|
Purpose: The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of childhood obesity and overweight in Iranian children under 5 years of age using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
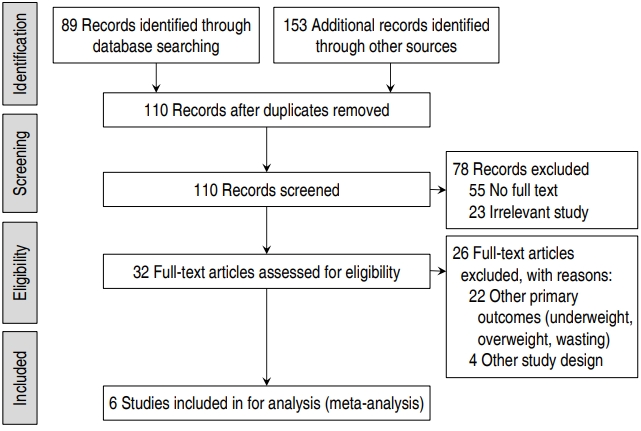
Methods: We searched MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus, CINHAL, and the Iranian databases, including Scientific Information Database (www.sid.ir), Iranian Research Institute for Information Science and Technology (Irandoc.ac.ir), Iranmedex (www.iranmedex.com), and... |






