Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of 2–6 weeks of systemic steroids on bone mineral density in children
- Athira Kuniyil, Somdipa Pal, Namrita Sachdev, Tribhuvan Pal Yadav
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):254-261. Published online November 18, 2021
-

Question: Does steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children affect bone mineral content (BMC) or density (BMD)?
Finding: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks significantly decreased BMC and BMD of the whole body, total body less the head, lumbar spine, and distal radius. A significant negative correlation was observed among BMD, duration, and cumulative dose.
Meaning: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children negatively affected BMC and BMD.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-
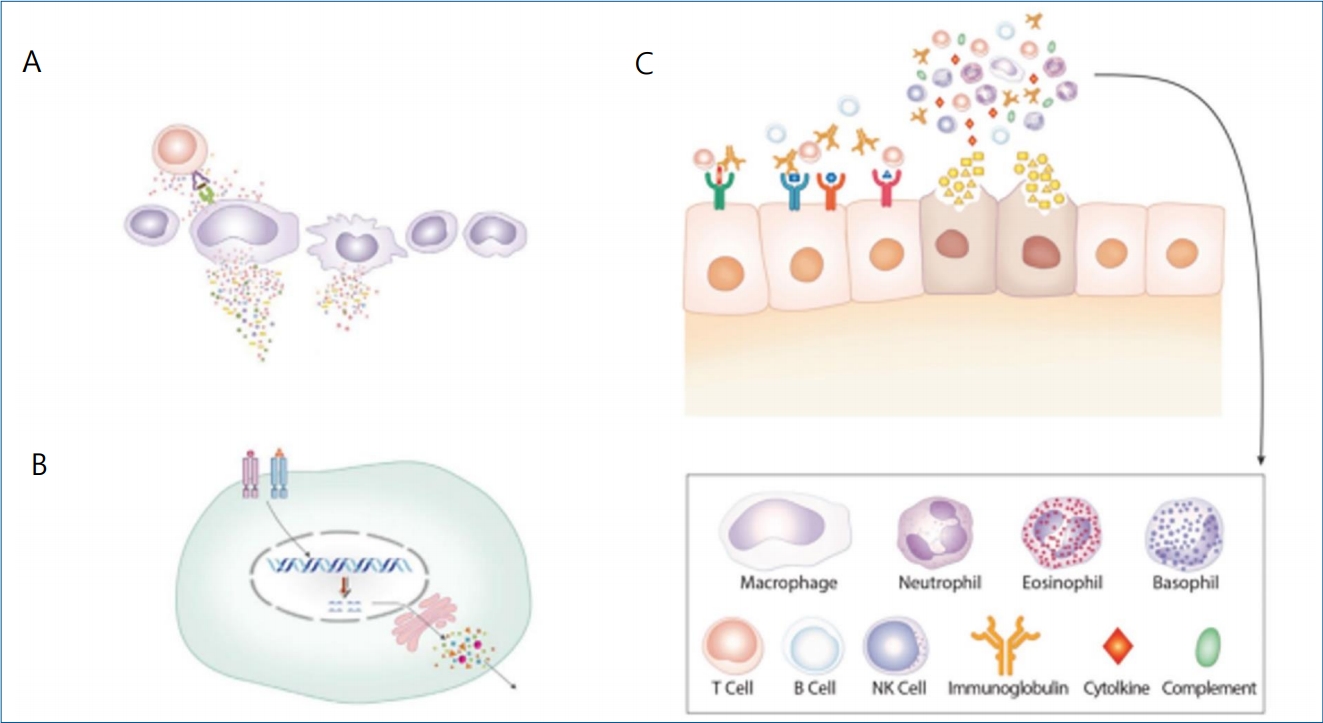
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Successful treatment of tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis with steroid and azathioprine in a 12-year-old boy
- Ji Eun Kim, Se Jin Park, Ji Young Oh, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Ji Hong Kim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S99-S102. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome is a rare disease, often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed in children. We describe the case of a 12-year-old boy who presented to Severance Hospital with a 1-month history of bilateral conjunctival injection. He was first evaluated by an Ophthalmologist in another hospital and diagnosed with panuveitis. Laboratory tests indicated renal failure, and a renal biopsy...
- Original Article
- High degree of supervision improves adherence to inhaled corticosteroids in children with asthma
- Geun Mi Park, Hye Won Han, Hee Se Kim, Jae Youn Kim, Eun Lee, Hyun-Ju Cho, Song-I Yang, Young-Ho Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Jinho Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):472-477. Published online December 22, 2015
-
Purpose Adherence to treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) is a critical determinant of asthma control. The objective of this study was to assess factors that determine adherence to ICS therapy in children with asthma.
Methods Fifty-eight children with asthma, aged 5 to 16 years, used ICS with or without a spacer for 3 months. Adherence rates as measured from questionnaires and canisters, asthma...
- Initial steroid regimen in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome can be shortened based on duration to first remission
- Hee Sun Baek, Ki-Soo Park, Hee Gyung Kang, Cheol Woo Ko, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):206-210. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose The use of a 12-week steroid regimen (long-term therapy, LT) for the first episode of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (NS) reportedly induces a more sustained remission and lower relapse rate than previous regimens, including an 8-week steroid regimen (short-term therapy, ST). Here, we assessed the potential for selective application of 2 steroid regimens (LT vs. ST) based on the days to...
- Case Report
- Pulmonary hemorrhage in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome
- Ji Soo Kim, Min Jae Kim, E Young Bae, Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):202-205. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome (LAHPS), a very rare disease that is caused by the presence of antifactor II antibodies, is usually counterbalanced by the prothrombotic effect of lupus anticoagulant (LAC). Patients with LAHPS are treated using fresh frozen plasma, steroids, immunosuppressive agents, and immunoglobulins for managing the disease and controlling hemorrhages. Notably, steroids are the important treatment for treating hypoprothrombinemia and...
- Original Article
- Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity in children with controlled asthma
- Ji-Yong Yoon, Sung-Il Woo, Heon Kim, Yong-Han Sun, Youn-Soo Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(9):330-336. Published online September 14, 2012
-
Purpose Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity (FEF25-75) are not included in routine monitoring of asthma control. We observed changes in FeNO level and FEF25-75 after FeNO-based treatment with inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in children with controlled asthma (CA).
Methods We recruited 148 children with asthma (age, 8 to 16 years) who had maintained...
- Review Article
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children- You-Sook Youn, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(2):42-47. Published online February 14, 2012
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP), the smallest self-replicating biological system, is a common cause of upper and lower respiratory tract infections, leading to a wide range of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary manifestations. MP pneumonia has been reported in 10 to 40% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia and shows an even higher proportion during epidemics. MP infection is endemic in larger communities of the...
- Original Article
- The role of inhaled and/or nasal corticosteroids on the bronchodilator response
- Ju Kyung Lee, Dong In Suh, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):951-956. Published online November 30, 2010
-
Purpose To compare the profiles of the bronchodilator response (BDR) among children with asthma and/or allergic rhinitis (AR) and to determine whether BDR in these children is reduced by treatment with inhaled and/or nasal corticosteroid.
Methods Sixty-eight children with asthma (mean age, 10.9 years), 45 children with comorbid asthma and AR (mean age, 10.5 years), and 44 children with AR alone (mean age,...
- Case Report
- A case of adolescent Kawasaki disease with Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis complicated by splenic infarction
- Byeong Sam Choi, Bo Sang Kwon, Gi Beom Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Jung-Eun Cheon, Eun Jung Bae, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1029-1034. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that affects children. There are few reports that describe the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) as the possible infectious agent of KD. Here, we describe a case of KD in a 15- year-old boy complicated with giant coronary artery aneurysms, pericardial effusion, and splenic infarction. The clinical course of KD was... -
- Original Article
- Effects of inhaled corticosteroids on bone mineral density and bone metabolism in children with asthma
- Ic Sun Choi, Jung Hye Byeon, Seung Min Lee, Kyong Suk La, Yeon Joung Oh, Young Yoo, Kee Hyoung Lee, Ji Tae Choung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(7):811-817. Published online July 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are used as first-line agents for the treatment of persistent asthma; however, their use is accompanied by apprehension of potential systemic adverse effects. This study aimed to assess the effects of ICS on bone mineral density (BMD) and bone metabolism in children with asthma. Methods : From February 2008 to September 2008, 26 asthmatic children treated... -
- Review Article
- Atopic dermatitis
- Bok Yang Pyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):589-592. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Atopic dermatitis is estimated to affect 15-20% of the childhood population and there id considerable evidence that the prevalence is increasing. But it is frequently under diagnosed and inappropriately treated yet. Atopic dermatitis can have a large social;. emotional and financial effect on the child and their family. Atopic dermatitis also commonly predated the development of asthma and allergic rhinitis.... -
- Original Article
- Association between the Human Surfactant Protein-A(SP-A) Gene Locus and Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Korean Neonates
- Jae Hoon Choe, Myung Ho Oh, Jung Ho Ko, Sun Young Kim, In Kyu Lee, Chong Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(7):735-739. Published online July 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Respiratory distress syndrome(RDS) is caused by a deficiency of pulmonary surfactant, which is a lipoprotein complex. Both low levels of surfactant protein A(SP-A) and SP-A alleles have been associated with RDS. However, the genes underlying susceptibility to RDS are insufficiently known. The candidate-gene approach was used to study the association between the SP-A gene locus and RDS in... -
- Case Report
- Fatal Doudenal Ulcer Bleeding in Status Asthmaticus Treated with Theophylline and Steroids
- Sang Woo Lee, Chang Keun Kim, Churl Young Chung, Young Doug Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(4):548-552. Published online April 15, 1998
-
It is generally agreed that theophylline preparations and steroids should be given intravenously for status asthmaticus. Theophylline can potentially have adverse gastrointestinal effects including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and hematemesis. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients treated with corticosteroids without a past history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding has been reported rarely. But the etiologic significance of the stress of status asthmaticus, administration of theophylline or corticosteroids... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







