Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Infection
- Pathogenetic and etiologic considerations of febrile seizures
- Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):46-53. Published online January 13, 2023
-
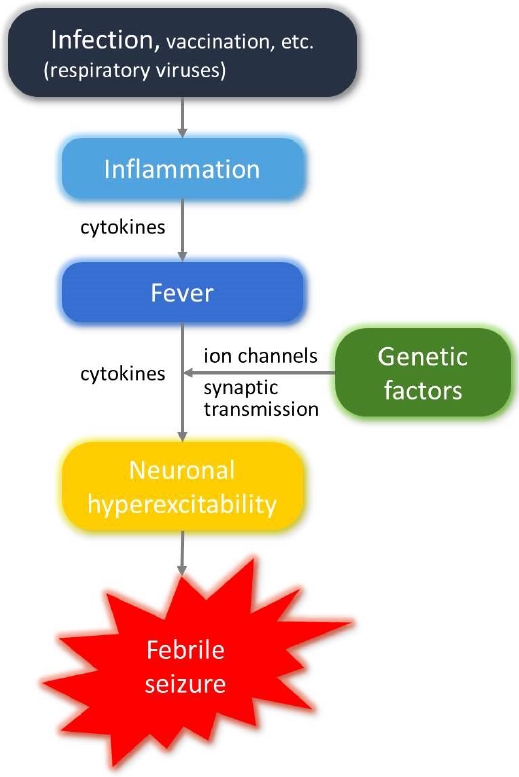
· Inflammatory responses accompanying fever increase neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, which in turn provokes seizures.
· Fever in children with febrile seizures is usually caused by common respiratory viruses, the distributions of which match those of seasonal community-acquired respiratory tract infections.
· Several genetic variations in ion channels seem associated with neuronal hyperexcitability in children with febrile seizures.
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
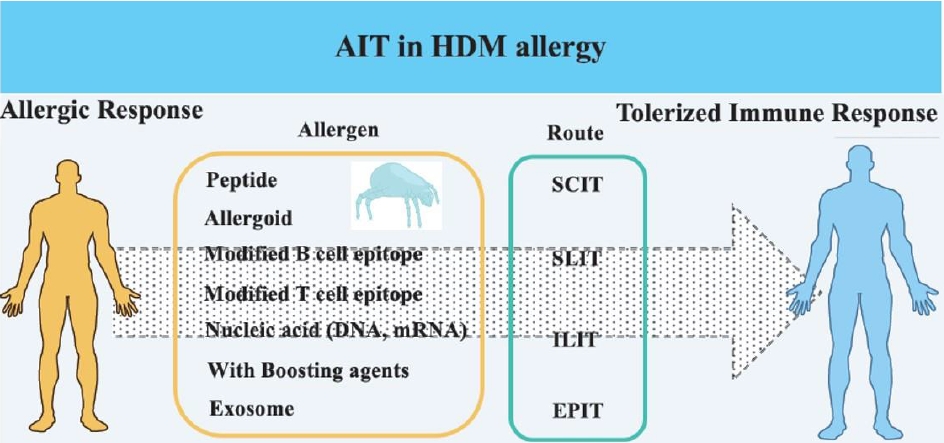
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Cardiology
- Research trends on causes of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 era: focus on viral infections
- Young Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):1-11. Published online June 22, 2022
-
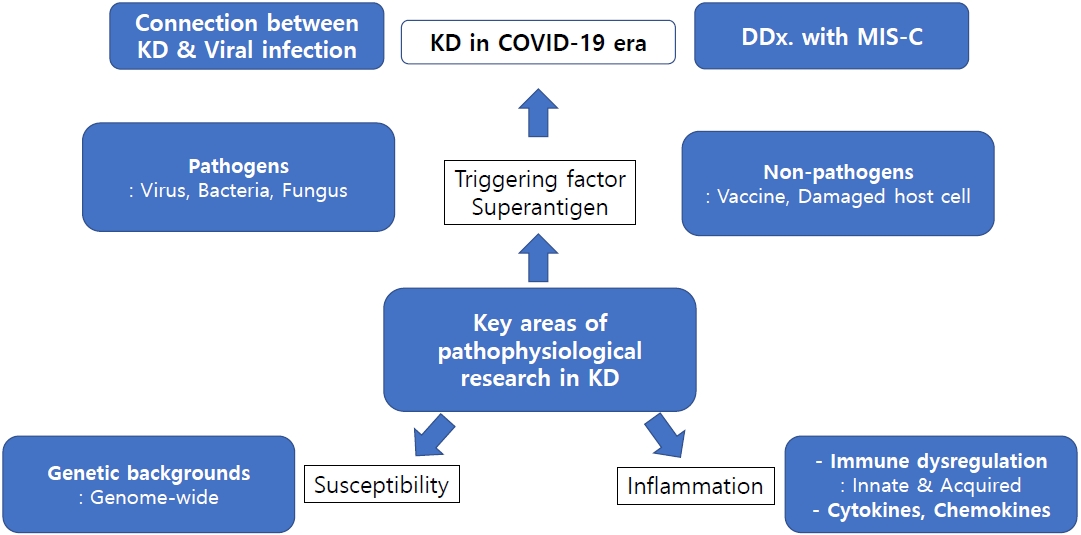
· The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unclear, but its clinical, epidemiological, and pathophysiological characteristics are strongly associated with infectious diseases.
· In the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic era, viruses are attracting the most attention. Sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection causes various hyperinflammation in children that require differentiation from KD.
· Immune responses in patients with KD may be induced by host cell damage. To effectively prevent and treat KD, the genetic background and immune responses of KD patients and triggering pathogens require identification.
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-

∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Trends in the use of antibiotics among Korean children
- Young June Choe, Ju-Young Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):113-118. Published online March 4, 2019
-
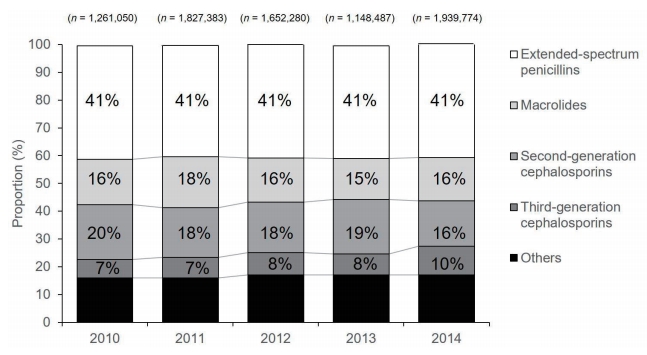
Inappropriate antibiotic use is the most important factor causing increased bacterial resistance to antibiotics, thus affecting patient outcomes. Multidrug-resistant bacteria have become a serious public health threat, causing significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. In Korea, the burden of antibioticresistant bacteria has become an important public health issue. There is increasing evidence of overuse and misuse of antibiotics in Korea, as...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- Ictal sinus pause and myoclonic seizure in a child
- Hye Ryun Kim, Gun-Ha Kim, So-Hee Eun, Baik-Lin Eun, Jung Hye Byeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S129-S132. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Ictal tachycardia and bradycardia are common arrhythmias; however, ictal sinus pause and asystole are rare. Ictal arrhythmia is mostly reported in adults with temporal lobe epilepsy. Recently, ictal arrhythmia was recognized as a major warning sign of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. We present an interesting case of a child with ictal sinus pause and asystole. A 27-month-old girl was...
- Review Article
- Hematology
- Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and recombinant factor VIIa treatment in pediatric patients
- Jeong A Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):105-113. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) is a life-threatening pulmonary complication in patients with hematologic malignancies or autoimmune disorders. The current treatment options, which include corticosteroids, transfusions, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and immunosuppressants, have been limited and largely unsuccessful. Recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) has been successfully administered, either systemically or bronchoscopically, to adults for the treatment of DAH, but there are...
- Original Article
- Clinical risk factors associated with the development of wheezing in children less than 2 years of age who required hospitalization for viral lower respiratory tract infections
- Joon Hwan Kim, Ji-Yeon Choi, Na Yeon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hye Sung Baek, Jung Won Yoon, Hye Mi Jee, Sun Hee Choi, Hyeung Yoon Kim, Ki Eun Kim, Youn Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(7):245-250. Published online July 22, 2015
-
Purpose Wheezing following viral lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in children <2 years of age is an important risk factor for the development of asthma later in life; however, not all children with viral LRTIs develop wheezing. This study investigated risk factors for the development of wheezing during viral LRTIs requiring hospitalization.
Methods The study included 142 children <2 years of age hospitalized...
- Detection rate and clinical impact of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease
- Ja Hye Kim, Jeong Jin Yu, Jina Lee, Mi-Na Kim, Hong Ki Ko, Hyung Soon Choi, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):470-473. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose The purpose of this prospective case-control study was to survey the detection rate of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease (KD) by using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and to investigate the clinical implications of the prevalence of respiratory viruses during the acute phase of KD.
Methods RT-PCR assays were carried out to screen for the presence of respiratory syncytial...
- Review Article
- Need for a safe vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus infection
- Joo-Young Kim, Jun Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(9):309-315. Published online September 14, 2012
-
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a major cause of severe respiratory tract illnesses in infants and young children worldwide. Despite its importance as a respiratory pathogen, there is currently no licensed vaccine for HRSV. Following failure of the initial trial of formalin-inactivated virus particle vaccine, continuous efforts have been made for the development of safe and efficacious vaccines against...
- Changes in the neonatal and infant mortality rate and the causes of death in Korea
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Yong-Sung Choi, Chong-Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(11):443-455. Published online November 30, 2011
-
Neonatal mortality rate (NMR) or infant mortality rate (IMR) are the rate of deaths per 1,000 live births at which babies of either less than four weeks or of one year of age die, respectively. The NMR and IMR are commonly accepted as a measure of the general health and wellbeing of a population. Korea's NMR and IMR fell significantly...
- Original Article
- Hu.4-1BB-Fc fusion protein inhibits allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma
- Byoung-Ju Kim, Ji-Won Kwon, Ju-Hee Seo, Won-Ah Choi, Young-Jun Kim, Mi-Jin Kang, Jinho Yu, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(9):373-379. Published online September 30, 2011
-
Purpose 4-1BB (CD 137) is a costimulatory molecule expressed on activated T-cells. Repression by 4-1BB is thought to attenuate Th2-mediated allergic reactions. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of 4-1BB on allergic airway inflammation in a murine asthma model.
Methods BALB/c mice were sensitized to and challenged with ovalbumin (OVA). Hu.4-1BB-Fc was administered 1 day before the first OVA...
- The effects of early allergen/endotoxin exposure on subsequent allergic airway inflammation to allergen in mouse model of asthma
- Yeong-Ho Rha, Sun-Hee Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):481-487. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Recently many studies show early exposure during childhood growth to endotoxin (lipopolysaccharides, LPS) and/or early exposure to allergens exhibit important role in development of allergy including bronchial asthma. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of endotoxin and allergen exposure in early life via the airways in the pathogenesis of allergic airways inflammation and airway hyperresposiveness... -
- A multidisciplinary approach for the treatment of child abuse in Korea
- Bong Kyu Song, Do Kyun Kim, Hye Young Park, Jun Won Hwang, Young Ho Kwak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1207-1215. Published online November 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To review and determine the complications in 76 child abuse cases recorded by a multidisciplinary hospital- based child protection team between 1987 and 2007. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the reports and medical records of child abuse cases maintained by a university hospital-based child protection team. We devised a questionnaire for standardized interviews with the victims’ guardians to... -
- Review Article
- Child sexual abuse and pediatricians
- Insil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1200-1206. Published online November 15, 2009
-
Child sexual abuse is not a rarely encountered problem. Child sexual abuse is a pediatric disease entity with lifelong impact. Child sexual abuse, different from sexual assault, is not always accompanied by violent force and usually repeated over a period of time. Child sexual abuse should be approached by multidisciplinary team experts. Every pediatrician should know the child protection network... -
- Child abuse, can we find child abuse? - Role of the pediatrician
- Ki Sik Min
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1194-1199. Published online November 15, 2009
-
Child abuse is defined by a recent act or failure to act that results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation, or imminent risk of serious harm; involved a child; and is carried out by a parent or caregiver. This report provides guidance in the clinical approach to the evaluation of suspected physical abuse in children,... -
- The present state of chid abuse in Korea and its system for child protection
- Ki-Soo Pai, Shin-Young Kim, Young Ki Chung, Kyeong Hee Ryu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(11):1185-1193. Published online November 15, 2009
-
An act of children’s welfare was made in 1961 for the first time in Korea but it had been nothing but the name in view of practical impact to prevention of child abuse. Real undertakings of Child Abuse Prevention were commenced overtly since 2000 in Korea, when the law for children’s welfare was revised to put protective settings for the... -
- Case Report
- A case of congenital syphilis mistaken for possible child abuse
- Soon Ju Kim, Seung Woo Lee, Jung Woo Rhim, You Sook Youn, Jun Sung Lee, Kyung Yil Lee, Ja Young Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(6):710-712. Published online June 15, 2009
-
We describe the case of a 4-month-old male infant diagnosed with early congenital syphilis during evaluation of a left distal humerus fracture. This report emphasizes the importance of screening for syphilis among pregnant women and newborns, and is a reminder of the continued existence of congenital syphilis. -
- Original Article
- Comparison of predicted adult heights measured by Bayley-Pinneau and Tanner-Whitehouse 3 methods in normal children, those with precocious puberty and with constitutional growth delay
- Yeon Joung Oh, Byung Keun Yu, Jung Yeon Shin, Kee-Hyoung Lee, Kwang Chul Lee, Chang Sung Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):351-355. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : This study compared bone ages measured by the Greulich-Pyle (GP) and Tanner-Whitehouse 3 (TW3) methods and investigated the differences in predicted adult heights measured by Bayley-Pinneau (BP) and TW3 methods. Methods : Bone ages were assessed from left-wrist radiographs by two investigators, one for each GP and TW3 methods in 85 normal children, 30 precocious puberty girls, and... -
- Review Article
- Acute viral lower respiratory tract infections in children
- Joon Soo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):269-276. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Viruses are the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in infants and young children and are a major public health problem in this age group. Viruses were identified in 54.9-70.4% of hospitalized infants and children with LRTIs in Korea. The viral pathogens identified included respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) A and RSV B, influenza (Inf) A, Inf B,... -
- Original Article
- A Clinical Study of Child Abuse
- Yoon Jin Choi, Shin Mi Kim, Eun Jung Sim, Do Jun Cho, Dug Ha Kim, Ki Sik Min, Ki Yang Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(5):436-442. Published online May 15, 2007
-
Purpose: To promote awareness and efforts by pediatricians to identity and prevent child abuse by investigation of characteristics of victim and types of injury caused by abuse. Methods: A retrospective study was performed with 20 patients who had been diagnosed or suspected as child abuse at Hallym University Hospital from January 1999 to December 2005. The medical records, radiologic documents,... -
-
- Child sexual abuse
- Hyun Joo Lee, Hye Jung Han, Ji Hee Kim, Hye Sun Lee, In Sil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(1):20-27. Published online January 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Child sexual abuse is a significant and serious problem that affects public health and society. Pediatricians are responsible for preventing and detecting sexual abuse of children. The aim of this study was to examine clinical findings of child sexual abuse. Methods : The authors retrospectively studied 292 patients between the ages of 0 and 18 who were referred for... -
- Cause of enteroviral infection in children in chungnam area summer, 2005
- Se Yun Jeon, Suk Joo Choi, Yong Bae Kim, Hae Seon Nam, Kwi Sung Park, Kyung Ah Baek, Joon Soo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1186-1193. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Enterovirus infection is a type of viral infection that occurs relatively frequently in children during summer. It has clinical symptoms of non-specific fever, aseptic encephalomeningitis, gastrointestinal diseases, skin rash and, hand-foot-mouth disease. However, it can also occcaisionally, result in fatal symptoms like myocarditis, epicardial inflammation, transverse myelitis, quadriplegia and etc. There have been epidemic enterovirus studies, but not... -
- Health and risk taking behaviors of freshmen in college
- Hong Ki Ko, Jae Joon Han, Yoon Lee, Young Yoo, Kee Hyoung Lee, Ji Tae Choung, Sang Hee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1042-1049. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to survey the preliminary data on risk behaviors and to identify the factors that prevent risk-behaviors in late adolescence. Methods : Freshmen(n=1,297) beginning the first semester in Korea University, Seoul, Korea completed self-administered risk behavior questionnaires, comprising 5 domains : demographics, smoking, drinking, drug abuse and sexual behavior. Results : The rate of smoking experience was... -
- Case Report
- Successful Management with Vincristine after Failure of Prednisolone Therapy for Diffuse Neonatal Hemangiomatosis
- Hak-Sung Lee, Soon-Young Heo, Won-Duck Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):1004-1008. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Hemangiomas are the most common benign tumors of infancy. Fifteen to 30% of these patients have multiple hemangiomas. Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis (DNH) is a disease that often has a fatal outcome if left untreated, and is characterized by multiple cutaneous and visceral hemangiomas. Corticosteroids are the commonly accepted first line treatment, but if no effect is seen, further treatment is... -
- A Case of Bronchogenic Cyst with Nausea and Epigastric Pain
- Ji-Hyun Kim, Kang-Won Rhee, In-Seok Lim, Byung-Hoon Yoo, Eung-Sang Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(3):333-336. Published online March 15, 2005
-
Bronchogenic cysts are rare congenital anomalies that arise early in gestation from abnormal budding of the developing respiratory system. Mediastinal bronchogenic cysts account for 10-15 percent of all primary mediastinal masses; 63.7 percent of patients are symptomatic. Common symptoms are fever, chest pain, cough, dyspnea, and dysphagia. Gastrointestinal symptoms except dysphagia are rare. It can be life threatening with compression,... -
- A Case of Diffuse Panbronchiolitis Developing in Childhood
- Jung Hoon You, Hyung Shin Lee, Kyung Yil Lee, Ja Hyun Hong, Mi Hee Lee, Byung Cheol Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(1):97-100. Published online January 15, 2005
-
Diffuse panbronchiolitis(DPB) is a chronic inflammatory airway disease predominantly affecting respiratory bronchioles, with distinct clinicopathological profiles. It was first described in 1966 by Yamanaka et al. The etiology of DPB is not yet clear, and the natural history of the disease is respiratory failure leading to cor pulmonale and ultimately death. But the long-term use of low-dose macrolide has proven... -
- Original Article
- Cause and Prognosis of Pediatric Acute Respiratory Failure by Intrapulmonary Lesion
- Hye-Young Lee, Ji-Suk Park, Hee-Ra Choi, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jeum-Su Kim, Jae-Young Lim, Myoung-Bum Choi, Chan-Hoo Park, Hyang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):555-560. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Respiratory failure arises from derangements in pulmonary gas exchange. The causes may be classified as due to either lung disease or respiratory pump dysfunction. Problems with lung mechanics is an important cause of acute respiratory failure in children clinically. The aims of this study were to survey the cause and prognosis of children diagnosed with acute respiratory failure... -
- Observation on Causes of Adoption and Social Background of Children in Adoption Institution(5th Report)
- Hak Sung Kim, Soo Yeon Kim, Sun Hee Kong, Dong Woo Lee, Kyung Eun Kim, Hye Jung Shin, Jae Yoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):264-268. Published online March 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Through a review of data provided by an adoption institution, this study was designed to provide a clue to help to reduce the abandonment of children by comparing the conditions at birth, social background, reason for request for adoption, and the degree of dependence on foreign adoption compared with the previous four reports. Methods : A total of 445... -
- Effect of Hypoxia on Antegrade and Retrograde Atrioventricular Conduction in Isolated Perfused Rabbit Heart
- Heon-Seok Han, Young Jun Song, Miran Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(9):1213-1223. Published online September 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Cyanotic congenital heart diseases patients are in a state of hypoxia since birth. In general, hypoxia delays atrioventricular conduction. The atrioventricular node in such a hypoxic condition would have a different function, and some possibility for arrhythmia. The authors studied atrioventricular nodal function during hypoxia to elucidate the relationship between hypoxia and arrhythmia, including atrioventricular node in terms... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







