Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Infection
- Etiological and pathophysiological enigmas of severe coronavirus disease 2019, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease
- Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):153-166. Published online November 23, 2021
-
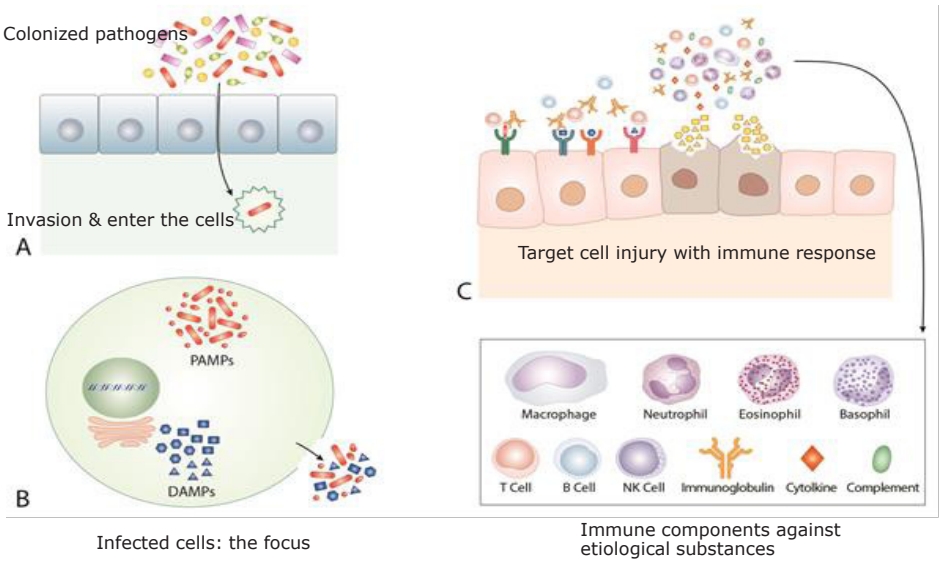
· Severe cases of coronavirus disease, Kawasaki disease (KD), and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) share similar findings: a protracted clinical course, multiorgan involvement, and similar activated biomarkers.
· Here we propose etiological agents in KD and MIS-C as species in the microbiota and introduce a common pathogenesis through the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis.
· Early proper dose of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulin may help to reduce morbidity and mortality in these diseases.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Effect of 2–6 weeks of systemic steroids on bone mineral density in children
- Athira Kuniyil, Somdipa Pal, Namrita Sachdev, Tribhuvan Pal Yadav
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):254-261. Published online November 18, 2021
-

Question: Does steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children affect bone mineral content (BMC) or density (BMD)?
Finding: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks significantly decreased BMC and BMD of the whole body, total body less the head, lumbar spine, and distal radius. A significant negative correlation was observed among BMD, duration, and cumulative dose.
Meaning: Steroid use for 2–6 weeks in children negatively affected BMC and BMD.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-
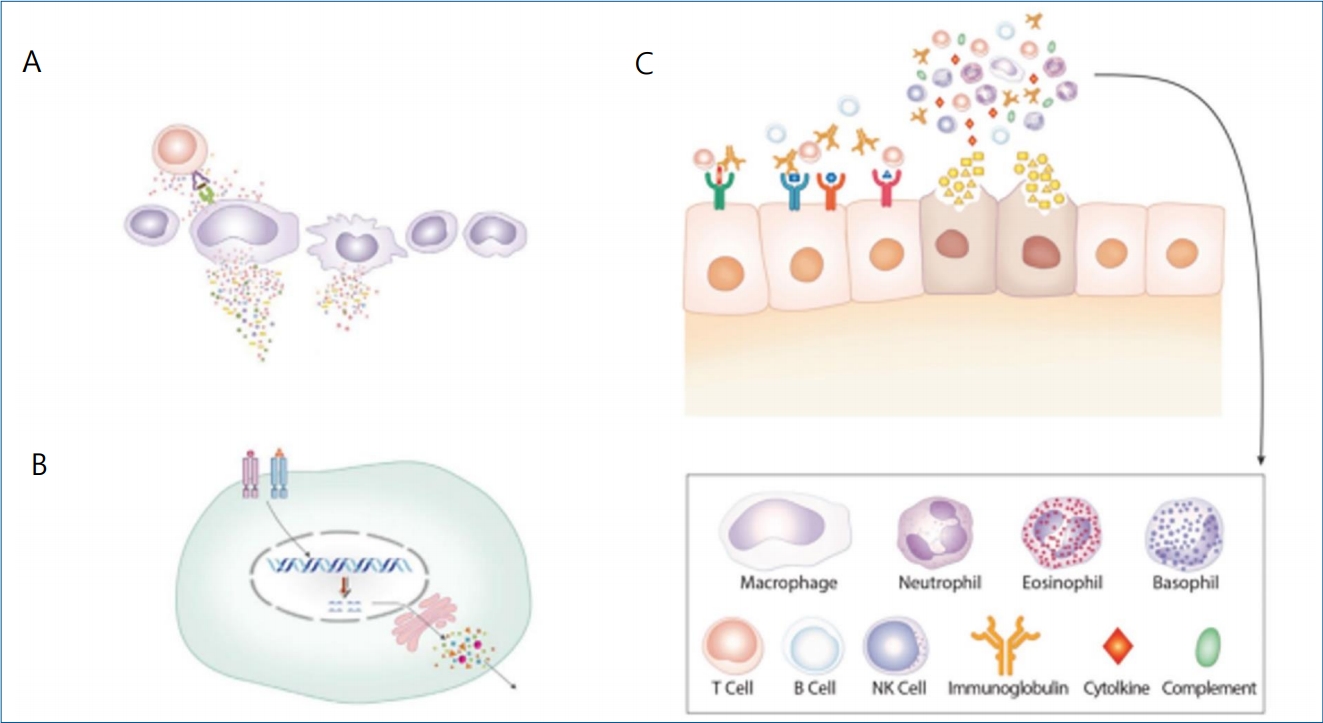
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Successful treatment of tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis with steroid and azathioprine in a 12-year-old boy
- Ji Eun Kim, Se Jin Park, Ji Young Oh, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Ji Hong Kim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S99-S102. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome is a rare disease, often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed in children. We describe the case of a 12-year-old boy who presented to Severance Hospital with a 1-month history of bilateral conjunctival injection. He was first evaluated by an Ophthalmologist in another hospital and diagnosed with panuveitis. Laboratory tests indicated renal failure, and a renal biopsy...
- Immunology
- Concomitant use of corticosteroid and antimicrobials for liver abscesses in patients with chronic granulomatous disease
- Kyung-Sue Shin, Mu Suk Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(4):196-201. Published online April 30, 2016
-
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare inherited disorder caused by defective nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase enzyme and characterized by recurrent bacterial and fungal infections. Although liver abscess is a common manifestation of CGD, its management in CGD patients is not well-defined. In addition, the generalized guidelines for treating liver abscesses do not necessarily apply to CGD patients. Corticosteroids...
- Original Article
- High degree of supervision improves adherence to inhaled corticosteroids in children with asthma
- Geun Mi Park, Hye Won Han, Hee Se Kim, Jae Youn Kim, Eun Lee, Hyun-Ju Cho, Song-I Yang, Young-Ho Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Jinho Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):472-477. Published online December 22, 2015
-
Purpose Adherence to treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) is a critical determinant of asthma control. The objective of this study was to assess factors that determine adherence to ICS therapy in children with asthma.
Methods Fifty-eight children with asthma, aged 5 to 16 years, used ICS with or without a spacer for 3 months. Adherence rates as measured from questionnaires and canisters, asthma...
- Initial steroid regimen in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome can be shortened based on duration to first remission
- Hee Sun Baek, Ki-Soo Park, Hee Gyung Kang, Cheol Woo Ko, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):206-210. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose The use of a 12-week steroid regimen (long-term therapy, LT) for the first episode of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (NS) reportedly induces a more sustained remission and lower relapse rate than previous regimens, including an 8-week steroid regimen (short-term therapy, ST). Here, we assessed the potential for selective application of 2 steroid regimens (LT vs. ST) based on the days to...
- Case Report
- Pulmonary hemorrhage in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome
- Ji Soo Kim, Min Jae Kim, E Young Bae, Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):202-205. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome (LAHPS), a very rare disease that is caused by the presence of antifactor II antibodies, is usually counterbalanced by the prothrombotic effect of lupus anticoagulant (LAC). Patients with LAHPS are treated using fresh frozen plasma, steroids, immunosuppressive agents, and immunoglobulins for managing the disease and controlling hemorrhages. Notably, steroids are the important treatment for treating hypoprothrombinemia and...
- Original Article
- Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity in children with controlled asthma
- Ji-Yong Yoon, Sung-Il Woo, Heon Kim, Yong-Han Sun, Youn-Soo Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(9):330-336. Published online September 14, 2012
-
Purpose Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity (FEF25-75) are not included in routine monitoring of asthma control. We observed changes in FeNO level and FEF25-75 after FeNO-based treatment with inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in children with controlled asthma (CA).
Methods We recruited 148 children with asthma (age, 8 to 16 years) who had maintained...
- Review Article
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children- You-Sook Youn, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(2):42-47. Published online February 14, 2012
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP), the smallest self-replicating biological system, is a common cause of upper and lower respiratory tract infections, leading to a wide range of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary manifestations. MP pneumonia has been reported in 10 to 40% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia and shows an even higher proportion during epidemics. MP infection is endemic in larger communities of the...
- Treatment of steroid-resistant pediatric nephrotic syndrome
- Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):317-321. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Children who suffer from steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) require aggressive treatment to achieve remission. When intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone fails, calcineurin inhibitors, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, are used as the first line of treatment. A significant number of patients with SRNS progress to end-stage renal disease if remission is not achieved. For these children, renal replacement therapy can also be...
- Original Article
- Clinical features of infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma
- Eun Hee Kim, Kyung Nam Koh, Meerim Park, Bo Eun Kim, Ho Joon Im, Jong Jin Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(6):260-266. Published online June 30, 2011
-
Purpose Infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma (IHHE) is the most common type of hepatic vascular tumor in infancy. We conducted this study to review our clinical experience of patients with IHHE and to suggest management strategies.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 23 IHHE patients (10 males, 13 females) treated at the Asan Medical Center between 1996 and 2009.
Results Median age at diagnosis was...
- The role of inhaled and/or nasal corticosteroids on the bronchodilator response
- Ju Kyung Lee, Dong In Suh, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):951-956. Published online November 30, 2010
-
Purpose To compare the profiles of the bronchodilator response (BDR) among children with asthma and/or allergic rhinitis (AR) and to determine whether BDR in these children is reduced by treatment with inhaled and/or nasal corticosteroid.
Methods Sixty-eight children with asthma (mean age, 10.9 years), 45 children with comorbid asthma and AR (mean age, 10.5 years), and 44 children with AR alone (mean age,...
- Review Article
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Kwang Nam Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(11):936-941. Published online November 30, 2010
-
The systematic approach to pharmacologic treatment is typically to begin with the safest, simplest, and most conservative measures. It has been realized that the more rapidly inflammation is under control, the less likely it is that there will be permanent sequelae. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the mainstay of initial treatment for inflammation. In addition, the slow-acting antirheumatic drugs (SAARDs)...
- Case Report
- A case of steroid-induced psychosis in a child having nephrotic syndrome with toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Sae Yoon Kim, Jae Min Lee, Yong Hoom Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):437-441. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) are rare, life-threatening mucocutaneous diseases, usually attributable to drugs and infections. Corticosteroids have been used in the management of TEN for the last 30 years. This remains controversial and is still much debated. TEN can occur despite administration of high doses of systemic corticosteroids. The psychiatric side effects of corticosteroids can include... -
- A case of adolescent Kawasaki disease with Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis complicated by splenic infarction
- Byeong Sam Choi, Bo Sang Kwon, Gi Beom Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Jung-Eun Cheon, Eun Jung Bae, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1029-1034. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that affects children. There are few reports that describe the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) as the possible infectious agent of KD. Here, we describe a case of KD in a 15- year-old boy complicated with giant coronary artery aneurysms, pericardial effusion, and splenic infarction. The clinical course of KD was... -
- Original Article
- Effects of inhaled corticosteroids on bone mineral density and bone metabolism in children with asthma
- Ic Sun Choi, Jung Hye Byeon, Seung Min Lee, Kyong Suk La, Yeon Joung Oh, Young Yoo, Kee Hyoung Lee, Ji Tae Choung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(7):811-817. Published online July 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are used as first-line agents for the treatment of persistent asthma; however, their use is accompanied by apprehension of potential systemic adverse effects. This study aimed to assess the effects of ICS on bone mineral density (BMD) and bone metabolism in children with asthma. Methods : From February 2008 to September 2008, 26 asthmatic children treated... -
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia: long-term follow-up of six cases
- Young Jun Son, Hee Jo Baek, Hoon Kook
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1211-1216. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA) is a rare heterogeneous genetic disorder of infancy and early childhood. It is characterized by red cell aplasia, congenital anomalies, and a predisposition to cancer. Corticosteroids and red cell transfusions are the mainstays of therapy. We describe our experience of 6 cases of DBA that were encountered over a period of 16 years. Methods :... -
- Case Report
- A case of testicular adrenal rest tumor in a male child with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Joo Hwa Kim, Kyong Ah Yun, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(9):1018-1022. Published online September 15, 2008
-
Testicular adrenal rest tumors are a well-known complication in male patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Corticosteroid suppressive therapy usually results in the regression of these tumors. We describe a patient with 21-hydroxylase deficiency who developed bilateral testicular masses. Despite steroid suppressive therapy, the tumors did not regress and hormonal control was poor. Consequently, bilateral partial orchiectomies were performed. -
- Original Article
- Epidemic acute interstitial pneumonia in children occurred during the early 2006s
- Chong Kun Cheon, Hyun-Seung Jin, Eun Kyeong Kang, Hyo Bin Kim, Byoung-Joo Kim, Jinho Yu, Seong Jong Park, Soo-Jong Hong, June Dong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(4):383-390. Published online April 15, 2008
-
Purpose : This study was aimed to analyze the clinical characteristics of patients with acute interstitial pneumonia who had presented similar clinical patterns from March to June, 2006 and to describe our experience of treatment and to identify risk factors associated with prognosis. Methods : The clinical characteristics, radiologic and histopathologic findings and response to steroids of 15 patients (non-survival... -
- Therapeutic response of cyclosporine and outcome in steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome
- Hyung Soon Choi, Joo Hoon Lee, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(3):293-298. Published online March 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of our study was to evaluate the therapeutic response to cyclosporine, time to remission and side effects in steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). Methods : This study included 22 children with idiopathic SRNS who were treated with cyclosporine between June 1989 and August 2006. Medical records were reviewed retrospectively. Results : The mean age of patients at diagnosis... -
- The impact of early detection through school urinary screening tests of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis typeⅠ
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Sung-Sin Park, Sung-Do Kim, Byoung-Soo Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(11):1104-1109. Published online November 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Since 1998, school urinary screening tests have been performed on Korean school children. We could detect and treat so many asymptomatic chronic renal disease in early stage. We investigated the efficacy of school urinary screening tests from children with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) type I. Methods : We analyzed the characteristics and prognosis of 18 patients with MPGN type I... -
- Clinical and Radiological Analysis of Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome in Children
- Hae-Ri Lim, Hye-Eun Seo, Sun-Hak Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):901-904. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome is a complex disorder with characteristic clinical and radiologic findings that mainly involve the white/gray matter of the parieto-occipital lobes. The purpose of this study was to determine its clinical and radiological characteristics. Methods : A total of 15 pateints were involved in the study. Their medical records and radiological features of brain MRI were... -
- Incidence, clinical features and prognosis of Bell's palsy in children
- Yoo Jong Won, Kyung Hee Moon, Wan Soo Lee, Seung Woon Keum, Taek Yu, Gyung Jae Oh, Chang Woo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(3):272-276. Published online March 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Bell's palsy is defined as an idiopathic facial nerve paralysis of sudden onset. In spite of intensive clinical and experimental investigation, there is still uncertainty in the incidence, etiology, and preferred mode of treatment in children. The objective of this study was to analyze clinical outcome and prognosis of children with Bell' palsy. Methods : We analyzed 61 cases... -
- Review Article
- Atopic dermatitis
- Bok Yang Pyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):589-592. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Atopic dermatitis is estimated to affect 15-20% of the childhood population and there id considerable evidence that the prevalence is increasing. But it is frequently under diagnosed and inappropriately treated yet. Atopic dermatitis can have a large social;. emotional and financial effect on the child and their family. Atopic dermatitis also commonly predated the development of asthma and allergic rhinitis.... -
- Case Report
- Steroid and enalapril therapy - possible cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Dong Wook Kim, Da Eun Jung, Ja Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):332-336. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a rare, acute and life-threatening cutaneous drug reaction. TEN is characterized by the sudden onset of extensive necrosis in the epidermis and frequent mucous membrane involvement. The pathogenesis has not yet been elucidated. In addition, no particular treatment for TEN has been established. We report a case of TEN in a 14-year-old-boy, which might have... -
- Original Article
- Comparison of Efficacy of Steroid Oint with Different Potency in Phimosis
- In Ok Hwang, Eun Sil Lee, Yong Hoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(6):594-598. Published online June 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Phimosis is the inability to retract the foreskin of the penis over the glans of the penis. Even though phimosis is not pathogenic, the presence of phimosis is known to increase the risk of urinary tract infection in infancy. The use of topical steroids has been advocated as a safe and economical alternative to surgical intervention. The purpose... -
- Association between the Human Surfactant Protein-A(SP-A) Gene Locus and Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Korean Neonates
- Jae Hoon Choe, Myung Ho Oh, Jung Ho Ko, Sun Young Kim, In Kyu Lee, Chong Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(7):735-739. Published online July 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Respiratory distress syndrome(RDS) is caused by a deficiency of pulmonary surfactant, which is a lipoprotein complex. Both low levels of surfactant protein A(SP-A) and SP-A alleles have been associated with RDS. However, the genes underlying susceptibility to RDS are insufficiently known. The candidate-gene approach was used to study the association between the SP-A gene locus and RDS in... -
- Risk Factors for the First-Year Relapse in Children with Nephrotic Syndrome
- Hye Kyoung Shin, Ji Hee Kim, Kee Hwan Yoo, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(9):889-892. Published online September 15, 2003
-
Purpose : This study aimed to evaluate risk factors of the first year relapse in children with nephrotic syndrome(NS) without the need for biopsy. Methods : We reviewed, retrospectively, 78 children diagnosed with steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome between July 1997 and June 2002. Median years to follow up were 4.4 years(range : 1-5 years). We divided the patients into two groups(group... -
- Allele Distribution and Frequency of Human Surfactant Protein-A2 in Korean Neonates
- Nyeon Cheon Kim, Hee Chul Yoon, Jung Su Suk, Jung Ho Ko, Ook Joon Yoo, In Kyu Lee, Myung Ho Oh, Chong Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(4):340-344. Published online April 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We evaluated allele frequencies and distribution of surfactant protein A2(SP-A2) in Korean neonates in order to estimate the prevalence of RDS, to find out new SP-A alleles, and to establish new steroid therapy. Methods : Genomic DNA was extracted from 71 neonates and served as a template in PCR for genotype analysis. SP-A gene-specific amplications and gene-specific allele determinations... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







