Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2022 ~ ).
- Original Article
- Emergency Medicine
- Nonfatal injuries in Korean children and adolescents, 2007–2018
-
Gyu Min Yeon, Yoo Rha Hong, Seom Gim Kong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):194-200. Published online September 9, 2021
-

|
Question: How many children and adolescents have experienced nonfatal injuries in the previous year?
Finding: Among Korean children and adolescents, 8.1% experienced at least one injury per year. We found no significant change in the incidence of injuries over the previous 12 years.
Meaning: The incidence of injuries is higher than this estimation; therefore, more attention and effort are needed to prevent injuries among children and adolescents. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Infection
- Importance of maintaining a high childhood vaccination rate and surveillance program against Japanese encephalitis in Korea
-
Su Eun Park
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):127-128. Published online February 16, 2022
-
|
∙ Recent epidemiologic changes of Japanese encephalitis (JE) in Korea are area (rural to urban or suburban) and age shift (children to adult).
∙ Although the main factors contributing to recent epidemiologic changes of JE are not well identified, maintaining high vaccination rates of JE appear to be important in preventing of JE in all age groups.
∙ Continuous surveillance for epidemiology and seroprevalence should be carried out. |
-
-
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
-
Jeana Hong
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
|
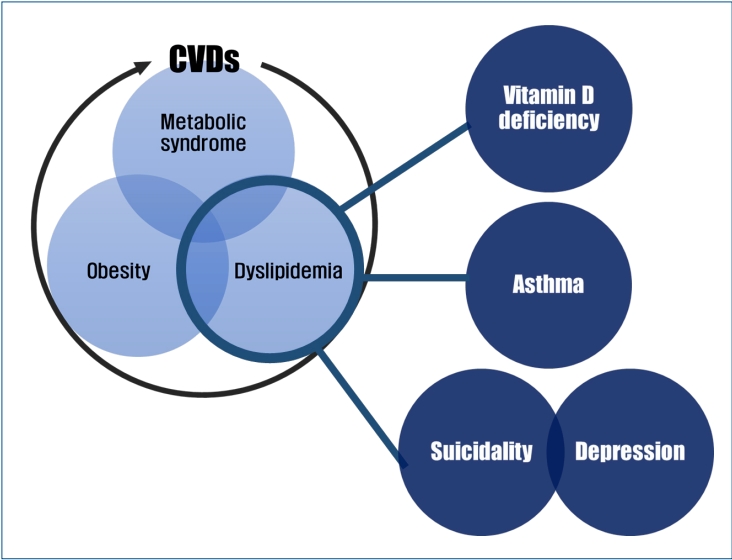
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in various pediatric neurologic diseases
-
Jeongho Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):81-82. Published online January 6, 2022
-

|
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has many important biomarkers that are commonly analyzed in pediatric neurologic diseases, including central nervous system infection and inflammation. Neurologic disease in pediatrics is difficult to diagnosis, there are challenges in developing CSF profiles. Some biomarkers are expected to help differential diagnosis. |
-
-
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Motor performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: focus on the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency
-
Khushboo Prashant Adhvaryu, Suruliraj Karthikbabu, Pratiksha Tilak Rao
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):512-520. Published online February 17, 2022
-
|
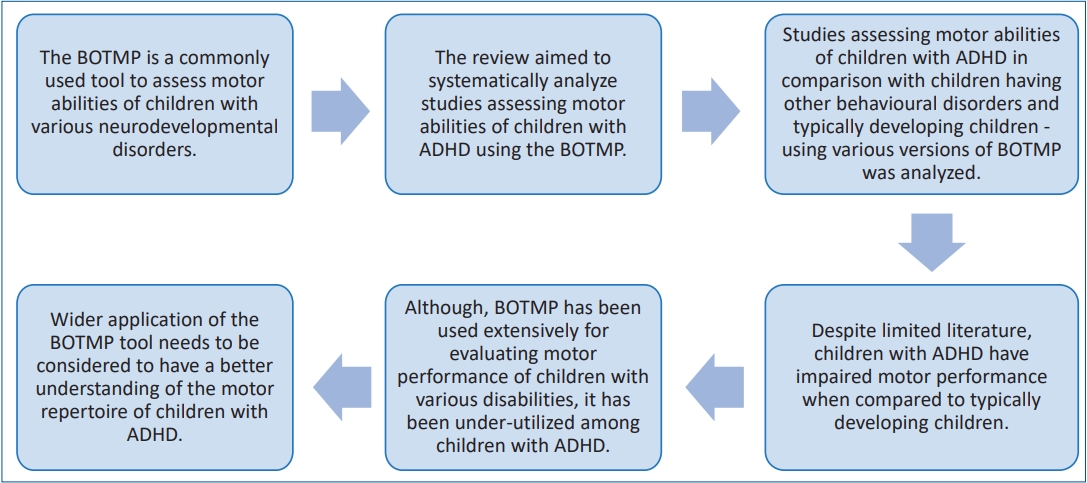
· Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tend to have impaired motor performance that may affect their growth and development.
· Although widely used among children with developmental disorders, the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP) is used sparsely among children with ADHD.
· Assessment by the BOTMP increases our understanding of the motor repertoire of children with ADHD.
· Wider usage of the BOTMP will enable more comprehensive planning of rehabilitation goals to enhance the motor abilities of children with ADHD. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Increasing our understanding of rotavirus-induced central nervous system manifestations
-
Jon Soo Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):536-537. Published online May 6, 2022
-
|
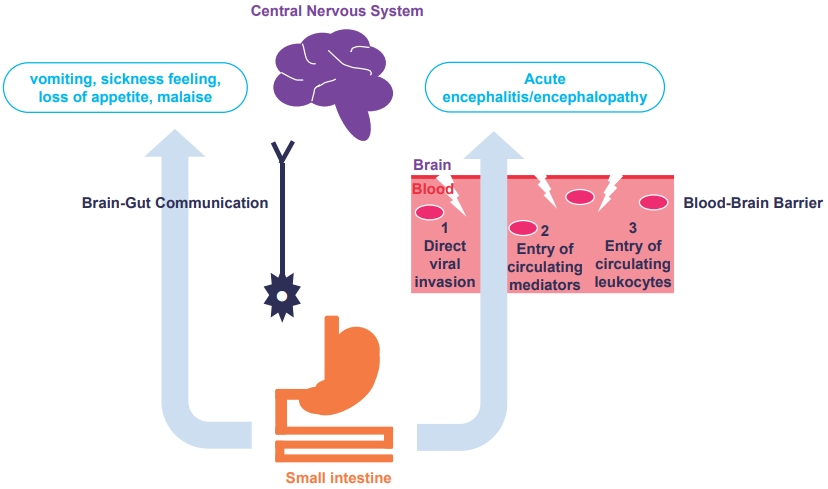
· Diverse clinicoradiological features of central nervous system (CNS) complications in rotavirus infection can be identified with the rapid and wide use of various brain magnetic resonance imaging protocols.
· An increased understanding of the various pathophysiological mechanisms of rotavirus-induced CNS manifestations will enable precise management in the future. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mediation effect of cord blood cortisol levels between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
-
Nisanth Selvam, Jayashree K, Prasanna Mithra
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):500-506. Published online July 29, 2022
-

|
Question: What is the association between cord blood cortisol and maternal weight, birth weight, and cord blood lipid profile?
Finding: Cord blood cortisol levels did not influence the relationship between maternal weight changes or birth weight. Maternal weight changes, birth weight, and cortisol levels altered the cord blood lipid profile.
Meaning: Our findings may aid United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being) achievement by 2030. |
-
-
- Cardiology
- Vasovagal syncope with mild versus moderate autonomic dysfunction: a 13-year single-center experience
-
Han Eoul Lee, Dong Won Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):47-52. Published online June 1, 2021
-
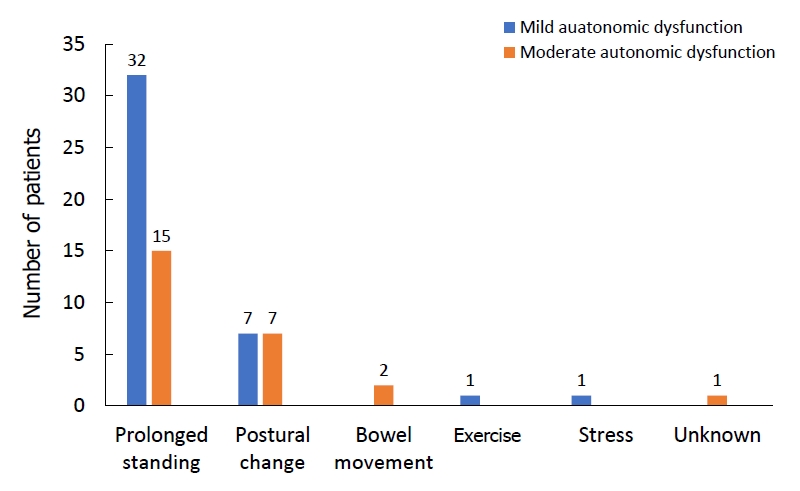
|
Question: It is well known that autonomic dysfunction contributes to vasovagal syncope (VVS). Does the degree of autonomic dysfunction contribute to clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis?
Finding: The clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis differ between patients with mild and moderate degrees of autonomic dysfunction.
Meaning: VVS is caused by autonomic dysfunction, but autonomic dysfunction severity need not be classified. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Growth patterns of preterm infants in Korea
-
Joohee Lim, So Jin Yoon, Soon Min Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):1-9. Published online July 8, 2021
-
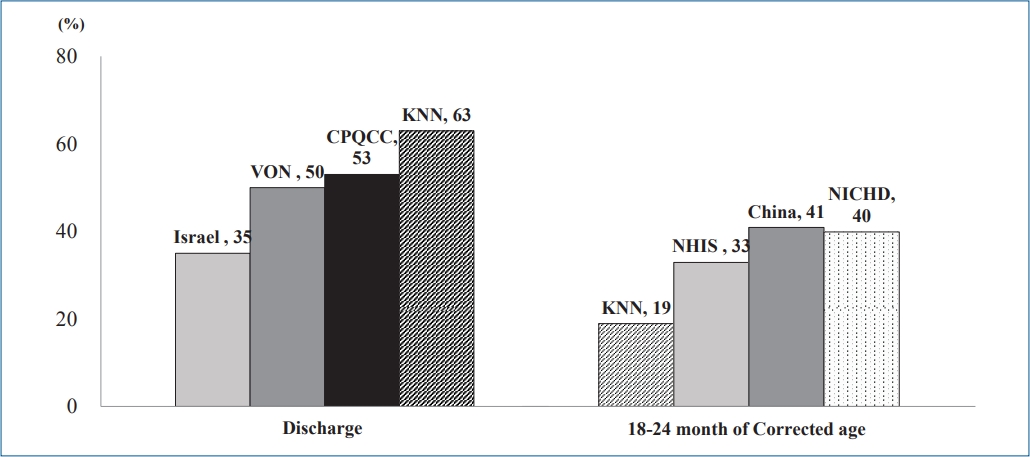
|
∙ The growth of preterm infants is a main focus of neonatology.
∙ Preterm infants in Korea, especially those with a very low birth weight, achieve retarded growth.
∙ Careful growth monitoring and early intervention will contribute to better development outcomes and quality of life for preterm infants and improve public health. |
-
-
- Letter to the Editor
- Other
- Evaluation of simulation-based ultrasound course for pediatricians: a starting point for future training curriculum
-
Chon In Kuok, Avis Siu Ha Leung, Jonan Chun Yin Lee, Winnie Kwai Yu Chan
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):53-55. Published online July 28, 2021
-
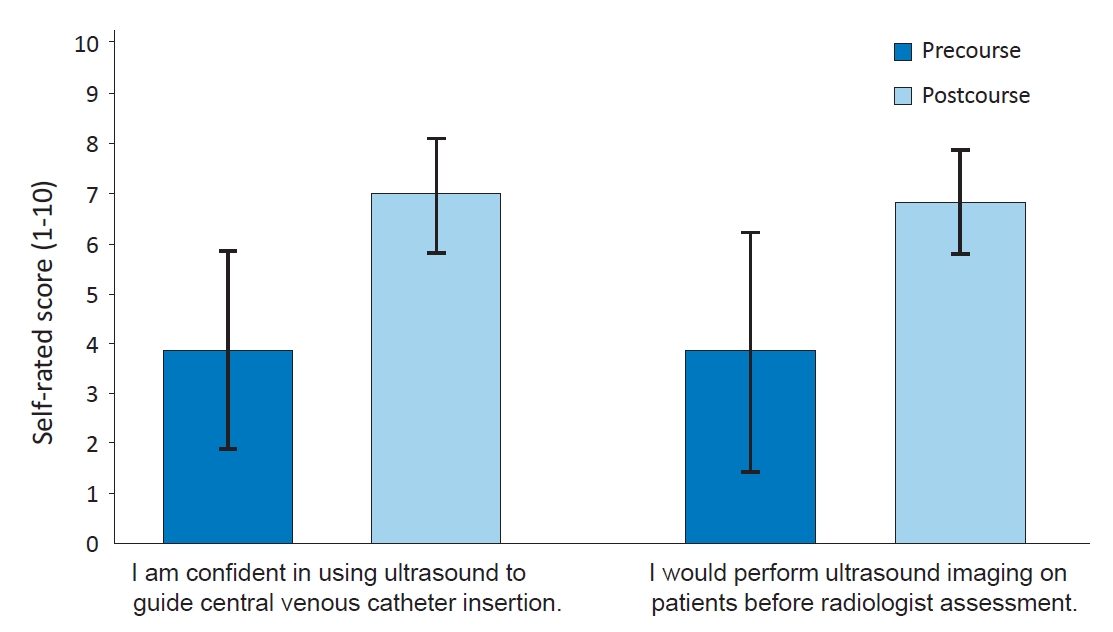
|
Question: Simulation-based ultrasound training is becoming more popular. Is there a role for pediatricians in such training programs?
Finding: Our program received promising feedback from its participants. Self-rated confidence in image interpretation and ultrasound-guided catheter insertion improved after the simulation. Participants reported a higher preference for performing ultrasound scans before radiologist assessment.
Meaning: Ultrasound training can be considered as part of the pediatric training curriculum in the future. |
-
-
- Editorial
- General Pediatrics
- Is it time to add point-of-care ultrasound education to pediatric residency curriculum?
-
Shin Ae Yoon
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(1):33-34. Published online October 12, 2021
-
|
|
Growing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) use in pediatric patients has led to the need for POCUS education for pediatric residents. Recent experimental studies have suggested that POCUS education improves self-rated POCUS confidence and comfort in pediatric resident training. Considering the effective and sustainable POCUS education curriculum in pediatric resident training, simulation-based education would be a solution. |
-
-





















