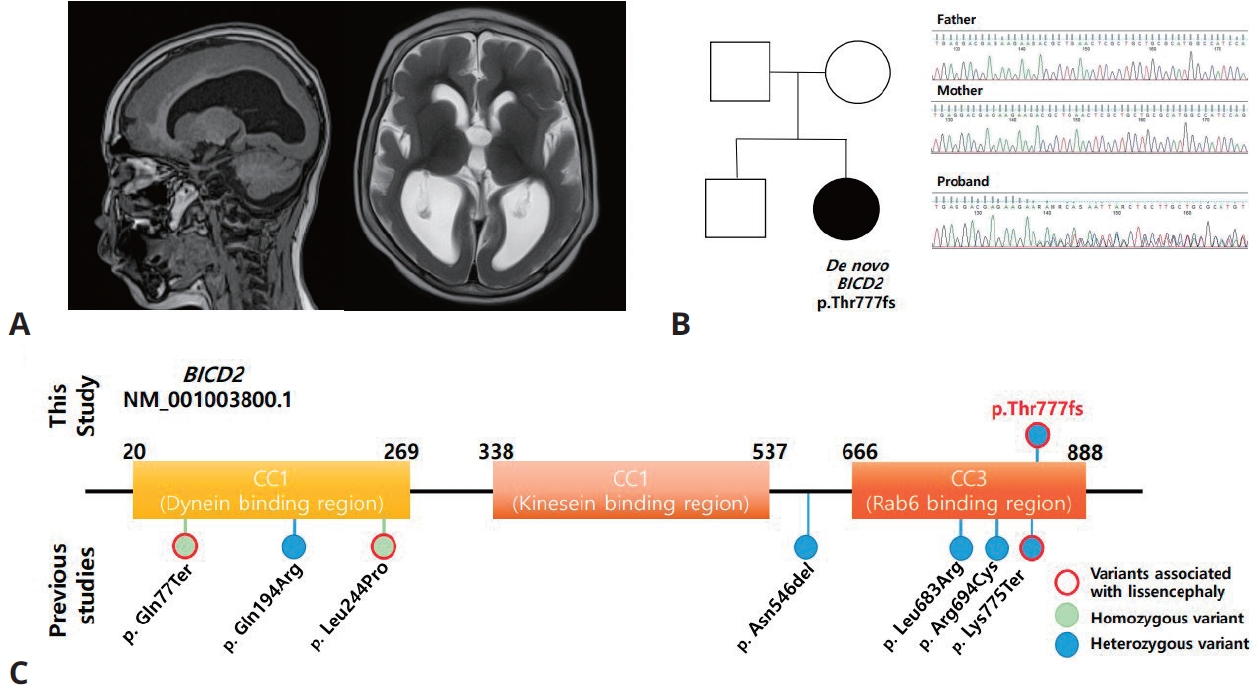
- Expanding association between BICD2 variants and brain malformations and associated lissencephaly (1,178 times)
- Jaeso Cho, Haeryung Kim, Seoungbok Lee, Jihoon G Yoon, HyeJin Kim, Minhye Kim, Seoyun Jang, Woojoong Kim, Soo Yeon Kim, Jong Hee Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):54-56. Published online December 21, 2023
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope with mild versus moderate autonomic dysfunction: a 13-year single-center experience (1,161 times)
- Han Eoul Lee, Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):47-52. Published online June 1, 2021
-
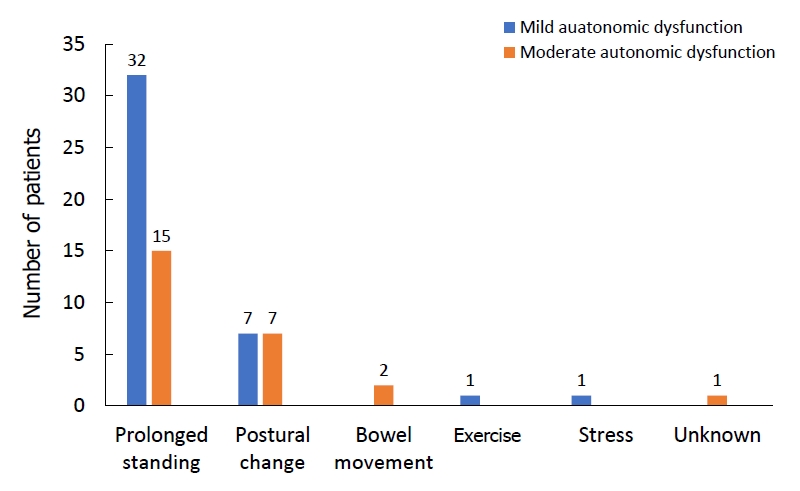
Question: It is well known that autonomic dysfunction contributes to vasovagal syncope (VVS). Does the degree of autonomic dysfunction contribute to clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis?
Finding: The clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis differ between patients with mild and moderate degrees of autonomic dysfunction.
Meaning: VVS is caused by autonomic dysfunction, but autonomic dysfunction severity need not be classified.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Gut microbiota affects brain development and behavior (1,161 times)
- Gun-Ha Kim, Jung-Ok Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):274-280. Published online November 8, 2022
-
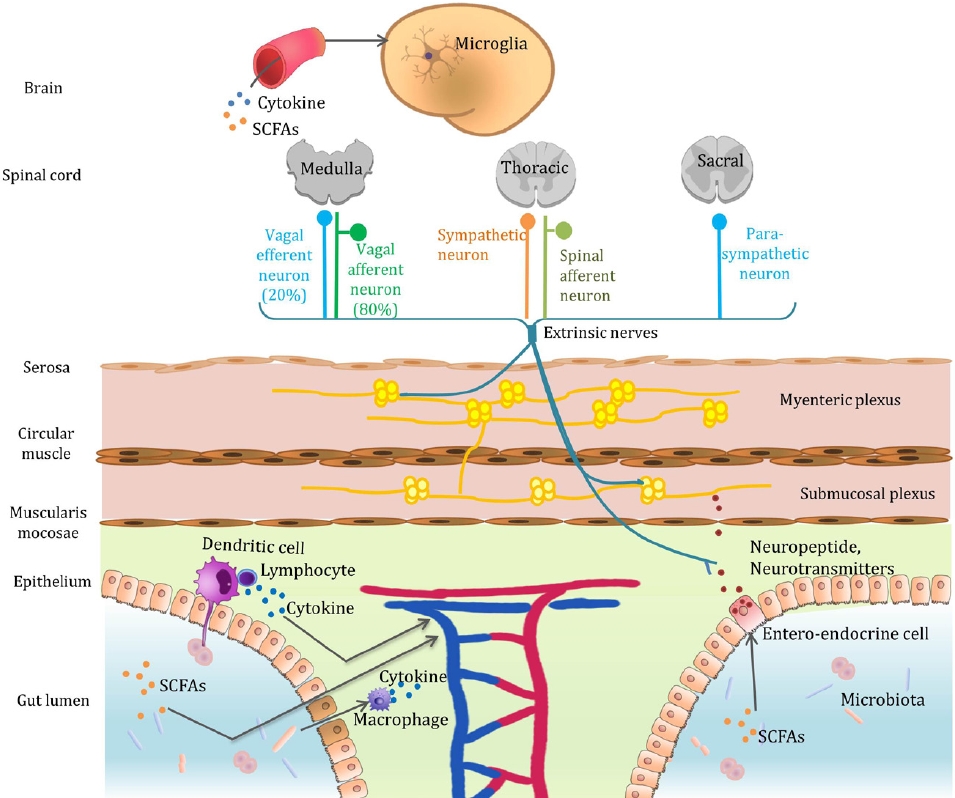
· The gut microbiota can alter a host’s brain development and behavior.
· Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
· Fecal microbial transplantation is a promising treatment strategy for autism spectrum disorder.
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model (1,152 times)
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
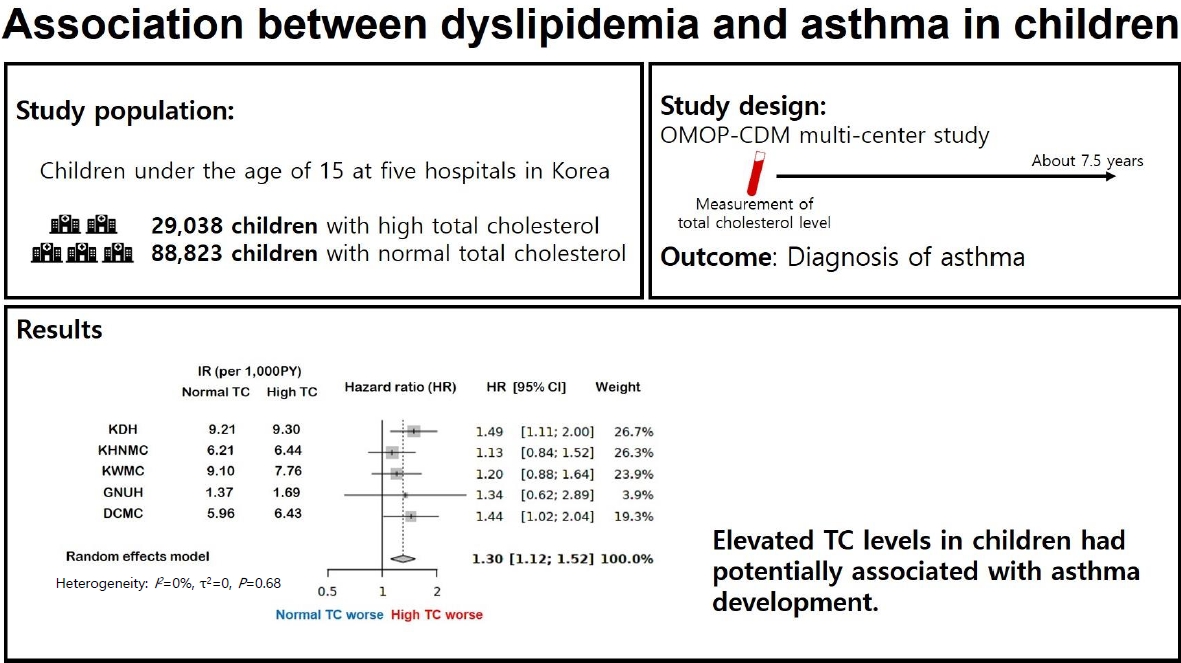
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Timing of parenteral nutrition initiation in critically ill children: a randomized clinical trial (1,141 times)
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Hesham M. Aboelghar, Nehad B. Abdelaty, Mohamed I. Garib, Asmaa A. Mahmoud
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):403-411. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: What is the ideal initiation timing of parenteral nutrition for critically ill children?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial of 140 children examined the effects of an early or late start of parenteral nutrition on mechanical ventilation need (primary outcome) and length of stay and mortality (secondary outcomes).
Meaning: Children who received early versus late parenteral nutrition had lower mechanical ventilation need and duration.
- Pulmonology
- Modified high-flow nasal cannula for children with respiratory distress (1,132 times)
- Sarocha Itdhiamornkulchai, Aroonwan Preutthipan, Jarin Vaewpanich, Nattachai Anantasit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):136-141. Published online May 24, 2021
-
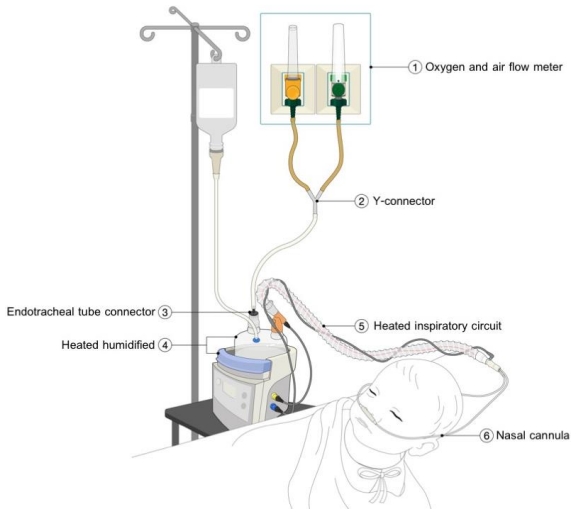
Question: Can the modified high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) provide alternative respiratory support for children with acute respiratory distress?
Finding: A total of 74 patients were assigned to the modified or commercial HFNC groups. The intubation rate, length of hospital stay, and adverse events did not differ between the 2 groups.
Meaning: The modified HFNC can provide alternative respiratory support for pediatric respiratory distress.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea (1,132 times)
- Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):415-423. Published online June 13, 2023
-

· Enhanced safety monitoring system of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines were implemented to detect signals rapidly as part of the national COVID-19 vaccination program.
· As of June 4, 2023, reported adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination was 0.38% among 125,107,883 doses of COVID- 19 vaccines administered.
· Most reported adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccinations have shown nonserious and mild intensity.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of 2–6 weeks of systemic steroids on bone mineral density in children (1,123 times)
- Athira Kuniyil, Somdipa Pal, Namrita Sachdev, Tribhuvan Pal Yadav
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):254-261. Published online November 18, 2021
-

Question: Does steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children affect bone mineral content (BMC) or density (BMD)?
Finding: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks significantly decreased BMC and BMD of the whole body, total body less the head, lumbar spine, and distal radius. A significant negative correlation was observed among BMD, duration, and cumulative dose.
Meaning: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children negatively affected BMC and BMD.
- Gastroenterology
- Risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old (1,115 times)
- Dedy Rahmat, Agus Firmansyah, Ina S. Timan, Saptawati Bardosono, Joedo Prihartono, Pramita Gayatri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):538-544. Published online November 16, 2023
-
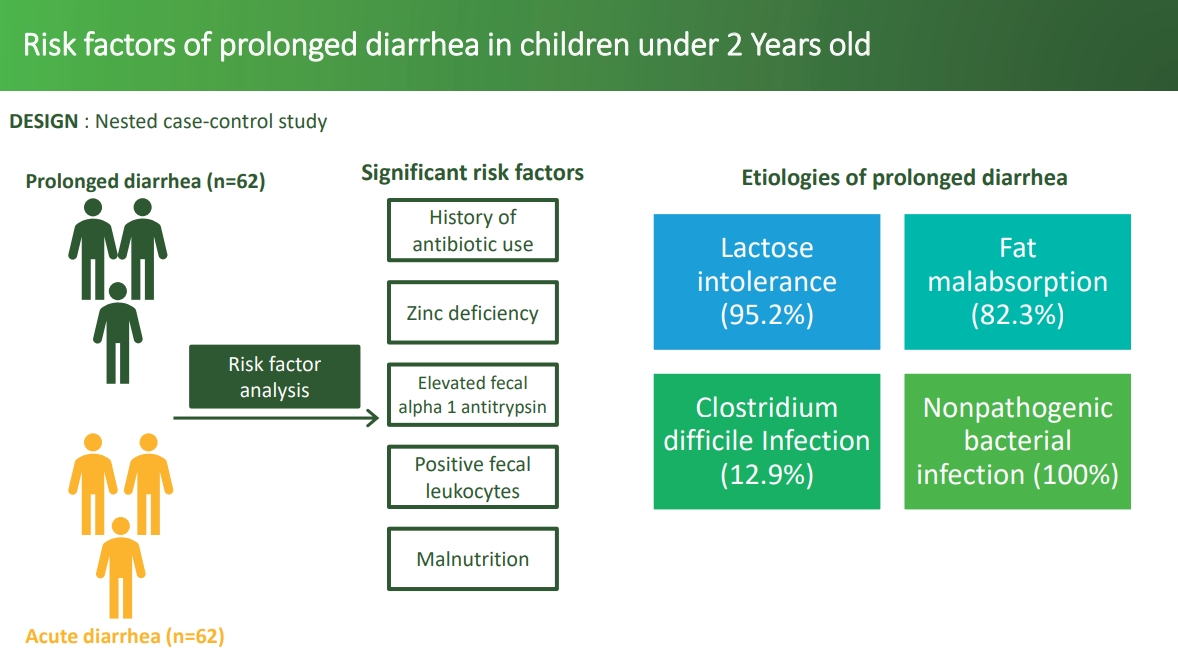
Question: What are the risk factors for prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old?
Finding: History of antibiotic use, zinc deficiency, and elevated fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels were the main risk factors of prolonged diarrhea in children under 2 years old with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Rational antibiotic usage is necessary as well as thorough testing of serum zinc level and fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin levels.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Characteristics of z score systems for diagnosing coronary abnormalities in Kawasaki disease (1,114 times)
- Gyeong-Hee Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):448-449. Published online March 14, 2022
-
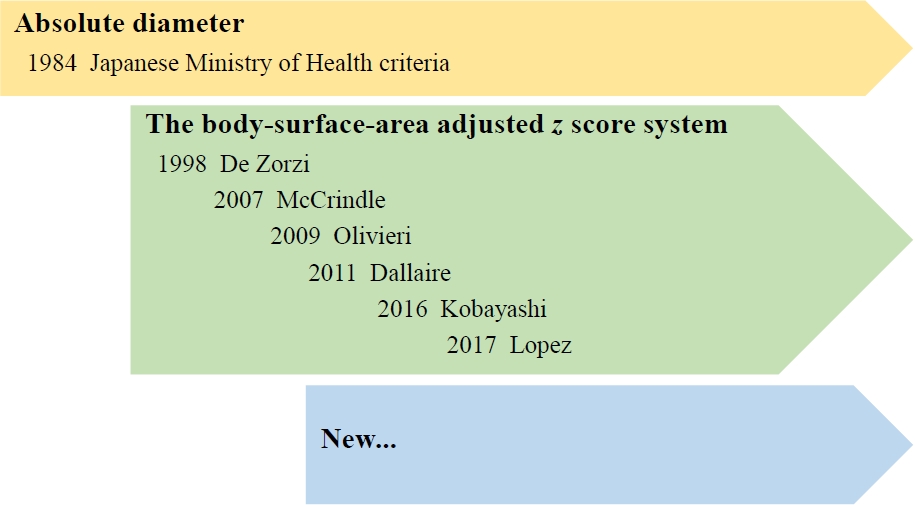
Because of the various body sizes of children with Kawasaki disease (KD), coronary artery diameter requires normalization to the body surface area as a z score.
In updated guidelines, coronary artery abnormalities are important criteria in the diagnosis of KD, and z score systems have been accepted to define coronary artery abnormalities.
However, the z score formula should be selected carefully because each yields different results.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
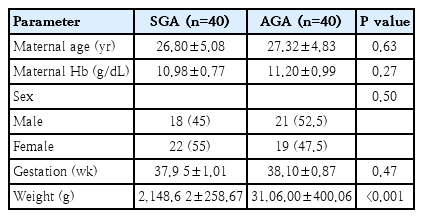
- Assessment of iron status and red cell parameters in healthy term small for gestational age neonates at birth (1,114 times)
- Arif Hossain, Shorna Rahman, Shahana Akter, Ismat Jahan, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):221-223. Published online March 19, 2024
-
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Is it time to add point-of-care ultrasound education to pediatric residency curriculum? (1,111 times)
- Shin Ae Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):33-34. Published online October 12, 2021
-
Growing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) use in pediatric patients has led to the need for POCUS education for pediatric residents. Recent experimental studies have suggested that POCUS education improves self-rated POCUS confidence and comfort in pediatric resident training. Considering the effective and sustainable POCUS education curriculum in pediatric resident training, simulation-based education would be a solution.
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Not breastfeeding and risk of autism spectrum disorders among children: a meta-analysis (1,107 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):28-31. Published online July 19, 2022
-
This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between not breastfeeding (versus breastfeeding) and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) among children. We found that the risk of ASD associated with not breastfeeding had an odds ratio of 1.81 (95% confidence interval, 1.35–2.27; I2=0 %). These findings suggest the importance of breastfeeding in decreasing the risk of ASD among children.
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials (1,098 times)
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis (1,083 times)
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
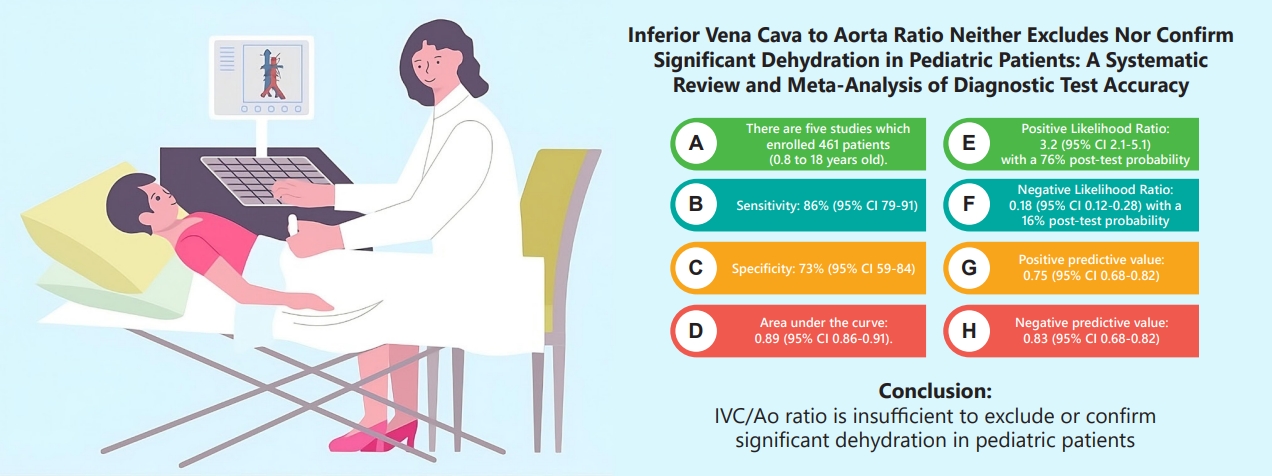
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







